Original Article
Prognosis of patients with acute respiratory failure and prolonged
intensive care unit stay
Chih-Cheng Lai1#, Kuei-Ling Tseng2#, Chung-Han Ho3,4, Shyh-Ren Chiang2,4, Chin-Ming Chen4,5, Khee-Siang Chan5, Chien-Ming Chao1, Shu-Chen Hsing2, Kuo-Chen Cheng2,6
1Department of Intensive Care Medicine, 2Department of Internal Medicine, 3Department of Medical Research, Chi Mei Medical Center, Liouying, Tainan; 4Department of Hospital and Health Care Administration, Chia Nan University of Pharmacy & Science, Tainan; 5Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Chi Mei Medical Center, Tainan; 6Department of Safety Health and Environmental Engineering, Chung Hwa University of Medical Technology, Tainan
Contributions: (I) Conception and design: CC Lai, KC Cheng; (II) Administrative support: None; (III) Provision of study materials or patients: None; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: CC Lai, SR Chiang, CM Chen, KS Chan, CM Chao, KL Tseng, SC Hsing; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: CC Lai, KC Cheng, CH Ho; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Correspondence to: Kuo-Chen Cheng. Department of Internal Medicine, Chi Mei Medical Center, 901 Zhonghua Road, Yongkang District, 71044, Tainan. Email: kcg.cheng@gmail.com; Chin-Ming Chen. Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Chi Mei Medical Center, 901, Zhonghua Road, Yongkang District, 71044, Tainan. Email: chencm3383@gmail.com.
Background: Reasons for the prolonged critical care support include uncertainty of outcome, the complex dynamic created between physicians with care team members and the patient’s family over a general unwillingness to surrender to unfavorable outcomes. The purpose of this study was to investigate outcomes and identify risk factors of patients with acute respiratory failure (ARF) who required a prolonged intensive care unit (ICU) stay (≥21 days). It may provide reference to screen patients who are suitable for hospice care. Methods: The medical records of all ARF patients with a prolonged ICU stay were retrospectively reviewed. The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality.
Results: We identified 1,189 patients. Sepsis (n=896, 75.4%) was the most common cause of prolonged ICU stays, following by renal failure (n=232, 19.5%), and unstable hemodynamic status vasopressors or arrhythmia (n=208, 17.5%). Using multivariable logistic regression, we identified eight risk factors of death: age >75 years, ICU stay for more than 28 days, APACHE II score ≥25, unstable hemodynamic status, renal failure, hepatic failure, massive gastrointestinal tract bleeding, and using a fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) ≥40%. The overall in-hospital mortality rate was 53.6% (n=637), and it up to 75.3% (216/287) for patients with at least three risk factors.
Conclusions: The outcome of patients with ARF who required prolonged ICU stay was poor. They had a high risk of in-hospital mortality. Palliative care should be considered as a reasonable option for the patients at high risk of death.
Keywords: Acute respiratory failure (ARF); prolonged intensive care unit stay (prolonged ICU stay); mortality;
prognostic factor
Submitted Dec 22, 2018. Accepted for publication Apr 17, 2019. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.04.84
Introduction
Acute respiratory failure (ARF) is the most common reason that critically ill patients require intensive care unit (ICU) admission (1-3). Although some patients have favorable outcomes and early ICU discharges, others require a prolonged ICU stay. However, some complications such as muscle weakness, pressure ulcers, device-associated infections, pulmonary embolism, and delirium can develop during a prolonged ICU stay (4). Moreover, a prolonged ICU stay can be associated with increased hospital mortality, increased morbidity and hospital stay and poor long-term prognosis (4-8). In addition, critically ill patients with a prolonged ICU stay will require a greater than average expenditure of healthcare worker time and medical resources (5).
Reasons for the prolonged critical care support include uncertainty of outcome, the complex dynamic created between a physician and the patient’s family over a general unwillingness to surrender to unfavorable outcomes, and the ethical, legal, and cultural implications of addressing end-of-life issues. These questions continue to make up one of the most difficult components of caring for critically ill patients after ARF and will most likely never have simple answers. To simplify decision-making, it is important to develop a more comprehensive understanding of the outcomes of these patients. Thus, we investigated outcomes and identified risk factors of ARF patients who required prolonged ICU stays.
Methods
Patients and hospital setting
This study was conducted in Chi Mei Medical Center, which has 96 adult ICU beds: 57 medical beds, 39 surgical beds, and 16 Respiratory Care Center (RCC) beds. The care in the medical and surgical ICU patients is covered by intensivists, senior residents, nurses, respiratory therapists, dietitians, physical therapists, and clinical pharmacists. The ICU team including intensivists makes rounds at least once daily, and is responsible for managing all critical illness (9,10). In our hospital, all patients who use MV for more than 21 days in the ICU undergo an assessment of the appropriateness of a transfer to the RCC for further weaning process after the stabilization of the clinical condition (11-14). The RCC admission decision is made by intensivists and RCC physicians. The objective of RCC admission is to aggressively wean PMV patients from
MV. The criteria of RCC admission included a stable hemodynamic status with no need for a vasopressor, no new development of complicated arrhythmia or signs of acute coronary artery syndrome, a stable renal function and normal acid-base balance, controlled infections, and being more than 17 years old (13,14). In contrast, patients meeting the following criteria were not admitted to the RCC on the ICU day 21: major organ dysfunctions: an unstable hemodynamic status that requires a vasopressor, arrhythmia, renal failure or required hemodialysis, liver failure, massive gastrointestinal tract bleeding, sepsis, required additional surgical intervention, unstable oxygenation status—using FiO2 ≥40% and positive
end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) ≥10 cmH2O to maintain SpO2
>90% (15). In this retrospective study, all patients with ARF who required a prolonged ICU stay but not eligible for RCC transfer between January 2000 and August 2015 (≥21 days) were identified. The study was approved by the institutional review board of Chi Mei Medical Center, and informed consent was waived.
Variable measurement
The medical records of all eligible patients were retrospectively reviewed, and the following information was collected: age, gender, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE II) scores upon ICU admission, causes of prolonged ICU stay, duration of MV use, and ICU stays. The outcome was in-hospital mortality. Data were routinely collected, and the analysis was retrospective.
Definitions
ARF was defined as the patients requiring endotracheal tube with invasive mechanical ventilation. Sepsis was defined as the systemic response to infection, manifested by two or more of the SIRS criteria as a result of infection. The definitions of organ dysfunctions were used according to previous study (10) as the following: cardiovascular failure: systolic blood pressure (SBP) of ≤90 mmHg or a mean arterial pressure (MAP) ≤65 mmHg for at least 1 h despite adequate fluid resuscitation or the need for vasoactive agents; metabolic failure: pH ≤7.30 and a plasma lactate level >3 mmol/L; hematologic failure: a platelet count <80,000 per mm3 or 50% decrease in platelet count from
the highest value recorded over the past 3 days; kidney failure: oliguria with an average urine output <0.5 mL/kg
per h for 4 h despite adequate fluid resuscitation or creatinine ≥2 mg/dL; hepatic failure: markedly increased serum bilirubin level ≥4 mg/dL.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and categorical variables are presented as frequency with percentage. Differences in baseline characteristics and clinical variables between survival and mortality groups were evaluated using Student’s t-test for continuous variables and Pearson χ2 tests for categorical
variables. The logistic regression model was used to examine the association between predictive variables and the mortality using odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The final prediction model was constructed from baseline characteristics and clinical variables with P<0.05 as candidates, and the multiple logistic regression analysis with the stepwise model-selection approach was used to present the final risk factors of mortality. SAS 9.4 for Windows (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) was used for all analyses. Significance was set at P<0.05 (two-tailed). Results
Demographic characteristics
During the study period, 1,189 patients [mean age: 68.2±15.6 years; >80 years: 521 patients (28.6%); men: 721 (60.6%)] with ARF who required a prolonged ICU stay were identified. The APACHE II scores upon ICU admission were 21.2±8.5. A total of 414 (34.8%) for patients who had undergone renal replacement therapy (RRT) during their ICU stay; continuous RRT (CRRT) was used in 255 (21.4%) patients. Pneumonia was the most common primary diagnosis in patients with a prolonged ICU stay (n=422, 35.5%), followed by an infection other than pneumonia (n=236, 19.8%), neuromuscular disease (n=185, 15.6%), decompensated gastrointestinal failure (n=165, 13.9%), decompensated heart failure (n=123, 10.3%), and other postoperative complications (n=28, 2.4%). In summary, sepsis (n=896, 75.4%) was the most common cause of prolonged ICU stays, following by renal failure (n=232, 19.5%), and arrhythmia or an unstable hemodynamic status requiring a vasopressor (n=208, 17.5%), massive gastrointestinal tract bleeding (n=115, 9.7%), using FiO2 ≥40% (n=111, 9.3%), needing
subsequent surgery (n=83, 7.0%), having a hepatic failure
(n=53, 4.5%), and using PEEP ≥10 cmH2O (n=53, 4.5%).
The ICU length of stay (LOS) was 31.0±11.6, and 533 (44.8%) patients stayed in the ICU for >28 days.
Outcome analysis
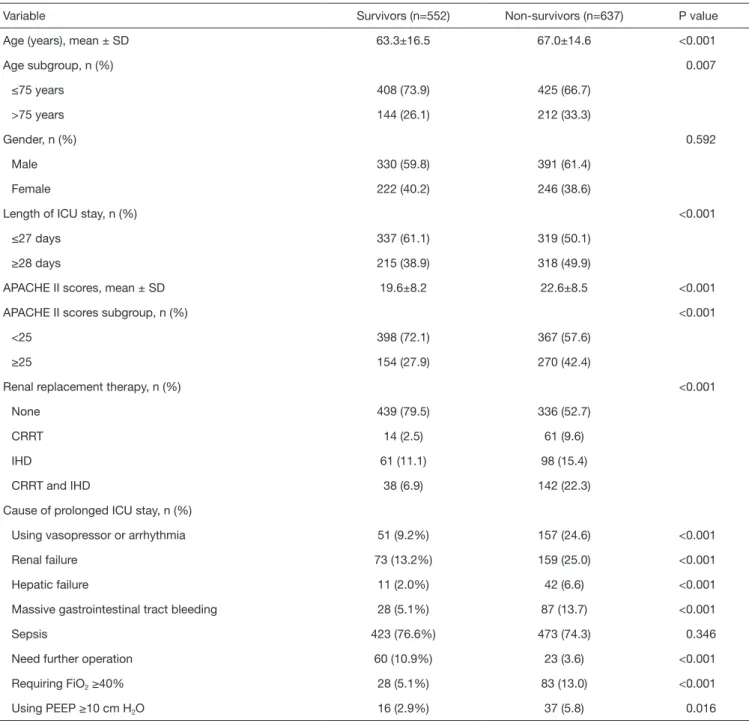
The in-hospital mortality rate was 53.6% (n=637). Non-survivors were significantly older, more likely to have an ICU stay ≥28 days or require CRRT, and to have higher APACHE II scores than were patients who survived (all P<0.0001) (Table 1). Additionally, among the causes of prolonged ICU stay, non-survivors were more likely to have used a vasopressor or had arrhythmia, renal failure, hepatic failure, or massive gastrointestinal tract bleeding, or to have required FiO2 ≥40% or PEEP ≥10 cmH2O than were
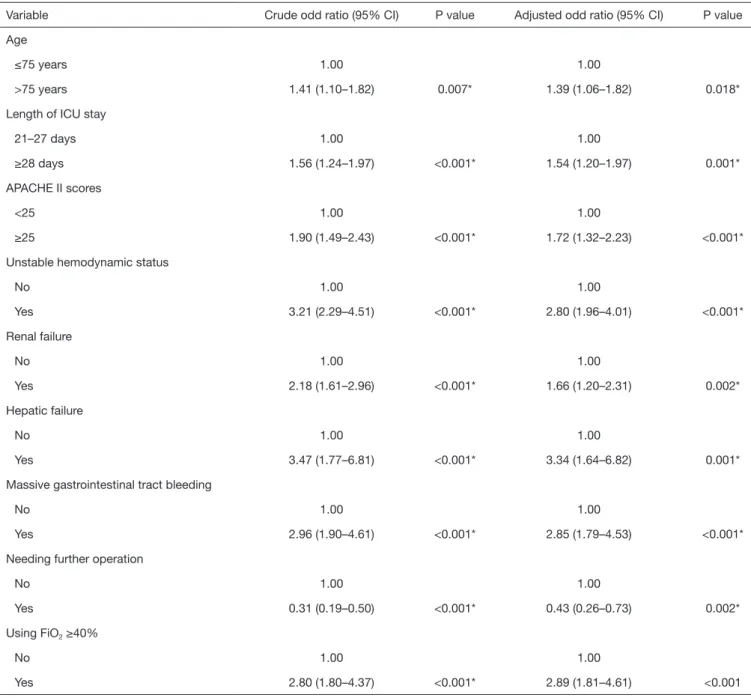
patients who survived. In contrast, patients who survived were more likely to need subsequent surgery than were non-survivors. Multivariable logistic regression showed that the risk of death was associated with being >75 years [adjusted OR (AOR): 1.39, 95% CI: 1.06–1.82, P=0.018], having an ICU LOS >28 days (AOR: 1.54, 95% CI: 1.20–1.97, P=0.001), an APACHE II score ≥25 (AOR: 1.72, 95% CI: 1.32–2.23, P<0.001), an unstable hemodynamic status (AOR: 2.80, 95% CI: 1.96–4.01, P<0.001), a renal failure (AOR: 1.66, 95% CI: 1.20–2.31, P=0.002), a hepatic failure (AOR: 3.34, 95% CI: 1.64–6.82, P=0.001), massive gastrointestinal tract bleeding (AOR: 2.85, 95% CI: 1.79–4.53, P<0.001), and using FiO2 ≥40% (AOR: 2.89, 95% CI: 1.81–4.61,
P<0.001) (Table 2). In contrast, the need for subsequent surgery was associated with better survival (AOR: 0.43, 95% CI: 0.26–0.73, P=0.002). Thus, eight poor and one favorable prognostic factor were identified. Patients with more poor prognostic factors had a higher mortality rate (Figure 1).
Discussion
We investigated the outcome and prognostic factors of 1,189 patients with ARF who required a prolonged ICU stay, and who had several significant findings. First, the mortality of this highly selective population is high. More than half of these patients died in the hospital. In Taiwan, if patients in the ICU require PMV for more than 21 days, physicians should consider transferring them to the RCC when their clinical condition is stable. Therefore, PMV patients in Taiwan have two further dispositions – remained stay in ICU due to unstable clinical condition and RCC transfer with stable clinical condition. Our hospital has this
Table 1 Comparison of clinical variables of all patients
Variable Survivors (n=552) Non-survivors (n=637) P value
Age (years), mean ± SD 63.3±16.5 67.0±14.6 <0.001
Age subgroup, n (%) 0.007 ≤75 years 408 (73.9) 425 (66.7) >75 years 144 (26.1) 212 (33.3) Gender, n (%) 0.592 Male 330 (59.8) 391 (61.4) Female 222 (40.2) 246 (38.6)
Length of ICU stay, n (%) <0.001
≤27 days 337 (61.1) 319 (50.1)
≥28 days 215 (38.9) 318 (49.9)
APACHE II scores, mean ± SD 19.6±8.2 22.6±8.5 <0.001
APACHE II scores subgroup, n (%) <0.001
<25 398 (72.1) 367 (57.6)
≥25 154 (27.9) 270 (42.4)
Renal replacement therapy, n (%) <0.001
None 439 (79.5) 336 (52.7)
CRRT 14 (2.5) 61 (9.6)
IHD 61 (11.1) 98 (15.4)
CRRT and IHD 38 (6.9) 142 (22.3)
Cause of prolonged ICU stay, n (%)
Using vasopressor or arrhythmia 51 (9.2%) 157 (24.6) <0.001
Renal failure 73 (13.2%) 159 (25.0) <0.001
Hepatic failure 11 (2.0%) 42 (6.6) <0.001
Massive gastrointestinal tract bleeding 28 (5.1%) 87 (13.7) <0.001
Sepsis 423 (76.6%) 473 (74.3) 0.346
Need further operation 60 (10.9%) 23 (3.6) <0.001
Requiring FiO2 ≥40% 28 (5.1%) 83 (13.0) <0.001
Using PEEP ≥10 cm H2O 16 (2.9%) 37 (5.8) 0.016
CRRT, continuous renal replacement therapy; IHD, intermittent hemodialysis.
policy, and the in-hospital mortality rate of PMV patients in RCC was only 17.6% (14), which was much lower than that of the present study. In contrast to previous study of all PMV patients, this study only focused on the PMV patients remained stay in the ICU and cannot be transferred to RCC due to the unstable clinical condition. Thus, the patients in this study were more critical and had worse outcome than
the PMV patients transferred to RCC. The differences exist most likely because the patients in the present study remained unstable after 21 days of ICU treatment, but ICU patients transferred to the RCC were stable. The outcomes of ICU patients not eligible for RCC transfer in Taiwan are poor.
Table 2 Risk factors associated with in-hospital mortality determined using logistic regression analysis
Variable Crude odd ratio (95% CI) P value Adjusted odd ratio (95% CI) P value Age
≤75 years 1.00 1.00
>75 years 1.41 (1.10–1.82) 0.007* 1.39 (1.06–1.82) 0.018*
Length of ICU stay
21–27 days 1.00 1.00
≥28 days 1.56 (1.24–1.97) <0.001* 1.54 (1.20–1.97) 0.001*
APACHE II scores
<25 1.00 1.00
≥25 1.90 (1.49–2.43) <0.001* 1.72 (1.32–2.23) <0.001*
Unstable hemodynamic status
No 1.00 1.00 Yes 3.21 (2.29–4.51) <0.001* 2.80 (1.96–4.01) <0.001* Renal failure No 1.00 1.00 Yes 2.18 (1.61–2.96) <0.001* 1.66 (1.20–2.31) 0.002* Hepatic failure No 1.00 1.00 Yes 3.47 (1.77–6.81) <0.001* 3.34 (1.64–6.82) 0.001*
Massive gastrointestinal tract bleeding
No 1.00 1.00
Yes 2.96 (1.90–4.61) <0.001* 2.85 (1.79–4.53) <0.001*
Needing further operation
No 1.00 1.00 Yes 0.31 (0.19–0.50) <0.001* 0.43 (0.26–0.73) 0.002* Using FiO2 ≥40% No 1.00 1.00 Yes 2.80 (1.80–4.37) <0.001* 2.89 (1.81–4.61) <0.001 *, P<0.05.
of this specific population, including age >75 years, an ICU stay >28 days, and an APACHE II score ≥25. This is reasonable that these three factors are associated with poor outcomes. In addition, several clinical conditions—unstable hemodynamic status, renal failure, hepatic failure, massive gastrointestinal tract bleeding, and requiring FiO2 ≥40%
on ICU day 21—were associated with a high risk of death. Each might indicate a specific organ dysfunction and can
be associated with a poor outcome. For example, both liver cirrhosis and end-stage renal disease increase the risk of death after MV, according to Taiwanese population-based studies (16,17). The previously cited Korean study (18) reported that needing vasopressors on ICU day 21 was an independent factor of mortality in patients who required PMV (HR: 1.822; 95% CI: 1.111–2.986; P=0.017). Moreover, we found that patients with more risk factors had
worse outcomes: the mortality rate was approximately 50% for patients with at least one poor prognostic factor, and >75% for patients with at least three. We identified eight risk factors of death patients who required a prolonged ICU stay; this should help us better predict outcomes for such patients. We suggest in those patients with over three risk factors who are at high risk of death, intensivists should evaluate daily as the introduction of further treatments may not be beneficial to them. The goals of care should be carefully assessed in collaboration with the patients and their families in this critical condition. The adoption of protocols related to end-of-life patients may be considered. A multidisciplinary team could help determining whether the withdrawal or withholding of advanced care is appropriate. In addition, patients and families should be informed that palliative care involves the best possible care for that specific situation, as well as respect for their wishes and the consideration of social and spiritual backgrounds.
Third, we found that patients who required a prolonged ICU stay because they needed additional surgery had a lower mortality rate. These patients were clinically relatively stable and were postoperatively transferred to a general ward or to the RCC. Therefore, their outcomes were unsurprisingly better than those of clinically unstable patients with more risk factors for mortality.
This study had one major limitation. It was conducted in a single medical center, and the final decision regarding whether the patients could be transferred to RCC was made by each patient’s physician. Thus, our findings might not be generalizable to other hospitals. However, our
long-term study included >1,000 patients. Therefore, our findings should be representative and should provide useful information on patients with ARF who require a prolonged ICU stay.
In conclusion, the outcomes of patients with ARF who required a prolonged ICU stay were poor. Age >75 years, an ICU stay >28 days, an APACHE II score ≥25, unstable hemodynamic status, renal failure, hepatic failure, massive gastrointestinal tract bleeding, and requiring FiO2 ≥40% on
ICU day 21 were associated with a high risk of in-hospital mortality. Palliative care could be a reasonable option in these patients at high risk of death.
Acknowledgments None.
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Statement: The Chi Mei Medical Center Institutional Review Board approved the study and specifically waived informed consent
References
1. Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA 2016;315:788-800.
2. Fowler RA, Abdelmalik P, Wood G, et al. Critical care capacity in Canada: results of a national cross-sectional study. Crit Care 2015;19:133.
3. Rhodes A, Moreno RP, Metnitz B, et al. Epidemiology and outcome following post-surgical admission to critical care. Intensive Care Med 2011;37:1466-72.
4. Loss SH, de Oliveira RP, Maccari JG, et al. The reality of patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation: a multicenter study. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva 2015;27:26-35. 5. Foxton MR, Al-Freah MA, Portal AJ, et al. Increased
model for end-stage liver disease score at the time of liver transplant results in prolonged hospitalization and overall intensive care unit costs. Liver Transpl 2010;16:668-77. 6. Smith JO, Shiffman ML, Behnke M, et al. Incidence
of prolonged length of stay after orthotopic liver transplantation and its influence on outcomes. Liver Figure 1 The number of cases and mortality rate of patients with
poor prognostic factors.
400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0
Case number Mortality rate
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Risk factors
Mortality cases Total caes Mortality rate 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 100% 94.7% 78.7% 71.9% 57.8% 49.9% 21.2%
Transpl 2009;15:273-9.
7. Yu PJ, Cassiere HA, Fishbein J, et al. Outcomes of Patients With Prolonged Intensive Care Unit Length of Stay After Cardiac Surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2016;30:1550-4.
8. Delle Karth G, Meyer B, Bauer S, et al. Outcome and functional capacity after prolonged intensive care unit stay. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2006;118:390-6.
9. Lai CC, Chen CM, Chiang SR, et al. Establishing predictors for successfully planned endotracheal extubation. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e4852. 10. Lai CC, Sung MI, Liu HH, et al. The Ratio of Partial
Pressure Arterial Oxygen and Fraction of Inspired Oxygen 1 Day After Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Onset Can Predict the Outcomes of Involving Patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e3333.
11. Cheng SH, Jan IS, Liu PC. The soaring mechanic ventilator utilization under a universal health insurance in Taiwan. Health Policy 2008;86:288-94.
12. Liu CJ, Chu CC, Chen W, et al. Impact of Taiwan's integrated prospective payment program on prolonged mechanical ventilation: a 6-year nationwide study. Respir
Care 2013;58:676-82.
13. Lai CC, Ko SC, Chen CM, et al. The Outcomes and Prognostic Factors of the Very Elderly Requiring Prolonged Mechanical Ventilation in a Single Respiratory Care Center. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e2479. 14. Lai CC, Shieh JM, Chiang SR, et al. The outcomes
and prognostic factors of patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation. Sci Rep 2016;6:28034. 15. Available online: http://www.nhi.gov.tw/Resource/
webdata/13988_1_1050002331-1.pdf
16. Lai CC, Ho CH, Cheng KC, et al. Effect of liver cirrhosis on long-term outcomes after acute respiratory failure: A population-based study. World J Gastroenterol 2017;23:2201-8.
17. Chen CM, Lai CC, Cheng KC, et al. Effect of end-stage renal disease on long-term survival after a first-ever mechanical ventilation: a population-based study. Crit Care 2015;19:354.
18. Kim MH, Cho WH, Lee K, et al. Prognostic factors of patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation in a medical intensive care unit of Korea. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 2012;73:224-30.
Cite this article as: Lai CC, Tseng KL, Ho CH, Chiang
SR, Chen CM, Chan KS, Chao CM, Hsing SC, Cheng KC. Prognosis of patients with acute respiratory failure and prolonged intensive care unit stay. J Thorac Dis 2019;11(5):2051-2057. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.04.84