Research Express@NCKU - Articles Digest
1 of 2
Research Express@NCKU Volume 27 Issue 1 - July 18, 2014 [ http://research.ncku.edu.tw/re/articles/e/20140718/4.html ]
Use of Dual-Energy CT in Detecting Bone Marrow Edema of Vertebral Compression Fractures
Chien-Kuo Wang1,* , Jen-Ming Tsai2, Ming-Tsung Chuang1, Min-Tsung Wang2, Kuo-Yuan Huang3, Ruey-Mo Lin3
1 Department of Radiology, National Cheng Kung University Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan 2 Department of Radiology, Kaohsiung Armed Forces General Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan 3 Department of Orthopedics, National Cheng Kung University Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan radwangck@mail.ncku.edu.tw
Radiology. 2013 Nov;269(2):525-33. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13122577. Epub 2013 Jun 25.
Fracture risk whether due to trauma or bone fragility is dependent on the bone mineral and matrix quantity and quality in addition to geometry and architecture. These fractures generally involve collapse and compression of the vertebral body, associated with a wedge deformity, which may lead to kyphotic angulation of the spine. A common cause of vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) is osteoporosis with increasing frequency as skeletal mass and bone strength diminish with the aging process.
Percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP), the percutaneous injection of polymethylmethacrylate into the affected vertebral body, has been proposed as a treatment for painful vertebral fractures. The treatment location is commonly determined from findings at imaging, which includes magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, bone scintigraphy, and computed tomography (CT).
The bone marrow edema (BME) in acute/subacute VCFs is useful in determining the vertebra that is to be treated.
MR imaging provides information on anatomic vertebral collapse and the loss of normal T1 high signal intensity from the marrow space of vertebrae with acute fractures. Loss of normal T1 high signal intensity indicates the presence of BME, which is the important sign for the PVP treatment of VCFs.
Single-energy CT images can offer precise information on bony structures including their degree of collapse and extent of fracture, but these techniques do not permit bone marrow to be visualized because the delicate trabecular structures surrounding the bone marrow are not resolved. Technologic advances in dual-energy (DE) CT triggered by the introduction of dual source spiral CT scanners heralded a new approach. This method has been used to create a virtual unenhanced scan by subtracting iodine from contrast agent–enhanced CT examinations. The virtual noncalcium images can provide the information of bone marrow if calcium from the bone is properly subtracted.
There is little study about the BME on CT published. We expect that DE CT virtual noncalcium technique can be used to allow vertebral marrow assessment. The study aims to assess bone marrow edema within the VCF by use of quantitative CT values on the DE CT virtual noncalcium images. The data were compared with MR imaging as standard reference.
In 112 VCFs, there are 46 edematous and 66 non-edematous bodies. The mean CT number of the edematous bodies is significantly higher than that of the non-edematous on the DE CT virtual noncalcium images. Using a cut-off value of -80 for the CT number to identify edematous bodies, we obtain an accuracy of 83.9%.
In conclusion, findings from our study show that we can evaluate BME in VCFs on noncalcium images reconstructed from DE CT when compared with MR imaging.
Research Express@NCKU - Articles Digest
2 of 2
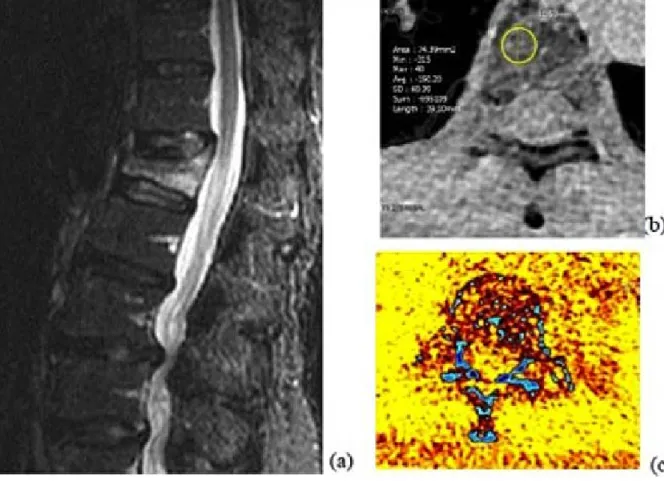
Fig. A 60-year-old man with a thoracic compression fracture. (a) Sagittal STIR MR image shows the edematous body of T2 high signal. (b) On the axial gray-scale virtual noncalcium image at the level of the collapsed body, the CT number of the circular region of interest is measured. (c) The corresponding axial color-coded virtual noncalcium image is depicted.