International Journal of Electronic Business Management, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 113-121 (2012) 113
SYSTEM DYNAMICS APPROACH TO VISITORS’
LONG-TERM SATISFACTION WITH MUSEUM:
A CASE STUDY OF THE NATIONAL MUSEUM OF
NATURAL SCIENCE
Chih-Tung Hsiao
1and Ming-Hung Yao
2*1
Department of Economics
Tunghai University
Taichung (407), Taiwan
2
Department of Public Finance and Taxation
National Kaohsiung University of Applied Sciences
Kaohsiung (807), Taiwan
ABSTRACT
The National Museum of Natural Science (NMNS) was established in 1986. By 1999, the NMNS exceeded the 3 million visitors mark, surpassing the National Palace Museum to become Taiwan’s largest museum, and established itself as one of the top five museums in the world. From 1999 to 2008, the NMNS received more than 3 million visitors, attaining the status of being the single most important leisure destination for the people of Taiwan. Like other Taiwanese museums, NMNS faces strong competition from other tourist and leisure attractions. How to attract more visitors will continue to be a challenge for years to come, and consequently the long-term satisfaction of visitors has become a key issue. The problem of satisfying visitors is dynamic and complicated involving the interaction of many factors such as government policies, museum service quality, visitor expectations, and social environments. This study utilized system dynamics approach to investigate the system structure of factors affecting the long-term satisfaction of NMNS visitors. The results showed that long-term satisfaction could be affected by the interaction of factors such as the quality of service, the availability of facilities, and accumulated number of visitors. Finally, this study simulated the implementation of a number of relevant policies; discussing the implications and results.
Keywords: System Dynamics, Dynamic Simulation, Long-term Satisfaction, The National Museum of Natural Science
1. INTRODUCTION
*Taiwan has actively promoted the tourism and cultural industries during the past two decades. New large-scale museums are appearing, and old ones are under expansion. Taiwanese museums such as the National Palace Museum, the National Museum of Natural Science (NMNS), and the National Museum of Science and Technology see over one million visitors each year. Cleary, Taiwanese museums are important tourist attractions. The successful development of the NMNS is notable. Taiwan established the NMNS in 1986. By 1999, the NMNS exceeded the 3 million visitors mark, surpassing the National Palace Museum’s record of 1.8 million
*
Corresponding author: mhyao@cc.kuas.edu.tw
visitors to become Taiwan’s largest museum. In 2000, the NMNS achieved a record 3.83 million visitors.
The NMNS is Taiwan’s first large-scale science museum and one of the top five largest museums worldwide. A 2003 report published by McKinsey, an international consulting firm, noted that, in a worldwide comparison of museum visitors in 2002, Taiwan’s NMNS ranked fourth, with 2.7 million visitors that year. The top three museums for that year included the France’s Louvre Museum with 5.8 visitors, the USA’s Metropolitan Museum of Art with 5.4 million visitors, and the UK’s National Gallery, with 4.9 million visitors. The NMNS was not far behind the top three museums, and established itself as an important tourist attraction not only in Taiwan, but worldwide [9, 10].
The NMNS and other Taiwanese museums face strong competition from other tourist and leisure
International Journal of Electronic Business Management, Vol. 10, No. 2 (2012) 114
attractions. Therefore, visitor satisfaction is an important issue that museums must address. Visitor satisfaction refers to the quality of service one experiences. Conversely, service quality is a standard for assessing management unit effectiveness for visitors or customers [1]. In other words, tourist attractions should focus on service quality [4, 13]. Museum managers must emphasize service quality, which may include commentary or other services provided by employees or volunteers. By improving customer satisfaction through increased service quality management, museums hope to enhance visitors’ perceptions and values associated with an enjoyable experience. Increasing service quality leads to long-term visitor satisfaction and repatronage intentions, which are important facets in museum management.
Many factors affect service quality in museums and perceived value and visitor’s long-term satisfaction. For example, some complex, influencing factors include service employee attitude, ticket prices, operation strategies, and the attractiveness towards competition. This study investigates factors influencing the visitor’s long-term satisfaction of the NMNS, and examines the development of a system structure to understand behaviors using a system dynamics approach. Finally, this study simulates relative policy effects and provides a pertinent discussion.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
Satisfaction with museums has been discussed in recent studies, namely those by Gau [7], Chen and Lin [3], Paulus [14], Mejon et al. [12], Harrison and Shaw [8], and Hsiao et al. [9].
Paulus [14] suggested that museum visitors anticipate brand connections. Once a consumer has visited a unique museum or art gallery, their pre-visit expectations and consuming experiences help determine their satisfaction level. Mejon et al. [12] suggested that managers should adopt professional attitudes, interactive displays, and live performances at their museums. Managers should also collaborate with educational institutions to provide internet applications for increasing the number of visitors, museum revenue, and operation efficiency [12]. Harrison and Shaw [8] examined the relationship between museum visitor satisfaction and post-visit intention. They examined the impact of population variables such as gender, age, and education and found that satisfaction relates to variables such as repatronage intentions, museum experience, post-visit intention, and employees [8]. Hsiao et al. [9] found that there is significant relationship between museum service quality and the perceived value and loyalty of visitors.
The above literature discusses museum satisfaction, service quality, perceived value, and loyalty. This study suggests that museums are institutions that possess the functions of collecting and storing relics, and educating the public. Museum services include physical equipment and facilities, the expert knowledge of employees, and convenient digital information services. In addition, the NMNS should provide education to the public. Furthermore, museum services should include hardware equipment, and tangible and intangible service qualities such as employee service, musical ambience, digital services, and education and promotion.
Two previous studies discussed museum service quality and satisfaction, taking NMNS as the example [3, 7]. However, these studies do not identify the impact of visitors’ long-term satisfaction on the overall development of museums. This study found that the NMNS’s main objective is to pursue long-term visitor satisfaction rather than “one-time” visiting behaviors, based on interviews from high-level managers at the NMNS. Secondly, many visitors possess “family membership cards” which allow multiple visits. Therefore, museum managers strive for long-term satisfaction. This study discusses the impact of long-term customer satisfaction.
3. MODELING
Visitors’ long-term satisfaction determines their intention of revisiting and recommending their experiences to others, which is intrinsically a dynamics and complex model with the internal and external interactions. The system dynamics (SD) was developed in 1950s, and was defined as the investigation of the information-feedback characteristics of managed systems and the use of models for the design of improved organizational form and guiding policy [5]. Wolstenholme [16] specified SD as a rigorous method for qualitative description, exploration and analysis of complex systems in terms of their processes, information, organizational boundaries and strategies, which facilitates quantitative simulation modeling and analysis for the design of system structure and behavior. Therefore, we considered the SD as the most suitable method for the problem in this study. We used the SD methodology to examine the critical causal loops that affect the long-term satisfaction of NMNS visitors. We constructed a dynamic model explaining systemic behaviors and simulated relevant policies [5, 11, 15].
3.1 Critical Causal Loop between Service Quality and Long-term Satisfaction
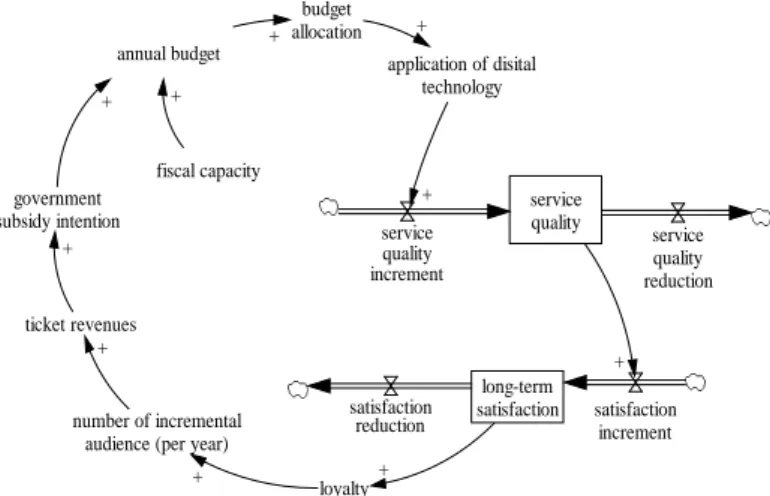
Figure 1 shows the critical causal loop between service quality and long-term satisfaction. First, the NMNS submits a budget request on an annual basis.
C. T. Hsiao and M. H. Yao:System Dynamics Approach to Visitors’ Long-term Satisfaction 115 If the government grants the NMNS a large yearly
budget, then funds invested in digital technology applications may increase. This may improve the NMNS’s service quality, and increase visitor satisfaction and loyalty. The goal is to increase the number of visitors. As a result, the NMNS’s ticket income may rise and government may be more willing to subsidize the NMNS in the following year, forming a positive loop.
3.2 Critical Causal Loop between Number of Visitors and Long-term Satisfaction
The number of visitors and long-term satisfaction create two critical causal loops. A higher number of visitors increase government willingness to fund the NMNS, thereby increasing the annual budget of the NMNS. As a result, the museum may increase personnel expenses and hire more employees with expert knowledge, which in turn improves the quality and service of the NMNS. This leads to an increase in visitors’ long-term satisfaction and loyalty, and enhances potential visitors’ intentions to visit the museum. This in turn increases the number of visitors each year, forming a positive feedback loop.
However, Figure 2 shows that an increasing number of visitors leads to crowding and reduces service quality, forming a negative feedback loop until it reaches equilibrium.
3.3 Loop between Accumulated Equipment and Budget Needs
Accumulated equipment and budget needs form two critical loops. The quality of the equipment accumulated by the museum directly influences the service quality of hardware equipment. As a result, the museum must allocate funds for purchasing materials and equipment maintenance on an annual basis to provide complete hardware and environmental quality. The acquisition of hardware on an annual basis increases the equipment accumulated by the NMNS. However, as equipment increases, maintenance fees increase. Therefore, the NMNS’s budget needs to increase continually, forming a positive loop. On the other hand, as Figure 3 shows, the depreciation of equipment causes accumulated equipment quality to reach equilibrium, forming a negative loop.
ticket revenues service quality long-term satisfaction application of disital technology government subsidy intention budget allocation + annual budget + + fiscal capacity satisfaction increment service quality increment + satisfaction reduction service quality reduction + + loyalty + + number of incremental audience (per year)
+
+
Figure 1: Service quality and long-term satisfaction loop
service quality long-term satisfaction personnel expenses government subsidy intention budget allocation annual budget + + number of accumulated audience satisfaction increment number of incremental audience service quality increment satisfaction reduction service quality reduction + + loyalty + + + + <Time>
C. T. Hsiao and M. H. Yao: System Dynamics Approach to Visitors’ Long-term Satisfaction 121