1002935 ■ 公開 □ 密件、不公開 執行機關(計畫)識別碼:070201U104
行政院農業委員會100年度科技計畫研究報告
計畫名稱:
畜牧污泥厭氧消化對溫室氣體減量之評估
(第
2年/全程2年)
(英文名稱)
Assessment of greenhouse gases emission
reduction from anaerobic digestion of
livestock sludges
計畫編號:
100農科-7.2.1-牧-U1(4)
全程計畫期間: 自 99年4月1日 至 100年12月31日
本年計畫期間: 自 100年4月1日 至 100年12月31日
計畫主持人:
林志高
研究人員:
莊維倫、廖南維
執行機關:
交通大學
一、執行成果中文摘要:
以序批式反應槽利用同時部分硝化、厭氧氨氧化和反硝化 (SNAD)處理養豬廢水厭氧 出流水,TKN、TN 與 COD 去除率,分別 100%、83%、80%,可達提升放流水回收再 利用之價值,調查平順養豬場每年產生廢水量80000 CMD,每年可降低排放 GHGs 之 潛勢約為 3200 噸 CO2(eq)。
二、執行成果英文摘要:
Using simultaneous partial nitrification, ANAMMOX and denitrification (SNAD) treating anaerobic effluent of manure wastewater, the removals of TKN, TN and COD were 100%, 83% and 80%, respectively. The effluent of SNAD is valuable for recycle in the plant. In addition, greenhouse gases emission reduction from anaerobic digestion of livestock wastewater treatment plant for a flow of 80000 CMD is assessed as 3200 tons/year.
2 2
三、計畫目的:
以厭氧氨氧化處理畜牧廢水,除氮以降低溫室氣體排放,提升放流水回收再利用之 價值。
四、重要工作項目及實施方法: 實驗設備與方法 1. 進流水特性 本研究所用進流水為平順養豬場厭氧出流水;水質特性如表1所示,COD平均濃度為 1220 mg/L,TKN 820 mg/L, NH4+-N 630 mg/L,屬高碳高氮有機廢水;鹼度平均為 3530 mg CaCO3/L。 2. 植種污泥植種污泥來自臺灣基隆天外天垃圾滲出水處理廠。植種污泥含 ANAMMOX 紅色顆粒。通過對進出流水中氮平衡計算分析,螢光原位雜交法 (FISH) 技術與聚 合酶鏈反應 (PCR) 技術均證實 ANAMMOX細菌的存在 (Wang et al., 2010)。除此之 外,植種污泥亦被證實存在AOB、NOB以及反硝化細菌。 3. 反應系統與操作步驟oC,最高26 oC,水溫變化係季節變化引起;控制 pH 7-8,DO < 0.5 mg/L。 4. 分析方法
本研究檢測項目COD、TKN、NH4 +-N、NO2-N、NO3-N、鹼度等,分析方法皆根據
Standard Methods (APHA, 1998)。
4 4
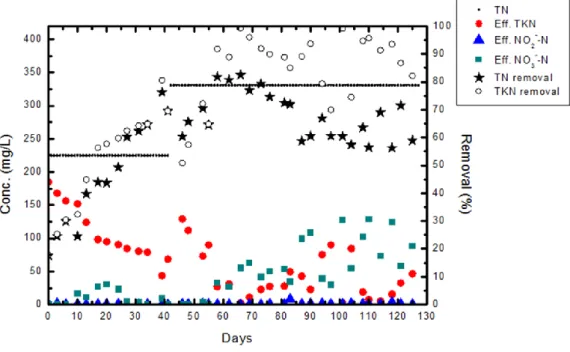
五、結果與討論: 1. pH與DO 圖2為研究期間反應槽pH與DO趨勢圖。反硝化過程會產生HCO3- 使得pH升高,但部分 硝化會消耗鹼度,使得pH降低。本實驗結果顯示,部分硝化過程對pH影響較大,導 致反應槽整體出現pH下降的趨勢。反應初期接種細菌在馴養階段,亞硝化反應尚未 達到最佳狀態,因此pH約為7.5-8;約50天以後,亞硝化以及ANAMMOX過程均達到良 好狀態,pH降至7.0左右。 在實驗初期 (第0 ~ 40天),溶氧值 (DO) 的測定為直接量測反應槽之出流水,然而 出流水是使用虹吸管抽出,因此在取樣過程中的擾動可能使空氣中的氧氣進入水中 ,而高估了實際溶氧值,為了取得更貼近反應槽內的溶氧值,量測方式改以 100 mL 燒杯將反應槽內混合液一併撈出,並使用溶氧計測定之。在整個實驗過程中,溶氧 將控制於0.5 mg/L 以下,若出流水中NH4+-N過高時,手動調節流量計提高曝氣速率 ,使硝化菌有足夠之氧氣將NH4+-N轉化為NO2--N並與剩下的NH4+-N繼續進行厭氧氨氧化 反應。然而在實驗的過程中,因曝氣量的大小不易掌握,使得溶氧有時上升至 4 左 右 (如圖2所示),極度促進硝化過程的發生,致使鹼度消耗及pH降低,當pH<6時 ,添加NaHCO3以補充鹼度。 2. 氮去除率與有機物去除率 第二階段 (42-83 d) 提高NLR至66 g/m3/d。此階段初期,由於ANAMMOX尚未適應此 NLR,因此並未表現出更好的處理效率。在ANAMMOX適應了此NLR之後,總氮 (TN) 與 TKN的處理效率均顯著提高。TKN處理效率最佳可達100%,對應的TN處理效率亦可達 為83%。第三階段 (84-127 d) 更將NLR提高至132 g/m3/d,平均 TKN 及 TN 處理效 率均可分別維持在87% 及62%。 進、出流水COD變化及處理效率如圖4所示;反硝化細菌為異養缺氧型細菌,它的代 謝過程需要消耗有機物,在單一反應器中同時部分硝化、厭氧氨氧化與反硝化 (SNAD) 程序正是利用了這一點來同時去除廢水中的有機物。由圖4可看出,在不同 階段COD處理效率皆呈現良好趨勢;處理效率逐漸上升,到第60天基本達到穩定 ,COD降解率為65%-80%;文獻記載ANAMMOX細菌的增殖需要7-11 d [3-4]。 Lan et al. (2011) 研究指出,提高NLR可以促進ANAMMOX細菌的繁殖。本研究實驗採 SBR,研究期間未排泥。在三個實驗階段,反應槽中MLVSS (mg/L) 分別為 2467 mg/L (第 1 天) 、2669 mg/L (第 60 天)、3733 mg/L (第 103 天)。 3. 溫室氣體排放成效評估
1 Kg N約同等50 Kg CO2(eq) (30~70 Kg CO2(eq)) (Oenema et al., 2006);由化學計量
厭氧出流水TKN 820 mg/L、COD 1220 mg/L (表一),亦即0.82 Kg TKN/d、1.22 Kg COD/d,T N 及COD去除率分別可達 83%、80%,每日可降低排放 GHGs之潛勢則分別 為34.03、6.3928 Kg CO2(eq),合計約40 Kg CO2(eq)。調查平順養豬場約有9600頭豬 ,每日產生廢水量約為170-250 CMD,夏季廢水量較大,冬季則較低,平均220 CMD;若每年產生廢水量80000 CMD則每年可降低排放 GHGs之潛勢約為3200噸 CO2(eq) 。 6 6 -1002935
六、結論: 本計畫研究證實,養豬廢水厭氧出流水很適合以厭氧氨氧化處理降解TKN,在室溫下 成功地建立了以養豬廢水厭氧出流水為進流水的SNAD系統。在NLR分別為45、66、 132 g/m3/d的情況下,均可取得很高的TKN、TN與COD去除率,最高分別可達100%、 83%、80%,可達提升放流水回收再利用之價值。調查平順養豬場每年產生廢水量 80000 CMD則每年可降低排放 GHGs之潛勢約為3200噸 CO2(eq)。
七、參考文獻:
APHA (1998) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 20th ed., American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Furukawa K., Lieu P.K., Tokitoh H., Fujii T. (2006) Development of singlestage nitrogen removal using anammox and partial nitritation (SNAP) and its treatment performances. Water Science Technology, Vol. 53, No. 6, pp. 83-90.
Hellinga, C., Schellen, A.A.J.C., Mulder, J.W., van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. and Heijnen, J.J. (1998 ) The SHARON process: an innovative method for nitrogen removal from ammonium-rich wastewater. Water Science Technology, Vol. 37, No.9, pp. 135-142.
Jetten, M. S. M., Fuerst, M. J., van Loosdrecht, M., Kuenen, G., Strous, M. (2001) Microbiology and application of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation ('Anammox') process. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, Vol. 12, No. 3, pp. 283-288.
Jetten, M.S.M., Strous,M., van de Pas-Schoonen, K.T., Schalk, J., Udo van Dongen, G.J.M., van de Graaf, A.A., Logemann, S ., Muyzer,G., van Loosdrecht, M.C.M., Kuenen,J.G. (1999) The anaerobic oxidation of ammonium. FEMS Microbiol. Rev 22, 421-437.
Lan, C. J., M. Kumar, C. C. Wang, J. G. Lin (2011) Development of simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) process in a sequential batch reactor. Bioresource Technology, Vol. 102, Issue 9, pp. 5514-5519.
Mulder, A., Graaf , A.A., Robertson , L.A.,Kuenen,J.G. (1995) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized bed reactor. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 16, 177-184.
Oenema, O., O. Diti, V. Gerard (2006) Nutrient losses from manure management. In: Proceedings at RAMIRAN Conference, Aarhus, Denmark.
Pynaert K., Smets B.F., Beheydt D., Verstraete W. (2004) Start-up of autotrophic nitrogen removal reactors via sequential biocatalyst
8 8
addition. Environmental Science Technology, Vol. 38, pp.1228-1235.
Sliekers, A.O., Derwort, N., Gomez, J.L., Strous, M., Kuenen, J.G. and Jetten , M.S. (2002) Completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite in one single reactor. Water Research, Vol. 36, No.10, pp. 2475-2482.
Strous, M., J. J. Heijnen, J. G. Kuenen and M. S. M. Jetten (1998) The sequencing batch reactor as a powerful tool for the study of slowly growing anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, Vol. 50, No. 5, pp. 589-596.
van de Graaf, A. A., P. de Bruijn, L. A. Robertson, M. S. M. Jetten, J. G. Kuenen (1996) Autotrophic growth of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing micro-organisms in a fluidized bed reactor. Microbiology (UK), Vol. 142, pp. 2187-2196.
van Dongen, U., Jetten , M.S.M. and van Loosdrecht , M.C.M . (2001) The SHARON ANAMMOX process for treatment of ammonium rich wastewater. Water Science Technology, Vol. 44, No. 1, pp. 53-60.
Wang C.-C., Lee P.-H., Kumara M., Huang Y.-T., Sung S., Lin J.-G. (2010) Simultaneous partial nitrification , anaerobic ammonium oxidation and denitrification (SNAD) in a full-scale landfill leachate treatment plant. Journal of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 175, No. 1-3, pp. 622-628.
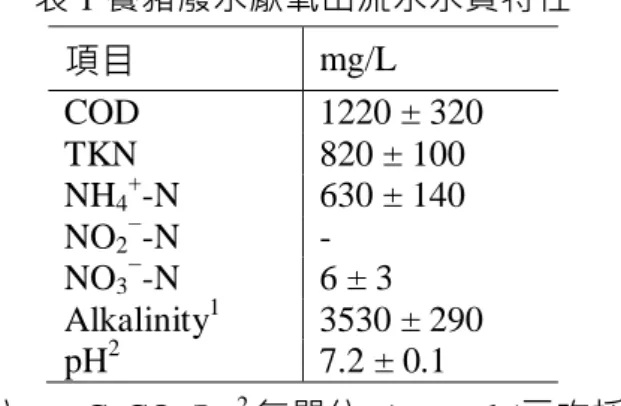
表 1 養豬廢水厭氧出流水水質特性 項目 mg/L COD 1220 ± 320 TKN 820 ± 100 NH4+-N 630 ± 140 NO2−-N - NO3−-N 6 ± 3 Alkalinity1 3530 ± 290 pH2 7.2 ± 0.1 1單位 mg CaCO 3/L, 2無單位, Ave±std (三次採樣) 表 2 反應系統操作條件 Stage 1 2 3 T (oC) Ambient temperature (14-26oC) Inf. TKN (mg/L) 225 330 330 Inf. COD (mg/L) 130 140 140 HRT (d) 5 5 2.5 Phase (d) 0-41 (41) 42-83 (42) 84-127 (43) NLR (g/m3/d) 45 66 132 10 -1002935
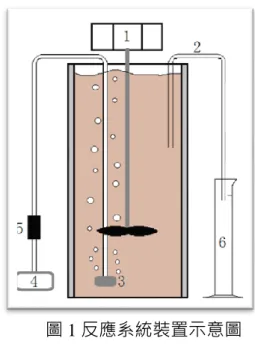
圖 1 反應系統裝置示意圖
1. 攪拌器, 2. 出流水管, 3. 曝氣頭, 4. 曝氣馬達, 5. 流量計 (用於控制曝氣速度), 6. 量筒 (用於接收出流水)
圖 3 進出流水含氮化合物變化及處理效率
圖 4 進出流水 COD 及處理效率
12