行政院國家科學委員會補助專題研究計畫 □ 成 果 報 告
□期中進度報告
(計畫名稱)
計畫類別:□ 個別型計畫 □ 整合型計畫 計畫編號:NSC93-2320-B-038-006-
執行期間:2004 年 8 月 1 日至 2005 年 7 月 31 日
計畫主持人:鄭幼文 共同主持人:蕭哲志 計畫參與人員:
成果報告類型(依經費核定清單規定繳交):□精簡報告 □完整報告
本成果報告包括以下應繳交之附件:
□赴國外出差或研習心得報告一份
□赴大陸地區出差或研習心得報告一份
□出席國際學術會議心得報告及發表之論文各一份
□國際合作研究計畫國外研究報告書一份
處理方式:除產學合作研究計畫、提升產業技術及人才培育研究計畫、
列管計畫及下列情形者外,得立即公開查詢
□涉及專利或其他智慧財產權,□一年□二年後可公開查詢
執行單位:台北醫學大學藥學系
2
中 華 民 國 九十四 年 十 月 三十一 日
附件一 中文摘要:
氧化性膽固醇已被證實存在於氧化性低密度脂蛋白中,且與粥狀動脈硬化的形成有關。在 本實驗中,我們針對三種常見的膽固醇氧化物:Cholesterol-5α,6α-epoxide
(Epoxide)、7-Keto-cholesterol(7-Keto)及Cholesterol-3β,5α,6β-triol(Triol)來做實驗,
我們發現此三種膽固醇氧化物會透過調節MAP kinase 的路徑在HUVECs 造成細胞毒性,同 時間也調節了另一條與Akt、eNOS phosphorylation相關的訊息傳遞路徑,而且,這三種氧化 膽固醇在 HUVECs 調節的機制皆不盡相同,但似乎都會同時調節了兩個相反的路徑:
apoptosis 和cell protection。我們發現Epoxide 在18 個小時並不會對HUVECs 造成嚴重的毒 性 , 並 且 在 短 時 間 內 ( 2h ) 同 時 活 化 了 與 細 胞 保 護 機 制 相 關 的 蛋 白 : ERK 、 Akt 及 eNOSphosphorylation。而Triol 則有明顯的雙向調節作用:apoptosis 和cell protection。A) apoptosis pathway:Triol 能在HUVECs 誘發caspase-3 的活化,而此活化作用會被SP(JNK inhibitor)所抑制,暗示了Triol 是透過活化JNK 來活化caspase-3。另外,此caspase-3 的活化 作用也會同時被L-NAME(eNOS inhibitor)及wortmannin(PI3 kinase inhibitor)所抑制,暗示 了 PI3 kinase pathway 及 eNOS 的 磷 酸 化 也 是 導 致 caspase-3 活 化 的 原 因 之 一 。 B) cell protection:Triol 同時也活化了另一個蛋白ERK,而PD98059(ERK inhibitor)會增強Triol 對 caspase-3 的活化,代表Triol 對ERK 的活化在HUVECs 為anti-apoptosis 的作用。我們發現 了膽固醇氧化物在HUVECs 的作用是多樣化的。Triol 及7-Keto 能誘發細胞的apoptosis,而 在同時間也會誘發另一條具細胞保護作用的路徑(ERK phosphorylation),而Epoxide 在本 實驗我們並沒有看到嚴重的毒性作用,誘發的作用似乎以細胞保護作用為主。有一些關鍵 的蛋白還需要再做進一步的確認,像是PI3 kinase 與Akt 的直接關係;7-Keto 在JNK 方面的 作用以及Triol 在c-jun的作用。而這些關鍵蛋白的確認可以幫助我們進一步去連結各個路徑 的直接上下游關係。此外在第二年的實驗中, 我們也設立了非放射性標誌之EMSA 測定 法,初步發現15d-PGJ2 並不影響這些ox sterols所導致的細胞毒性,但的確參與了一條藉由 p65 translocate induced NF-kB 的訊息傳遞。
英文摘要
Oxidation products of cholesterol have been shown to be present in oxidizedlow density lipoprotein and in atherosclerotic lesions. Here we shown three oxysterols,Cholesterol-5α-6α-epoxide (EPO), 7-keto-cholesterol (7-Keto) and Cholesterol-3α5〈-6β-triol (Triol) induced cytotoxicity were regulated by MAP kinase and Akt,eNOS phosphorylation pathway through diversal pathways in human umbilical endothelial cells (HUVECs). Three oxysterols shown different mechanisms and dual aspects of regulation pathway, apoptosis and cell protection, in HUVECs. Epoxide did not cause cytotoxicity within 18 hrs and show the induction of cell protection proteins, ERK, Akt and p-eNOS in HUVECs within 2 hrs at lower concentration (0.1 ~10 ⎧g/ml). Triol have obvious dual effects in apoptosis and cell protection. a) Apoptosis pathways: Triol caused JNK phosphorylation leading the caspases-3 activation and apoptosis, and this effect can be inhibited by JNK inhibitor (SP). The activation of caspase-3 also can be inhibited by L-NAME and wortmannin, indicated the role of PI3 kinase and eNOS phosphorylation were leading to apoptosis. b) Cell protection: Triol also induced ERK phosphorylation, when administrated ERK inhibitor, PD98059, can promote caspase-3 activity and apoptosis. 7-Keto induced ERK, eNOS and c-JUN phosphorylation. Although 7-keto can induced
caspase-3 activation, but it might not through JNK, PI3 kinase or eNOS pathway, because SP, wortmannin and L-NAME did not inhibited 7-keto induced caspase-3 activation. Finally, the role of oxysterols in HUVECs is contraversal, we found that triol and 7-Keto can induced apoptosis in higher concentration. But there is still a cell protection pathway going in the same time. Different with triol and 7-keto, epoxide only shown the benificial effect in this study. Some key proteins involve in these signaling pathway still await to confirm, like PI3 Kinase and Akt in three oxysterols, JNK in 7-keto, and p-cJUN in triol. We need more information to fill in the pathway and make final conclusion when available.
報告內容
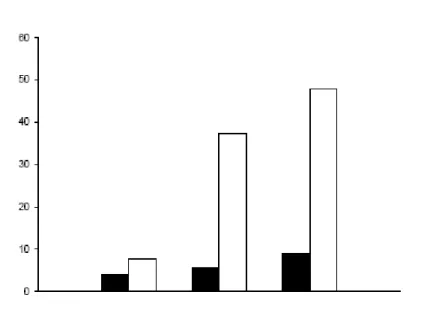
氧化性膽固醇對人類臍靜脈內皮細胞的毒性在MTT 的結果
本實驗以測定細胞粒線體對MTT 的還原能力,間接評估細胞的存活率,以 瞭解氧化膽固 醇在人類臍靜脈內皮細胞(HUVECs)的毒性作用耐受程度,作為 評估實驗藥物濃度投予 的 依 據 。 在 細 胞 長 滿 之 後 , 分 別 給 予 7-keto-cholesterol 、 cholesterol-5α,6α-epoxide 、 cholestane-3β, 5α,6β-triol 0.3 μg/ml 至50 μg/ml 處理18及36 小時。由結果發現,Epoxide 在36 個小時內都不會對HUVECs 造成嚴重的細胞毒性(Fig. 1B),而7-Keto 及Triol 則在 10 μg/ml 以上呈現劑量-效應關係的細胞毒性,且Triol 的曲線下降得比7-Keto 快(Fig. 1),
由此可知,此三個膽固醇氧化物對HUVECs 的毒性大小為:Triol>7-Keto>Epoxide。另外,
隨著處理藥物的時間增加,其對HUVECs 的毒性也隨之增加,在處理18 小時後,Triol及 7-Keto 在50 μg/ml 的濃度下分別造成約70 %及30 %的細胞死亡(Fig. 1A);而在處理36 小 時後,7-Keto 在50 μg/ml 的濃度下造成約70 %的細胞死亡,而Triol 在30 μg/ml 即能造成 約90 %的細胞死亡(Fig. 1B)。因此,在後續的實驗操作中,藥物濃度皆不超過20 μg/ml,
而處理時間也以不超過36 小時為原則。
氧化性膽固醇在人類臍靜脈內皮細胞造成necrosis 及apoptosis 的現象接著我們利用核酸 染劑propidium iodide 和phosphatidyl serine 的特異性染劑annexinⅤ-FITC 來針對HUVECs 做 雙染,再用流式細胞儀來作分析。當細胞早期走向凋亡時,其細胞膜內面的phosphatidyl serine 會翻轉至細胞膜外,因此annexinⅤ-FITC 可以染上,但由於此時的細胞膜仍然維持完整狀 態,對於無法通透細胞膜的核酸染劑propidium iodide 拒染,因此在流式細胞儀分析鑑定為 走向apoptosis 的細胞;而若是為necrosis 細胞,沒有細胞膜內面的phosphatidyl serine翻轉至 細胞膜外的現象,而且細胞膜會有碎裂的情形,此時propidium iodide 就可以染上,在流式 細胞儀分析鑑定為necrosis 的細胞。由於Lizard 等人(1999)曾經報導氧化膽固醇造成的細 胞死亡包括了細胞壞死(necrosis)和細胞凋亡(apoptosis),而且通常這兩者是伴隨發生的,
因此我們利用此一技術,來判斷這三種氧化性膽固醇在HUVECs 所造成的細胞死亡分別是 哪一種死亡型態。Triol—我們發現Triol 在給予2 個小時之後即能在HUVECs 誘發apoptosis 與necrosis(Fig. 2A),在10 μg/ml 的濃度下約有10 %的apoptosis 與40 %左右的necrosis 現 象產生,而在20 μg/ml 的濃度下約有25 %的apoptosis 與將近70 %左右的necrosis 現象產 生。而在給予15 個小時之後(Fig. 2B),同樣的隨著給予濃度的增加,從0.5 μg/ml、1 μg/ml、
3 μg/ml、5 μg/ml 到10 μg/ml,apoptosis 的現象分別約為10 %、25 %、20 %、20 %、50 % 及25 %,而necrosis 的現象分別約為15 %、30 %、35 %、40 %、80 %及90 %,可以明顯的發 現Triol 所誘發的死亡型態necrosis 多於apoptosis,也就是說,Triol 在HUVECs 同時誘發 necrosis與apoptosis 兩種死亡型態,但是以necrosis 為主。
4
7-Keto—而在給予7-Keto 36 小時之後,我們發現有很明顯的apoptosis 現象產生(Fig. 3),
隨著給予的濃度增加,從5 μg/ml、10 μg/ml 到20 μg/ml,造成的apoptosis 現象分別為30
%、40 %及50 %,而necrosis 的現象分別為4 %、4%及10 %,可以很明顯的發現7-Keto 所誘 發的死亡型態主要是apoptosis,而7-Keto在20 μg/ml 所造成的necrosis 有統計上的意義,因 此我們認為7-Keto 在HUVECs主要誘發的死亡型態以apoptosis 為主,但在高濃度時,例如 像是20 μg/ml,同時會伴隨有小量的necrosis 現象產生。
Epoxide—至於Epoxide,我們不但在MTT 36 個小時內的結果沒有發現其毒性,在雙染的結 果中,我們發現在HUVECs 給予0.5 ~ 20 μg/ml 的Epoxide 36 小時之後,Epoxide 對於 HUVECs 仍然沒有造成明顯的細胞死亡現象,沒有apoptosis的現象也沒有necrosis 的現象出 現(data not shown),顯示Epoxide 在HUVECs的角色可能不是負面的,至少在36 個小時之 內不會造成細胞死亡。
氧化性膽固醇能誘發MAP kinases 及c-Jun 的磷酸化
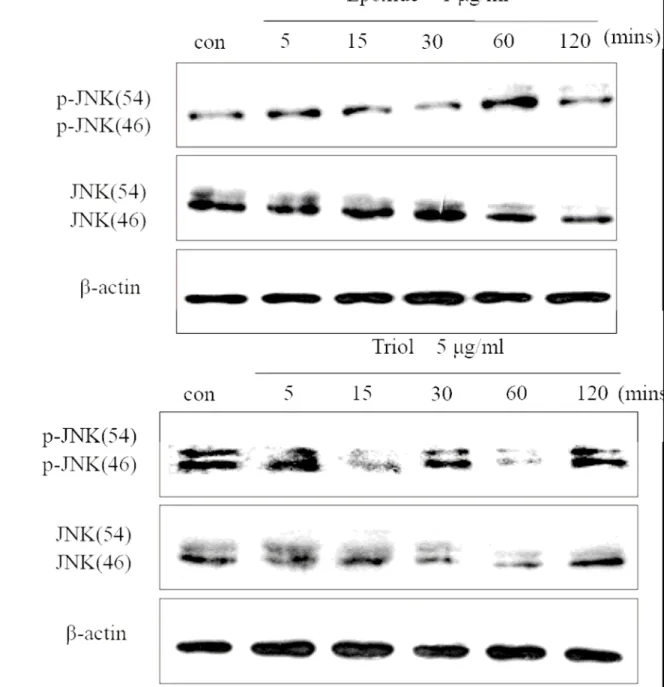
在過去許多的研究中,MAP kinases 及其相關的訊息傳遞在主宰細胞的命運上扮演著重要的 角色。因此,本實驗即是藉由西方墨點法來探討氧化性膽固醇在人類臍靜脈內皮細胞所造 成的細胞毒性是否涉及了MAP kinases 的磷酸化。我們利用西方墨點法來觀察p-ERK、p-JNK 以及p-p38 的蛋白表現。分別給予Triol 10 μg/ml、7-Keto 10 μg/ml 及Epoxide 10 μg/ml,處 理經5、15、30、60以及120 分鐘五個時間點。我們發現此三種膽固醇氧化物皆能誘導p-ERK 的表現,Triol 大約在15 分鐘左右會出現(Fig. 4A),7-Keto 大約在30 分鐘大量出現且持 續至120 分鐘(Fig. 4B),而Epoxide 大約在30 分鐘達到最大值(Fig. 4C);至於p-JNK 蛋 白的表現,在Triol 5 μg/ml 的濃度(Fig. 5A)與Epoxide 1 μg/ml的濃度(Fig. 5B)之下可在 2 個小時之內被誘導出來,而在7-Keto 的部分,我們只看到在10 μg/ml 的濃度之下,p-c-Jun 蛋白的表現能在15 分鐘左右被大量誘導出來(Fig. 5C),由於p-c-Jun 為p-JNK 的下游蛋白,
若是p-c-Jun 有被誘導出來代表在之前p-JNK 已被誘導出來,因此我們認為,7-Keto 也會誘 導p-JNK 的表現;另外,我們發現Triol 和7-Keto 都具有誘導p-p38 蛋白表現的能力,在處 理12 個小時之後,Triol 10 μg/ml 的濃度(Fig. 6A)與7-Keto 1 μg/ml 的濃度(Fig.6B)與 控制組比起來有明顯的增加p-p38 蛋白的表現,至於Epoxide,在相同的處理條件之下我們 並沒有發現Epoxide 具有誘導p-p38 蛋白表現的能力(data notshown)。
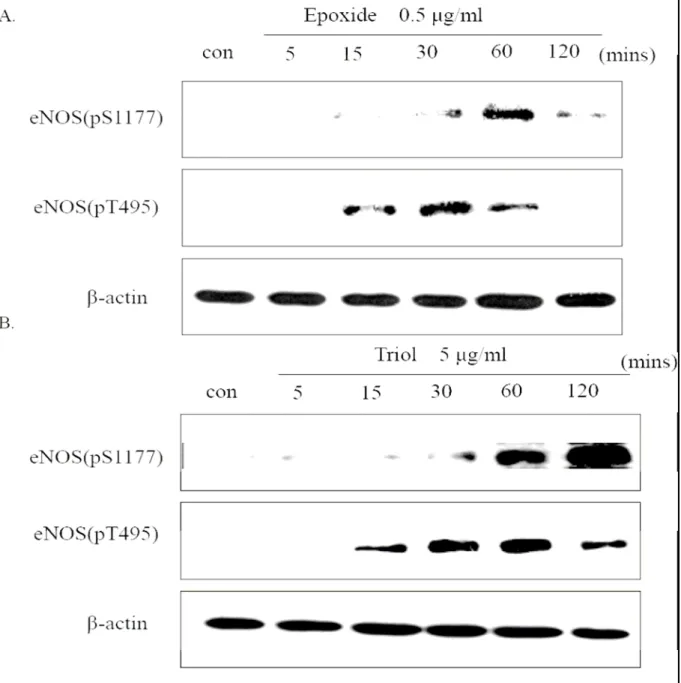
氧化性膽固醇能誘發eNOS 在Serine-1177 及Threonine-495 位置上的磷酸化反應近年 來,許多對於eNOS 蛋白的研究都探討到其相關位置的磷酸化反應,其中目前最被感興趣 的 即 是 在 位 於 eNOS 蛋 白 還 原 區 的 serine-1177 及 位 於 calmodulin 結 合 位 置 上 的 threonine-495 , 由 於 這 兩 個 位 置 的 磷 酸 化 對 於 eNOS 活 性 的 調 節 作 用 是 相 反 的 , 因 此 p-eNOS(S1177)與p-eNOS(T495)的蛋白表現對於eNOS 的活性具有關鍵的決定性。此外,已經 有一些研究報導指出MAP kinases與eNOS 之間的關聯性,像是Hisamoto 等人(2001)指出 在血管內皮細胞,LY117018 能透過p-ERK 進一步誘導eNOS 蛋白的磷酸化;而Go 等人
(2001)也曾發表過oxLDL 在血管內皮細胞會透過eNOS 的活化進一步誘發p-JNK 蛋白 的表現。在前面我們已經證實MAP kinases 參與在反應中,因此在本實驗中,我們便進一步 探討氧化性膽固醇在HUVECs 對於eNOS 是否會透過此兩個位置的磷酸化作用去調節eNOS 的活性。分別給予Triol、7-Keto 及Epoxid 處理5、15、30、60 及120 分鐘五個時間點,我 們發現他們皆能同時誘導p-eNOS(S1177)及p-eNOS(T495)的表現。Triol 5μg/ml 的濃度之下,
p-eNOS(S1177)會在60 ~ 120 分鐘大量被誘導出來,而p-eNOS(T495)約在15 分鐘左右被誘導 出來,30 ~ 60 分鐘左右達到最大量(Fig.7A);7-Keto 在10 μg/ml 的濃度之下,p-eNOS(S1177)
約在30 ~ 60 分鐘被誘導出來,而p-eNOS(T495)則在15 ~ 60 分鐘被誘導出來(Fig. 7B);至 於Epoxide 則在0.5 μg/ml 的濃度之下,p-eNOS(S1177)蛋白的表現約在60 分鐘達到最高 點,而p-eNOS(T495)則在15 ~ 30 分鐘被誘導出來(Fig. 7C)。可以發現三個氧化性膽固醇 對p-eNOS(S1177)及p-eNOS(T495)都會誘導表現,但在誘導表現的時間點上,p-eNOS(T495) 出現得比較早,消失得也比較早,而p-eNOS(S1177)表現的時間比較晚,消失得也比較晚。
氧化性膽固醇能誘發Akt 的磷酸化反應Akt 是PI3 kinase 依賴的蛋白,當PI3 kinase 被活化 之後,會進一步將下游的Akt 蛋白磷酸化,而p-Akt 已被證實能進一步在eNOS 蛋白的 serine-1177 位置上作磷酸化反應(Fisslthaler et al., 2000),此一個位置的磷酸化反應會增加 eNOS蛋白的活性,增加NO 的生成。既然前面我們看到了Triol、7-Keto 及Epoxide皆能誘發 p-eNOS(S1177)的表現,因此我們進一步去探討Akt 是否也參與反應。分別給予Triol 10 μg/ml 與Epoxide 20 μg/ml,處理5、15、30、60 及120 分鐘五個時間點,可以發現Triol 在濃度10 μg/ml 之下,p-Akt 大約在30 ~ 60 分鐘左右被大量誘導表現(Fig. 8A);而Epoxide 在濃 度20 μg/ml 之下,p-Akt 的表現大約在15 ~ 30 分鐘左右達到最高點(Fig. 8B);至於7-Keto 在相同的處理條件之下,我們並沒有發現它能誘導p-Akt 的表現(data not shown),這一點 可能需要再進一步的釐清。
eNOS 蛋白參與調控氧化性膽固醇對p-ERK 的表現調節
為了進一步釐清這些參與的蛋白之間的關係,我們使用一些特異性蛋白抑制劑來作進一步 確認。PD98059 為選擇性的MEKs 抑制劑(Pang et al., 1995),可以抑制ERK 上游激酶MEK1/2 的活性;SP600125 為選擇性的JNK 抑制劑;Wortmannin 為PI3 kinase 的選擇性抑制劑(Ui et al., 1995),可以進一步抑制Akt的活化;L-NAME 為eNOS 的抑制劑,可以抑制eNOS 的 活性,抑制NO 的生成。操作前先分別以25 μM 的PD98059、20 μM 的SP600125、100 nM 的Wortmannin 及100 μM 的L-NAME 進行前處理30 分鐘之後,再分別給予Triol 10μg/ml、
7-Keto 20 μg/ml 及Epoxide 20 μg/ml 刺激30 分鐘。實驗結果顯示,當eNOS活性受到抑制 時,Triol、7-Keto 及Epoxide 所誘發的p-ERK 表現也很明顯的受到抑制(Fig. 9A、B、C),
也就是說,Triol、7-Keto 及Epoxide 所引發的p-ERK的表現是透過eNOS 蛋白的活化而來。
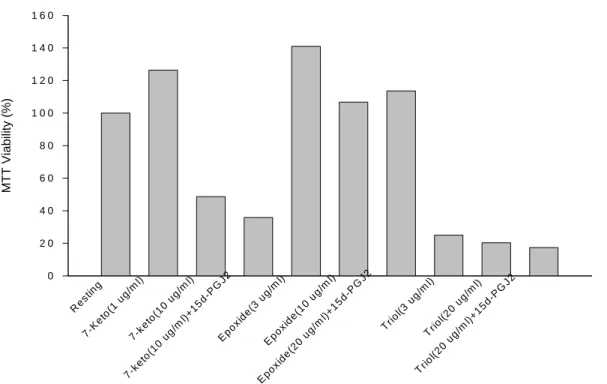
15d-PGJ2 對 Trio , 7-Keto 與 Epoxide 所誘發之細胞毒性之影響方法之建立
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma) 為細胞核內之接受器, 需要 ligand 活化以執行轉錄功能。15-deoxy-Delta-PGJ2 (15d-PGJ2) is a natural PPARgamma ligand 具有強的 anti-inflammatory properties. 我們利用培養之HUVECs 來看15d-PGJ2 是否影響 oxysterol 所誘發的作用。發現15d-PGJ2並不參與 oxysterols 所誘發的細胞毒性作用。
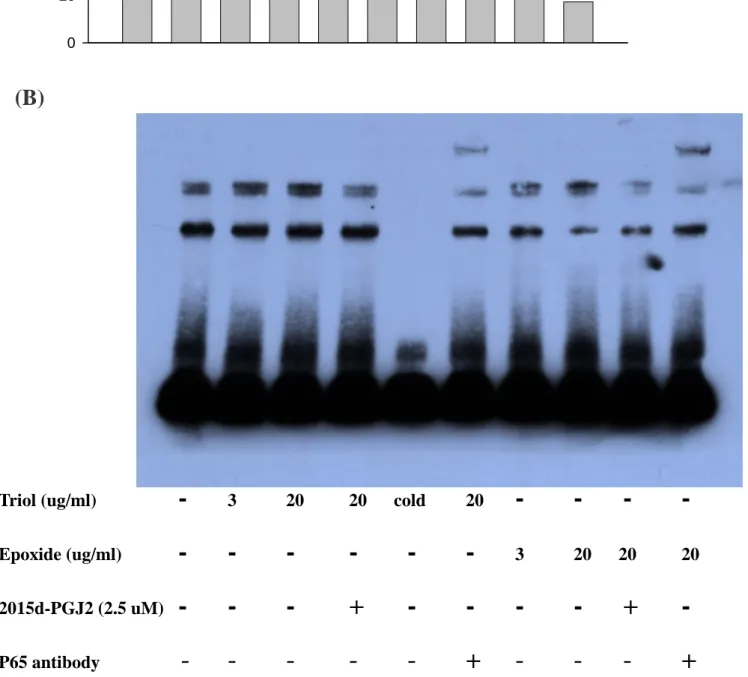
15d-PGJ2 對 Trio 與 Epoxide 所誘發P65 之影響及非放射性標誌EMSA 方法之建立 我們利用非放射性標誌EMSA 方法測定oxysterols 在NF-kB 訊息傳遞的影響, 初步發現 Triol 與 Epoxide 具有影嚮 p65 translated 至 NF-kB promotor side 之作用, 顯示oxysters 的作用可能牽涉到NF-kB 的調控。
結論
1. 此三種膽固醇氧化物在HUVECs 所造成的影響皆不相同,而且能同時雙向調節相反方向 的兩個路徑:apoptosis 及cell protection。
2. 2. Epoxide 在MTT 的結果發現在18 個小時之內並不會對HUVECs 造成嚴重的毒性,而 且在Western 的結果發現低濃度的Epoxide(0.5 ~ 10 μg/ml)能活化
一些走向cell protection 的蛋白:ERK, Akt, eNOS。
3. Triol 有明顯的雙向調節作用在走向apoptosis 與cell protection 之間:(A)apoptosis pathway:Triol 在HUVECs 會造成caspase-3 的活化,而此活化作用會被SP(JNK inhibitor)
所抑制,暗示了Triol 是透過活化JNK 來活化caspase-3。另外,此caspase-3 的活化作用也會 同時被L-NAME(eNOSinhibitor)及wortmannin(PI3 kinase inhibitor)所抑制,暗示了PI3 kinasepathway 及eNOS 的磷酸化也是導致caspase-3 活化的原因之一。(B)cellprotection:
Triol 同時也活化了另一個蛋白ERK,而PD98059(ERK inhibitor)會增強Triol 對caspase-3 的 活化,代表Triol 對ERK 的活化在HUVECs 為anti-apoptosis 的作用。
4. 我們發現了膽固醇氧化物在HUVECs 的作用是多樣化的。Triol 及7-Keto 能誘發細胞的 apoptosis,而在同時間也會誘發另一條具細胞保護作用的路徑(ERK phosphorylation),而 Epoxide 在本實驗我們並沒有看到嚴重的毒性作用,誘發的作用似乎以細胞保護作用為主。
5. 我們發現了膽固醇氧化物在HUVECs 所造成的細胞毒性作用似乎與 15d-PGJ2無關。
6. 5-deoxy-Delta-PGJ2 (15d-PGJ2) is a natural PPARgamma ligand 具 有 強 的 anti-inflammatory properties. 我們利用培養之HUVECs 來看15d-PGJ2 是否影響oxysterol 所誘發的作用。發現15d-PGJ2並不參與 oxysterols 所誘發的細胞毒性作用。
7. 利用非放射性標誌EMSA 方法測定oxysterols 在NF-kB 訊息傳遞的影響, 初步發現Triol 與 Epoxide 具有影嚮 p65 translated 至 NF-kB promotor side 之作用, 顯示oxysters 的作用 可能牽涉到NF-kB 的調控。
結果圖表
6
Figure 1. The concentration-dependent cytotoxic effects induced by oxysterols inHUVECs. Cells were treated with different concentrations of oxysterols and MTTassay was performed after 18h (A), 24h (B), and 36h (C). The cytotoxicity effect wasoccurred between 10 μg/ml and 30 μg/ml. The percentage of
cell viability wasexpressed as mean ± S.E.M. (n≧3) .
Figure. 2 Cells were treated with different concentrations of Triol for 2h (A)and 15h (B). Apoptosis was determined by annexin V-PI double staining and analyzed by flowcytometry.
Triol induced apoptosis in HUVECs depended on the concentration.
Figure. 3 Cells were treated with Triol 20 μg/ml for 2h(A) and 7.5 μg/ml for 15h(B).Apoptosis was
determined by annexin V-PI double staining and analyzed by flowcytometry.Fig 4 Cells were treated with 10 μg/ml of (A) Epoxide, (B) Triol, (C) 7-Keto for theindicated time.
Equal amounts of soluble lysates (10 ~ 50 μg) were subjected toelectrophoresis. The blots were analyzed using a specific antibody against. ERK andβ-actin for loading control. Con : control
8
Fig 5 Cells were treated with (A) 1 μg/ml Epoxide, (B) 5
μg/ml Triol for theindicated time. Equalamounts of soluble lysates (10 ~ 50 μg) were subjected toelectrophoresis. The blots were analyzed
using a specific antibody against p-JNK.JNK and β-actin for loading control. Con : control
Fig 6 Cells were treated with 10
μg/mlof 7-Keto for the indicated time. Equalamounts of soluble lysates (10 ~ 50 μg) were subjected to electrophoresis. The blotswere analyzed using a specific antibody against p-c-jun, and β-actin for loadingcontrol. Con : control
10
Fig 7 Cells were treated with (A) Epoxide 0.5 μg/ml, (B) Triol 5μg/ml, (C) 7-Keto10μg/ml for the indicated time. Equal amounts of soluble lysates (10 ~ 50 μg) weresubjected to electrophoresis. The blots were analyzed using a specific antibodyagainst p-eNOS(pS1177), p-eNOS(pT495), and β-actin for loading control. Con :control
Fig 8 Cells were treated with (A) Epoxide 10 μg/ml, (B) Triol 20 μg/ml for theindicated time. Equal
amounts of soluble lysates (10 ~ 50 μg) were subjected toelectrophoresis. The blots were analyzed using a specific antibody againstp-Akt(thr308), and β-actin for loading control. Con : control
MTT Viability (%)
0 2 0 4 0 6 0 8 0 1 0 0 1 2 0 1 4 0 1 6 0
Re sting
7-Keto(1 ug/
ml)
7-k eto(10 ug/
ml)
7-keto(10 ug/
ml)+15d- PGJ2
Epoxide(20 ug/ml)+15d-
PGJ2
Epox ide(
10 ug/
ml)
Epox ide(
3 ug/
ml)
Triol (20
ug/ml)+15d- PG
J2
Triol(20 ug/
ml)
Triol (3 u
g/ml)
Figure 9. The effects of 15d-PGJ2 on oxysterols induced cytotoxicity inHUVECs. Cells were treated with different concentrations of oxysterols and MTTassay was performed after 24h with and without 15d-PGJ2. The cytotoxicity effect wasoccurred between 10 μg/ml and 30 μg/ml. The percentage of
cell viability wasexpressed as mean ± S.E.M. (n≧3) .(A)
R TNF A1 A5 cold supershift
supershift
12
0 20 40 60
MT T V
(B)
Triol (ug/ml)
-
3 20 20 cold20
- - - -
Epoxide (ug/ml)
- - - - - -
3 20 2020
2015d-PGJ2 (2.5 uM)
- - - + - - - - + -
P65 antibody - - - - - + - - - +
Figure 10. The effects of 15d-PGJ2 on oxysterols induced p65 trabslocation inHUVECs. Cells were treated with different concentrations of oxysterols and EMSA was performed after 30 min with and without 15d-PGJ2. The supershift effect was occurred when P65 antibody was added.