Construct Validation of a Web-based Imagination Assessment
Su-Pin Hunga* Hung-Yu Huangb, Po-Hsi Chenc
a Center of Teacher Education, National Cheng Kung University
Tainan, Taiwan
b Department of Psychology and Counseling, University of Taipei
Taipei, Taiwan
c Department of Education and Counseling, National Taiwan Normal University Taipei, Taiwan
*Corresponding Author: suping0612@gmail.com
Abstract
Imagination contributes the development of humanity civilization. Education should encourage children to imagine future life rather than impede their abstractive thinking. Examining the efficiency of imagination training program requires an appropriate assessment however, because of “imagination” is an abstract concept and thus enhances the difficulty of measuring. To date, rarely measurements are developed to assess imagination. The previous imagination assessments are relying on paper-based thus spent a lot of time on scoring and coding (e.g., Karwowski, 2008; Ward, 1994; Ward, Patterson & Sifonis, 2004; Ward & Wickes, 2009).
Furthermore, scoring indices (i.e., originality, flexibility and fluency) which applied in these imagination assessments are similar with those applied in traditional creativity performance assessments. Since the construct of creativity and imagination are different. Consequently, more specific scoring indices (i.e., expansion imagination; correlation imagination) should be included to assess imagination. Hence, in the present study the meaning of imagination is clearly defined and scoring indices are proposed to assess imagination. Finally, a web-based imagination assessment is then developed to measure one’s imagination and examined its construct validity.
There are four subsystem included in the web-based imagination assessment, including: subject interface, automatic rating program, rater interface, management interface. For the subject interface, two sections are included. Section 1: participants are required to imagine the circumstance on earth after 1000 years. Section 2: participants are required to do follow up imagination after accomplish section 1. Participants are asked to typing possible function, design and related components in detail of transportation that will need in future (after 1000 years) separately in the follow up layers. Overall, we adopted 11 scoring indices in the newly developed assessment. These scoring indices including: the amounts of responses in level 1; average of category by computing the average of categories that appeared in each level which are intended to assess divergent thinking; average of originality by
computing average of originality that appeared in each level; the amounts of responses in level 2; the amounts of responses in level 3; the amounts of responses in level 4; the average of levels; the maximum levels which are intended to assess expansion imagination; connection of level 1 and level 2; connection of level 2 and level3 and connection of level 3 and level 4 which are intended to assess correlation imagination. Only 4 rating indices rely on rating.
The sample consisted of 1022 high school students and 644 undergraduates. Informed consent was obtained from every participant. Participants were informed of the type of study as well as the aims, and method to be used. All participants were invited to attend group assessment sessions in their classrooms to complete the newly developed imagination assessment. The imagination task had a time limit of 18 minutes, and students were required to finish the test within that limit, as fast and effectively as possible.
To assure construct validity of our imagination assessment, confirmatory analysis is applied to analyze two data pools high school students and undergraduates. As listed in the Table 1, the results from confirmatory factor analysis suggested that the three factors with 10 indices structure perform better than another one, similar results also can be found in undergraduates. The three factors are divergent thinking which including numbers of level 1, average numbers of classes, uniqueness of imagination; expansion imagination which including numbers of level 3 and level 4, numbers of maximum level and numbers of average level; and correlation
imagination which including relationship between each level and it’s follow-up level. Table 1 Summary of confirmatory analysis
High school N=1022 University N=644 Model1 1:L1 N. of Class Uni 2:L2~L4 max_level Average_level 3:L1L2 L2L3L3L4 Model2 1:L1 N. of Class Uni 2:L3~L4 max_level Average_level 3:L1L2 L2L3L3L4 Model1 1:L1 N. of Class Uni 2:L2~L4 max_level Average_level 3:L1L2 L2L3L3L4 Model1 1:L1 N. of Class Uni 2:L2~L4 max_level Average_level 3:L1L2 L2L3L3L4 df 41 32 41 32 χ2 822.04 637.79 658.15 490..07 SRMR 0.098 0.095 0.11 0.11 GFI 0.87 0.89 0.84 0.87 NFI 0.88 0.90 0.82 0.86 CFI 0.89 0.91 0.83 0.86
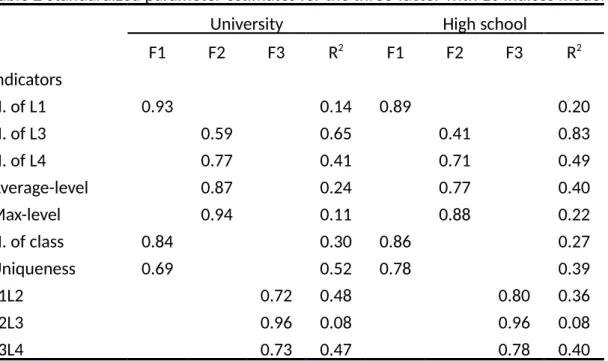
Standardized parameter estimates for the model are presented in Table 2. As shown, model parameters were all significant (p<.01) and explained substantial amounts of
item variance (R2 ranged from 0.08 to 0.83). Among the three factors, expansion
imagination and correlation imagination were significantly correlated in the two samples ( r=.43 and r=.37). The result also indicated that the three factor model of imagination is supported in both groups.
Table 2 Standardized parameter estimates for the three-factor with 10 indices model
University High school
F1 F2 F3 R2 F1 F2 F3 R2 Indicators N. of L1 0.93 0.14 0.89 0.20 N. of L3 0.59 0.65 0.41 0.83 N. of L4 0.77 0.41 0.71 0.49 Average-level 0.87 0.24 0.77 0.40 Max-level 0.94 0.11 0.88 0.22 N. of class 0.84 0.30 0.86 0.27 Uniqueness 0.69 0.52 0.78 0.39 L1L2 0.72 0.48 0.80 0.36 L2L3 0.96 0.08 0.96 0.08 L3L4 0.73 0.47 0.78 0.40
Note: F1= Divergent thinking, F2=Expansion imagination, F3= Correlation imagination In sum, in contrast of the previous creative imagination measures, the newly developed imagination assessment has many advantages. First of all, the newly developed imagination assessment is a web-based assessment tool; responses of participants can be collecting on line so that saving time to recording. Second, most of the scoring procedures are automatically proceed thus reduce the laborious scoring demand. Third, in contrast to the previous assessment may restricted in specific domain (i.e., make up a story), the newly measurement we design can be applied in various field. For example, in the present study, the condition we set is asking participant to think about transportation in future. However, the demand could be change very easily and will not affect scoring. Forth, the scoring indices included in the present study are more general and appropriate to assess
imagination. Finally, result of construct validity asserted that the scoring indices proposed in the present study met our expectation.