Natural frequency analysis of tooth stability under various simulated types and degrees of alveolar vertical bone loss
全文
數據
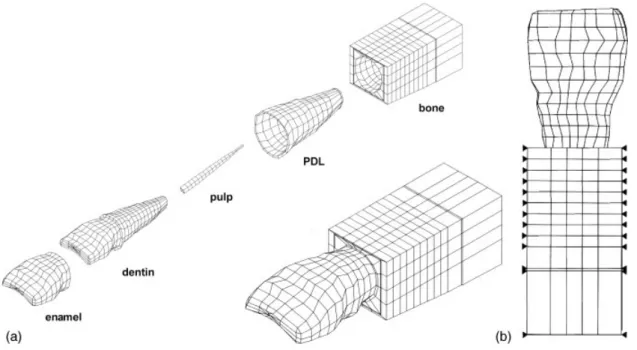

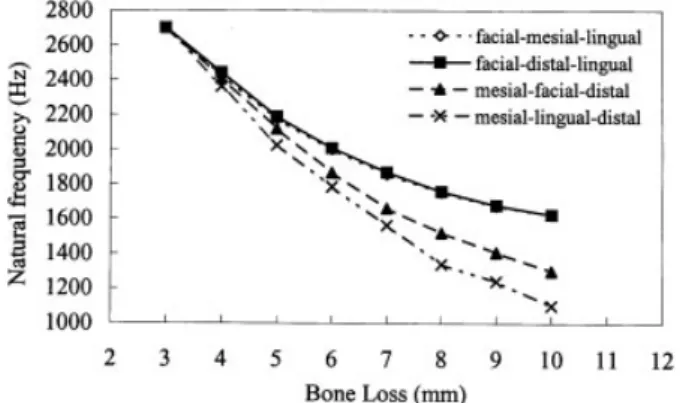
相關文件
There is a well-defined unilocular round shaped radiolucence with a corticated margin over the apex of tooth 32,33, which extending from mesial aspect of tooth 34 root apex to
posterior maxilla, extending from the distal side of tooth 24 to the left maxillary tuberosity, and from 2/3 height of left maxillary sinus to the left maxillary.. alveolar crest
margin over left posterior maxilla, extending from the distal side of tooth 24 to the mesial side of tooth 26 , and from the border of left maxillary sinus to the left
¾ Alveolar bone loss leads to generalized tooth mobility, which when coupled with signs of periodontal disease in a child should raise suspicions of systemic disease affecting
To overcome this, palatal root torque is needed during orthodontic movement of the tooth to increase the buccal bone thickness, decrease the risk of bone dehiscence and decrease
• A considerable hypodense area in the left side of the mandibular body affected the mental foramen area and extended back to the apex of the mesial root of tooth #178.
In this case report an extreme case of severe multiple idiopathic cervical root resorption in a healthy young adult male, involving every tooth and leading to the loss of 14
The present case represents an extreme example of multiple cervical root resorption, involving every tooth and leading progressively to the loss of 14 teeth, at a relatively