班級族群組成對學生學業成績的影響
全文
數據
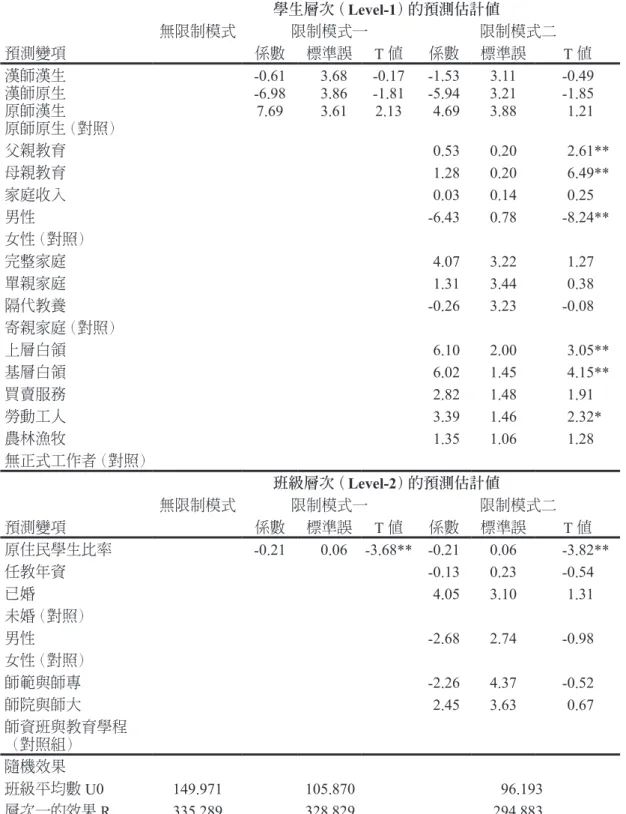
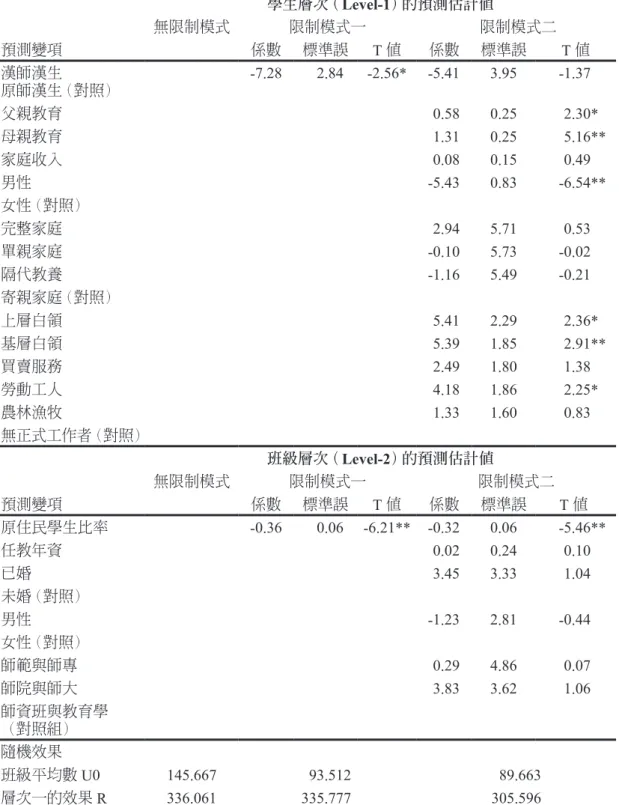
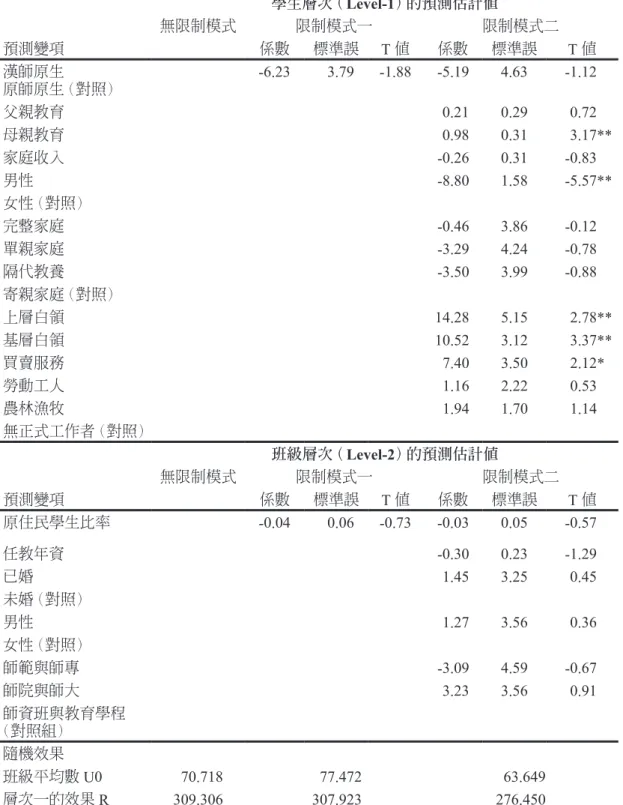
相關文件
(a) Classroom level focusing on students’ learning outcomes, in particular, information literacy (IL) and self-directed learning (SDL) as well as changes in teachers’
• Teaching grammar through texts enables students to see how the choice of language items is?. affected by the context and how it shapes the tone, style and register of
• Flipped Classroom: Promote students to do pre-study tasks and allow teachers to make effective use of lesson time. Major platforms
Subject/Topic: English Language/Endangered Animals Characteristics of Gifted/More Able students in class:. 8 students displaying high creativity and English abilities
A majority of the secondary schools adopted project learning to develop students’ language development strategies and generic skills but this was only evident in a small number of
educational needs (SEN) of students that teachers in the mainstream English classroom need to address and the role of e-learning in helping to address these needs;.. O To
educational needs (SEN) of students that teachers in the mainstream English classroom need to address and the role of e-learning in helping to address these needs;.. O To
The results revealed that (1) social context, self-perception, school engagement, and academic achievement were antecedents of dropping out; (2) students’ self-factor was a