行政院國家科學委員會補助專題研究計畫成果報告
※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※
※ ※
※ 利用即時定量 PCR 方法偵測急性骨髓性白血病病人 ※
※ 治療前後之微量殘存腫瘤細胞
※
※
※
※
※
※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※
計畫類別:V 個別型計畫
□整合型計畫
計畫編號:NSC
90-2314-B-002-244-執行期間:
89
年
08
月
01
日至
91
年
07
月
31
日
計畫主持人:唐季祿
共同主持人:田慧芬, 陳耀昌, 姚明
本成果報告包括以下應繳交之附件:
□赴國外出差或研習心得報告一份
□赴大陸地區出差或研習心得報告一份
□出席國際學術會議心得報告及發表之論文各一份
□國際合作研究計畫國外研究報告書一份
執行單位:國立台灣大學醫學院內科
中
華
民
國
91 年
12
月
30
日
行政院國家科學委員會補助專題研究計畫成果報告
利用即時定量 PCR 方法偵測急性骨髓性白血病病人治療前後之微量
殘存腫瘤細胞
計畫編號:NSC
89-2314-B-002-344-執行期限:89 年 08 月 01 日至 91 年 07 月 31 日
主持人:唐季祿 國立台灣大學醫學院內科
共同主持人:田慧芬 國立台灣大學醫學院內科
共同主持人:陳耀昌 國立台灣大學醫學院內科
共同主持人:姚明 國立台灣大學醫學院內科
一. 摘要The 8;21 translocation is one of common karyotype abnormalities in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). AML1 and ETO gene were fused in t(8;21) and can be consistently detected by RT-PCR. In this study, therapeutic monitoring of minimal residual disease (MRD) using a novel, quantitative, real-time RT-PCR was evaluated in AML with t(8;21) as a model. A t(8;21)-positive cell line, Kasumi-1, was used for constructing standard curves and the corrected AML1-ETO mRNA level relative to the expression of the GAPDH housekeeping gene was calculated. At optimal condition, this assay yield an excellent log-linear relationship of PCR threshold cycle number (CT) with
wide-range of initial target mRNA concentration (correlation of coefficient, r > 0.99, n=13) and sensitivity of detecting MRD as low as 10-5 level. Sequential measurement of AML1-ETO level was performed in 40 t(8;21)-positive patients and correlated with their clinical outcome. At diagnosis, the AML1-ETO levels ranged between 0.26~1.45-fold compared with Kasumi-1 standard. Those patients with MRD level > 10-2 after induction therapy and/or > 10-3 after 1-2 courses of consolidation therapy had higher risk of leukemic relapse, even treated with high-dose Ara-C or bone marrow transplant (BMT). Those patients failed to achieve MRD level < 10-4 within 6 months after BMT eventually relapsed unless chronic
graft-versus host disease occurred in time. No residual MRD (i.e. less than 10-5) was detectable in 9 patients in continued remission > 2 years. These data suggest that this simple and sensitive assay is very useful in therapeutic monitoring of AML treatment, in identifying high-risk patients, and in early detection of leukemic relapse.
Keywor ds: real-time PCR, quantitation, minimal residual disease, acute myeloid leukemia.
二. 緣起與目的
Intensive chemotherapy can achieve high complete remission rate(CR) of 60~80% in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, many patients will relapse eventually. Sensitive and accurate detection of minimal residual disease (MRD) after chemotherapy may not only facilitate in predicting relapse and continuing treatment, but also monitor the effectiveness of therapy and conceivably reduce treatment needs in patients who may already be cured. The sensitivity of MRD detection by current PCR technique can reach the level of one tumor cell in 103 to 10-6 of normal cells. However, previous PCR techniques had limitations either not sensitive enough or requiring time-consuming procedures. Recently, a novel technique, Real-Time PCR, promises to provide more appealing molecule tool for a rapid and accurate quantitation of nucleic acid sequences.
Table 1 Nucleotide sequences of PCR primers and probes
Gene Primer Sequences
AML1-ETO AML1 TCAAAATCACAGTGGATGGGC
ETO CAGCCTAGATTGCGTCTTCACA
Probe FAM-AACCTCGAAATCGTACTGAGAAGCACTCCAC-TAMRA
GAPDH Forward GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGT
Reverse GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC
Probe JOE-CAAGCTTCCCGTTCTCAGCC-TAMRA
The objective of this study was to develop an automated real-time quantitative PCR assay will be developed for detection of MRD of AML after chemotherapy. The results will be evaluated for clinical utility in measuring residual leukemia in selecting high risk patients and predicting leukemic relapse.
三、結果與討論
Design of r eal-time RT-PCR and establishment of standar d cur ve
Two leukemia cell lines were used in this study. Kasumi-1 had AML1-ETO gene and NB4 cells with PML-RARa gene. GAPDH housekeeping gene was used as internal control of RNA integrity and normalization of loading RNA amount. The PCR primers and TaqMan fluogenic probes was designed with Primer-Express software (Perekin-Elmer) and their sequences were listed in Table 1. Collection of samples, separation of mononuclear cells, and RNA extraction were performed as reported
previously. One-step RT-PCR was
performed using EZ RT-PCR kit on Taqman PRISM 7700 sequence detector (ABI, Foster city, CA) as manufacturer’s recommendation. Briefly, serial 10-fold dilution of total RNA from 1,000 to 0.01ng NB4 or Kasumi-1 was mixed with another negative cell line, KG-1 to keep final RNA at 1,000ng.
Duplicate samples were subjected to RT-PCR in a total volume of 50 µl containing 1x buffer, 200 µmol primers, 200nmol probe, 1,000ng total RNA and 0.25U rTth DNA polymerase. The RT reaction was done at 50 ℃ for 30 min followed by 45 cycles of PCR with 95℃ for
15 sec and 62℃ for 1 min. All experiments were done in duplicates and including no-template control and negative control RNA to prevent PCR carryover. Fluoresence spectra were continued monitored and analyzed by 7700 with detection software version 1.6.
Fig. 1. Standard curve of AML1-ETO real-time
RT-PCR by correlation of PCR threshold cycle number (CT) and log(initial Kasumi-1 RNA amount).
As shown in Fig. 1, there was an excellent log-linear relationship (correlation of coefficient, r > 0.99) of PCR threshold cycle number (CT) with wide-range of initial
target mRNA concentration between 1,000ng and 0.01ng ranges. MRD was calculated as measured target RNA/GAPDH mRNA ratio. The data was qualified as evaluable only if the measured GAPDH RNA > 10ng. The sensitivity of detecting MRD could reach the level of 10-5 with AML1-ETO genes. Furthermore, there was very little intra-assay and inter-assay variability (Fig.1). The standard error of CT
at 10-4 was 1.37 cycles for AML1-ETOgene and. This corresponded to target RNA measured error at ± 2-4 x 10-4. Conventional cytogenetic analysis was found insensitive to detect MRD, its detection limit at 10-2 level only (data not shown).
Monitor ing of MRD in AML with t(8;21)
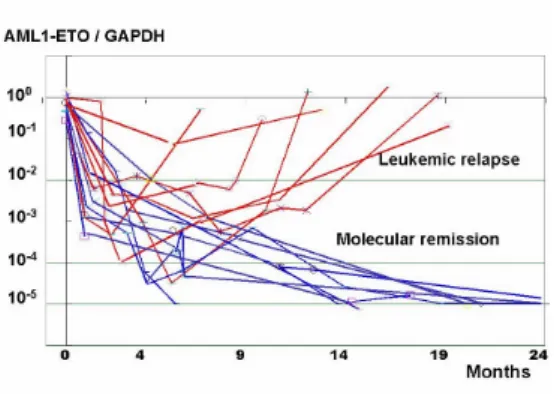
Fig. 2. Sequential monitoring of MRD in 40 AML
patients with t(8;21). The red lines depict patients who relapsed and blue lines indicating patients in continued remission.
Sequential monitoring of MRD after HSCT was performed in 40 AML patients with t(8;21). There were 23 males and 17 females with a median age of 31 years (ranges, 4-60). At first study of RT-PCR, 35 patients were at first diagnosis, 2 patients in first complete remission (CR), 2 patients at first relapse, and 1 patient at CR3. After achieving CR, 22 patients received
high-dose consolidation, 4 with
standard-dose, 3 low-dose, and 11 with bone marrow transplantation. As shown in Fig. 2, there was significant variation in the dynamic changes of their MRD levels following therapy. Two groups of patients appeared after 1 year: 19 patients with persistent low level of MRD < 10-4 (molecular remission group), while 21 patients relapsed between 6 to 19 months after initial CR. For the 11 patients receiving BMT, one died of complication early and one was refractory to BMT. MRD dropped to < 10-5 in 5 cases and remained in CCR, while relapsed occurred in 3/3 whose MRD persistently > 10-3. In one patient, the MRD was >10-3 at 6 months. Molecular CR occurred after chronic graft-versus-host
disease (GVHD) occurred and CR
maintained for > 60 months (Fig. 3).
From these data, we can develop a risk-adapted strategy in AML treatment based on the MRD level at different phases (Fig.4). After 1-2 courses of induction chemotherapy with standard dose regimen (such as I3A7), A few patients were very
sensitive to chemotherapy and MRD dropped to < 10-4 rapidly within 1-3 months (line A, molecular CR, MCR) and could achieved long-term CR by high-dose Ara-C. But most patients still had MRD level between 10-2 and 10-3 (hematological and cytogenetic CR, line B). Some patients entered MCR after 1-3 courses of High-dose Ara-C consolidation (line B-3) or by BMT B2-b). Those patients who failed to achieved MCR within 6-12 months will finally relapsed (B-1, B2-a).
However, molecular CR does not ensure cure of leukemia. Four patients with MCR status relapsed between 11 and 66 months. Patient 4 had extramedullary relapse involving orbit 5 years after allo-BMT. Interestingly, there was no detectable leukemic cells by RT-PCR from bone marrow at time of relapse.
Fig 3. Molecular remission induced by graft-versus
leukemia (GVL) effect after BMT in patient 4. Sequential monitoring of MRD level showed that the MRD remained > 10-3 at 6 months after allo-BMT and dropped to < 10-5 after onset of chronic graft-versus-host disease. L o g (A M L -E T O/G A P D H ) 0 1~ 3 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 -6
BuCy2 + ABMT Cytogenetic remission HD consolidation Induction 4 ~ 6 6 ~ 12 months A B B-1 B-2 B-3 A B-2-a B-2-b
Fig.4 Risk-adapted stratification based on MRD level in AML. (For detailed description, please see result section.
四. 成果自評
In this study, we had successfully developed a quantitative real-time RT-PCR assay with high sensitivity and specificity in assessing MRD level in AML patients with t(8;21). In each patient, treatment policy and outcome prediction can be made based on serial monitoring of MRD level. This method can stratify patients at risk of leukemic relapse, avoid unnecessary high-dose chemotherapy and transplantation. However, this assay can only be applied in a minority of AML patients < 10-15%. Therefore, we are currently explore similar MRD detection in other patients by WT-1 gene expression (grant supported by NSC 91-92).
The results of this study had been presented in the 2001 annual meeting of Hematology Society of Taiwan and in the
2nd meeting of 海峽兩岸血液病研討會 in
Shanghai in November, 2001 and
manuscript are prepared for publication.
五、計畫成果發表:
[1] Therapeutic monitoring of minimal
residual disease by real-time RT-PCR in AML with t(8;21). (manuscript prepared for publication and had been presented in Annual meeting of Hematology Society of Taiwan, March 17, 2001).
[2] Therapeutic monitoring of minimal
residual disease in hematological malignancy. 2nd meeting of 海峽兩岸 血液病研討會, Shanghai, November 12, 2001.