行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫 成果報告
校長領導與學校組織效能關係之後設分析研究
計畫類別: 個別型計畫 計畫編號: NSC92-2413-H-004-003- 執行期間: 92 年 08 月 01 日至 93 年 07 月 31 日 執行單位: 國立政治大學教育學系 計畫主持人: 秦夢群 報告類型: 精簡報告 處理方式: 本計畫涉及專利或其他智慧財產權,1 年後可公開查詢中 華 民 國 93 年 11 月 3 日
校長轉型領導與學校組織效能
之後設分析研究
中文摘要
本研究之主要目的在探討校長轉型領導與學校產出(教師工作滿足 感、教師知覺之學校效能、學生成就)之間的關係。為達此目的,本研究 應用後設分析之相關統計加以分析。就台灣與美國之二十四篇博士論文 中,發現轉型領導對學校產出確有中度效應(以 Cohen 之標準而言)。在 中介變項部分,轉型領導在小學與教師工作滿足感及教師知覺之學校效能 之間有較大之關係。在轉型領導與學生成就之研究中,中學比小學則有較 大之關係。During the last three decades, there was a growing body of research dealing with transformational leadership. Initially outlined by James Burns in his book of 1975, the theory of transformational leadership was
reconceptualized and developed by Bernard Bass in 1985. Bass views that transformational leadership as an expansion of traditional leadership that goes beyond simple exchange rewards and promises of reward for effort. Rather than focusing just on the leader or follower, transformational leadership examines the relationship between leader and follower and reckons that by engaging followers’ higher needs, instead of merely working for the greater good, the followers become self actualizing and finally grow to be leaders themselves.
Theoretically, transformational leadership redefined the vision and mission of an organization by proposing that leadership is not just a set of behavior or traits of an individual but a process whereby the individual
interrelates with the organization as a whole. Transformational leadership is a process to shape and elevate goals and abilities so as to achieve significant improvements through common interests and cooperative actions (Bennis & Nanus, 1985).
In describing transformational leaders, Burns (1978) concluded, “Leaders engage with followers but from higher levels of morality; in the enmeshing of goals and values, both leaders and followers are raised to more principled levels of judgment” (p.455). Leithwood (1992) also declares that
goals: helping staff members develop and maintain a collaborative,
professional school culture, fostering teacher development; and helping them solve problems together more effectively.
Literature Review
Overall speaking, transformational leadership has been shown to be most effective for obtaining superior performance, a higher subordinate perception of the leader’s effectiveness, more subordinate satisfaction, and a greater willingness by the subordinate to give extra effort for the leader (Avolio, Bass, & Jung, 1995; Hater & Bass, 1988; Hoernemann, 1998; Howell & Avolio, 1993; Philbin, 1997).
A study conducted by Kirby, Paradise, and King (1992) using the MLQ concluded that employees prefer leaders who engage in transformational leadership behaviors associated with individualized consideration, intellectual stimulation. It also was found that specific leader behaviors, rather than personality, inspirer followers to higher levels of performance.
Masi (2000) discusses that there is significant relationship between transformational leadership and motivation, together with the negative
relationships between transactional leadership and both commitment to quality and organizational productivity.
Carr (1997) examines the leadership styles of principals in four schools that were seeking to expand parental and community participation. Based on the results, it was suggested that administrators who wish to foster empowered involvement in schools should move toward a transformational leadership style with an emphasis on shared power in decision making; and that principals should exhibit the sort of behaviors and values they wish their groups to emulate.
Chirichello (1999) observes transformational leadership in his study and defined it as an influencing relationship between inspired, energetic leaders and followers who have a mutual commitment to a mission that includes a belief in empowering the members of an organization to effect lasting change. Also, transformational leadership can facilitate change for implementing a more collective design for school governance.
Daughtry and Finch (1997) conducted a study in which they addressed leadership effectiveness of vocational administrators as function of leadership style. It revealed that transformational leaders as more effective than those who had other types of leadership styles. Also, significant correlations existed
between transformational leadership factors and perceived effectiveness. Evans (1996) studied the relationship between elementary use of transformational leadership strategies and social organizational factors associated with effective schools. Eighteen elementary principals and their teachers’ perceptions utilized the MLQ and a Social Organizational factors Questionnaire. Evans concluded that achieving school improvements that improve a schools’ effectiveness is related to principal’s leadership style. Principals with high transformational leadership behaviors had higher social organization than those principals with low transformational behaviors.
In an effort identify how to create and sustain teacher efficacy, Hipp (1997) found that transformational leadership greatly impacted teacher efficacy. Hipp found that those principals who believed in teacher capacity, promoted teacher empowerment, recognized the accomplishments of teachers, provided support, managed student behavior, and promoted a sense of community, had a high effort on teacher efficacy.
Principals of effective and exemplary schools were described to be
transformational leaders (Liontos, 1993; Kendrick, 1988; Sagor, 1992; Amory, 1993; Rodgers, 1994; Weltman, 1996). Principal leadership was related to attributes of effective schools, namely, increased student achievement (Liontos, 1993; Kendrick, 1988; Sagor, 1992; Amory, 1993); declining drop out rates (Liontos, 1993); high student and faculty morale (Sagor, 1992); and improved school climate (Kendrick, 1988).
Also, when teachers evaluated the transformational leadership of their principals, results suggested significant relationships between principal
leadership and student academic achievement (Edington and Benedetto, 1988; Silins, 1994; Weltman, 1996).
In sum, there is considerable evidence that transformational leadership is effective. Most studies have demonstrated that transformational leadership is positively related to indicators of leadership effectiveness or educational outcomes including follower satisfaction, motivation and student performance. However, whether the effect sizes vary across related studies and the robust of the overall effect size remain unrequited
Purpose of this study
This article aims to investigate the impact of transformational leadership on school outcomes including teacher job satisfaction, school effectiveness perceived by teacher, and student achievement. The study reported here used a
quantitative meta-analysis to estimate the effect size of transformational leadership on school effectiveness among multinational research reports. The study also attended to which factors (or moderators) might account for the variation in effect sizes.
Selection of Studies
The studies used in this meta-analysis are studies using quantitative designs that focus on the effects of transformational leadership on school outcomes. The criteria for inclusion in this study were as follows:
1. quantitative results of transformational leadership and school outcomes including teacher job satisfaction, school effectiveness, and student achievement
2. use MLQ as an instrument to measure transformational leadership 3. school sites of primary through higher education
4. sample size of at least 40 subjects 5. release date of studies of 1990 or later 6. analyses based on the direct effect models
7. statistical data must include sample size, Pearson r or t value or F value for calculating the effect size.
A meticulous search of databases containing abstracts of empirical studies related transformational leadership and school outcomes was conducted.
Studies were searched and collected from Dissertation and Thesis Abstract System of Taiwan and ProQuest that is a database for information about
doctoral dissertations and master’s theses from over 1,000 graduate schools and universities. In total, 28 studies were selected (see Appendix A). Among them, 24 studies have explicit measure of the association between transformational leadership and teacher job satisfaction; 14 between transformational leadership and school effectiveness perceived by teacher; and 11 between transformational leadership and student achievement
.
Statistical Procedure
Meta-analysis is utilized because that it can, as a secondary analysis, provide additional information by integrating statistically the quantitative results of primary research (Rosenthal, 1984; Niemiec, 1984). The essence of
meta-analysis is the conversion of diverse outcome measures into a common standardized scale that can be combines for analysis.
To permit comparability across studies, results of each study are converted to a standardized effect size. Hedges and Olkin (1985) referred to effect sizes derived from different scales of measurement as a “scale-free index of effect magnitude”. The results can be combined meaningfully in statistical analysis.
To investigate the effect of transformational leadership, Fisher’s Z transformation of the correlation coefficient was used. When the research findings involve bivariate relationships in which both the variables are
continuous, the product-moment correlation coefficient is the straightforwardly appropriate effect size statistic (Lipsey & Wilson, 2001). The Fisher’s Zr
transform can be defined as ) 1 1 log( 5 . 0 r r ES ES − + zr ES
Where r is the correlation coefficient and loge is the natural logarithm. Expressed in the forms we have used for other effect size statistics which can be presented the correlation coefficient as an effect size statistic.
From a statistical perspective, effect size values based on larger samples are more precise estimates of the corresponding population value than those based on smaller samples. Once the Fisher’s Zr was calculated, the next step was to measure the actual weights based on the inverse of the squares standard error value that is called the inverse variance weight.
Also, the homogeneity test was done in this study. If the statistical test rejects the null hypothesis of homogeneity indicates that each effect size does not estimate a common population mean. In other words, there are differences among the effect sizes that have some source other than subject-level sampling errors, perhaps differences associated with different study characteristics, In this study, the type of schools (primary v. secondary) and nations (America v. outside America) were tested followed by the significance of the Q values.
Table 1
Teacher Job Satisfaction Studies Year N Country Type of
School ESr ESzr p
Tucker, M. L. 1990 106 U.S. university .700 .376 .000 Chu, I. Y. 1993 627 Taiwan secondary .600 .301 .000
Pinegar, K. K. 1994 93 U.S. university .280 .124 .231 Philbin, L. P. 1997 218 U.S. elementary .743 .415 .000 Liao, Y. Y.(廖裕月) 1997 117 Taiwan elementary .580 .287 .001 Hoernemann, M. E. 1998 468 U.S. secondary .880 .597 .000 Palczewski, S. 1999 495 U.S. secondary -.060 -.026 .563 Chiou, S. P.(邱勝濱) 1999 915 Taiwan secondary .670 .352 .000 Tsai, C. H.(蔡進雄) 1999 875 Taiwan secondary .616 .312 .000 Wu, M. H.(吳明雄) 2000 666 Taiwan elementary .613 .309 .000 Chang, H. Y.(張宏毅) 2001 761 Taiwan elementary .694 .371 .000 Liang, D. T.(梁丁財) 2001 686 Taiwan elementary .880 .597 .000 Wang, J. S.(王金香) 2002 318 Taiwan special .570 .281 .000 Chen, C. Y.(陳佳渝) 2002 332 Taiwan university .745 .417 .000 Dono-Koulouris, M. J. 2003 42 U.S. elementary .505 .241 .115 Layton, J. K. 2003 478 U.S. secondary .846 .539 .000 Martino, A. M. 2003 381 U.S. elementary .430 .199 .000 Niedermeyer, B. H. 2003 403 U.S. elementary .620 .314 .000 Small, S. K. M. 2003 253 U.S. elementary .820 .502 .000 Stobaugh, R. R. 2003 340 U.S. elementary .950 .795 .000 McAdam, D. J. 2002 146 U.S. elementary .720 .394 .000 Chang, S. K.(張賜光) 2003 688 Taiwan secondary .572 .282 .000 Wang, S. Y.(王秀燕) 2003 525 Taiwan elementary .666 .348 .000 Fisher, M. W. 2003 640 U.S. elementary .876 .589 .000
合計 10,573
Special:School of Special Education
Table 2
Effectiveness Studies Year N Country Type of
School ESr ESzr p
Tucker, M. L. 1990 106 U.S. university .840 .530 .000 Philbin, L. P. 1997 218 U.S. elementary .764 .436 .000 Hoernemann, M. E. 1998 468 U.S. secondary .857 .556 .000 Tsai, C. H.(蔡進雄) 1999 875 Taiwan secondary .677 .357 .000 Wu, M. H.(吳明雄) 2000 666 Taiwan elementary .627 .319 .000 Lin, H. C.(林蕙質) 2001 219 Taiwan secondary .622 .316 .000 Chang, H. Y.(張宏毅) 2001 761 Taiwan elementary .797 .473 .000 Wang, J. S.(王金香) 2002 318 Taiwan special .318 .344 .000 Lin, H. J.(林漢政) 2002 521 Taiwan elementary .350 .158 .000
Niedermeyer, B. H. 2003 403 U.S. elementary .670 .352 .000 Small, S. K. M. 2003 253 U.S. elementary .710 .385 .000 Stobaugh, R. R. 2003 340 U.S. elementary .940 .754 .000 McAdam, D. J. 2002 146 U.S. elementary .710 .385 .000 Wang, S. Y.(王秀燕) 2003 525 Taiwan elementary .733 .406 .000
合計 5,819
Special:School of Special Education
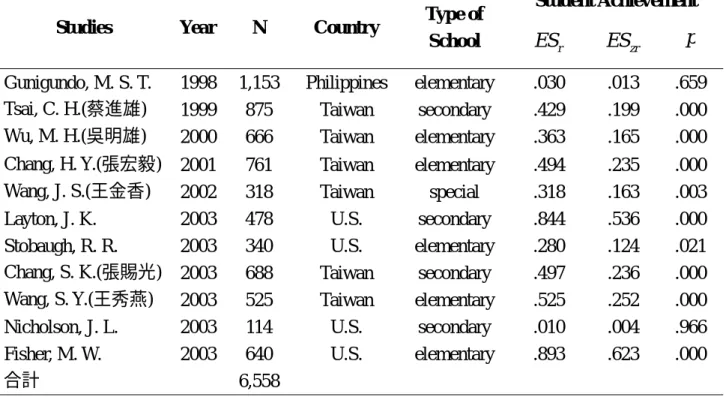
Table 3
Student Achievement Studies Year N Country Type of
School ESr ESzr p
Gunigundo, M. S. T. 1998 1,153 Philippines elementary .030 .013 .659 Tsai, C. H.(蔡進雄) 1999 875 Taiwan secondary .429 .199 .000 Wu, M. H.(吳明雄) 2000 666 Taiwan elementary .363 .165 .000 Chang, H. Y.(張宏毅) 2001 761 Taiwan elementary .494 .235 .000 Wang, J. S.(王金香) 2002 318 Taiwan special .318 .163 .003 Layton, J. K. 2003 478 U.S. secondary .844 .536 .000 Stobaugh, R. R. 2003 340 U.S. elementary .280 .124 .021 Chang, S. K.(張賜光) 2003 688 Taiwan secondary .497 .236 .000 Wang, S. Y.(王秀燕) 2003 525 Taiwan elementary .525 .252 .000 Nicholson, J. L. 2003 114 U.S. secondary .010 .004 .966 Fisher, M. W. 2003 640 U.S. elementary .893 .623 .000
合計 6,558
Special:School of Special Education
Results of the Meta-analysis
Table 1 to table 3 shows the estimated effect size in terms of the Fisher’s Zr. The results indicate that transformational leadership does have a positive and significant effect on teacher job satisfaction (.395), school effectiveness perceived by teacher (.409), and student achievement (.244). In Cohen’s terminology, the values of the three mean effect size demonstrate medium effects. It also indicates that 15.6%, 16.7%, and 6% of variance in teacher job satisfaction, school effectiveness perceived by teacher, and student
achievement are associated with differences in transformational leadership. The following questions concerning whether effect sizes vary across studies were analyzed next. The rejections of the null hypothesis of the
homogeneity indicate that there are differences associated with different study characteristics. In other words, there should have moderators that have
profound influences on the estimated effect sizes. The results of analyses dealing with bivariate relationships between moderators and effect sizes are presented in Table 4 and Table 5.
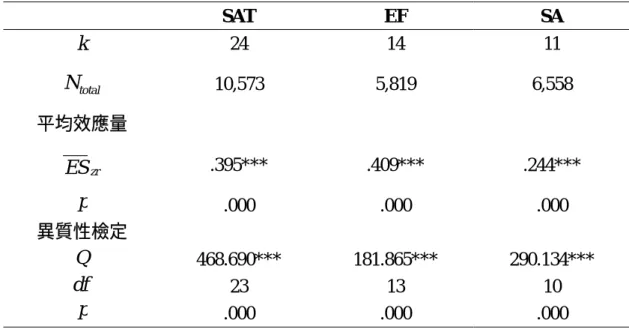
Table 4 學校效能後設分析摘要表 SAT EF SA k 24 14 11 total N 10,573 5,819 6,558 平均效應量 zr ES .395*** .409*** .244*** p .000 .000 .000 異質性檢定 Q 468.690*** 181.865*** 290.134*** df 23 13 10 p .000 .000 .000 * p<.05 ** p<.01 ***p<.001 表 5 中介變項檢定 SAT EF SA B Q (type of school) 81.060*** 5.356* 4.830* df 1 1 1 p .000 .020 .028 ElementaryESzr(k) .467(13)*** .426(9)*** .229(6)*** SecondaryESzr(k) .311(7)*** .363(3)*** .283(4)*** B Q (country) 28.352*** 51.752*** 10.922** df 1 1 1 p .000 .000 .001 TaiwanESzr(k) .360(11)*** .353(7)*** .211(6)***
Non-TaiwanESzr(k) .450(13)*** .515(7)*** .289(5)***
*p<.05 ** p<.01 *** p<.001
The results show that both types of school and nation, served as
moderators in this study have significant relationship with the effect sizes. The results are not altogether consistent in direction. For example, the effect sizes in elementary schools are significantly higher than effects sizes in secondary schools from studies related to transformational leadership and teacher job satisfaction, and studies related to transformational leadership and school effectiveness perceived by teachers. However, studies of transformational leadership and student achievement show that the effect sizes in secondary schools are significant higher than those in elementary schools. In addition, all the studies conducted in Taiwan have less effect sizes than those in United States.
Conclusion
Generally speaking, researches regarding school leadership and school outcomes have shown contradictory results (Witziers, Bosker, & Kruger, 2003). While some researchers found that school leadership have significant
influences on school outcomes, others indicate no effects of leadership on school outcomes. However, the statistical results of meta-analysis in this study suggest that the direct effects of transformational leadership on school
outcomes that including teacher job satisfaction, school effectiveness, and student achievement are medium. Additionally, analyses in which differences between countries are modeled give consistent indications that transformational leadership matters less in Taiwan than in United States. The main findings of this study are summarized in Table 6.
Table 6
SAT EF SA
zr
ES .395(medium effect) .409(medium effect) .244(medium) Moderator
Type of school primary>secondary primary> secondary secondary> primary Country U.S > Taiwan U.S > Taiwan U.S > Taiwan
Appendix A
Selected researches in this study (sorted by publishing year)
Tucker, M. L. (1990). Higher education leadership: Transformational
leadership as a predictor of satisfaction, effectiveness, and extra effort.
Dissertation of the University of New Orleans, unpublished.
Chu, I. Y. (1993). The relationship of teachers’ job satisfaction and their
perceptions of principals’ leadership styles in private vocational high schools in a selected metropolitan area of Taiwan. Thesis of University of
Northern Iowa, unpublished.
Pinegar, K. K. (1994). An investigation of the effect of transformational
leadership and substitutes for leadership upon the job satisfaction of academic professionals in higher education. Dissertation of University of
Alabama, unpublished.
Philbin, L. P. (1997). Transformational leadership and the secondary school
principal. Dissertation of Purdue University, unpublished.
Liao Y. Y. (廖裕月)(1997). The study of principals' transformational leadership
styles and leadership effectiveness in the elementary schools: take four countries of North Taiwan as examples.Thesis of National Taipei Teacher College, unpublished.
Hoernemann, M. E. (1998). Transformational leadership and the elementary
school principal. Dissertation of Purdue University, unpublished.
Palczewski, S. (1999). A study of the relationship between transformational
leadership and teacher attitudes. Thesis of Western Michigan University,
unpublished.
Chiou S. P.(邱勝濱) (2000). Relationships among leadership behaviors,
leadership attributes and leadership effectiveness of principals at private vocational high school. Thesis of National Changhua University of
Education, unpublished.
Tsai C. H. (蔡進雄)(1999). The study of the relationship among
transformational and transactional leadership, school culture and school effectiveness in junior high schools in Taiwan. Doctorial Dissertation of
National Taiwan Normal University, unpublished.
Wu M. H.(吳明雄) (2000). A Study of Elementary School Principals’
Transformational Leadership and School Effectiveness. Thesis of National
Chang H. Y.(張宏毅) (2001). The Relationship between the Principal's
Transformational Leadership and the School Effectiveness for the Elementary School of Taipei County and Taipei City. Thesis of National
Taipei Teacher College, unpublished.
Liang D. T. (梁丁財)(2001). A Study of Elementary School Principals’
Transformational Leadership and Teachers’ Satisfaction. Thesis of
National Taichung Teacher College, unpublished.
Wang, J. S.(王金香) (2003). A Study of the Relationship Between Principal's
Transformational Leadership and School's Effectiveness In Special Educational Schools. Thesis of National ChiangHwa University,
Unpublished.
Chen, C. Y. (陳佳渝)(2003). The Study of Relationship among President`s
Transformational Leadership and Effectiveness of Leadership at Universities in Taiwan. Thesis of NationalChiao Tung University,
Unpublished.
Dono-Koulouris, M. J. (2003). Leadership style, teacher empowerment, and
job satisfaction in selected catholic elementary schools. Thesis of St. Johns
University, School of Education and Human Services, unpublished. Layton, J. K. (2003). Transformational leadership and the middle school
principals. Dissertation of Purdue University, unpublished
Martino, A. M. (2003). Leadership style, teacher empowerment, and job
satisfaction in public elementary schools. Thesis of St. John’s University,
School of Education and Human Services, unpublished.
Niedermeyer, B. H. (2003). The relationship of principal leadership style and
student achievement in low socio-economic schools. Dissertation of
Purdue University, unpublished.
Small, S. K. M. (2003). The relationships of transformational/transactional
leadership behavior of elementary school principals with teacher
outcomes: Extra effort, effectiveness and satisfaction. Dissertation of Our
Lady of The Lake University, unpublished.
Stobaugh, R. R. (2003). School reform, transformational leadership, and
student achievement. Dissertation of University of LouisVille,
unpublished.
McAdam, D. J. (2002). Elementary principals’ facilitative leadership. Dissertation of University of Arizona, unpublished.
Chang, S. K.(張賜光)(2004). A Study on Relationships between Principals’
Transformational Leadership and School Effectiveness of Junior High Schools in Taoyuan County. Thesis of National Taiwan Normal University,
Unpublished.
Wang, S. Y.(王秀燕)(2004). The Study on the Relationship between Femal
Principal's Transformational Leadership and School Effectiveness in Taipei City and County Elementary Schools. Thesis ofTaipei Municipal
Teachers College, Unpublished.
Fisher, M. W. (2003). Effects of principal leadership style on school climate
and student achievement in select Idaho schools. Dissertation of