а٢܊ឪቹྣ࣬ኳԄୖԵࡰຑ٢܊ឪቹᒟᏊໆϐӼӄ܄
RADIATION DOSE SAFETY IN MAMMOGRAPHY BY
EVALUATION OF EXPOSURE PARAMETER SETTINGS
ླྀᝩ1 ৪ࡌ1 ߋݥЎ1 ഋҥሎ1 ᄃДऍ2 Ꮉ܍ക2 Chi-Sheng Yang1 Chien-Yeh Hsu1 Hung-Wen Chiu1
Li-Ming Chen1 Yue-Mei Liao2 Cheng-Zhang Lu2
1ѠчᙴᏢεᏢᙴᏢၗૻ܌ 2Ѡчѱҥޱᙴଣܫࣽ
1Graduate Institute of Medical Informatics, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan 2
Radiology Department, Taipei Municipal WanFang Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
ǵύЎᄔा
ऍ୯ܭ 1992 ԃुۓ٢܊ឪቹࠔᆅྗݤਢ (MQSA: Mammography Quality Standard Act)Ǵ၀ ݤਢύೕۓ٢܊ឪቹТϐѳ֡٢ဏᏊໆ ϐനεॶаόຬၸ 300 డႜቺࣁྗ[7]Ƕ٢܊ឪ ቹࠔ፦ᆅڋᅌࣁܫບᘐሦୱ܌ख़ຎЪόё ۹ౣޑҞϐǶ ҁࣴزܭѠчࢌѱҥᙴଣᖏෳ၂ΠǴ 320 Տڙ၂ޣՏՉ 4 ಔ٢܊ឪቹྣ࣬Ǵѳ֡ڙෳ ԃសࣁ 51.3 ྃǶ่݀ᡉҢ҅Տӛᆶ௹Տӛϐ٢܊ ᓸॐࠆࡋڀԖᡉৡ౦(p<0.001)Ƕܫৣ܌ᒧۓ ϐྣ࣬ kV ᆶڙᔠޣϐ٢܊ࠆࡋܭྗѤಔ X Ӏ ྣفࡋڀԖଯࡋϐ҅࣬ᜢ܄(p<0.001*Ƕ! ܭ٢܊ឪቹྣ࣬ኳԄୖԵࡰΠௗڙी ޑ 1280 ಔ٢܊ឪቹТύǴ 87%٢܊ឪቹТ٬Ҕ Mode 1ᆶ Mode 2 ྣ࣬ኳԄୖԵࡰǴځ܌ௗڙ ϐ ᒟ Ꮚ ໆ ᇻ ե ܭ 300 డ ႜ ቺ ( Mode 1: Mean=118.4²71/3 డႜቺ with 571 D.F., p<0.001; Mode 2: Mean=200.8²96/5 డႜቺ with 537 D.F., p<0.001*!Ƕڙ၂ޣܭ Mode 3 ΠऊԖ 5%ଯܭന εᒟ֎ԏᏊໆ 300 డႜቺ(Mean=314.4²251/7 డႜቺ with 147 D.F., p=0.292) Ƕ ྣ࣬ኳԄୖԵࡰΠ Mode 1 ϐ٢܊ᓸॐࠆ ࡋۓࣁ 0 Կ 30 డԯǹMode 2 ϐ٢܊ᓸॐࠆࡋ ۓࣁ 31 Կ 45 డԯǹMode 3 ϐ٢܊ᓸॐࠆࡋ ۓࣁ 46 Կ 60 డԯǶ่݀ᡉҢڙᔠޣܭྣ࣬ኳԄ ୖ Ե ࡰ Π ܌ ௗ ԏ ϐ ᒟ ֎ ԏ Ꮚ ໆ ಄ ӝ ݤ ਢ MQSAύ܌ुۓϐྗǶ аҁԛी่݀ᡉҢѳ֡٢܊ᓸॐࠆࡋࣁ 32.3డԯ(p<0.001)Ǵךॺࡌଞჹ٢܊ᓸॐࠆࡋ եܭ 45 డԯаΠޣǴځ܌ௗڙϐѳ֡٢ဏᏊໆ аόଯܭ 200 డႜቺࣁୖԵࡰǶനࡕຑڙ၂ ޣϐԃសܭௗڙ٢܊ឪቹ܌ௗڙϐᒟ֎ԏᏊ ໆҭคᡉৡ౦(p<0.001)Ƕ Abstract
Mammography Quality Standard Act (MQSA) was enacted in United States since 1992, and Mammography Quality Standard Reauthorized Act
(MQSRA) also has been enacted in 1998. The maximum limitation of Average Glandular Dose (AGD) is 300mrad (3mGy) per film [7].
320 subjects are participant in our study, every subject takes 4 exposure views(mammograms). Average estimated age is 51.3 years old. There is a significant difference between CC and MLO breast thickness (p<0.001). Technologists selected proper exposure parameter settings.
The results show 87% mammograms have significantly lower absorbed radiation dose compared with 300mrad when breast compressed thickness below 45mm( Mode 1: Mean=118.5 ² 71/3mrad with 571 D.F., p<0.001; Mode 2: Mean=200.8²96/5mrad with 537 D.F., p<0.001*. About 5% estimated mammograms result in higher absorbed radiation dose (>300mrad) when breast thickness between 46mm to 60mm (Mode 3: Mean=314.4²251/7nsbe with 147 D.F., p=0.292). We recommend AGD reference shouldn’t exceed 200mrad when Breast compressed thickness smaller than 45mm, On the other hand, we estimated relationship between patient age and absorbed radiation dose. There is no significant between age and absorbed radiation dose (p<0.001).
Keywords: Average glandular dose, AGD, HVL, Breast compressed thickness, Exposure Parameter Setting
ΒǵBackground
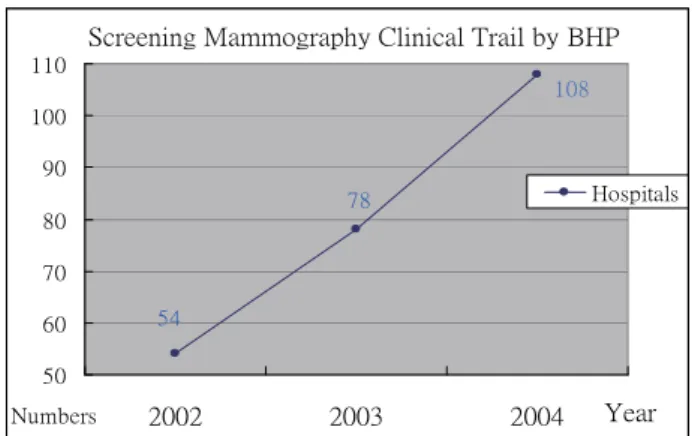
Since 2002, Bureau of Health Promotion (BHP), Department of Health starts breast screening clinical trail in Taiwan [1]. There were 54 hospitals joined this project in 2002, 78 hospitals joined in 2003, and it will be 108 hospitals joined this clinical trail in 2004(see Figure1).
Department of Health, Executive Yuan, Taiwan also announced that government insurance starts screening mammogram on July, 2004. Woman who more than 50 years old can get mammogram cost-free every one to two years.
ŔŤųŦŦůŪůŨġŎŢŮŮŰŨųŢűũźġńŭŪůŪŤŢŭġŕųŢŪŭġţźġŃʼnő Ķĵ IJıĹ ĸĹ Ķı ķı ĸı Ĺı ĺı IJıı IJIJı ijııij ijııĴ ijııĵ ŚŦŢų ŏŶŮţŦųŴ ʼnŰŴűŪŵŢŭŴ
Figure 1 Screening Mammography Clinical Trail joined hospital numbers in Taiwan
The average glandular dose is one of the estimated procedures of clinical trails. Nevertheless, the techniques of positioning and exposure parameter settings are very important in mammogram. Wrong positioning of breast and poor image quality of mammogram are the major features of retake mammogram behaviors. And these behaviors are the major point of increasing unnecessary patient radiation dose.
In United States, radiologists and technicians need to get lots of training courses and certifications. And also mammographic units must be under certain quality control procedures [6]. All these above are based on government act named Mammography Quality Standard Act (MQSA) since 1992 [7]. The final corrected rules named Mammography Quality Standard Reauthorized Act (MQSRA) have been published in 1998[7]. All facilities have been followed final corrected rules since 28, Oct. 2002.
In Taiwan, The Radiology Society Republic of China (RSROC) and Association of Radiology Technologist of ROC (ARTROC) also start mammography course training for radiologists and technologists. Of course Both RSROC and ARTROC follow accredited rules.
The way of select X-ray parameter settings including target, filter, kV, and Automatic Exposure Control (AEC) is done by specialist heuristic and experience. The glandular tissue is the most sensitive tissue in related to x-ray penetration and also the major tissue of considering breast cancer
[2].
Measuring methods such as radiation beam quality(i.e. Half Value Layer (HVL) value), entrance radiation dose, and calculating the AGD are followed American College Radiology(ACR) standard and the FDA published law [5][8].
This evaluation records the X-ray tube target material, filter setting, kV, mAs, compression thickness, and volunteer’s age to estimate the radiation dose. Not only the unique of breast tissue
but also the whole procedure is highly sensitive if one of them is not within quality criterion.
ΟǵMaterial and Method
We Selected Siemens Mammomat 3000 Mammographic unit and ACR approved Phantom (type RMI-156) to estimate AGD references [6]. The standard phantom is composed with 50% adipose and 50% glandular tissue.
Estimating X-ray Beam Quality (HVL)
There are three x-ray exposure parameter setting modes in the followings: Mode 1: Choose Molybdenum/Molybdenum (Mo/Mo) X-ray tube Target/Filter material, select 25kVp and Automatic Exposure Control (AEC) mode [3]. Mode 2: Choose Mo/Mo combination, select 26kVp and
AEC mode. Mode 3: Choose
Molybdenum/Rhodium (Mo/Rh) X-ray tube combination, select 27kVp and AEC mode.
We used 99.9% pure aluminum filters, ionization chamber and electrometer to measure the x-ray beam quality base on ACR procedure [6]. All 3 mode HVL values are measured.
Establishing AGD Reference
We used RMI-156 phantom to estimate entrance radiation dose. Then we calculated AGD via entrance dose and HVL value. Three AGD reference modes are established through this procedure.
The AGD equation shows as following:
AGD=DgN * XESE
Where DgN is Glandular dose (in mrad) for 1 Roentgen(R) entrance exposure conversion factor, XESE is entrance dose on the surface of phantom
[8].
Mammogram Exposure Data Evaluation
Total 1280 mammograms were examined in our study, we recorded patient ID, age, and compressed breast thickness. And we collected every X-ray exposed parameters including kV, mAs, target, and filter.
Because of the mAs value is proportional to radiation dose[4], we can use mAs value to simulate the patient radiation dose.
major statistical terms in the study. ѤǵResult
AGD Reference in 3 modes
The technologists established 3 modes HVL values (see Table 1) .Too low HVL value shows the worse efficiency of photon energy which is produced. On the other hand, too high HVL value shows the hard (Strong) photons; it reduced the latitude (dynamic) of breast tissue and got the poor image quality result.
Table 1 HVL Value in mm Aluminum
Nominal kVp setting 25 26 27 Target material Mo Mo Mo Filter Mo Mo Rh mAs 56 50 56 Calculated HVL (mm Al) 0.334 0.350 0.438 Minimum allowed HVL 0.28 0.29 0.3 Maximum allowed HVL 0.37 0.38 0.46
The maximum limitation of AGD is 300 mrad, we obtained 198.2 mrad, 185.9 mrad, and 124.7 mrad individually (see Table 2). That means the mammographic unit is fulfilled the AGD criteria.
Table 2 Calculated AGD Value in 3 Different Modes
Mode 1 2 3
Nominal kVp setting 25 26 27
Target /Filter Mo/Mo Mo/Mo Mo/Rh
mAs 141.3 112 65.1
Entrance Dose(mGy) 10.13 9.23 5.2 Calculated
AGD(mrad) 198.2 185.9 124.7
Breast Compressed Thickness Analysis
The breast compressed thickness is the most important feature in exposure parameter settings. The average compressed breast thickness (n=1280) in four views are showing in the following (see
Table 3): RCC=33.8mm, RMLO=31.0mm,
LCC=33.5mm, LMOL=31.0mm.
The breast compressed thickness on left side CC view and left side MLO view are significant different (t =8.658 with 319 D.F., p<0.001).
Table 3 Breast Compressed Thicknesses in 4 Views
Field Mean S.D. Min Max
RCC 33.8 12.04 3 80
RMLO 31.0 11.43 3 66
LCC 33.5 11.77 3 73
LMLO 31.0 10.84 5 64
The breast compressed thickness on right side CC view and right side MLO view are also significant different (t = 8.158 with 319 D.F., p<0.001). We conclude that breast compressed thickness on CC view and MLO view are significantly different.
kVp setting estimation
To evaluated the relationship between kVp and breast compressed thickness, we obtained significant positive correlation coefficient(p<0.001) (see Table 4), so we can state that all four views of kVp are proper settings by technologists.
Table 4 Correlation Regression Results in kVp and Compressed Breast Thickness.
Project View R- Square T-Value RCC 0.8242 38.61 (p<0 .001) LCC 0.8152 37.45 (p <0 .001) RMLO 0.7301 29.33 (p <0 .001) LMLO 0.7692 32.56 (p<0.001)
Radiation Dose Safety evaluation
On mode 1 and mode 2, we got lower X-ray absorbed radiation dose through subjects estimations The results show 87% cases have significantly lower X-ray absorbed radiation dose when breast compressed thickness below 45mm( Mode 1(0 to 30mm): t= -72.99 with 571 D.F., p<0.001; Mode 2(31 to 45mm): t= -26.94 with 537 D.F., p<0.001* . On mode 3, About 5% estimated mammograms result in highly X-ray absorbed radiation dose when breast compressed thickness between 46mm to 60mm (Mode 3: t= 1.06 with 147 D.F., p=0.292).
ϖǵConclusion
One of Our hypothesis is that younger women who will get the higher radiation dose. On the regression of age and mAs values, we got partial
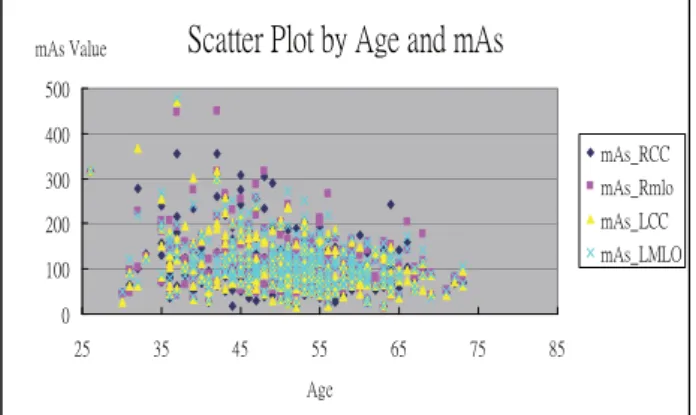
positive relationship (r-square between 0.0606~0.0899, p<0.001) on 4 views, the result shows no significant between age and radiation dose. It means younger woman who takes mammogram wouldn’t cause higher radiation dose. But in the scatter plot, it shows a positively skewed distribution trend that the less of the age the higher of the mAs value. (see Figure 2).
ŔŤŢŵŵŦųġőŭŰŵġţźġłŨŦġŢůťġŮłŴ
ı IJıı ijıı Ĵıı ĵıı Ķıı ijĶ ĴĶ ĵĶ ĶĶ ķĶ ĸĶ ĹĶ łŨŦ ŮłŴġŗŢŭŶŦ ŮłŴŠœńń ŮłŴŠœŮŭŰ ŮłŴŠōńń ŮłŴŠōŎōŐFigure 2 Scatter Plot by Age and mAs Value
Due to “As Low As Reasonably Achievable” (ALARA) X-ray radiation protection philosophy, we recommend to establish a lower AGD maximum limitation for patient with thinner breast. When Breast compressed thickness smaller than 45mm, the AGD reference shouldn’t exceed 200mrad for the purpose of patient safety.
ϤǵReference
[1] Οᆜ,ۚ၈,܃⪭,ླྀᝩ (2004) ٢܊
X Ӏឪቹࠔ፦ᇡڋࡋϐᖏ၂ᒤीฝ;Չࡹଣ
ፁғ.
[2] Aichinger H., Dierker J., Saabel M., et al. (1994)
Image Quality and dose in Mammography.
Electromedica 62 no.2:7-11.
[3] Anne C., Per H. R., et al (1997) Influence of
Anode-Filter Combinations in Image Quality and Radiation Dose. Radiology vol. 203, No.2.
[4] Bushong Stewart C.(1997) Radiology Science
for Technologists. P131-137.
[5] Dance DR (1990) Monte Carlo calculation of
conversion factors for the estimation of mean glandular breast dose. Phy.Med.Biol.
35:1211-1219.
[6] Hendrick R. Edward, Bassett Lawrence, Botsco Margaret A., et al (1999) Mammography Quality
Control Manual. American College of Radiology.
[7] Mammography Quality Standard Act (MQSA) (1992). FDA; (Public Law 102-539),
Mammography Quality Standard Reauthorization Act of 1998 (MQSRA) (Public Law 105-248). [8] Wu X , Gingold E , Barnes G et al (1994)
Normalized Average Glandular Dose in
Molybdenum Target – Rhodium Filter and Rhodium Target – Rhodium Filter Mammography. Radiology