138.6
Propagation
of
Electromagnetic Waves in Laminated
Periodic Composite Structures
Huann-Ice Chiu, Hsiao-Ckang Chu. and Chun Hsiung Chen Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University.
Taipei, Taiwan 10617
A b s t r a c t
A new model based on filament-current and thin-current assumptions
together with suitable phase correction is proposed for discussing the elec- tromagnetic fields in a multi-layered and lossy periodic composite structure which has circular conductiIig fibers embedded in a dielectric matrix. In this
study, numcrical results for graphitc/cpoxy
(G/E)
composites are presentedand compared with previous investigation. This new model is useful in char-
acterizing the composite materials even up to the higher frequency range. I n t r o d u c t i o n
Advanced composite materials have recently been suggested as substi- tutes for metals in modern aircraft systems due to their superior mechanical properties. But the shieldiiig and reflection properties of advanced composite
materials are significantly different from those of metals, making the study
of their electromagnetic characteristics an important issue in electromagnetic
compatibility
(EPIC).
Previous electromagnetic investigations of composite materials were mostly in the lower frequency range in which the fiber spacing is much less than the wavelength. Under such a condition, the composite material may be modeled as a laminated anisotropic medium and bulkily represented by a
complex permittivity tensor
[l].
But this bulk tensor model is inadequate inanalyzing the reflection and transmission characteristics in higher frequency range in which the fiber spacing is comparable to the wavelength.
In higher frequency range, the composite material should be modeled as a lossy periodic structure of having conducting fibers embedded in a di-
electric matrix. Recently, a filament-current phase-correction model
[a]
hasbeen proposed to analyze its higher frequency effect for the
T M
case. Hovv- ever, only single-layer composite structures are analyzed. In this study, a simplified model is proposed to analyze the plane-wave shielding and reflec- tion properties of a laminated periodic fiber-matrix composite structure.Formulation
Consider an electromagnetic propagation problem in which a plane
wave i s obliquely incident upon an N-ply laminated periodic composite struc-
ture as shown in Fig. 1. Each individua.1 lamina has conducting fibers of radius a and conductivity D embedded in a dielectric matrix of thickness
t
0-7803-4178-3/97/$10.00
0
1997IEEE
and dielectric. constant e,. The periodic spacing is d and the strilcture is uniform in Q’ direction.
LVe first use the filament-current model [2] to discuss the induced cur- rent along the fiber direction in each fiber and assume that the fiber current is concentrated along the fiber center. We then use the thin-current model to treat the induced current perpendicular to the fiber direction and assume that the induced current is concentrated on the plane z’ =
0.
Next, the scat- tering effect of the fibers is dealt with by calculating the scattered field from the induced currents both parallel and perpendicular to the fiber direction. Finally, by including the effect of the dielectric matrix. multiple reflection and transmission at the air-matrix interfaces, as well as the phase correction across the fiber grating [2], one may obtain the reflected and transmitted Floquet mode fields from which the shielding effectiveness( S E )
and reflec- tion loss( R )
may be calculated.Results
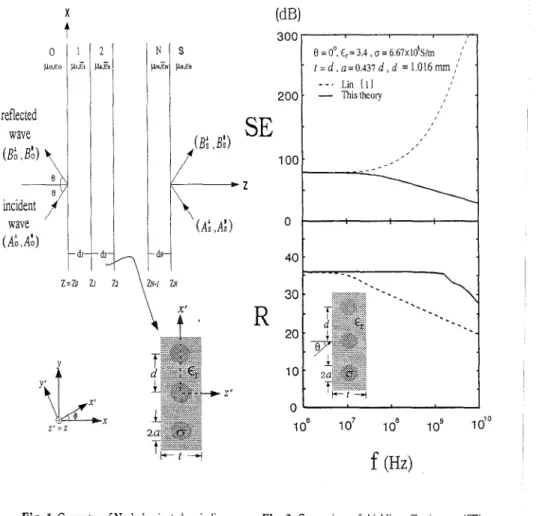
.A
comparison of our results for a single-layerG/E
composite with those of Lin [I] is shown in Fig. 2. The effect of varing the layer number :V is presented in Fig. 3 , where the results of Lin [l] are also included. Good agreement between both results again supports the superiority of the bulk tensor model [l] in the lower frequency range(f
<
10’ Hz). Fig. 4 shows the effect of varing the incident angle 8 for 4-plyG/E
composite. Results of thebulk tensor model and the approximate model which only takes the filament current into consideration ace also included for comparison. It is found that there is no evident distinction for the incident angle 8
<
70”.Conclusion
A new model based on filament-current and thin-current assumptions
together with suitable phase correction has been proposed to analyze the
propagation chaxacteristics of a multilayer composite material. This model
can efficiently handle the complicated laminated periodic structure with re-
duced
CPU
time in computation even up t o the higher frequency range.Acknowledgment
Republic of China under Grant NSC 56-2213-E-002-020.
References
[I]
&I.-S.
Lin and C.H.
Chen, “Plane-wave shielding characteristics ofanisotropic laminated composites,”
IEEE
Trans. Electromagn. Compat.,[2]
H.-C.
Chu aridC. H.
Chen, “Shielding and Reflection Propertiesof Periodic Fiber-Matrix Composite Structures,’IEEE Trans. Electromagn.
Compat., vol. 35. no. 1, pp. 1-6, Feb. 1996.
This study was supported by the National Science Council of Taiwan,
vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 21-27, Feb. 1993.
(dB)
8=0°.E,=3.3 , a = 6 . 6 7 ~ 1 d S / m300r---l
1 = d , a=0.337 d , d = 1.016 ,' Xt
I
1
reflected
(Bi
,Bb)
wave
incident
wave
c
d,-(A'~,A:)
I \
I
&- I Z' Y xFig.
1. Geometry of N-ply laminated periodic composite structures. Lin [ i l 200.
-
Thistheorj_ _ - -
100. O t - - - l 40Fig.
2. Comparison of shielding effectiveness(SE)
and reflection loss
(R)
for single-layer GIE compositewith those of Lin [l].
![Fig. 4. SE and R of 4-ply G/E composite with different incident angle 0. Results of Lin [l] are also included for](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/9libinfo/8850398.241935/4.920.461.695.102.564/fig-composite-different-incident-angle-results-lin-included.webp)