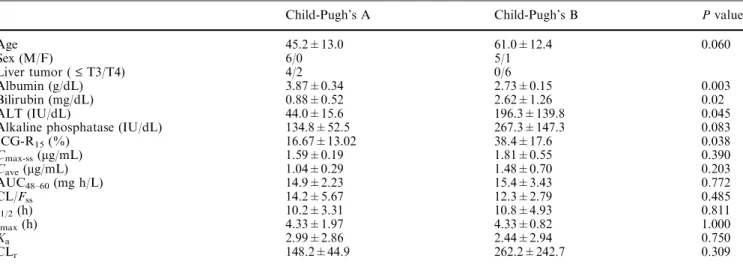
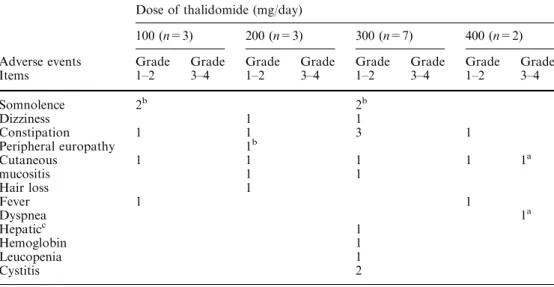
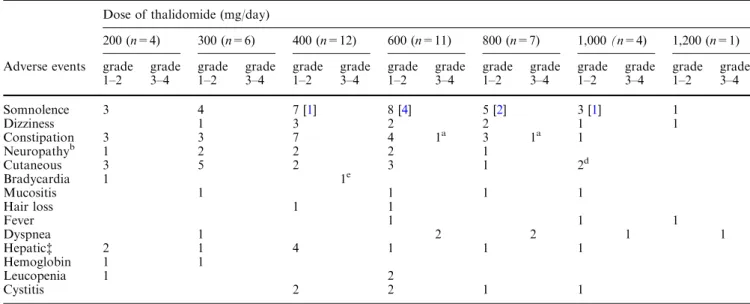
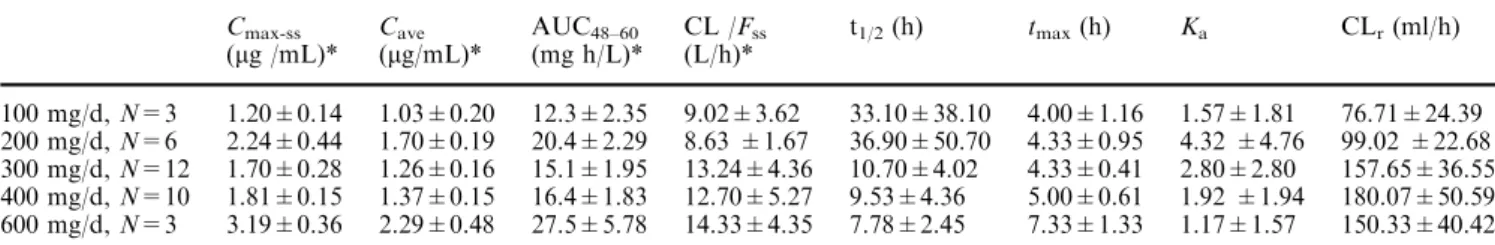
Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of oral thalidomide in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
全文
數據

相關文件
While Eneroth [47], in his study of incidence and prognosis of 2632 patients with tumors of the major and minor salivary glands, found an incidence of 15-25% of malignant neoplasms
In the present study, we reported a case of oral candidiasis where the association of a variety of factors linked to the patients’ systemic health and local environment disturbances
Aim: This study examined and classified patients who were treated at the Faculty of Dentistry at Ankara University Dentistry to determine the incidence of different types of
Background: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the immunohistochemical expression of NF-κB and IL-6 in oral premalignant and malignant lesions and to
pylori in pathogenesis of oral mucosal lesions or ulcerations is still unclear, it seems that patients with oral lesions as leukoplakia and oral lichen planus, and concurrent
To evaluate the clinicopathologic features, prognostic factors, and management of patients in the North Chinese population with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)
Objectives This study investigated the clinical effectiveness of intervention with an open-mouth exercise device designed to facilitate maximal interincisal opening (MIO) and
In this respect, the aim of the present study was to as- sess volumetric as well as morphological surface changes of the orbital cavity in patients treated with both tooth- borne