行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫 期中進度報告
克雷白氏肺炎桿菌訊息傳遞系統 KvgASQR 和 KvgASII 的分
子調控研究(2/3)
計畫類別: 個別型計畫 計畫編號: NSC91-2311-B-009-001- 執行期間: 91 年 08 月 01 日至 92 年 07 月 31 日 執行單位: 國立交通大學生物科技研究所 計畫主持人: 彭慧玲 報告類型: 精簡報告 報告附件: 出席國際會議研究心得報告及發表論文 處理方式: 本計畫可公開查詢中 華 民 國 92 年 5 月 27 日
ABSTRACT
Key words: Klebsiella pneumoniae; two-component system (2CS); kvgASQR; kvhAS;
Electrophoretic mobility shift assays; LacZ reporter system; activator; anti-oxidation and/or anti-stress regulation; RpoS; 2D-PAGE
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a common opportunistic pathogen, which often causes suppurative lesions, septicemia, urinary and respiratory tract infection in immunocompromised patients. Two gene clusters, kvgASR and kvhAS, have previously been isolated from a highly virulent strain Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43 and identified as two-component systems (2CS). According to sequence analysis, KvgS and KvhS are sensory histidine kinases which allow bacteria to sense and respond to the changes in their environment. KvgA, KvhA and KvgR are responsible for regulating the expression of the signal induced genes. Both kvgAS and kvhAS have been demonstrated respectively having an operon structure by RT-PCR and southern blot analysis. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) have shown that the KvgA is capable of specifically binding to not only its own promoter, but also the putative promoters of kvgR and kvhAS. To investigate the roles of the two component systems in Kp CG43, the experiments had been finished in the past year are:
The related publication:
Identification and characterization of KvgAS, a two-component system in Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43. 2003. FEMS Microbiology Letters 218:121-126
Southern blot analysis demonstrated the deletions of the kvgA
-,kvgS-, kvgR-, kvhA-, and kvhS- obtained in the first year. However, no apparent effect of any of the mutations on bacterial virulence was observed in a mouse peritonitis model. A LacZ reporter system was constructed in K. pneumoniae CG43 which included
placZ15, a lacZ reporter in pYC016, and lacZ16, a K. pneumoniae CG43 lacZ deletion mutant. The LacZ16-derived mutants kvgA- (A18), kvgS- (S01), kvgR- (R16), kvhA- (HA01) and kvhS- (HS01) were also obtained.
Both electrophoretic mobility shift assay and in vivo assay using the LacZ reporter system suggested that the KvgA acts as a positive autoregulator for expression of the kvgAS and also as an activator for that of kvgR.
Paraquat and EDTA affected both kvgAS and kvgR promoters by increasing the reporter LacZ activities which implied that the two-component system is responsible for an anti-oxidation and/or anti-stress regulation in K.
pneumoniae CG43. However, the signals for the KvhAS have yet to be
The global stress protein- RpoS mutant was then constructed which allowed to demonstrate that the RpoS acts as an activator for kvgAS expression but as a repressor for the expression of kvhAS. Whereas, the RpoS mutation did not affect the promotewr activity of kvgR.
Moreover, we have tried to employ 2D-PAGE for a comparative analysis of the protein patterns among the parental strain, kvgA, kvgR, and kvhA mutants. Preliminary results revealed that the proteomic technology is promising for us to identify the targets under control by the 2CSs.
In the last year (the third year), we will determine the target genes that are regulated by kvgASR and kvhAS with both a promoter trap using LacZ as a reporter and the proteomic technology. In the mean time, the mutants kvgAkvgR, kvgAkvhA, kvhAkvgR, kvgAkvgRkvhA will also be constructed and their phenotypic properties analyzed. Taken together, the regulatory circuits and functional roles of kvgASR and kvhAS would be identified.
中文摘要: 關鍵詞:克雷白氏肺炎桿菌;訊號傳遞基因組;kvgASQR;kvhAS;電泳膠遲滯 實驗;LacZ 報導系統 ; 活化子 ; 專一結合啟動子;相互作用 克雷白氏肺炎桿菌 (Klebsiella pnenmoniae) 是造成糖尿病人肝膿瘍及院內病人 尿道、呼吸道感染常見的伺機性病原菌。本實驗室在具高毒性的克雷白氏肺炎桿 菌 CG43 內得到兩套特有的訊號傳遞基因組- kvgASR 以及 kvhAS。由序列分析結 果發現,其中 KvgS 和 KvhS 則可能是負責接受外來訊息的感應蛋白,KvgA、 KvhA 和 KvgR 的相似度很高,可能是扮演訊息傳遞系統中調控蛋白的角色。先 前 我 們 實 驗 室 已 經 由 反 轉 錄 聚 合 酉 每 連 鎖 反 應 (RT-PCR) 和 南 方 墨 點 法 (southern blot) 證實 kvgAS 及 kvhAS 與其他細菌中負責訊息傳遞系統相同具有基
因組 (operon) 結構的特性。利用電泳膠遲滯實驗證明 KvgAt以及 KvhA 皆具有
結合本身啟動子的能力,並且發現 KvgAt可專一結合 kvhA 及 kvgR 的啟動子,顯 示 kvgASQR 與 kvhAS 這兩套訊息傳遞基因組可能具有相互作用。為了探討這兩 套訊息傳遞系統在克雷白氏肺炎桿菌中的生物功能,我們在過去一年發表了一篇 論文、並完成實驗如下﹕ 建構了 LacZ 報導系統,包括一個包含具有酵素功能的 LacZ 完整基因的載 體以及建構在克雷白氏肺炎桿菌 CG43 中 lacZ 基因的突變株,並且為了探 討 kvgASR 以及 kvhAS 之間的關係,也建構了 kvgA- lacZ-- (A18), kvgR- lacZ --(R16) 以及 kvgS- lacZ-- (S01) 的雙重突變株。
經由電泳膠遲滯實驗以及 LacZ 報導系統證明 KvgA 可以進行正向的自我調 控,並且 KvgA 對於 KvgR 的表現為一個活化子。
利用 LacZ 報導基因活性偵測發現 Paraquat 以及 EDTA 可以增強 KvgAS 啟 動子的活性表現,因此推測 KvgAS 可能與抗氧化及抗壓力的功能具有相關 性。然而,KvhAS 所偵測的訊息還沒確定。
為了進一步了解 KvgAS 與抗氧化及抗壓力的相關性,我們也以同源互換的 方式獲得細菌中主要的調控抗壓蛋白 RpoS 突變株。而以 LacZ 報導系統分 析發現 RpoS 為 KvgAS 啟動子的活化子;相反的,RpoS 為 KvhAS 基因表 現的抑制子。此外,RpoS 的突變並不影響 KvgR 啟動子的活性表現。 由初步二維電泳膠分析野生株以及 KvgA 和 KvhA 突變株蛋白質表現量差異
的結果可以明顯發現可能的標地。
未來的一年,我們將同時利用 LacZ 報導系統篩選啟動子以及二維電泳蛋白 體系統來找尋可受 KvgASR 以及 KvhAS 調控的基因。另外,我們將建構
KvgAKvgR、 KvgAKvhA、 KvhAKvgR 雙基因突變株以及 KvgAKvgRKvhA 三 基因突變株並分析這些突變株的生理特性、活性的改變。最後,希望整合這些結 果能讓我們了解這些雙分子調控系統之間的關係、此雙分子調控訊息傳遞系統在 克雷白氏肺炎桿菌中所扮演的角色。
INTRODUCTION
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an opportunistic pathogen which often causes pneumonia, septicemia, bacteremia, suppurative lesion, wound infection, burn infection, and urinary or respiratory tract infections in chronic alcoholics and immunocompromised patients (9, 23). Two-component systems (2CS), consisting of a sensor histidine kinase and a response regulator, act to recognize specific signals and convert this information into specific transcriptional or behavioral responses (6, 10, 11, 12, 16, 20, 21, 24, 25). We have previously identified a novel two-component system, kvgASQR ( Klebsiella virulence gene ) by PCR-supported genomic subtractive hybridization from a highly virulent strain K. pneumoniae CG43 (1, 17). In the genome of K. pneumoniae strain MGH78578 (Genome Sequencing Center of Washington University, http://genome.wustl.edu/gsc/ ), a sequence exhibiting high homology with the kvgAS was identified by Blast analysis. The sequence was then isolated by PCR-based cloning from K. pneumoniae CG43 and designated kvhAS (Klebsiella virulence homolog)(2, 4) .On the basis of sequence analysis, KvgS and KvhS are sensory histidine kinases, KvgA, KvgR and KvhA are response regulators, and the orfQ is likely a transmembrane protein (2, 3, 4). The kvgAS and kvhAS, especially the residues near the biological active sites, were found to be the homologs of bvgAS and evgAS which are the two-component systems for regulating the virulence gene expression of Bordetella pertussis and Escherichia coli respectively (3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 14, 15, 22, 26, 27, 28).
In the first year, we have used RT-PCR analysis to demonstrate that the kvgA and kvgS are expressed in a transcription unit (19). Electrophoresis mobility shift assays (EMSA) have shown that the KvgA is capable of specifically binding to not only its own promoter, but also the putative promoter of kvgR. These results suggested an interaction is likely present inbetween kvgASR and kvhAS.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
To investigate the roles of the two component systems in Kp CG43, the experiments had been finished in the second year of the project are:
Related publication:
Identification and characterization of KvgAS, a two-component system in Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43. 2003. FEMS Microbiology Letters 218:121-126
(1) A good reporter system is required in order to investigate the respective functions of KvgASQR and KvhAS. Since K. pneumoniae is a lactose fermenter, K. pneumoniae CG43 lacZ deletion mutant LacZ16 was firstly constructed. The LacZ reporter plasmid placZ15 containing a promoterless lacZ gene in pYC016 was obtained subsequently. Using the reporter system, we were able to determine the signals that are likely sensing by KvgS and KvhS. A serial LacZ16-derived mutant strains including kvgA- (A18), kvgS- (S01), kvgR- (R16), kvhA- (HA01) and kvhS- (HS01) were also generated for the following analysis (Table 1).
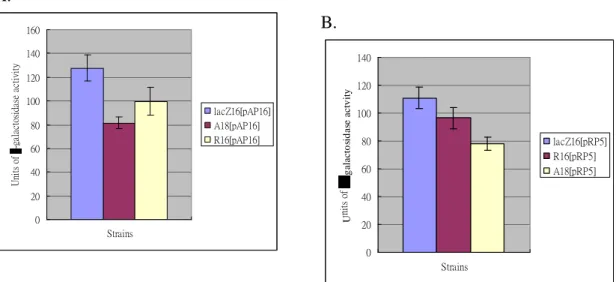
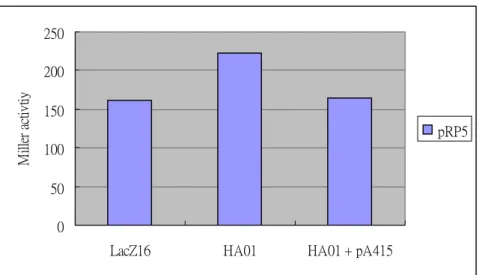
(2) The previous study by gel mobility shift assay suggested the presence of a cross-talk between kvgASQR and kvhAS. The LacZ reporter system allowed us measure the activities of p-kvgAS (pAP16), p-kvhAS (pHA01) and p-kvgR (pRP5) respectively in LacZ16, A18 and R16. As shown in Fig. 1, LacZ activities of kvgAS and kvgR promoters were found to decrease in the kvgA- mutant (A18). However, disruption of KvgR had no apparent effect on the promoters. The results suggested that the KvgA acts as a positive autoregulator and also as an activator for the expression of kvgR. Whereas, the kvgR promoter activity increased in the kvhA- mutant (HA01) suggesting a negative regulation of the the kvgR promoter by KvhA. No apparent changes of the activity of p-kvhAS in LacZ16 and the kvhA- mutant implying that KvhA does not control its own promoter (Figure 2). The interaction circuit between among KvgAS, KvgR, and KvhAS will be determined while more mutants are available.
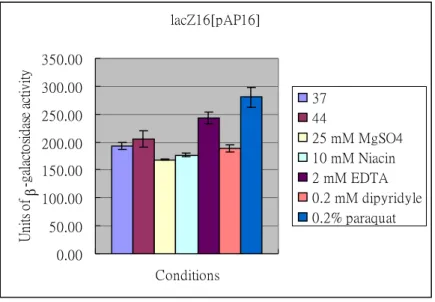
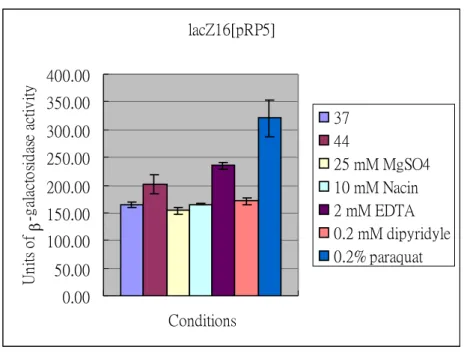
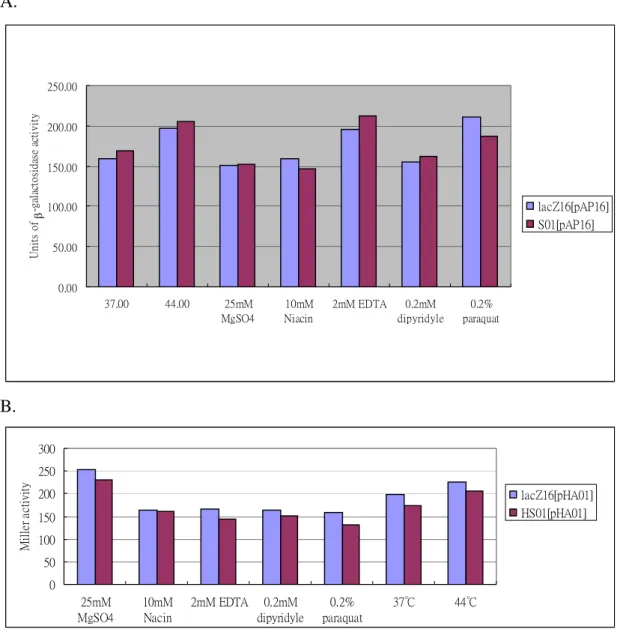
(3) The possible signals sensed by KvgS and KvhS were also identified by measuring the promoter activity with LacZ as the reporter. As shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, we have found that 0.2 % paraquat and 2 mM EDTA are likely the inducing signals for expression of either kvgAS or kvgR. However, the chosen signals were not sensed by p-kvhAS suggesting the signals are yet to be identified. Paraquat
and EDTA affected both kvgAS and kvgR promoters by increasing the LacZ activities implying that the two-component system is responsible for an
anti-oxidation and/or anti-stress regulation in K. pneumoniae CG43. The possibility will be evaluated in the next year. Interestingly, both the kvgS and kvhS mutations did not affect either promoter under these effectors implying that signals for the sensors are yet to be found (Figure 5). Thus, either paraquat or EDTA might be an indirect signal conveyed by other regulatory system for the expression of the kvgAS and kvhAS.
(4) The alternative sigma factor S
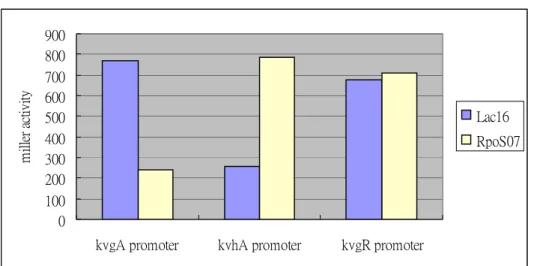
plays a key role in the survival of bacteria under stress conditions, which is a likely regulator to interact with kvgAS or kvhAS. In order to assess the role of the global stress protein RpoS on the expression of kvgASR and kvhAS, the rpoS deletion mutant was constructed and activities of the promoters p-kvgAS, p-kvgR, p-kvhAS were measured in the mutant. The p-kvgA activity decreased significantly in the RpoS mutant suggesting a positive control of the RpoS on the expression of kvgAS. On the other hand, the activity of p-kvhA increased apparently in the mutant indicated that the RpoS is likely a repressor for kvhAS. Whereas, disruption of RpoS had no effect on p-kvgR activity (Figure 6).
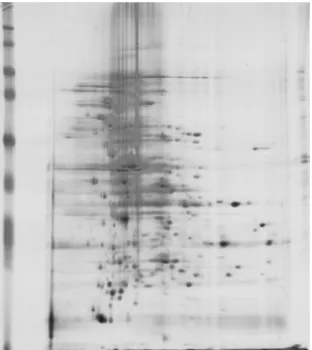
(5) In order to explore the fine map and interacting circuit of the two 2CSs KvgASR and KvhAS, two approaches including promoter trap analysis and proteomic technology to help for identification of the target genes under control by the 2CSs will be applied. Total proteins of the parental K. pneumoniae strain, kvgA mutant and kvhA mutant grown in M9 medium were respectively isolated and resolved by 2D-PAGE (Figures 7 and 8). The preliminary results indicated that the proteomic technology is promising for us to identify the target proteins under control by the two 2CSs. In the coming year, we should be able to determine not only the functional roles of the two component systems but also a constructive map of the regulatory pathways.
REFERENCE: 1. 楊淑理,肺炎克雷白氏毒力菌株特異性基因的鑑定:kvgASQR 基因群的序列 及表現分析,國立清華大學生命科學研究所碩士論文,民國八十九年六月。 2. 賴旻初,克雷白氏肺炎桿菌 KvgAII 基因之選殖與表現分析,國立交通大學生 物科技研究所碩士論文,民國八十九年七月。 3. 林靖婷,克雷白氏肺炎桿菌 KvgAS 雙分子訊息傳遞系統的功能探討,國立交 通大學生物科技研究所碩士論文,民國九十年六月。 4. 黃騰逸,克雷白氏肺炎桿菌 KvhAS 雙分子調控系統的特性分析,國立交通大 學生物科技研究所碩士論文,民國九十一年六月。
5. Arico, B., Miller, J. F., Roy, C. R., Stibitz, S., Monack, D., Falkow, S., Gross, R. and R. Rappuoli. 1989. Sequence required for expression of Bordetella pertussis virulence factors shares homology with prokarytic signal transduction proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 86: 6671-6675.
6. Barrett, J.F. and J.A. Hoch. 1998. Two-component signal transduction as a target for microbial anti-infective therapy. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 42: 1529-1536.
7. Beier, D., H. Deppisch, and R. Gross. 1996. Conserved sequence motifs in the unorthodox BvgS two-component sensor protein of Bordetella pertussis. Mol. Gen.Genet. 252: 169-176.
8. Boucher, P. E., Menozzi, F. D. and C. Locht. 1994. The modular architecture of bacterial response regulators Insights into the activation mechanism of the BvgA transactivator of Bordetella pertussis. J. Mol. Biol. 241:363-377.
9. Chang Chien, H. Y., N. C. Chiu, W. C. Li, and F. Y. Huang. 2000. Characteristics of neonatal bacterial meningitis in a teaching hospital in Taiwan from 1984-1997. J. Microbio. Immunol. Infect. 33:100-104.
10.Fabret, C., Feher, V. A. and J. A. Hoch. 1999. Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: How one organism sees its world. J. Bacteriol. 181(7): 1975-1983.
11.Georgellis, D., A. S. Lynch, and E. C. C. Lin. 1997. In vitro phosphorylation study of the Arc two-component signal transduction system of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 179:5429-5435.
12.Hsing, W. and T. J. Silhavy. 1997. Fuction of conserved histidine-243 in phosphtase activity of EnvZ, the sensor for porin osmoregulation in Escherichia coli. J. Bacterol. 179 (11): 3729-3735.
13.Hengge-Aronis R. 2002. Signal transduction and regulatory mechanisms involved in control of the sigma(S) (RpoS) subunit of RNA polymerase. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66(3):373-95.
14.Karimova, G., J. Bellalou, and A. Ullmann. 1996. Phosphorylation-dependent binding of BvgA to the upstream region of the cyaA gene of Bordetella pertussis. Mol. Microbiol. 20: 489-496.
15.Kato, A., H. Ohnishi, K. Yamamoto, E. Furuta, H. Tanabe, and R. Utsumi. 2000. Transcription of emrKY is regulated by the EvgA-EvgS two-component system in Escherichia coli K-12. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 64(6):1203-9
16.Kwon, O., D. Georgellis, and E. C. C. Lin. 2000. Phosphorelay as the sole physiological route of signal transmission by the Arc two-component system of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 182:3858-62.
17.Lai, Y. C., Yang, S. L., Peng, H. L. and H. Y. Chang. 2000. Identification of genes present specifically in a virulent strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 68: 7149-7151.
18.Lai, Y. C., Peng, H. L. and H. Y. Chang. 2001. Identification of genes induced in vivo during Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. Infect. Immun. 69: 7140-7145. 19.Lai, Y. C., Lin, G. T., Yang, S. L., Chang, H. Y., Peng, H.L. 2003. Identification
and characterization of KvgAS, a two-component system in Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43. FEMS Microbiol Lett 218(1):121-6
20.Miller, J. F., Mekalanos, J. J. and S. Falkow. 1989b. Coordinate regulation and sensory transduction in the control of bacterial virulence. Science. 243: 916-922. 21.Mizuno, T. 1997. Compilation of all genes encoding two-component
phosphotransfer signal transducers in the genome of Escherichia coli. DNA Res. 4:161-168.
22.Nishino, K., and A.Yamaguchi. 2001. Overexpression of the response regulator evgA of the two-component signal transduction system modulates multidrug resistance conferred by multidrug resistance transporters. J. Bacteriol. 183(4):1455-8
23.Peng, H-L., P.-Y. Wang, J.-L. Wu, C.-T. Chiu, and H.-Y. Chang. 1991. Molecular epidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Chinese J Microbiol and Immun. 24:10-17.
24.Soncini, F. C, and E. A. Groisman. 1996. Two-component regulatory systems can interact to process multiple environmental signals. J. Bacteriol. 178:6796-6801. 25.Stock, J. B, and A. M. Stock. 1989. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of
adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 53: 450-490.
26.Tanabe, H., K. Yamasaki, A. Katoh, S. Yoshioka, and R. Utsumi. 1998. Identification of the promoter region and the transcriptional regulatory sequence of the evgAS operon of Escherichia coli. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 62(2):286-90 27.Uhl, M. A. and J. F. Miller. 1994. BvgAS is sufficient for activation of the
28.Zu, T., Manetti, R., Rappuoli, R. and V. Scarlato. 1996. Differential binding of BvgA to classes of virulence genes of Bordetella pertussis directs promoter selectivity by RNA polymerase. Mol. Microbiol. 21(3): 557-565.
期中報告成果自評
In the past year, we have established the promoter-trap assaying system and 2D-gel electrophoretic technology which is a big breakthrough for us to explore more
concerning the map of the KvgASR and KvhAS interacting circuit. We’ve also published part of the result earlier this year (FEMS Micro. Lett. 218:121-126) and a manuscript is in preparation. It is apparent that we have accomplished 100% of the work as we planned.
Table 1. Bacterial strains and plasmids used and constructed in this study
Bacterial strain and
plasmids Genotypes or relevant features Source
Bacterial strain
K. pneumoniae
CG43-S3 rspL mutant Laboratory stock
Lac16 △lacZ in Kp CG43-S3 This study
S01 △kvgS in LacZ16 This study
A18 △kvgA in LacZ16 This study
R16 △kvgR in LacZ16 This study
HS01 △kvhS in LacZ16 This study
HA01 △kvhA in LacZ16 This study
RpoS07 △RpoS in LacZ16 This study
Plasmids
pYC016 IVET selection vector Ref. 18
placZ15 Contained a lacZ gene in pYC016 This study
pAP16 p-kvgAS::lacZ in pYC016 This study
pRP5 p-kvgR::lacZ in pYC016 This study
A. B. 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 Strains U nit s of g ala cto sid a se a c tv it y lacZ16[pRP5] R16[pRP5] A18[pRP5] 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Strains U ni ts of -g al ac to si da se a ct iv it y lacZ16[pAP16] A18[pAP16] R16[pAP16]
Figure 1. The promoter activities of kvgAS (pAP16) and kvgR (pRP5) in K. pneumoniae CG43 lacZ- (lacZ16), lacZ-kvgA- (A18) and lacZ-kvgR- (R16). (A) The plasmid pAP16 (which carries a p-kvgAS-lacZ fusion) and (B) plasmid pRP5 (which carries a p-kvgR-lacZ fusion) were transferred into LacZ16, A18 and R16 respectively by conjugation. The cells were grown in LB medium for OD600 about 0.4, and the level of -galactosidase activity was determined as described (J. H. Miller, 1972). The values are the averages of four independent experiments.
0 50 100 150 200 250
LacZ16 HA01 HA01 + pA415
M ill er a ct ivt iy pRP5
Figure 2. The promoter activities of kvgR (pRP5) in K. pneumoniae CG43 lacZ- (lacZ16), lacZ-kvhA- (HA01) and HA01 that contains a plasmid with kvhA (pA415). The plasmid pRP5 was transferred into LacZ16, HA01 and HA01[pA415] respectively by conjugation. The cells were growth in M9 medium till OD600 of about 0.4, and the level of -galactosidase activity were determined.
Figure 3. Identification of the signaling factors that affect the promoter activity of kvgAS. The -galactosidase activities of pAP16 in K. pneumonia CG43 lacZ16 was determined under the indicated condition. The overnight-growth cells were transferred into M9 medium and the cultures grown at 37 ℃ for 2 h. The signaling factors including 25 mM MgSO4, 10 mM Niacin, 2 mM EDTA, 0.2 mM dipyridyl and 0.2 % paraquat were then added respectively to the cultures and the mixture incubated at 37 ℃ for another 1 h. The temperature effect on pAP16 was also determined by transferring the M9-grown cells carrying pAP16 to 44 ℃ incubator and the cells cultured for 1 h. The values are averages of two independent experiments.
lacZ16[pAP16] 0.00 50.00 100.00 150.00 200.00 250.00 300.00 350.00 Conditions U ni ts o f -ga la ct os id as e act iv ity 37 44 25 mM MgSO4 10 mM Niacin 2 mM EDTA 0.2 mM dipyridyle 0.2% paraquat
Figure 4. Identification of the signaling factors that affect the promoter activity of kvgR. The -galactosidase activities of pRP5 in K. pneumonia CG43 lacZ16 was determined under the indicated condition. The overnight-growth cells were transferred into M9 medium and the cultures grown at 37 ℃ for 2 h. The signaling factors including 25 mM MgSO4, 10 mM Niacin, 2 mM EDTA, 0.2 mM dipyridyl and 0.2 % paraquat were then added respectively to the cultures and the mixture incubated at 37 ℃ for another 1 h. The temperature effect on pRP5 was also determined by transferring the M9-grown cells to 44 ℃ incubator and the cells cultured for 1 h. The values are averages of two independent experiments.
lacZ16[pRP5] 0.00 50.00 100.00 150.00 200.00 250.00 300.00 350.00 400.00 Conditions Un its o f -g al ac to sid as e ac ti v ity 37 44 25 mM MgSO4 10 mM Nacin 2 mM EDTA 0.2 mM dipyridyle 0.2% paraquat
A. 0.00 50.00 100.00 150.00 200.00 250.00 37.00 44.00 25mM MgSO4 10mM Niacin 2mM EDTA 0.2mM dipyridyle 0.2% paraquat U n it s of -g al ac to si da se a ct iv it y lacZ16[pAP16] S01[pAP16] B. 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 25mM MgSO4 10mM Nacin 2mM EDTA 0.2mM dipyridyle 0.2% paraquat 37℃ 44℃ M il le r a ct ivit y lacZ16[pHA01] HS01[pHA01]
Figure 5. The sensor KvgS (S01) and KvhS (HS01) mutations do not affect the p-kvgAS (pAP16) and p-kvhAS (pHA01) activities under the indicated conditions. The overnight-grown cells were transferred into M9 medium and the cells grown at 37 ℃ for another 2 h.
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
kvgA promoter kvhA promoter kvgR promoter
m ill er a ct ivi ty Lac16 RpoS07
Figure 6. The activities of p-kvgAS (pAP16), p-kvgR (pRP5) and p-kvhAS (pHAP01) in K. pneumoniae CG43 lacZ16 and lacZ-rpoS- (RpoS07). The plasmids (pAP16, pRP5 and pHAP01) have been transferred into LacZ16 and rpoS mutant respectively by conjugation. The cells were grown in LB medium till OD600 of about 0.4, and the level of -galactosidase activity was determined.
A.
Figure 7. 2D-PAGE patterns of the proteins isolated form K. pneumonia CG43-U9451 (A) and K. pneumonia CG43-U9451KvgA (B).
B.
Figure 8. 2D-PAGE patterns of the proteins isolated from K. pneumonia CG43-U9451 (A) and K. pneumonia CG43-U9451KvhA (B).