The assessment of possible parental effects on BMI
status of university students
Yan-Han Yu , Jun-Ting Chen, Shwu-Huey Yang*
School of Nutrition and Health Sciences, Taipei Medical UniversityIntroduction
Materials and methods
Results and discussion
The global epidemic of overweight and obesity -"globesity“ –is rapidly becoming a major public health problem and further, the new burden in many parts of the world. World Health Organization ( WHO )’s previous data release indicates that in 2005 more than 1 billion adults were over-weight globally and at least 300 million of them obese. In the dimension of disease prevention, overweight and obe-sity are of the top awareness for they pose a major risk for chronic diseases, including typ-2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, stroke, and certain type of carcinoma. The dramatic shift in diet pattern and trend towards sedentary life style take place while genetic predisposition lies underneath. The purpose of this study is to assess the possible relation-ship between parental BMI and the BMI status of their off-spring using their anthropometric measurements.
Subject characteristics
A total sample of 160 college students were recruited from class 2004 and 2005, aged 20 ~22 yrs, in the School of Nutrition and Health Sciences at Taipei Medical University in March, 2007 and 2008.
Anthropometric data
The BMI of students and their parents was calculated from reported weight and height for both classes but the self-perceived anthropometric status and current living arrange-ments were collected from 69 junior students in class 2005. Statistical analysis
The prevalence of overweight and obesity was calculated and the relative risk referring to acceptable parental weight as the reference category was used to describe the associ-ation of offspring overweight between different parental overweight status.
Relative risk of offspring overweight
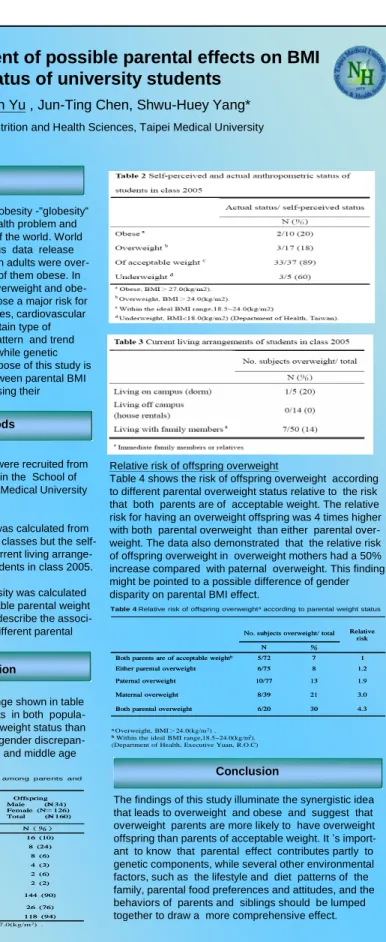
Table 4 shows the risk of offspring overweight according to different parental overweight status relative to the risk that both parents are of acceptable weight. The relative risk for having an overweight offspring was 4 times higher with both parental overweight than either parental over-weight. The data also demonstrated that the relative risk of offspring overweight in overweight mothers had a 50% increase compared with paternal overweight. This finding might be pointed to a possible difference of gender disparity on parental BMI effect.
Weight status of participants
The ratios for being within ideal BMI range shown in table 1 demonstrated that the female subjects in both popula-tions were more likely to stay in normal weight status than their male counterparts and the idea of gender discrepan-cy in prevalence of overweight at young and middle age
might be suggested. Conclusion
The findings of this study illuminate the synergistic idea that leads to overweight and obese and suggest that overweight parents are more likely to have overweight offspring than parents of acceptable weight. It’s import-ant to know that parental effect contributes partly to genetic components, while several other environmental factors, such as the lifestyle and diet patterns of the family, parental food preferences and attitudes, and the behaviors of parents and siblings should be lumped together to draw a more comprehensive effect. 118 (94) 122 (76) Female 26 (76) 83 (52) Male 144 (90) 205 (64)
Within ideal BMIrangeb
2 (2) 12 (8) Female 2 (6) 24 (15) Male 4 (3) 36 (11) Obesitya 8 (6) 38 (24) Female 8 (24) 77 (48) Male 16 (10) 115 (35) Overweighta N(%) N (%) Offspring Male (N=34) Female (N=126) Total (N=160) Parents Male (N=160) Female (N=160) Total (N=320) 118 (94) 122 (76) Female 26 (76) 83 (52) Male 144 (90) 205 (64)
Within ideal BMIrangeb
2 (2) 12 (8) Female 2 (6) 24 (15) Male 4 (3) 36 (11) Obesitya 8 (6) 38 (24) Female 8 (24) 77 (48) Male 16 (10) 115 (35) Overweighta N(%) N (%) Offspring Male (N=34) Female (N=126) Total (N=160) Parents Male (N=160) Female (N=160) Total (N=320)
Table 1 Prevalence of overweight and obesity among parents and
Offspring
aOverweight and obese, BMI>24.0(kg/m2) and>27.0(kg/m2) .
bIdeal BMI range,18.5~24.0(kg/m2). (Department of Health, Executive Yuan, R.O.C)
4.3 30 6/20 Both parental overweight
3.0 21 8/39 Maternal overweight 1.9 13 10/77 Paternal overweight 1.2 8 6/75 Either parental overweight
1 7 5/72 Both parents are of acceptable weightb
% N
Relative risk No. subjects overweight/ total
4.3 30 6/20 Both parental overweight
3.0 21 8/39 Maternal overweight 1.9 13 10/77 Paternal overweight 1.2 8 6/75 Either parental overweight
1 7 5/72 Both parents are of acceptable weightb
% N
Relative risk No. subjects overweight/ total
Table 4 Relative risk of offspring overweightaaccording to parental weight status
aOverweight, BMI>24.0(kg/m2) .
bWithin the ideal BMI range,18.5~24.0(kg/m2). (Department of Health, Executive Yuan, R.O.C)