Associations between Arsenic in
Drinking Water and the Occurrence of
End-Stage Renal Disease with Modifications
by Comorbidities: A Nationwide
Population-Based Cohort Study in Taiwan
Ya-Yun Cheng, How-Ran Guo
Department of Environmental and Occupational Health
College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University
Tainan, Taiwan
27 Sep. 2017
Arsenic Important
Nevertheless, epidemiology studies on the
association between arsenic exposure and the
occurrence of ESRD are still limited.
260-75%
10-15%
10-20%
Blood
Liver
Liver
(Vahter M, 2000; Kitchin, 2001; Stýblo M et al., 2002; Hayakawa et al., 2005)
Monomethylarsonic Acid (MMA)
Dimethyarsinic Acid (DMA)
MMA3+>As3+>As5+>MMA5+=DMA5+
3
Arsenic concentrates in the kidney
during its urinary excretion that
affects the function of proximal tubules and glomerulus
Mechanisms pertaining to arsenic toxicity. Toxicol Int. 2011 Jul;18(2):87-93.
As ROSBUN+Cr
(Singh et al. 2011)
(Liao et al. 2009) 4
NCKU 5
Objective
1. To evaluate the associations between arsenic
exposure and the occurrence of ESRD in
Taiwan.
We conducted a nationwide population-based
study including both the BFD endemic area
and other areas in Taiwan.
NCKU 6
Materials and methods
NCKU 7
Arsenic exposure index
Data on well water arsenic were obtained from a
nationwide survey conducted by the Taiwan
Provincial Institute of Environmental Sanitation
using the standard mercuric bromide stain method.
(Lo et al.,1977; APHA, 1985)
There were more than 80,000 wells, mostly
between 1974 and 1976, and were available for
311 townships (85%).
According to the cut-offs adopted by the survey
reports, which was the regulatory standard at the
time of the survey, we defined a high arsenic level
as ≥ 50 µg/L
Jan 1,
1996
Jan 1,
1998
Dec 31,
2010
New ESRD cases once diagnosis
with Catastrophic illness code 001
Prevalent
CKD / ESRD
Follow up 13 years
Allowing at least 24 months wash-out period
LHID2000 Population-based ecological cohort study:
1,000,000 random sampling enrollees during 1996-2010
Adjust comorbidity
With 3 times OPD
diagnosis by a physician
SL Wang, 2003 National Health Insurance (NHI)
Longitudinal Health Insurance Database (LHID)
Evaluate the associations between arsenic exposure
and the occurrence of ESRD.
Drinking history
Address at 1998
Age ≥40 at 1998
NCKU 9
Risk factors of renal disease
Epidemiological and clinical evidence have shown a
link between hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and
metabolic syndrome (Comorbidity) and the onset
and progression of CKD.
SEX, Age, Edu, SES
(Yang WC, 2008; Wen CP, 2008) Western medicines
NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
Acetaminophen
(Chiu et al. 2008; Wen et al. 2008; Lai et al. 2009; Lai et al. 2010) Chinese herbal medicine (Aristolochic acid)
(Vanherweghem JL, 1993; Yang CS, 2000; Chang CH, 2001; Yang HY, 2006)
Disease ICD-9-CM / A-CODE Criteria
ESRD Dialysis 585-586 combined with copayment code ‘‘001’’
(indicated the presence of a Catastrophic illness)
1 OPD visits
Hypertension 401- 405, A260 ≧3 OPD visits
Diabetes 250, A181 ≧3 OPD visits
Hyperlipidemia 272.0-272.4, A182 ≧3 OPD visits
CAD 410-414 ≧3 OPD visits
CHF 428.0 ≧3 OPD visits
Stroke 430-438 ≧3 OPD visits
Anemia 280-285 ≧3 OPD visits
Assessment of renal disease and comorbidity
International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM)
NCKU 11
Statistic
• Chi-square test, T-test, ANOVA
• Cox PH regression (Survival analysis): ESRD
Kaplan–Meier, Log-rank
Cox regression: Hazard Ratio, 95% C.I.
Single, multiple, backward stepwise (inclusion set at
p<0.05; exclusion set at p>0.15)
• SAS 9.3 + SPSS1 17.0
• Two-side p<0.05
NCKU 12
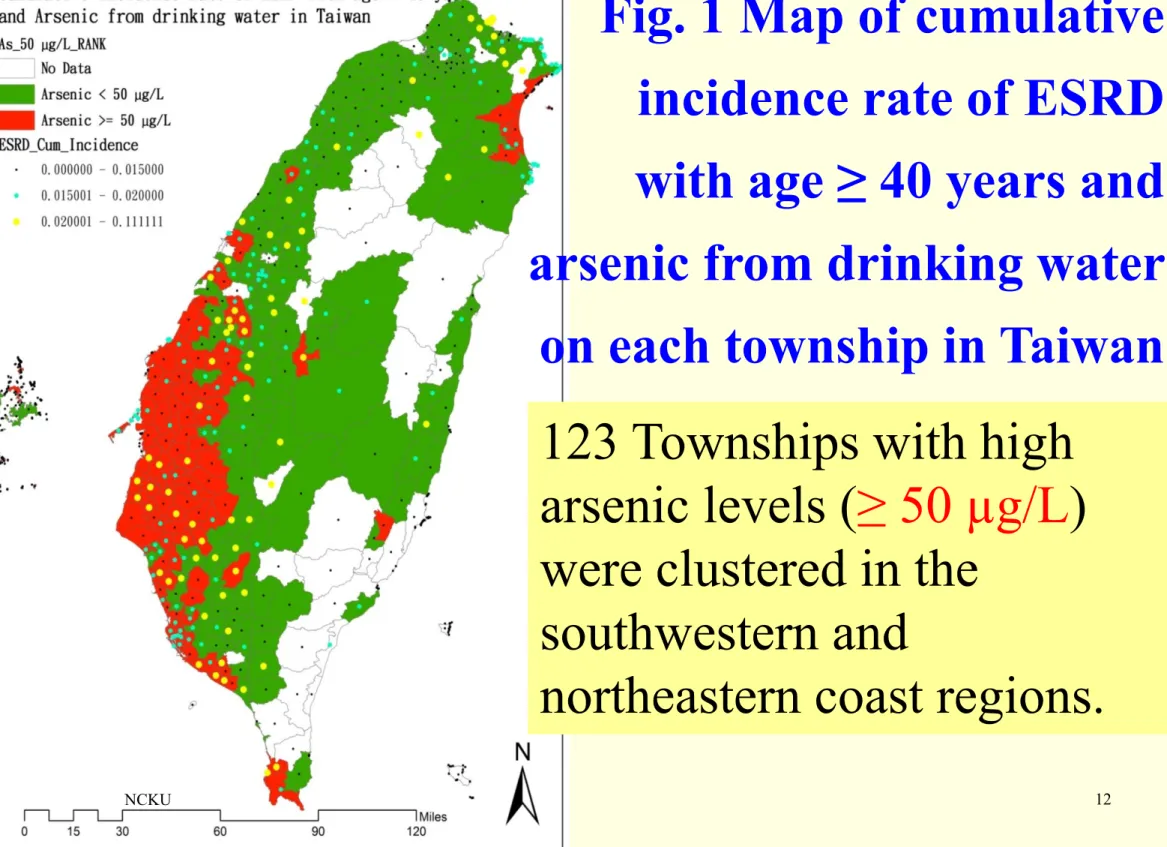
123 Townships with high
arsenic levels (≥ 50 µg/L)
were clustered in the
southwestern and
northeastern coast regions.
Fig. 1 Map of cumulative
incidence rate of ESRD
with age ≥ 40 years and
arsenic from drinking water
on each township in Taiwan
13
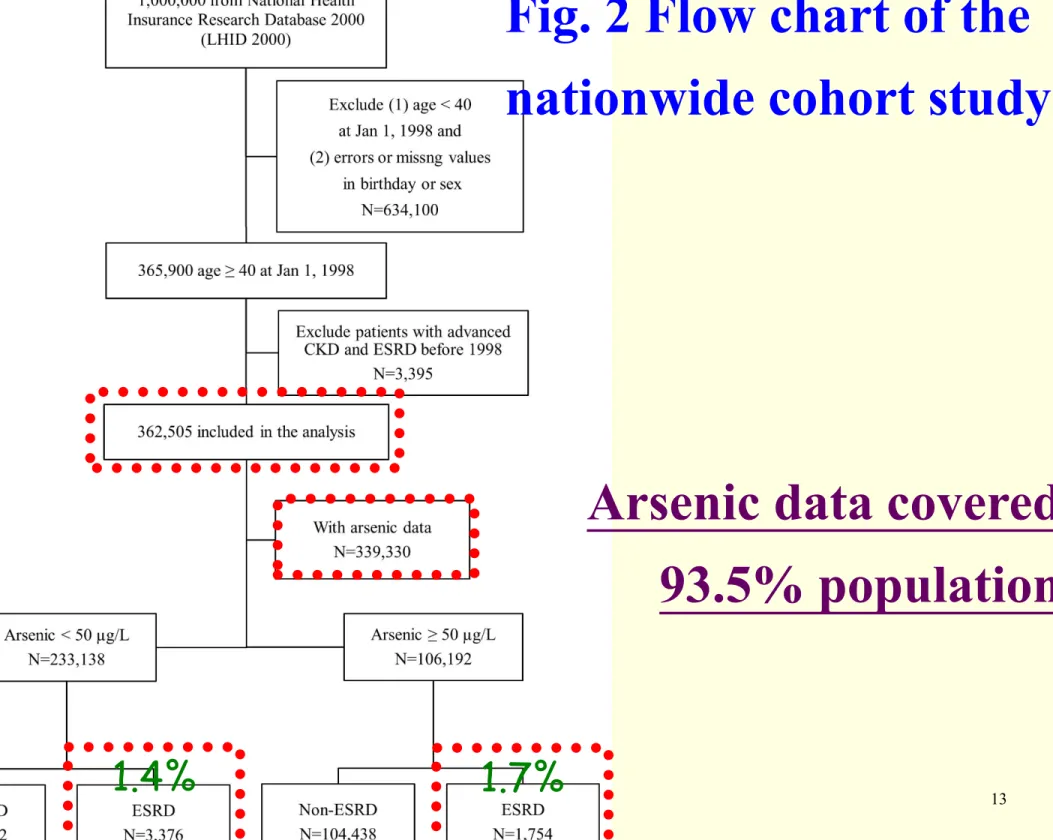
Fig. 2 Flow chart of the
nationwide cohort study
1.4%
Arsenic data covered
93.5% population
1.7%
NCKU 14
1-1
TABLE-1 Cox regression models for occurrence of end-stage renal disease
(N=362,505).
NCKU 15
1-2
TABLE-1 Cox regression models for occurrence of end-stage renal disease
(N=362,505).
NCKU 16
1-3
TABLE-1 Cox regression models for occurrence of end-stage renal disease
(N=362,505).
1~2 3~7
NCKU 17
TABLE-2 Cox models for the effect modification of comorbidity on 2-1
the association between arsenic exposure and end-stage renal disease.
NCKU 18
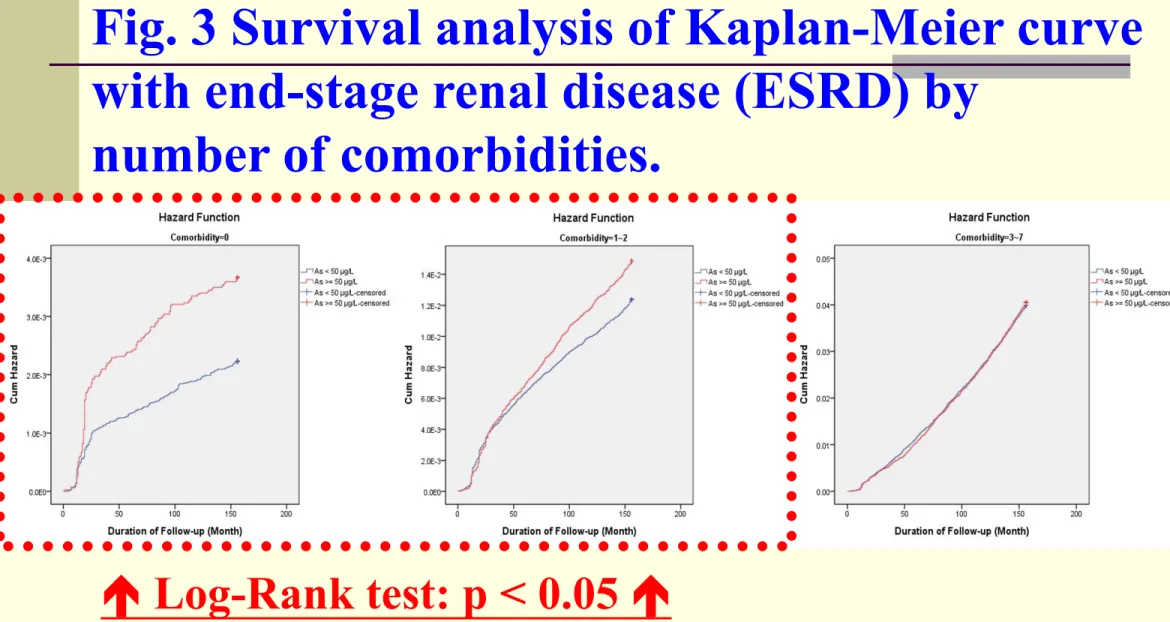
Fig. 3 Survival analysis of Kaplan-Meier curve
with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) by
number of comorbidities.
Log-Rank test: p < 0.05
Strengths and limitations
A large sample size and a long duration: therefore,
the results should be more reliable than those from
smaller case-control or cross-sectional studies.
Ecological fallacy.
Ours study using resident area measurements
instead of personal exposure data: series of studies
have been conducted using similar approaches and
identified increased risk of cerebrovascular
disease, pterygium, and liver cancer.
(Lin et al., 2008; Cheng et al., 2010; Chung et al., 2013; Lin et al., 2013)
NCKU 19
Conclusion
Using 50 µg/L as the cut-off, we found that a higher
level of arsenic in the drinking water was positive
associated with AHR of 1.12 (95% CI: 1.05-1.18, p <
0.001) for the occurrence of ESRD in Taiwan,
independent of most documented risk factors including
age, sex, SES, Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia, Stroke,
CAD, CHF, DM, and Anemia.
We observed a effect modification of arsenic on ESRD
by comorbidities, especially in less than two.
Intervention programs for the prevention and control of
comorbidities should be implemented in endemic areas
of exposure to slow the occurrence of renal disease
especially on early CKD.
NCKU 20
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants NSC102-
2314-B-006 -026-MY2 and MOST-104-2314-B-
006 -021 -MY2 from the Ministry of Science and
Technology of Taiwan, R.O.C.
The database in our study was established by the
National Health Insurance Research Database
(NHIRD).
Co-author: How-Ran Guo (M.D., Sc.D.), Junne-Ming Sung
(M.D.), Yu-Tzu Chang (M.D.)
Travel Awards from National Cheng Kung
University (NCKU) and Foundation for the
Advancement of Outstanding Scholarship (FAOS).
NCKU 21
NCKU 22
Thank you for
your attention!
Q & A
NCKU 23
NCKU 24
2014 Environmental Health Perspectives • volume 122 P.213 2009 The Lancet Oncology, Volume 10, Issue 5, Pages 453 - 454
http://research.stevens.edu/index.php/sers-on-site-analysis
This graphic illustrates global occurrences of arsenic in groundwater
In TAIWAN 0.5 million
were exposed to arsenic concentration
in drinking water above 50 µg/L
which was the regulatory standard at the time of survey.
(Lo et al. 1977, Guo et al. 1997; Guo et al. 1998)
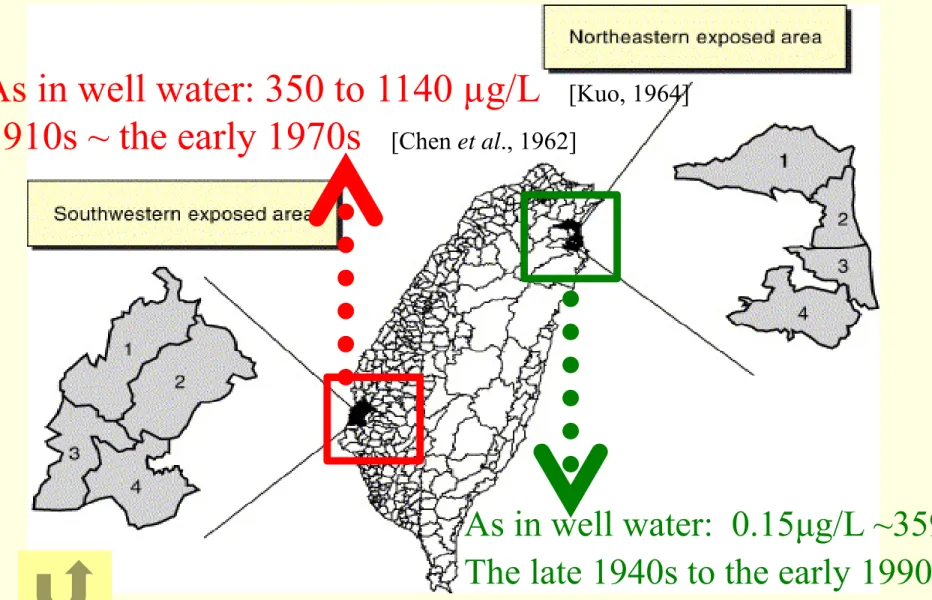
25As in well water: 350 to 1140 µg/L
[Kuo, 1964]1910s ~ the early 1970s
[Chen et al., 1962]Arsenic-exposed areas in Taiwan
Fig. Map of southwestern and northeastern arsenic-exposed areas in Taiwan. There
are four townships in the southwestern exposed area: Putai (1), Ichu (2), Peimen
(3), and Hsuehchia (4); and four townships in the northeastern exposed area:
Chiaohsi (1), Chuangwei (2), Wuchieh (3), and Tungshan (4).
(Guo et al.,1998, 2008) 26
As in well water: 0.15μg/L ~3590μg/L
The late 1940s to the early 1990s
[Chiou et al., 1997]NCKU 27
Mechanisms pertaining to arsenic toxicity. Toxicol Int. 2011 Jul;18(2):87-93.
Arsenic-Induced Nephro-toxicity
By ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species)
Enhances lipid peroxidation and
cellular damage in renal tissue.
Acute renal dysfunction due to
arsenic exposure is characterized
by acute tubular necrosis and
cast formation with increasing in
blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and
creatinine (Cr) levels.
(Giberson et al. 1976, Sasaki et al. 2007)
27
Epidemiology: As – kidney disease
Reference Design Arsenic exposure Main findings
(Chen et al. 2011) Chemosphere
Community-based cross-sectional study from central Taiwan
Urine As U-As might relate to renal
dysfunction even other important risk factors were taken into
account. (β2MG > 0.154 mg/L) U-As > 35 lg/g
(eGFR < 90 mL/min/1.73 m2/year) U-As > 75 lg/g (Hsueh et al. 2009)
American Journal of Kidney Diseases
Hospital based Case- control study
125 CKD patients and 229 controls
Urine As Total arsenic level was
associated significantly with CKD in a dose-response relationship.
(Chiu and Yang 2005) Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health - Part A
Standardized mortality ratios
(SMRs) for the years 1971–2000.
Residents BFD endemic area in the southwestern coast of Taiwan more than 50 yr.
(SMRs) for renal diseases were positively correlated.
(Chiou et al. 2005a) International Journal of Epidemiology
National Health Insurance (NHI) database.
1999-2000 prevalence
Residents BFD endemic area in the southwestern coast of Taiwan
An increased prevalence of microvascular diseases,
including neurological and renal disorders, is associated with arsenic ingestion.
NCKU 28
Arsenic level was positively associated significantly
with kidney disease and renal dysfunction.
28
NCKU 29
American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 2007 Vol 49, No 1 : pp 46-55
Epidemiology of
Chronic Kidney Disease
In NHIRD
(Kuo et al. 2007) (Wen et al. 2008)
They were significantly higher
in southwestern Taiwan with
an increasing trend.
NCKU 30
(United States Renal Data System, USRDS 2012)
12% CKD 2.7 million in 2012
0.26% ESRD cost NHI: 7 % $
30