行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫 成果報告
以多片(16 排)螺旋式電腦斷層掃描攝影完整評估嬰幼兒複
雜性先天性心臟病
計畫類別: 個別型計畫 計畫編號: NSC93-2314-B-002-184- 執行期間: 93 年 08 月 01 日至 94 年 07 月 31 日 執行單位: 國立臺灣大學醫學院放射線科 計畫主持人: 陳世杰 共同主持人: 邱英世,王主科 計畫參與人員: 陳世杰、邱英世 、王主科 報告類型: 精簡報告 處理方式: 本計畫可公開查詢中 華 民 國 94 年 10 月 27 日
行政院國家科學委員會補助專題研究計畫成果報告
※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※
※
以多片(16 排)螺旋式電腦斷層掃描攝影完整評估先天性心臟病
※
※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※
計畫類別: 一般個別型研究計畫
計畫編號: NSC 93-2314-B-002-184
執行期間: 93 年 08 月 01 日至 94 年 07 月 31 日
計畫主持人:陳世杰
共同主持人:王主科、邱英世
執行單位:台大醫學院
放射線科
中
華
民
國
94 年
10
月
24
日
以多片(16 排)螺旋式電腦斷層掃描攝影完整評估先天性心臟病
Integrated Evaluating the Congenital Heart Disease by
Multi-detectors (16) Spiral Computed Tomography
計畫編號:NSC 93-2314-B-002-184 執行期限:93 年 08 月 01 日至 94 年 07 月 31 日 主持人:陳世杰 台灣大學 醫學系 放射科 共同主持人:王主科 台灣大學 醫學系 小兒科 共同主持人:邱英世 台灣大學 醫學系 外科 一、中文摘要 本計劃的目的為以多片(16 排)螺旋式 電腦斷層掃描攝影完整評估先天性心臟病 的應用。在過去 12 個月中,吾等執行了 305 個電腦斷層掃描攝影檢查的病例(男:女 =188:117 ; 年齡=1 天~71 歲 8 月) 。所有 的病人都是接受靜脈注射顯影劑之電腦斷 層掃描攝影的檢查,且其影像取得皆位於 終心舒張期時。重組的 3D 影像採用漸層陰 影的表面呈現模式。與電子射東電腦斷層 的經驗比較,多片(16 排)螺旋式電腦斷層 掃描攝影,仍可以有效的將包括發育不良 之肺動脈、肺靜脈之異常回流、肺靜脈阻 塞之有無、異常冠狀動脈分枝、合併氣道 異常及有無狹窄、異常心內或心外構造之 奇特三度空間相互關係...等異常清楚的 呈現出來。再加上以三度空間立體影像呈 現出極度複雜的解剖構造及虛擬心臟內視 鏡影像完整呈現前所未有的心內異常變 化。 關鍵詞:先天性心臟病;三度空間立體影 像;電腦斷層掃描攝影。 ABSTRACT
To evaluate the clinical usefulness of multi-detector (16 detectors) spiral
cardiac anatomy in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD). In the past 12 months, 305 cases (male : female = 188 : 117; age = 1 days ~ 71-year-8-month) with CHD were analyzed. All MDCT images were taken at the end-diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle with intravenous injection of iodinated contrast medium. 3D reconstructed EBCT pictures were created with gradient shading surface rendering. In compare to the electron beam computed tomography, MDCT is reliable to well delineate the hypoplastic pulmonary artery, anomalous drainage of the pulmonary vein, where or not the presence of the pulmonary venous obstruction, abnormal branching of the coronary artery, associated tracheobronchial anomalies and stenosis, abnormal intra-cardiac and adjacent unusual three-dimensional spatial relationship. By adding the capability of three-dimensional demonstration and virtual reality cardioscopy, MDCT could show the extremely complex CHD completely and vividly.
Keywords: Congenital heart disease;
three-dimension; Computed tomography.
二、BACKGROUND & PURPOSE
Many factors influence the management of an infant with congenital heart disease. Clinically, the most important one thing is
group is a big trauma that does not need second revision at best. Thereafter,
comprehensive and complete evaluation of these anomalies before surgical intervention is absolutely mandatory. Echocardiography, cardiac catheterization are routinely used with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging as another alternative , but have their own disadvantage [1,2,3,4].
Our hospital is a major referring center for patient with congenital heart disease. In the past 8 years, our extensive experience in such disease group by electron beam
computed tomography revealed usually there are some weak points need to be further clarified even after echocardiography and cardiac angiography in order to make the surgical correction smoothly [5,6,7,8]. Multi-slice spiral computed tomography has rapid rotation X-ray tube and 16 rows
detectors. It examines the heart synchronized with ECG by prospective and retrospective scanning. Because of rapid scanning time, one study could be completed only in 3 minutes and has some advantage [5,9]. Moreover, those reconstructed 3D images provide a vivid picture for surgeon to make individualized surgical planning [7,10,11,12]. In this project, we plan to verify the
diagnostic power of this new technology in patient with CHD.
三、RESULTS
The diagnostic power of axial imaging
In compare to the previous experience from electron beam computed tomography, the diagnostic capability of MDCT is equal. There unclear points from the precordial echocardiography and the
cardio-angiography include the detail of the hypoplastic pulmonary artery, abnormal pulmonary venous drainage, pulmonary venous obstruction or not, unusual pattern of coronary artery, associated airway abnormality/stenosis, uncommon three dimensional relationship of abnormal intra-/extra-cardiac structures are all well delineated by the MDCT. However, due to the scanning time in one section in MDCT is slightly longer than electron beam computed tomography, the image quality in marginal sharpness is less well than electron beam computed tomography.
Useful post-processing imaging
With the accompanied advanced
software, MDCT provides better and more function in post-processing of the raw data and results in much more applications. Figure 1 demonstrates the use of the multi-plane reformatted image. Figure 2 clearly shows the status of the peripheral pulmonary arteries by computed
tomographic angiography. Figure 3
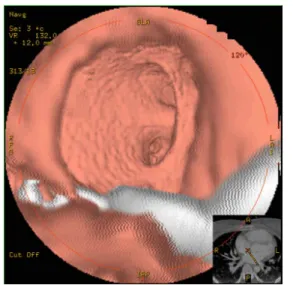
delineates the application of the thick-slab image to prevent the partial volume effect. Figure 4 reveals the classical usage of the three-dimensional image. Figure 5 creates the virtual cardioscopy image that is impossible in reality.
四、DISCUSSION
Using axial images by EKG-gated MDCT, this project has proved the comparative diagnostic reliability to electron beam computed tomography in detecting cardiac pathology that was poor or hardly disclosed by echocardiography or cardioangiography. In adding the information from three-dimensional reconstruction and/or virtual reality in the intra-cardiac viewpoint, surgeon can make a better planning in real intervention. We conclude that 16 rows detector MDCT
could be used to replace the electron beam computed tomography in diagnosis of the congenital heart disease. And, with the advanced post-processing software, more and more images by three-dimensional reconstruction and/or virtual reality can be applied easily and practically.
五、REFERENCES
1. Lee JJ, Kang D. Feasibility of electron beam tomography in diagnosis of congenital heart disease: comparison with
echo-cardiography. European Journal of Radiology. 38(3):185-90, 2001 Jun.
2. Russell J, Justino H, Dipchand A, et al. Freedom RM. Noninvasive imaging in congenital heart disease. Current Opinion in Cardiology. 15(4):224-37, 2000 Jul. 3. Tonkin IL. Imaging of pediatric congenital heart disease. Journal of Thoracic Imaging. 15(4):274-9, 2000 Oct.
4. Haramati LB, Glickstein JS, Issenberg HJ, et al. MR imaging and CT of vascular
anomalies and connections in patients with congenital heart disease: significance in surgical planning. Radiographics. 22(2):337-47; discussion 348-9, 2002 Mar-Apr.
5. Chen SJ, Lee WJ, Wang JK, et al. Usefulness of three-dimensional electron beam computed tomography for evaluating tracheobronchial anomalies in children with congenital heart disease. American Journal of Cardiology. 92(4):483-6, 2003 Aug 15.
by electron beam computed tomography in children with congenital heart disease. American Journal of Cardiology. 87(5):589-93, 2001 Mar 1.
7. Chen SJ, Li YW, Wang JK, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of abnormal ventriculoarterial relationship by electron beam CT. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography. 22(4):560-8, 1998 Jul-Aug.
8. Chen SJ, Li YW, Wang JK, et al. Usefulness of electron beam computed tomography in children with heterotaxy syndrome. American Journal of Cardiology. 81(2):188-94, 1998 Jan 15.
9. Kim YM, Yoo SJ, Kim TH, et al.
Three-dimensional computed tomography in children with compression of the central airways complicating congenital heart disease. Cardiology in the Young. 12(1):44-50, 2002 Jan.
10. Yamagishi M, Fujiwara K, Yamada Y, et al. Norwood operation for left isomeric heart with aortic atresia: evaluation with
three-dimensional computed tomography. Journal of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery. 121(6):1205-7, 2001 Jun. 11. Kawano T, Ishii M, Takagi J, et al. Three-dimensional helical computed tomographic angiography in neonates and infants with complex congenital heart disease. American Heart Journal. 139(4):654-60, 2000 Apr.
Three-dimensional helical CT of pulmonary arteries in infants and children with congenital heart disease. AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 173(1):109-15, 1999 J
六、SELF-EVALUATION
The result of this project revealed very consistent with the original proposal. Investigators have established a good protocol for perform the scanning of the MDCT and the post-processing procedures for three-dimensional and/or virtual reality reconstruction of the internal cardiovascular structures. The expected goal has successfully achieved by setting up a practical guideline and vivid delineation for diagnose different kinds of cardiac pathology in CHD. The clinical application of this result is great. Because this information will provide surgeon a clear road map of diseased heart before operation that help them decide a better manipulations.
七、FIGURES
Figure 1. Curved reformatted image in disclosing the status of the pulmonary artery of this patient after right side Glenn’s shunt and central Sano’s shunt. Focal stenosis in the proximal right pulmonary artery and intimal hyperplasia oftheSano’sshuntarerecognized.
Figure 2. Computed tomography pulmonary angiography in coronal projection reveals the normal branching of the bilateral peripheral pulmonary arteries and veins. The distal coronary sinus is dilated with an un-roofing communication upward to the floor of the left atrium.
Figure 3. Thick-slab computed tomography image in axial projection shows the free end of the implanted Button device atrial septal defect occluder penetrates through the dorsal wall of the left atrium.
Figure 4. Surface-shaded rendering three dimensional volume reconstruction of the pulmonary artery and the aorta delineates the presence of a patent ductus arteriosus as well as the unusual right sided origin of the left pulmonary artery.
Figure 5. Virtual cardioscopy in a patient with a residual atrial septal defect. She received an atrial septal defect occluder months ago, but a residual shunt was suspect by cardioechography. This virtual cardioscopy is viewing from the right atrium into the left atrium through this round residual defect. The two orifices in the center of this image are the orifices of the left upper & lower pulmonary veins. The white shadow in this virtual cardioscopy is the malposition of this occluder device.