Emergency
Care
Management
with Location-Aware
Services
Shih-wei Lee* ,
Shao-you
Cheng*,
Jane
Yung-jen Hsu*,
Polly Huangt, Chuang-wen
You** Department ofComputer Science andInformation Engineering
National Taiwan
University,
Taiwan{r94094, r93070, yjhsu, f91023}@csie.ntu.edu.tw t Department of ElectricalEngineering, National Taiwan
University,
Taiwanphuang@cc.ee.ntu.edu.tw
Abstract- As indoor localization technologies become need is themost critical.
Therefore,
wetry toimplement
more affordable and sophisticated. An emerging market and experiment a set of location-aware services to as-has yet to be realized commercially in the indoor envi- sist in the management of emergency department (ED). ronment. We think that the first adopter will arise from This paper introduces an integrated project that brings
the healthcare domainwhere the need is the mostcritical. m
Thus,Weaimtoimplementasetof location-awareservices
. I.
otoassist in the management of the emergencydepartment. atNTU
Hospital,
theengineers
ofIBMTaiwan,
and theWe apply NTU Taroko, an active RFID module for to researchers in NTU iSpace Lab. The three parties support
real time location tracking on patients, hospital assets, respectively the application, service, and infrastructure
and medical staffs. In addition,weintegratecontext-aware aspects of the ERmanagement system.
system proactively to infer event notifications for remind- The statistical data shows that NTU Hospital treats ing physicians and nurses. With the proposed system, we about 250 emergency patients a day. This amount is can shorten the process of emergencyvisit effectively and much more than many other countries. However, only improve the quality ofemergency care. one-fourth require admission or stay for observation.
With
triage,
the criticalpatients
would be servedfirstly,
I.
INTRODUCTION but most of the non-emergent patients feel dissatisfied Outdoor localization systems such asGlobal Position- after a long-term wait. Halfof them want to be treated ing System (GPS) have enabled a number of commer- in ten minutes, only11%
could accept 30 minutescial location-aware services, for
example,
the vehicular wait [4]. Because of patients are many andtheir expectednavigation systems that are routinely used by many waiting time is short, how to speed up the process of
drivers today. An
emerging
market that has yet to be emergency visit becomes primary subject to improverealized commercially is at the location-aware services the patients' satisfaction. We learn from doctor's de-for indoor environment. As indoor localization technolo- scription that nursing staff often spend much time in
gies becomemoreaffordable and sophisticated, location- findingpatients, hospital assets (e.g. sickbeds,pumps, or awareservices for indoor environments areofgreatcom- wheelchairs). If we can track their position in the ED,
mercialization potential. To some
degree,
commercial then we can spend less time to find particular patients applications such asbuilding security
and assettracking
and have better utilization of medical resources. This fall also into the location-aware service category. also means we shorten theprocessofemergencyvisit. InWhile many of the indoor location-aware
applications addition, patient
and stafftracking
enable the chances of have beenprototyped andprovenuseful. There aremanyproviding
various of location-aware servicestoimprove
indoor positioning solutions available on the
market,
the qualities ofemergency care. This is the main idea such like Ekahau [1], Sonitor [2], or Versus [3], etc. for us to construct a location-aware ED managementThese companies apply WiFi,
ultrasound/RFID,
or in- system.frared/RFID technologies in real time
locating
systems 1. SCENARIOand have
successfully
deployed
these systems in theTriag Patientsareservedaccordingtoseverity
-~~~~~~~~~~~andacuity,notbyorder. EA R TSa
...L evel...C ondition... elC ndon..Waiting.. ...T.
...Peio d.... try... ...Several-ill....or..injured...whoPehas ...Level..2.stable...vital..signs..but..need..10..mins Physiian.ork.p.urgnt.mdica.caror...injured....patients....who...need.~~ ~ Il Level 4
clinic-Treatment~~~~~~~~~~ptin
Thepat entwith inunresledo wohsymtm a
Discharge to stay in the observation unit...
Fig... 1..The..process..of.emergency...visit.at..NTU.Hospital..Fig...2..Deployment
Lvof
thealocationsgsystem
indthemED
"Bob...was.involved...in..a.car..accident...and..hurt..his..legs...of.location...system...in.the..ED..at NTU..Hospital....In..our
He..was..sent..to..N...Hospital...by..the..ambulance....Upon..current...prototype,...the..location...system..supports...location. urgetptiet ad tgge wih a aciveRFI bage.
Thetrakedasstsgnclde
ickedsandwhelchirsthe on-calldoctor
who~~~~~~~
wase
takloringjcredo tepatientslocalization.n
The Mphysicm
ian and nussalowaratv in the observation unit, and~~~Sinfoereamedt
hrtataut
patient RDAbadge for thkeirP siftor vii.Eahptendoljustregistered and
need~~~~~~~~edvae.
Wihot>n
delaJane
be.. assigned.... anatv..D ag fe amfighexamines....
Bob,..and..orders...for..an..X-Ray..to..be..taken....badge..has..ID..number...that..is..associated....to.the..patient.ni
In..the.. meantime,...Polly..retrieves...the..nearest..wheelchair...The..emergency...physicians...and..nurses..can..also..use..their
available...with..the..help..of.the..location...system...After..the..badges..as..identification...to..log.into..the..emergency...care while...waitingHHHHHfor.th.X-Ra.outcme..Twnty.mnutes succesful.lgin.he.meical.taffs.an.acess.lcatio
late,te mnagmentsysem.ot..e.Janeas.oonas.nfomatin.acoringto.heirrols.o.shfts
Bob...s.XRay.ecoes.aailble.Jan.dianoss.tht.Te.R.D.bdgesbascall.ar.R..eceverstha
Bob...HM4
hasaisurefrctrebasd.n.heX-Ry.eslt.peioicllylite.fr.te.igal.frm.heRI.trnseierBob... is.mmditey. octe.ad.rete.wthstbiizng cale.bacn.Afercoletig.hesinas,th.bdg
casts... on ...his...legs...Aftr.pyin.th.meica.exenss.ad.sndsthedat.tan te...eevr,cle.rly h thehospital."
infrastructuresileexaintio toluesdra
the...F 3loctin ngnewhc detemie(taggingand untagging
~~~~~~~The
patient)
oftunrsingltedsysptems
iasho.t.omut bag'spsiin.sgie.i.ecin.
minimalcomparedwi~~~~~~th
stheitotlhmonfsrato time. for the B.onurse to look froresvrous
thirgngyvsitandfo
NThedocptorlt
ContexisDpoyeto
inomtonctatinste
the canthel
copue disove test results. Theeffiacideny
ofd
emergencycaegs
flctosystemsocarceize
theuEr'
sitNUation,suchtas. theou
andiflow can
bhe
grepiatly
impovedwbyelasimindatls rcing
suhnsr'
hysiclpoital,
andts memoional inaformad
ation.the
unnecessanryedselay
wtthhe
location-awarieservicaesJn,
mhyain cotexasg
fegrfred
tihatveRI odteusers
loc-ation
the n-cll octo wh wa
taing
areof therpatent
lactiviyaietity,
andtie
[5].can
ansyrstems lontextawartie
inIhIbsraio.nt,adi
EMERENCCAErMNAGMEN SYTEifipueaonettopoidieevnenfraiotn
Toenablethe improed
scenaifo,h
rooe RsericeD tthdeso
useir.shnfour
EDsimanageen
systiem,weulmanaghemeantisysem
canl betviewedh cnaeptuahellyhasia
dheveo
eeaemergencychscasarenuservcsbanasedone
thei
interatin otwosystms,the ocaion yste an the conext espiectiailcation olointext toe improvencpatien
We acquire location context by
utilizing
the location system, however, we are not limited to usesingle
typeof context. We have considered other useful contexts, X _g
e.g.
time,
patient's
treatment status, staff'sactivities,
test
progress,
etc. In Section Il-A, we introduce threecommon
problems
in the ED andrespectively
develop
their context-aware solutions.
.1...
A. Emergency Care Services
Fig. 3. Main components of theproposed emergencycare manage-First, "'uninformed discharges"' usually troubles the ment system
medical staffs, i.e. apatient who leaves ED
prematurely
without
completing
theregular
ERprocedures.
Themain reason is due to
long-term
wait [6]. To manage treatment instructions, software events fromHIS1
andsuch accidental
situations,
wedevelop
a location-awarePACS2,
and temporal information.notification service to support detection of uninformed
discharges. Our system
continuously
monitorpatients'
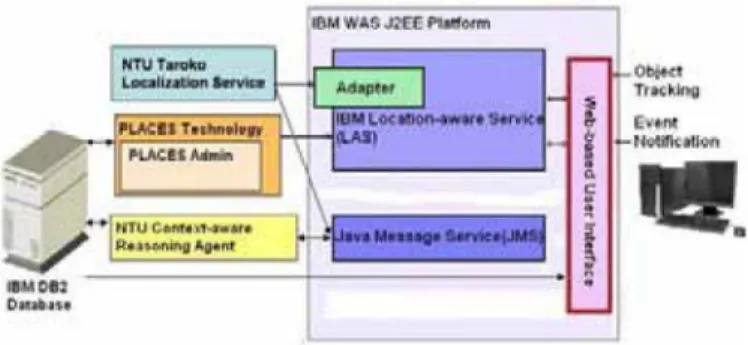
IV. SYSTEM COMPONENTSlocation and their treatment status, once such situation The
proposed
emergency caremanagement system
occurs, the notification will
immediately
inform the iscomposed by
fivecomponents,
including
hardwaremedical staffs. and software. As
Fig.
3shows,
these components are:Second, the emergency
patients
expect to be treated(1)
active RFID module, (2) NTU Taroko Localizationas soon as
possible,
but most of them are not emergent Service, (3)IBM
Enterprise Location Aware Service cases. To control theirstaying
timeclearly,
the system Technology, (4) Context-aware Reasoning Agent, andcontinuously monitors
patients'
room-level location in (5) Web-based User Interface. We further describe eachthe ED and also their treatment status to estimate their component's technical details as follows.
waiting time. Ifthere are any
patient
who haslong-term
staying without
taking
anymedicalservice,
their location A. Active RFID Modulewill be
displayed
on the map to remind the emergency Thepassive
RFIDtechnology
allows identificationnurses. Moreover, as the
study
suggests[7],
the more ofobjects
and persons in shortsensing
range. Limited responses andconcernsthe medical staffsgive,
the moreby
the radio range, thepassive
RFIDtechnology
cansatisfaction the
patients
feel. Based on thisidea,
we de- notsupport
indoor localization in our emergency carevelop atime-based notification that
proactively
informsapplications.
Therefore,
wechoose active RFIDtoenablethe medical staffs when there are
patients'
waiting
timeexceeding30minutes.
~~~~both
identification andlocalization
forthelocation-aware
exceeding 30 minutes. services.
Third,
additional clinical examination isquite
often Taroko is a ultra low power, low cost, wireless em-in the emergencyvisit,
however,
such test often results bedded device. The module consists of aTI
MSP430
in some delays. Forexample,
apatient
who needs tomicrocontroller,
an IEEE802.15.4/Zigbee
radio,
andtake X-Ray, but can not find where to take it.
Maybe
1024kB size external flash memory. TheMSP430
micro-the
patient
completes
theexamination,
but he does not controller operates at 8MHz and hasl0kB
RAM. Theknow where to go next, etc. There are many
possible
Chipcon CC2420 Radio Transceiveroperated at 2.4GHzsituations, however,
waiting
for final results is a com- with250kbps
data rate and iscompliant
with IEEE mon delay. Therefore, wedevelop
an event notification802.15.4/Zigbee.
The flash memory allowsdevelopers
service that
proactively
informs thephysician
or nurses to store data such as the identification or radiosignal
when
particular
patient's
X-Ray result is available. Thestrength
for locationcomputation.
Data collection andnotification has two ways, one is
flashing
badge's
LED communication to PC are via standard USB interface.light, and the other is
sending
text messagesto the web- Taroko also supportsintegrating
with additional sensors basednotification
board.RSSIinfoKNesCtoain_o_i g
RSSIFirgerprint Refposition Fingedpmintgcon
RSSIFingerprnot2 Refposition2Dtbs
R.SSIFiogerpoiot3 Refpositioni3
V ~~~~~Locations
Positio ring__ Paee ittem Dataobase signal ---o Recoganitino
feceivedbv Alg6e savetimaotmpiede
fRemobile ol cationin b
nodes deitabas s
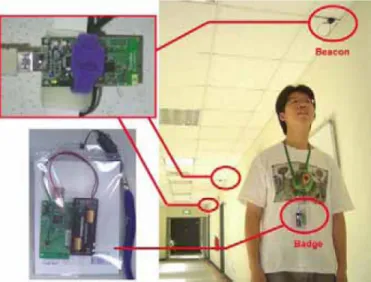
Fig. 4. RF-based location systemwith fingerprinting approach Taroko is a
programmable
module.Developers
cancode in NesC programming language and run the
pro-
Fig. 5. IndoordeploymentofTaroko-based locationsystem;
beaconsgram upon TinyOS [8], a small and open-source soft- and
relays
are attached to ceilings in passages, anda badge is worn wareoperating system designed
for sensor networks. byaperson
Alternatively,
thedeveloper
can choose toprogram
inC and
compile
the codeby
commercialcompilers (e.g.
JAR embedded
workbench)
orGNU MSPGCCcompiler
asbadge.
Fig.
5depicts
the
environmentsetting.
Thefor the MSP43 0 microcontroller. The
compiled
machinebadge regularly
collects beacon messages and forwardscode can be uploaded to Taroko via USB
port.
the average RSSI values to the location server tocom-B.rNTUaTarokodiocalizationoService
pute its location. In our preliminary experiments, theB.hNTU
Taroko
Localrprizatswion Sesorvced
inth Fngr average accuracy is 1 to 2 meters. To compareTaroko-The localization service
[9]
takes thefingerprinting
based locationsystem
with traditional WiFi-based(using
approach
and works in twophases.
The firstphase
is 802.11standard)
locationsystem.
The former has somecalled
offline
training
phase
in which a humanoperator
advantages, including inexpensive
RFID module(about
performs
a site surveyby measuring
the receivedsignal
60 USD perTaroko),
small(about
the size ofacigarette-strength
indicator(RSSI)
from different beacon nodescase), low-power (powered by
two AAAbatteries),
and(BNs)
at some fixedsampling points
inthe environment,easily programmable (programming
andcommunicating
Given these RSSI measurements, one can compose a via USBport).
radio fingerprint of BNs at different sampling points.
C.
c erprise Location ServiceThese radio
fingerprints
will be stored in theFinger-
C.pIBMent
ation Aae Service Technlgprinting
Database. The second phase is known as online IBMEnterprise
Location Aware Service(LAS) [10]
is estimationphase.
Each mobile node is carried by a a software middleware that leverages IBM WatsonRe-personoraffachedto an
object,
itgathers
the RSSI values search Center's PLACES(Points-of-interest,
Locations,
from BNs and sends the databack
through
beacon nodes and AssetCatalog
for EnterpriseServices)
Technology.
orotherrelay
nodes toa backend location server.Finally,
It provides a set of Java APIs tocompatibly
imple-the location ofmobile node is determined
by matching
ment certain core services ofOpenGIS
Location Service the measuredRSSIvaluestothe stored radiofingerprints. (OpenLS) implementation specification [11],
such asThe
matching
process
iscomputed
byapplying
apaffern
Presentation Service(map
portrayal),
LocationUtility
recognition algorithm.
The location servercontinuously
Service(a
reversegeocoder
to transform ageometry
computes
the location ofmobile nodes. Fig. 4 shows the position toparticular place).
IBM Enterprise LAS aimsmain elements in the RF-based location
system.
tohelp developers
build their locationtracking
webWe have
deployed
a number of Tarokos as BNs inapplications effortlessly
and consolidate different po-both NTU CSIEbuilding
and IBM China Software De-sitioning technologies (e.g.
RFID,
Zigbee,
orUWB)
manage various spatial entities belonging to different
layers in a single map. The preferred map is in scalable
vector
graphics (SVG)
format. SVG is a XMLmarkup
.'~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~.
..H_...
._...
language
fordescribing
two-dimensional vectorgraph-ics both static and animated.
By
using PlacesAdmin,
weimport
SVG mapinto the database andcreateCoordinateReference
System
(CRS)
for the map.Then,
we startto create various spatial entities to
represent
real worldobjects
in different layers, like rooms, hospital assets,and
people,
etc. -AWe develop a dynamic web site with ED's map _______
as our main user interface. In addition, we use
Ajax
technique to enhance our web application. Because of the requirement for frequently updating the position of
mobile nodes, the Ajax-enhancedwebpage allows users Fig. 6. Web-based user interface for the location-aware emergency
to select multiple pre-defined objects on the single map care
and render the map without heavy page-reloading. It is
especially useful when performing user's query, since software components to support different functionalities the query results are expected to display continuously in our emergency care management system. We apply snd
smoothly
on the map.By
utilizing
SVG andAjax
event-driven architecture design based on Java Messagetechniques,
our webapplication
presents
objects'
loca-..
tion in a more
dynamic
manner andgreatly
avoids the cen(JMS
facilita
pealitycbetweentse
reloading
delay
resulted fromre-generating
the wholecomp onent
nsupports
publish/describe
mechanism
map.
~~~~~~~~~~~~for
thereasoning
agent tosubscribe
the updated contextand relevant events from HIS or PACS. These
envi-D. Context-aware Reasoning Agent ronmental events enrich the
agent's
KB for performingThe context-aware system should automatically pro- context-aware
reasoning.
vide relevant services at
right
time and inright place.
Sofar,
weimplement
the inferred actionsby
publish-To infer
appropriated
actions in theright situation,
weing
messages to any interested web-based clients in the develop a software agent that makes context-aware rea- ED over JMS. Forexample,
if thephysician
wants tosoning.
Theagent
performs
reactive rule-basedreasoning
be notified after his caredpatients
takesX-Ray.
Afterby utilizing
the Context-AwareRuleEngine (CARE) [12]
he subscribes to the notification under thisparticular
as its knowledge baseKBtodedu t R situation defined inrules,
thereasoning
agent
starts toas
itS
knowledge base(KB)
todleduce
actions.
Rule-based
programming gives developers
theflexibility
and monitor location context when thepatient
leaves formaintainability
to manage thesystem's
behaviorsby examination,
andfinally
infers the notification while theloading
different rule sets and facts. Ingeneral,
we buildpatient
finishes the examination and exits theX-Ray
area.CARE as the context-sensitive version of Jess [13], a E. Web-based User
Interface
general purpose rule engine purely developed by Java
language. Because of context rapidly changes, CARE We design a web-based user interface to display
asserts context as dynamic facts and maintains them by location information and to provide a query interface
keeping
context updates from the sensors (e.g. RFID). forusersto search forperson and medical resource. The When context information changes, it will be coded main searching page can be divided into five parts, asand sent to the reasoning agent to update its KB. For Fig. 6 depicts, each part is labeled in capital. Next, we
example, if a patient moves from hallway to the adult describe each part and its main functionalitiesasfollows.
medicine area in the ED, such room-entrance event A is a mapthat shows whole emergency care areas in
will be detected by the location system. The agent the ED. After user selects some items in part B, C,
also displays important signs, including restrooms, Lab (CSDL) in Taiwan for their technical support of
public telephones, convenient stores, etc. IBM Enterprise LAS and PlacesAdmin. We would like
C is a specialized search bar for looking for specific to thank other members ofiSpace Laboratory, especially medical staff in the ED. In the current prototype, Prof. Polly Huang, Prof. Hao-hua Chu, and Chuang-wen we supports searching for physician, nurse, and You for their discussion and support of NTU Taroko patient. Ifthe person's role has been selected, the location system. Special thanks should go to the
pro-second combo box will retrieve their names from fessionals of the Department ofEmergencyMedicine of thehospital database and list thesenamesfor further NTU Hospital, Hui-Min Chen and Ken-Shiao Lin for
selection. their valuable suggestions.
D is an event notification board that automatically
shows the unread notification messages ofpresent REFERENCES
login user. [1] Ekahau. [Online]. Available: http://www.ekahau.com
E is a context-aware
panel
to search for user related [2] Sonitor. [Online]. Available:http://www.sonitor.com
[3] Versus. [Online]. Available: http://www.versustech.cominformation. For example, if a physician logins, it [4] M. H. Chen and Y C. Huang, "Public awareness of triage allows the physician to select his cared patients, andwaitingtime atemergency department,"JournalofTaiwan
collaborated nurses, and available assets. Emergency Medicine, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 128-131, September
2003.
V. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK [5] A. K. Dey and G. D. Abowd, "Towards a better understanding ofcontextandcontext-awareness,"GeorgiaInstitute of Technol-In this paper, we introduce the emergency care man- ogy, College ofComputing, Tech. Rep. GIT-GVU-99-22, June
agement system with location-aware servicesto improve 1999.
patientcare
andemegencyvsitflo.Bas[6]
S. J.Liaw,P. M. Hu,and H. C.Liao,"Patients who leaveemer-patient
care and emergencyvisit
flow. Based on the gency departments prematurely," Journal of Taiwan EmergencyRF-based indoor location system, we support patient Medicine, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 40-50, June 2002.
tracking, staff tracking, andassettracking. The delaycan [7] M. L. Liou, "Perceived waiting times, actual waiting times be reduced by proactive context-aware notifications. We and their relations to satisfaction ofpatients of the emergency
department in a medical center," Master's thesis, Graduate
develop an agent-based context-aware system to infer Institute of Health Care Organization Administration, NTU,
appropriate notifications and apply event-driven design Taiwan, 2001.
to better integrate these multi-functional components. [8] TinyOS. [Online]. Available: http://www.tinyos.net
[9] C. W. You, Y C. Chen,H. H. Chu,P.Huang, J. R. Chiang,and
Up until now, our system has been successfully de- S. Y Lau, "Sensor-enhanced mobility prediction for energy-ployed and experimented in NTU CSIE building and efficient localization," To appeared in IEEE SECON 2006,
IBM CSDL to fully test its functionality. To avoid Reston, VA, USA,
September
25-28 2006.bothering the emergency
patients,
we are working on[10]
S.
C. Shen and Y C. Chang, "Bestprac-the deal ihamnsesofDprmn
fEegtices
for location-aware services," Jun 2006. [On-the details with administers of Department of Emergency line]. Available: http://www- 128.ibm.com/developerworks/edu/Medicine ofNTUHospitaltofindout anappropriate area wi-dw-wi-best-i.html?S-TACT=105AGX05&S-CMP=HP for real deployment and evaluations.
[I
1] The OpenGIS Location Service (OpenLS). [Online].Available:The current prototype system deals with
simple
emer-[12]http://www.opengeospatial.org/standards/olscore
[12] W. R. Jih, J. Y J. Hsu, C. L. Wu, C. F. Liao, and S. Y Cheng, gency care scenarios to demonstrate the benefits of "A multi-agent service framework for context-aware eldercare,"
the location-aware services. Our future work includes inAAMAS'2006WorkshoponService-OrientedComputingand exploring other complex scenarios for real problems in Agent-Based Engineering (SOCABE'2006), May 8-12 2006,pp.the ED and ealuating ho much improvment we may 61-75.
the ED and evaluating how much improvement we may [13]
E. F. Hill,
"Jess, the rule engine for the java platform,"achieve with the emergency care services. Thought we Sandia National Laboratories. [Online]. Available: http:
incorporate a location-aware middleware into the sys-
//herzberg.ca.sandia.gov/jess
tem, we still need more experiences to fully understandits advantages and supports of building location-aware applications.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by IBM Taiwan and by a grant from the Advanced eCommerce Institute of the Institute for Information Industry (III) in Taiwan. We would like to thank IBM China Software Development