Title: Huge Primary Soft Tissue Sarcoma of the Breast on Bone Scan
Authors: Yeh-You Shen, MD,*Þ Yu-Chin Wu, MD,þ Chia-Hung Kao, MD,§¶ and Te-Chun Hsieh, MD§|| Abstract: A 54-year-old woman had a primary breast sarcoma with rapid enlargement in 3 months. The mass became so huge that it was more than
20 cm in diameter and occupied the entire right breast on presentation. Extraosseous uptake was present in this mass and demonstrated a unique picture, mimicking the posture of a racing driver who holds a helmet under the armpit, on the bone scan.
Key Words: primary breast sarcoma, bone scan, CT (Clin Nucl Med 2014;39: 99Y101)
REFERENCES
1. Al-Benna S, Poggemann K, Steinau HU, et al. Diagnosis and management of primary breast sarcoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;122:619Y626.
2. Voutsadakis IA, Zaman K, Leyvraz S. Breast sarcomas: current and future perspectives. Breast. 2011;20:199Y204.
3. Zelek L, Llombart-Cussac A, Terrier P, et al. Prognostic factors in primary breast sarcomas: a series of patients with long-term follow-up. J Clin Oncol.
2003;21:2583Y2588.
4. Pandey M, Mathew A, Abraham EK, et al. Primary sarcoma of the breast. J Surg Oncol. 2004;87:121Y125.
5. Barrow BJ, Janjan NA, Gutman H, et al. Role of radiotherapy in sarcoma of the breastVa retrospective review of the M.D. Anderson experience. Radiother Oncol. 1999;52:173Y178.
6. Moore MP, Kinne DW. Breast sarcoma. Surg Clin North Am. 1996;76:383Y392.
7. Fields RC, Aft RL, Gillanders WE, et al. Treatment and outcomes of patients with primary breast sarcoma. Am J Surg. 2008;196:559Y561.
8. Bousquet G, Confavreux C, Magne N, et al. Outcome and prognostic factors in breast sarcoma: a multicenter study from the rare cancer network. Radiother Oncol. 2007;85:355Y361.
9. McGregor GI, Knowling MA, Este FA. Sarcoma and Cystosarcoma phyl- lodes tumors of the breastVa retrospective review of 58 cases. Am J Surg.
1994;167:477Y480.
10. Confavreux C, Lurkin A, Mitton N, et al. Sarcomas and malignant phyllodes tumours of the breastVa retrospective study. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42:2715Y2721.
Tc-99m MDP bone scintigraphy. Clin Nucl Med. 2006;31:611Y613.
12. Lee JK, Sun SS. Primary osteogenic sarcoma of the breast demonstrated by Tc-99m MDP scintigraphy. Clin Nucl Med. 1998;23:619.
13. Ellmann A, Jawa ZM, Maharaj M. Primary osteogenic sarcoma of the breast detected on skeletal scintigraphy. Clin Nucl Med. 2006;31:474Y475.
14. Yang JG, Li CL, Hao RR, et al. Primary osteogenic sarcoma of breast detected on Tc-99m MIBI scintigraphy and Tc-99m MDP skeletal scintigraphy. Ann Nucl Med. 2008;22:79Y82.
15. Yang H, Miroshnichenko T. A large soft-tissue lipoma shown on bone scin- tigraphy. Clin Nucl Med. 2013;38:484Y485.
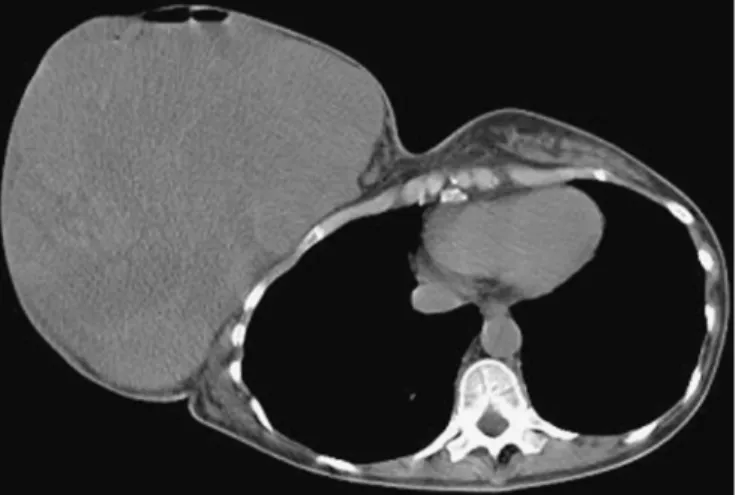
FIGURE 1. A 54-year-old woman had a rapidly growing mass in her right breast in the recent 3 months. Core needle biopsy confirmed a high-grade soft tissue sarcoma with focal muscular differentiation. She never received any radiotherapy before, and hence a primary breast sarcoma was regarded. CT of the chest revealed apparent huge soft tissue mass, more than 20 cm in diameter, in the right breast region. On the other hand, there was no metastatic lesion in the lungs.
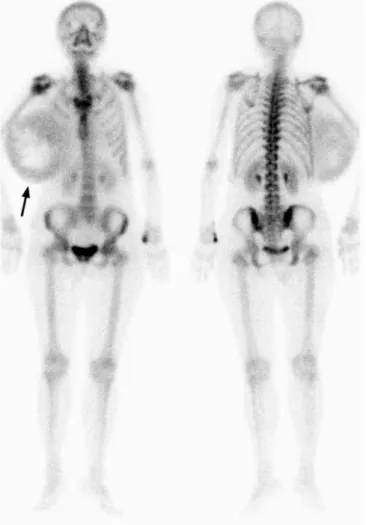
FIGURE 2. Bone scan did not show any suspicious focus of bone metastasis. However, there was round extraosseous uptake over the right anterolateral chest region (arrow). The overall scintigraphic images looked like the posture of a racing driver who holds a helmet under the armpit. Although a resectable disease was considered based on the preoperative surveillance, the surgery was eventually done with R1 resection (microscopic residual disease) of the tumor. Unfortunately, recurrent disease came rapidly in 1 month with local recurrence and distant metastases to the lungs before the planned adjuvant
radiotherapy. She was then treated with palliative chemotherapy. Breast sarcoma is mostly diagnosed in patients aged 40 to 60 years. Primary breast sarcoma is an extremely rare and heterogeneous disease, accounting for less than 1% of all primary breast malignancies and less than 5% of all sarcomas, which precludes prospective studies and makes difficulty in the clinicopathological analyses.1,2 The annual incidence is estimated fewer than 5 new cases per million women.3 Clinical presentation of the primary breast sarcoma is similar to those of the trunk and extremity, and the first recurrence is mainly local failure or lung metastasis. Surgery remains the most important treatment of primary breast sarcoma. Free of disease at the margin of surgical resection is of prognostic importance.1,4 Adjuvant radiotherapy may
improve local control for large or high-grade sarcomas.3,5,6 Adjuvant chemotherapy may be usable for patients with the worst prognosis but with conflicting results to improve overall survival.7Y10
Although the precise mechanism of extraosseous accumulation of bone-seeking radiopharmaceuticals is still unknown,11 there have been sporadic case reports describing increasing extraosseous uptake in primary breast sarcomas, mostly osteogenic sarcomas, on the bone scan.12Y14 The current case, in
contrast, is a high-grade soft tissue sarcoma and its unusual huge size contributes to a unique picture on the bone scan. Nevertheless, such extraosseous finding, whether or not it accumulates bone-seeking
radiopharmaceuticals, may obscure the overlapped skeletal area and challenge the interpretation of bone scan if there is unawareness of its potential change.15