The Participants and Their Motivation of "Human Flesh Search"
--Comparing the Phenomena in Taiwan and the Chinese Mainland
Du Sainan National Chengchi University
Abstract
Although having been emerging human flesh search ( HFS ) in America, British,Japan, the Chinese regions are the places where HFS has been the most frequent,Especially in Taiwan and China. This study comparing differences between the two regions of the “ participants”, “motivation” and “participation”, through an empirical way,online survey, Study results indicate that: (1) China HFS is higher than Taiwan in the participation degree;(2) Taiwan users status and motivation to participate in a correlation;(3)The relationship between the motivation and participation of participants on the “altruism”, but the correlation between the "pleasure" and "public individuation " in Taiwan is also related to the degree of participation.
Keywords: human flesh search、comparative study、social media、participating motivations
Introduction
At the beginning of 21st century, Blog, weblog, BBS, Facebook, forum, post bar and microblog emerged rapidly both in Taiwan and the mainland. With the evolution of network, the social media attracted many people's attentions and became a noisy place. Around 2001, a Chinese man posted a girl's photo on Mop net and claimed the girl was his lover, which proved to be wrong by netizens; meanwhile, the girl's personal information including her name and company was exposed on the Internet later on. It marks the beginning of human flesh search(Wang, Hou, Yao, & Chen ,2010). In 2006, the cat cruelty case in Taiwan caused the netizens to make a search, and the people who involved in this case had strong pressure from the public opinion. Therefore, some scholars regarded it as a specific network phenomenon of China(Li Tuo, 2009). In fact, this kind of search also happened in other countries and regions. According to Wang, et al. (2010), the cyber manhunt cases also occurred in Japan, Korea, and America from
2001 to 2007; after 2008, the similar cases also appeared in England and France. Lin Qixiu (2011) also illustrated that the human flesh search had happened in America, Korea, Hongkong and other regions in the world. Apparently, it is not a specific Chinese phenomenon.
The causes of human flesh search can be divided into two kinds. The first kind is, the international network has developed constantly, the network construction has been improved perfectly day by day, and human beings are volunteered to create personal profiles which are not easily deleted for the convenience of Internet services. Therefore, all these provided rich data resources for the emergence of human flesh search. The research of Emily, Amy & Serge (2009) indicated that the users of Facebook were willing to disclose their personal details, such as their birthday (72%), E-mail (85%), place of residence (85%), relationships (81%) and their schools or organizations (72%), etc. The second kind is, the technology progress of the search engine also contributes to Internet users to obtain information. For instance, the search engine of ZabaSearch or Pipl which searches people’s names specially, can automatically sort out the information related to people’s name into a single dossier and provide it for Internet users to inquire (Richards, 2006).
It is worth thinking deeply that the "information superhighway" in the Internet age has spread in the world, and although HFS happened in other countries or regions, it occurred mostly and frequently in the Chinese residential regions indeed from the perspective of current numbers. The cultures in Taiwan and the mainland are very close, but since 1949, the martial law has been implanted in Taiwan, and under the control of different ruling parties, different phenomena about speech have been appeared, which made people spontaneously think the questions what is the root causes or motivations of human flesh search in Taiwan and the Chinese mainland, who are the participants of human flesh search, whether their participation is same or not, and whether human flesh search, as one cultural phenomenon of network, reflect the different cultural construction in Taiwan and the Chinese mainland?
Literature review
What “Human flesh search” is?
definition about it generally accepted by the academic circles (Bing, Bonan, Yiping & Laibin, 2009). It was called as "Chinese style Internet man hunt" The New York Times,
Forbes Magazine and Daily Mail, which thought it was a hunting action on the Internet
with Chinese characteristics.
When reporting the news about Chinese human flesh search, BBC News translated it directly into “human flesh search engine” (Celia, 2014), which aims to make the western people understand its meaning deeply and describe it as an intense action just like “witch hunt”. It emphasized that the purpose was not just to find the person but to punish him or her. According to this definition, Zhang Xian (2010, p.39) regarded human flesh search as a behavior that searching for the participants of a public event and the truth of this event.
However, this goal-oriented defining way cannot explain some network phenomena that the participants of an event become popular due to human flesh search. For instance, in December 2009, a photo of Zhang Zetian who took a cup of milk tea was uploaded to the community by her net friends of MOP, and then she was searched and became a celebrity and was called as “milk tea sister” by the netizens. From the cause of the "milk tea sister" event, it can be seen that the searching result is not to punish, and the netizens do not have the strong purpose to find the truth. The phenomenon of becoming a celebrity on the Internet does not have the objective-oriented characteristics, and netizens do not have a clear purpose in the flesh search behavior which aims to find the truth. For the “event of south China tiger” which was very popular in the Chinese mainland in 2007, the involver Zhou Zhenglong uploaded the photo of a south China tiger on the Internet, which he said was taken with a digital camera and a film camera. However, the authenticity of this photo was questioned by some netizens and experts. This event had become a hot issue in the public along with the heated discussion of netizens. In November 2008, after experts’ actual verification, Zhou Zhenglong was found guilty due to fraud.
In the “event of south China tiger”, the netizens focused on the photo of the south China tiger firstly but not the involver Zhou Zhenglong, and their purpose for searching this event first was not to make Zhou bear the legal responsibility. However, with the intervention of the photographic experts, research institutions, and traditional medias, the influence of this event had been expanded gradually, and Zhou born the blame because of uploading false photos eventually. Just like that, in the events of Zhou Juigeng[1] and Yang Liancai[2], the motivations triggering netizens to do "human flesh search" were both because of the speech or behavior mistake. With the expansion of the
"flesh search" groups, the focus of netizens has shifted gradually, which attracted the attention of the authorities eventually and made them investigate the involvers in order to achieve the purpose of "punishment" or "sanction".
It can be seen that, the goal-oriented definition cannot cover all "flesh search" behaviors, but the human resources in the search mechanism can highlight the core of "flesh search". Therefore, this paper defines the "human flesh search" as a behavior which is intervened by social media and is focused on through some related words or pictures. It appears by forwarding, posts, tweets, etc, to form a emergent online group, then the public use the interactive mechanism provided by the network to reason, do trial-and-error, search and share together, and explore how to search for the specific person, thing, and how to use the information they found to complete the final goal.
Participants of human flesh search
The different research methods about human flesh search in Taiwan and the mainland lead people to rethink the origin of "human flesh search" phenomenon, that is, rethink some questions such as who are willing to do "flesh search", and why they do that. The mainland scholar Yin Jun(2009)put the participants of "human flesh search" in the construction of network culture, and thought it was the special structure of netizens, such as the younger Internet users, that caused the netizens have some similarities such as the passionate and emotional characteristics and strong social justice in psychology and physiology; meanwhile, with the technology development of Web 2.0, people are willing to communicate with each other. However, the netizens at this time are influenced by the traditional Confucian culture as well as the Internet culture. For these people in the period of social transition, the conflict between the change of their interest relationship and the value has been growing, so "flesh search" become an important platform of public opinion at this time. Therefore, the Internet in the mainland has been always regarded as the most lively and noisy network culture with the most public opinions in the world.
But in Taiwan, disclosing one person’s privacy on the Internet may violate the personal information protection law. Huang Houming and Lin Yiren(2013)used “mobility” to re-explain the virtual community and found that the modern individualized process deeply influenced the contemporary network culture. However, Internet users at the same time also enjoyed the demand of emotional empathy in the
collective, but this demand cannot be turned into individualism or utilitarianism. In addition, the participants of "human flesh search" are also limited by the construction of different interactive way of social media. One place in the mainland where "human flesh search" appeared in is Tianya Forum which established in March 1999. This forum has three core functions of BBS, which are seeing, releasing and replying a post. After the Chinese embassy in Yugoslavia was bombed, netizens had a fierce debate on this forum, so that it attracted the attention of the traditional media. Besides, there are numerous disclosers in Tianya gossip platform which also makes Tianya Forum become the original place of many human flesh search events(Xu Qirong,2011). Although some social media such as MOP Forum and micro blog are different from Tianya Forum in layout, content and interactive way, they all appeared due to some events or celebrities; for instance, micro blog attracted a lot of fans because of some pop stars’ registration and propaganda. Compared with Tianya Forum and MOP Community, the target group of PTT and Facebook in Taiwan was students when they were established at first. The campus, as an important recruiting and reproducing mechanism, accelerated the expansion of PTT in the 1990s; and it also became a node to connect the powers of “ministry of education university standing party the user” (Li Shaoliang, 2011).
To sum up, both the different network culture background and the different construction of virtual community in Taiwan and the Chinese mainland have an impact on the participants of human flesh search. Taking the identity background of the participants as one variable, this paper will explore the difference between the participants in Taiwan and the mainland.
Participants’ motivation
Zhang Junpei, a scholar of Taiwan, and Shi Da, a scholar of the mainland, think that it is easy for people to obtain pleasure by peeping others’ privacy, venting their emotions and role play in human flesh search, and even produce the orgiastic phenomenon in the interaction with others; meanwhile, they also point out that pleasure is an important factor for Internet users to participate in the community. Chen Ran also emphasizes the sense of belonging of BBS and the influence of upholding justice. Li Huiting (2010) proposed that the "structural stress" was the background of "human flesh search", and the social factors such as the economic depression, natural disasters, and poverty would have a psychological pressure on people; the stress triggered people to
pursue the social justice and fairness. Therefore, Internet users get together in the network spontaneously and hope to solve these problems together. Yi Zhenzhen (2009) regarded “flesh search” as a kind of action which was organized by ordinary people and proposed by the public, and found that altruism can also trigger people to participate through the in-depth interview and the content analysis method.
Unlike the "altruism" motivation of the mainland participants, study of the flesh search in Taiwan emphasizes the public to show their personality. Huang Houming & Lin Yiren (2013, p38) pointed out that, For the modern personal development, netizens have the space to pursue for freedom with all their strength, and try their best to highlight their individuality as an independent person. Therefore, the ambiguous nature of the Internet which is isolated but connected just provides a flexible medium for netizens to pursue for freedom or safety, as well as the satisfaction of individuality or collectivity.
Thus, some people became the main group members of participating in the flesh search and kicking up a fuss. Those people, on the one hand, don't want to be limited by the social media and be restricted by the specification; on the other hand, they are happy to show their personality under the cover of their pseudonyms. Therefore, the public want to show their individuality becomes one participation motivation of the participants.
To sum up, the motivations of participating in the flesh search in Taiwan and the Chinese mainland can be divided into five kinds of a sense of joy, a sense of belonging to the forum, the altruism, showing personality and upholding the justice. According to the identity background of the participants, this paper will put forward the first hypothesis.
H1: The participants of human flesh search in Taiwan and the mainland are different, and their motivations are different as well.
The participating degree of participants in the flesh search
The search behavior of Human flesh search is different from that of other search engines such as Google, Baudu and yahoo. According to the experience of ethnic Chinese on the Internet, the netizens’ participation and cooperation have played a fairly important role in the search process.
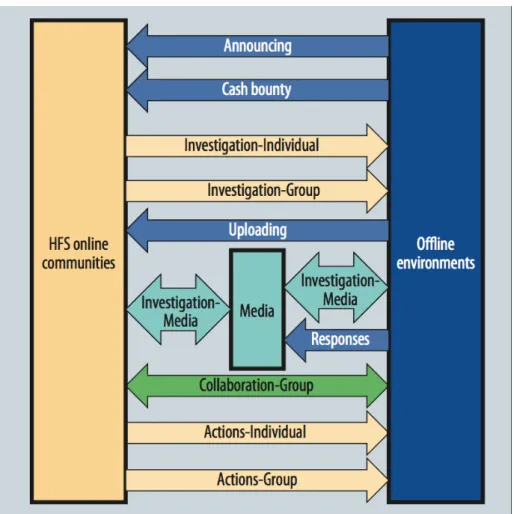
figure source :“ A study of the human flesh search engine: Crowd-powered expansion of online Knowledge,” by F.Y. Wang, D. Zeng, J. A. Hendler, Z. Qingpeng, F. Zhuo, G. Yanqing, et al., 2010, Computer, 43(8), p. 48.
As this figure 1 shows, according to the case analysis of "human flesh search" from 2001 to 2010, it was found that the order of events occurred most times in flesh search was publishing, uploading, survey by the media, individual survey and replying post, but all posts caused by these behaviors just accounts for less than0.9% of the total posts. Therefore, it can be concluded that most posts do not provide substantial information.
Then, are there same participation degrees for people who involve in the flesh search? Yuan Hanyu & Chen Bailing (2013) classified the involvers of the flesh search into different roles according to their participation degrees by sorting out the previous literature about the network group actions and functions. This classification cannot directly show the correlation between their participation motivations and participation
degrees, but from the role definition, the contribution of participants and the flesh search event and their correlation degree can be understood, and the difference in participation degrees of different participation motivations can be known from their roles.
This paper will divide the resources provided by the participants into five kinds of acting roles, and then divide the participation degrees into five levels according to their different roles. The first level participants are those who just know a little about the event; the second level participants are those who know and focus on the event comprehensively; the third participants pay full attention to the event, but they do not reply, forward and participate in the event; the fourth level participants pay their entire attention to the event and provide some information relevant to the event actively; the fifth level participants participate in the event actively, organize people to do flesh search, and take the initiative to provide and sort out the relevant information. The higher the participation level is, the larger their contribution is. According to the classification of the participation degrees, the analysis of participants’ identity background and the discussion about the participants’ motivations, this paper will put forward the second hypothesis.
H2: If the participants’ motivations were different, the netizens’ participation degrees would be different.
Assumptions, research framework of this study In figure 2:
Figure 2. The Participants and Their Motivation of HFS framework
Figure source :This study summarize.
Case and methodology
relevance of participants in "human flesh search", their participation motivations and degrees. The questionnaire used in the mainland will be designed on http://www.weidiaocha.corn/, while the questionnaire in Taiwan will be written through https://docs.google.com/forms/. The main original platform of human flesh search in Taiwan and the mainland will be taken as the questionnaire content.
The network questionnaire in the mainland will be issued in December 10, 2016. In order to enhance the validity of the questionnaire, this paper will choose four communities where the flesh search occurred frequently to do a questionnaire survey. These four communities are PPT, Facebook, Tianya Forum and MOP. Till February 20, 2016, 234 questionnaires were recycled, and among them, 104 questionnaires were collected in the mainland, including 100 valid questionnaires, and 130 questionnaires were recycled in Taiwan, including 120 valid questionnaires, and there were 14 invalid questionnaires together in Taiwan and the mainland.
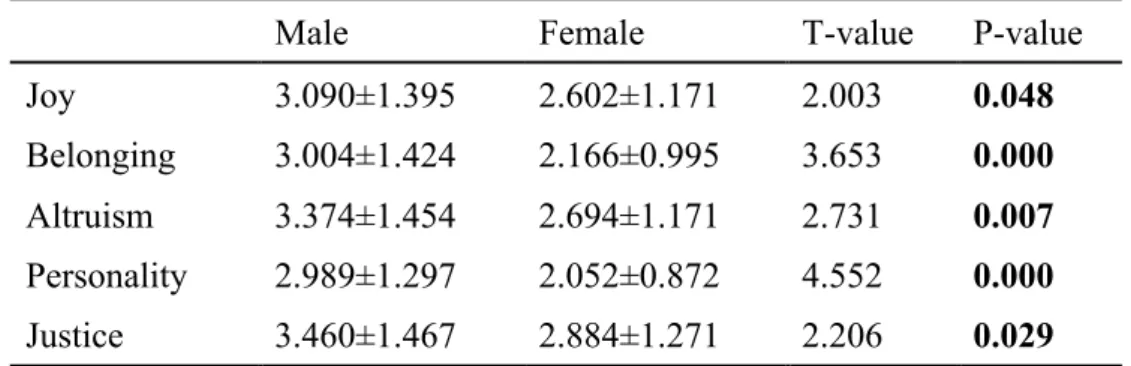
The participants and their motivations in HFS between Taiwan and China Table 4-2-1:Correlation between gender and motivation of Internet users in
Taiwan
Male Female T-value P-value
Joy 3.090±1.395 2.602±1.171 2.003 0.048
Belonging 3.004±1.424 2.166±0.995 3.653 0.000 Altruism 3.374±1.454 2.694±1.171 2.731 0.007 Personality 2.989±1.297 2.052±0.872 4.552 0.000 Justice 3.460±1.467 2.884±1.271 2.206 0.029 Note: the significance level of the test was 0.05
source :This study summarize.
From table 4-2-1, gender of Taiwan's Internet users HFS motivation (joy, sense of belonging, altruism, public personality, sense of social justice), there were significant differences, and Taiwanese male Internet users on the motivation of mean score was significantly higher than that in female's.
Taiwan
12-22 23-33 34-44 45-55 above55 F-value P-value
Joy 2.85±1.09 2.86±1.36 3.29±2.16 2.30±1.24 1.08±0.14 1.844 0.126 Belonging 2.45±1.15 2.57±1.34 2.97±2.14 2.84±0.55 1.73±0.64 0.615 0.653 Altruism 2.85±1.22 2.92±1.24 3.33±1.86 4.72±0.67 2.73±2.83 2.547 0.044 Personality 2.25±0.85 2.58±1.27 3.22±2.01 2.20±0.38 3.00±2.62 1.433 0.228 Justice 2.85±1.00 3.26±1.55 3.37±2.05 4.68±0.52 2.93±2.69 2.385 0.056 Note: the significance level of the test was 0.05
source :This study summarize.
From the figure 4-2-2, Taiwan's Internet users age and altruism motivation exists significant difference. And high age of Taiwan's Internet users on "altruism" was significantly higher than that of the lower .
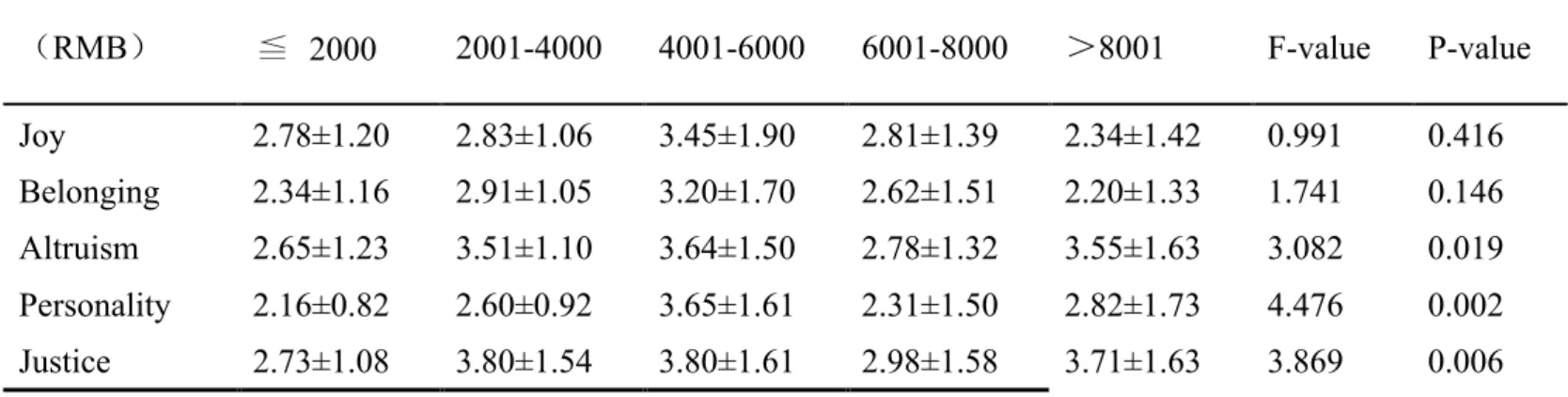
Table 4-2-3:Correlation between income and motivation of Internet users in Taiwan (RMB)
≦
2000 2001-4000 4001-6000 6001-8000 >8001 F-value P-value Joy 2.78±1.20 2.83±1.06 3.45±1.90 2.81±1.39 2.34±1.42 0.991 0.416 Belonging 2.34±1.16 2.91±1.05 3.20±1.70 2.62±1.51 2.20±1.33 1.741 0.146 Altruism 2.65±1.23 3.51±1.10 3.64±1.50 2.78±1.32 3.55±1.63 3.082 0.019 Personality 2.16±0.82 2.60±0.92 3.65±1.61 2.31±1.50 2.82±1.73 4.476 0.002 Justice 2.73±1.08 3.80±1.54 3.80±1.61 2.98±1.58 3.71±1.63 3.869 0.006 Note: the significance level of the test was 0.05source :This study summarize.
From table 4-2-3 can be seen that, income and Taiwan's Internet users "altruism, public personality, social justice sense of motivation, there was a significant difference, and higher income users in Taiwan in this three motivation scores was significantly higher than that of low income of Taiwan's Internet users.
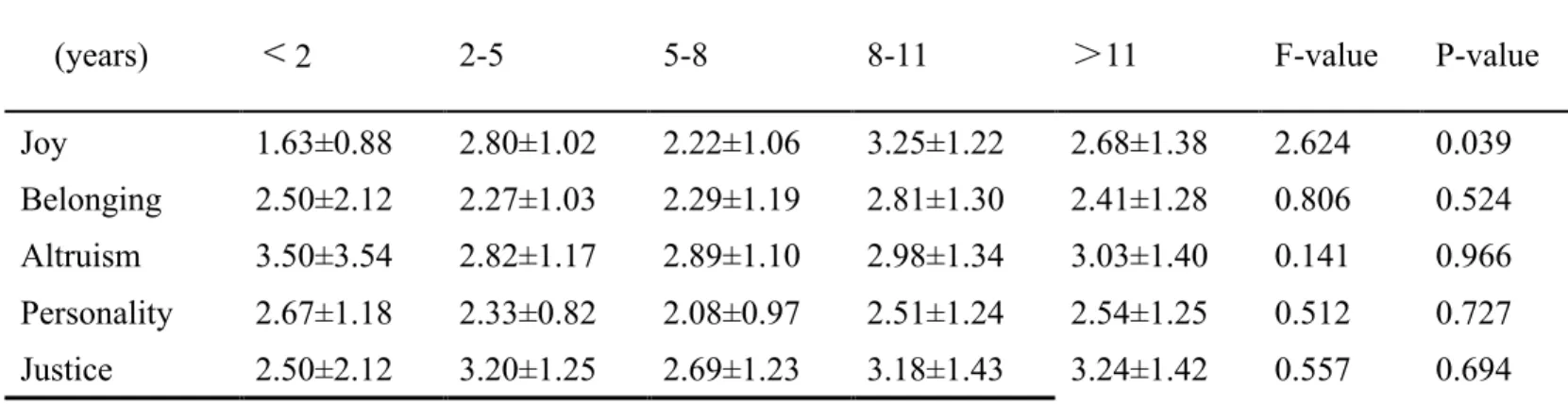
Taiwan
(years)
<
2 2-5 5-8 8-11 >11 F-value P-valueJoy 1.63±0.88 2.80±1.02 2.22±1.06 3.25±1.22 2.68±1.38 2.624 0.039 Belonging 2.50±2.12 2.27±1.03 2.29±1.19 2.81±1.30 2.41±1.28 0.806 0.524 Altruism 3.50±3.54 2.82±1.17 2.89±1.10 2.98±1.34 3.03±1.40 0.141 0.966 Personality 2.67±1.18 2.33±0.82 2.08±0.97 2.51±1.24 2.54±1.25 0.512 0.727 Justice 2.50±2.12 3.20±1.25 2.69±1.23 3.18±1.43 3.24±1.42 0.557 0.694 Note: the significance level of the test was 0.05
source :This study summarize.
From table 4-2-4 shows that the net age and the "pleasure" motivation of Taiwan Internet users are significantly different, and the average age of Taiwan Internet users in the "pleasure" score is significantly higher than the net age of the Internet users in Taiwan.
Relevance analysis of HFS participation motivation and participation--China For discovery on both sides of the HFS participation motivation and participation degree of correlation, the study respectively questionnaire data of China and Taiwan were regression analysis, which was explained by the amount for HFS participation and explanatory variables for the sense of "pleasure", "sense of belonging", "altruism", "the public personality" and "social justice". The mainland regression model 1 results as table 4-3-2, 4-3-1, 4-3-3:
Table 4-3-1:Model 1 the results of regression analysis in China
Model R R-squar Adjusting
R-squar Durbin-Watson
1 0.526 0.277 0.238 1.966
Figure source :This study summarize.
to this table, and the decision coefficient of model 1 adjustment is 0.238. In addition, the Durbin-Watson value of the test value is 1.966, which indicates that the residual error of the model 1 does not exist.
Table 4-3-2:Variance analysis of regression analysis
Model Sum of squares df mean square F Sig. 1 Return 40.840 5 8.168 7.194 0.000 Residual 106.720 94 1.135 Total 147.560 99
source :This study summarize.
4-3-2 can be seen from table, the number of samples for 100 data, model 1 explanatory variables of the total sum of squares of deviations 147.560, regression sum of squares and mean square respectively for 40.840 、8.168 and residual sum of squares and mean square respectively 106.720 and 1.135. F test statistics of the observations 7.194, corresponds to a probability of SIG. Value of 0.000, smaller than the significance level 0.05. Should be refused to regression equation was the null hypothesis, that model 1 in the partial regression coefficient are not 0 ,at the same time, be explained is a significant linear relationship between the variables and explanatory variables, linear model is established.
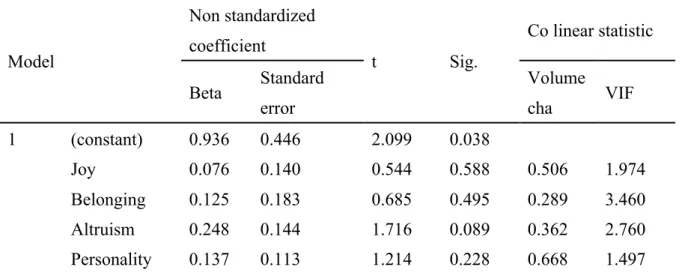
Table 4-3-3:Regression coefficient
Model Non standardized coefficient t Sig. Co linear statistic Beta Standard error Volume cha VIF 1 (constant) 0.936 0.446 2.099 0.038 Joy 0.076 0.140 0.544 0.588 0.506 1.974 Belonging 0.125 0.183 0.685 0.495 0.289 3.460 Altruism 0.248 0.144 1.716 0.089 0.362 2.760 Personality 0.137 0.113 1.214 0.228 0.668 1.497
Justice 0.083 0.128 0.651 0.517 0.523 1.912 source :This study summarize.
From the table shows 4-3-3, according to the table of collinearity diagnosis, Vif said variance inflation factor, each variable in the Vif values were small in 10, shows that the multivariate regression model 1 does not exist the problem of multicollinearity, so model 1 regression analysis results are credible.
From the regression coefficient significance angle of view, altruism of HFS in the level of regression coefficients with significance (SIG. Value < 0.10); and pleasure, sense of belonging, present the public personality, social justice sense of HFS in the regression coefficient of the level of no significant (SIG. Value > 0.10). Model 1 of the multiple regression equation: HFS to participate in the degree of =0.936+0.076* pleasure +0.125* sense of belonging +0.248* altruism +0.137* public presentation of personality +0.083* social justice.
As the equation show, altruism of HFS participation has a significant positive effect, the regression coefficient is 0.248, mainland netizens altruistic tendencies more obvious, China netizens HFS participation will be higher and higher.
Relevance analysis of HFS participation motivation and participation--Taiwan In this study, the model 2 is defined as HFS in Taiwan. The regression analysis model of motivation and participation degree is analyzed, and the results of regression analysis are shown in table 4-4-2, 4-4-1, 4-4-3.
Table 4-4-1:Model 2 the results of regression analysis in Taiwan
Model R R-squar Adjusting
R-squar Durbin-Watson
2 0.568 0.323 0.291 1.805
source :This study summarize.
According to the table 4-4-1 can be seen, according to the table can be the goodness of fit test, model 2 adjustment of the decision coefficient of 0.291, we can see that the model of the goodness of fit is smaller. In addition, the Durbin-Watson value
of the test value is 1.805, which indicates that the residual error of the model 2 does not exist.
Table 4-4-2:Variance analysis of regression analysis
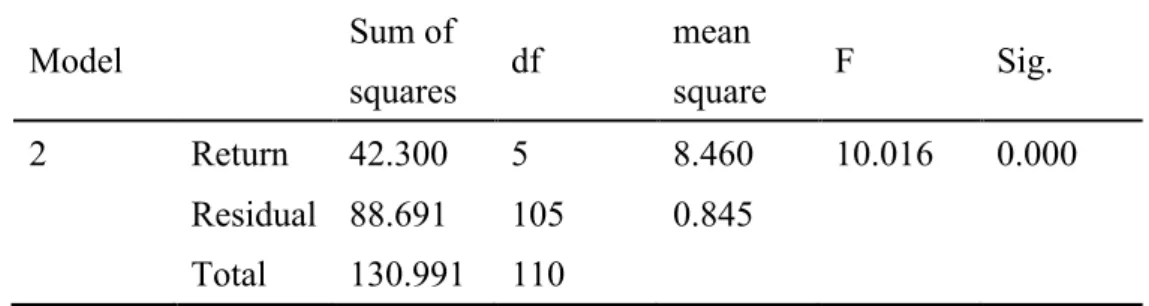
Model Sum of squares df mean square F Sig. 2 Return 42.300 5 8.460 10.016 0.000 Residual 88.691 105 0.845 Total 130.991 110
source :This study summarize.
Table 4-4-2 shows that the model 2 is explained by the total deviation square and 130.991, and the regression square sum and mean square are 8.460 and 42.300, respectively, and the residual sum of squares are 88.691 and 0.845. F test statistics of the observations 10.016, corresponds to a probability of SIG. Value of 0.000, smaller than the significance level 0.05. Should be refused to regression equation was tested for the null hypothesis, that model 2 partial regression coefficients are not 0 at the same time, is interpreted is a significant linear relationship between the variables and explanatory variables, linear model is established.
Table 4-4-3:Regression coefficient
Model Non standardized coefficient t Sig. Co linear statistic Beta Standard error Volume cha VIF 2 (constant) 0.431 0.246 1.754 0.082 Joy 0.248 0.103 2.404 0.018 0.434 2.305 Belonging -0.209 0.128 -1.635 0.105 0.296 3.375 Altruism 0.354 0.121 2.921 0.004 0.293 3.416 Personality 0.186 0.106 1.748 0.083 0.503 1.988 Justice -0.033 0.109 -0.305 0.761 0.338 2.957
4-4-3 can be seen from table, according to the table of collinearity diagnosis, Vif said variance inflation factor, each variable in the Vif values are less than 10, indicating the multiple regression model 2 does not exist the problem of multicollinearity, so model 2, the regression analysis result is credible.
From the regression coefficient significance angle of view, pleasure, altruism, public personality of HFS in the level of regression coefficients with significance (SIG. Value < 0.10); and ownership feeling, sense of social justice, the HFS in the regression coefficient of the level of no significant (SIG. Value > 0.10).
Model 2 of the multiple regression equation: human flesh search to participate in the degree of =0.431+0.248* pleasure -0.209* sense of belonging +0.354* altruism +0.186* public presentation of personality -0.033* social justice.
Thus equation shows, pleasure, altruism, public personality of HFS participation has a significant positive effect, the regression coefficients were: 0.248, 0.354, 0.186, Taiwan Internet users is the pursuit of pleasure, altruism tendency of Taiwan's Internet users more obvious, Taiwan's Internet users increasingly seeking public appear appeared to have a personality, then the Taiwanese netizens human flesh search participation will be higher and higher.
Findings
Demographic statistics of participants
The information about 100 respondents in the mainland in this study will be shown in the following: gender (61.0% female), age (68% of netizens are 23-33 years old), income (NT10001 ─ ─ NT20000 accounts for 40%, NT20001 ─ ─ NT30000 accounts for 30%, and both of them account for 70% of the total income of the group), times working with network (19% (2-5 years), 20% (5-8 years), 30% (8-11 years), 27% (more than eleven years)).
For 100 respondents in Taiwan, gender (58% female), age (48% (12-22 years old), 37% (23-33 years old), both of them accounts for 85%), income (less than NT10001 accounts for 54%, NT10001-- NT20000 account for 17%, NT20001-- NT30000 account for 17%, but NT40001 and above account for 12%, which is 5% more than that of the mainland), time working with network (39% (8-11 years), 40% (more than 11 years), both of them accounts for 79%). It can be seen from the above descriptive
statistics that, there are more female participants than the males in the flesh search both in Taiwan and the mainland; there are more middle-aged participants in the mainland and the participants in Taiwan are relatively young; the participants in the mainland are wage-earning class while most participants in Taiwan are young students (54% of them have less than NT10001); from the time working with network, the time distribution of participants in the mainland is relatively diverse, while most participants in Taiwan have worked with network for over eight years.
For the participation degree of the 100 respondents respectively in Taiwan and the mainland, the respondents’ participation degree in the mainland is significantly higher than that in Taiwan. In the mainland, the second level participants (accounting for 26%) and the fourth level participants (accounting for 32%) are in the majority, the fifth level participants account for 21; while in Taiwan, the first level participants (35%) and the second level participants (39%) are in the majority and the fifth level participants just account for 3%.
It can be seen from the distribution that the mainland respondents’ participation degree is higher than that in Taiwan, and most mainland respondents have taken the actions of transponding and replying post and even providing some relevant information to consult; whereas in Taiwan, most respondents just know the event but do not transpond or reply posts.
H1: The correlation between the variable of participants’ population and their participation motivations
It was found from comparing the analyzing results in Taiwan and the mainland that, the population variable in the mainland has no significant correlation with the participation motivation, but there are correlations between the participation motivation and gender, income, age and time working with network respectively for the netizens in Taiwan. There are significant differences between the netizens’ gender in Taiwan and the sense of pleasure, the sense of belonging, altruism, individuality shown by the public, and the social justice respectively, and the mean scores of male netizens in these five aspects are higher than those of female netizens. Although Zhang Junpei (2011) did not discuss the gender difference in the study of flesh search, he found in the interview that the male interviewees would know and pursue for some females by the flesh search, but female interviewees did not disclose the information in this aspect. Therefore, in the process of human flesh search, men are more active than women, and
they are more willing to show themselves, and try their best to search for something in order to obtain the sense of pleasure. In addition, Jiang Yixuan (2014) explored the sense of engaging in Facebook and the consciousness of community from the experience of media, namely, the sense of belonging means that male users have stronger engaging experience in the media engagement of the community, which makes them more active in using the media, producing, transponding and replying posts, etc.
It can be seen from age that there is a significant difference in the aspect of altruism for the netizens in Taiwan, and the mean score of the older netizens is clearly higher than that of the younger netizens. For the development of Chinese culture, Confucianism has always occupied an important position. Although Confucianism in Taiwan has experienced the “existing but not disappearing” low tide during the period of controlling by Japan, Taiwan's Confucian scholar took protecting the traditional Chinese culture as their own duty, which makes it possible for the Confucian culture to continue. The monthly magazine E Hu, founded in 1975, established the thought position of "Oriental humanities academic research foundation" in Taiwan, and in which, the Confucian essence such as benevolence, courtesy, and moral essence is regarded as an important part of Confucianism. Therefore, when some persons or events who or which violate the moral beliefs and value pursuit occur, netizens in various fields in the whole world will focus on and participate in them actively, regardless even though knowing they are not their business. However, after the 1980s and 1990s, with the increasing grow of local consciousness, the difficult evolution of the democratic process and the spread of postmodernism have made Confucianism confront the transformation and the challenge in Taiwan, and the conflict and the thought development during this period have been also reflected in the network culture. In the group of flesh search, the people with different ages will have different value views and moral views due to different social and growing background, which results in different network behaviors.
There are significant differences among the participation motivations of altruism, individuality shown by the public, and social justice in the aspect of netizens’ income in Taiwan, and the mean scores of netizens with higher income in these three motivations of are higher than the mean scores of netizens with lower income. Although the previous literature showed that there was not much correlation between the income and the netizens’ participation motivations, Bourdieu (1984) pointed out there was significant correlation between the cultural and social capital and the cognition and
behavior of the community. In other words, different participants will have different participation motivations due to different offline social capital. Therefore, the variables such as the education level and the profession can be included in the future study. Finally, there is a significant difference between the time working with network of netizens in Taiwan and the sense of pleasure, and the mean score of netizens with longer time working with network in the sense of pleasure is higher than that of netizens with shorter time working with network. According to the concept of “game”, Zhang Junpei (2011) pointed out, when people involve in the flesh search event, the sense of pleasure came from many levels and aspects, and the interaction with the online netizens, the importance of the information they provided, the information recognition and extension, and the skilled use of technology all affect the pleasure, and even the perception of "pleasure". However, the search technology of information and the online connections and capital accumulation are often limited by the netizens’ times working with network.
In contrast, the development of some social media such Tianya Forum and MOP community, as the original platform of the flesh search in the mainland, is benefited by the discussion of netizens with different backgrounds for this event, which makes the participants come from different fields. In addition, after exposed by the media, the "human flesh search" events attracted more people’s attention, which would be used by businesses to become a new marketing and advertising means. For instance, the “milk tea sister Zhang Zetian” and the “Gan Lulu event” appeared due to the actions of the Internet marketer. Although this behavior of using viral marketing and event marketing to impact the netizens fragmentarily is not the mainstream of the flesh search, it wants to be the unique mode of the flesh search in the mainland. In short, in the development process of “human flesh search” in the mainland, there are various participants from different fields, and the participation motivations are increasingly more and more different.
H2:The correlation between the participation motivations and the participation degree
In the mainland, "altruism" has a significant positive effect on the participation degree, and the regression coefficient is 0.248, that is, the more obvious the mainland netizens’ altruism is, the higher the mainland netizens’ participation degree is. In contrast, the sense of pleasure, altruism, and individuality shown by the public all have
significant positive effects on the participation degree, and the regression coefficients are 0.248, 0.354, and 0.186 respectively, which means that the more Taiwan netizens pursue for the sense of pleasure, altruism, and individuality, the higher their participation degree is.
When analyzing the phenomenon of human flesh search in the mainland, Yan Jun (2009) thought that the dialogue mechanism of “human-machine-human” in the “flesh search" caused the “inverted spin of silence”. Different from the previous real life, now the public opinion is controlled by the utterance mechanism of a few people. In the network society, especially with the participation of social media, participants will have the tendency of altruism to disclose the truth due to the anonymity of network even though their opinions are different from the main public opinion, which makes a few people who have different opinions do not keep silent. However, under the diverse participation motivations, why the mainland participants have a further search only with the drive of altruism? Zheng Zhibin (2012) thought that with the increasing development and expansion of flesh search in the mainland, its operation efficiency is becoming higher and higher, and the speed is even faster than the speed of police’s detection, especially after experiencing a series of major events, the flesh search has been equal to the moral criticism, social supervision, relief and aid, and even the freedom of speech. At present, it has become an important method of focusing on the current events, doing evaluation about the public opinion and implementing the social intervention from a method which just searched and released information to entertain the public at the early stage.
However, in Taiwan taking "democracy" and "freedom" as the brand, the network environment is much too loose and open; therefore, the participation motivations in the "human flesh search" tend to be more diverse. Huang Houming & Lin Yiren (2013) illustrated the netizens’ participating behavior in this era from the concept of “flowing group”. They insisted that Taiwan was experiencing the transition from the traditional society where the society took the first place to the modern individualization, and then to the post-modern society. During this period, people use the Internet and take the individual form to pursue for the satisfaction of the emotional empathy brought by the community or social life. In this network group which pursues for individual and society, and freedom and security, Internet users are more willing to participate in the network group events under the influence of different motivations.
Notes
[1] Zhou Jiugeng Event (2008): a Chinese corrupted official and former director of Real Estate Council of Jiangning district of Nanjing city in Jiangsu province. He was human-flesh searched by Chinese netizens due to his inappropriate remarks that the developer who sold houses at a price lower than cost should be punished. An official photo of him shot when he attended the conference of Land and Resource bureau was widely spread on the Internet. After close scrutiny, it was found by netizens that Zhou Yonggeng was wearing a Vacheron Constantin, an imported watch which cost 100 thousand yuan, he was taking the most expensive cigarette in Nanjing, which cost 1500 yuan every five packages and he was driving Cadillac, a luxury car made in America. In October 10th of 2009, Zhou Yonggeng was sentenced 11 years due to bribery.
[2] Yang Dacai Event (2012): the Party secretary of Security Supervision Bureau and director. He was human-flesh searched by netizens due to his photo on which he smiled at the site of accident of Baomao highway. He was investigated by relevant department due to that he wore luxury watches on different occasions. In September of 2013, Yang Dacai was sentenced 14 years in jail due to bribery and large amount of money of unknown source.
[3] Cat Abuse Event (2006): at 22:00 on February 26th, a netizen named broken glass posted an article named Anger: Cat abuse by a middle-aged female on Mop. This article introduced a sexy female who abused a little cat cruelly with a high heeled shoe. She claimed than these pictures were captured from a film about crushing little animals. This article was hotly replied. The name and occupation of the person involved as well as some personal information of the film maker were disclosed. The person involved was finally punished by her employer to a suspension of work and salary.
Reference
Bing Wang,Bonan Hou,Yiping Yao,Laibin Yan, (2009,Oct.).Human Flesh Search Modle Incorporating Network Expansion and GOSSIP with Feedback [Electronic version]. Simulation and Real Time Applications,10,82-88.
Bourdieu.P.(1984). Distinction:A Social Critique of the Judgement of Taste.United States of America.
Celia,H.(2014).China’s internet vigilantes and the human flesh search engine [Electronic version].BBC News, 1,1-3.
Emily,C.,Amy,M.,&Serge,D.(2009).Information Disclosure and Control on Facebook: Are They Two Sides of the Same Coin or Two Different Processes?CyberPsychology & Behavior, 12(3): 341-345.
Huang, Hou Ming&Lin, Yi Ren ( 2013 ) . Mob-ility: The Social Psychological
Foundation of Online Rabbling,The study of Journalism,4:1-50。
Jiang, Yi Xuan(2014).A study of the influence of face book input on the virtual
community consciousness from the perspective of media experience,Electronic
commerce research,12(4):357-376。
Li, Hui Ting (2010). Culture of Human Flesh Search in Taiwan, National Chiao Tung University.
Li, Shao Liang(2011).How is 150000 users' BBS possible:the study of PTT 's
technological change,Master thesis, Institute of social studies, National Zheng
Chi University.
Li, Tuo (2009). Research on the phenomenon of "human flesh search" in the view of media communication ,News knowledge,10:89-91.
Lin, Qi Xiu(2011).Human flesh search,Bulletin of Library and Information Science,11:31-47.
Richards,D.V.(2006).Posting Personal Information on the Internet:A Casefor Changing the Legal Regime Created by Sec. 230 of the Communications Decency Act.Taxes Law Review,85, 1321-1357.
Shi, Da (2009).Research on the relationship between Internet customer experience
and customer website loyalty -- Based on structural equation model, Research on Financial and Economic Issues,1:2-6。
Wang, B., Yao, Y., Hou, B., Liao, D., & Chen, D. (2010).Knowledge aggregation in human flesh search. Simulation and Real Time Applications,(4),82-88.
study of the human flesh.Computer Society,10:45-53 .
Xu, Qi Rong(2011). From virtual to real network culture: from the Gordon forum to
see the local mainstream media, popular culture and the interaction of the network community and conflict, Cultural Studies.22:1-27.
Yi, Zhen Zhen(2009).An analysis of the phenomenon of "human flesh search" in the
view of collective action ,The seventh academic annual conference of Social
Sciences in Shanghai.
Yin, Jun(2009).From the hustle and bustle of public opinion to the rational return -- A Study on the multi dimension of human flesh search, Sichuan University press. Yuan, Han Yu& Chen, Bai Ling(2013 年 7 月).The event to see the network collective
action by human flesh search: search behavior, together with the role of plot,Annual meeting of the China Communication Association.
Zhang, Jun Pei(2011). A preliminary study of the game experience of human flesh
search, Shih Hsin University.
Zhang, Xian(2010). Network cluster events between virtual and reality ,Journal of Social Science,6:37-41。
Zheng, Zhi Bin(2012). The wonderful gate: China's Internet event study. BeiJing.Communication University of China press.