科技部補助專題研究計畫成果報告 期末報告
黃腐醇對於大鼠血管鈣化之影響及其相關機轉研究
計 畫 類 別 : 個別型計畫
計 畫 編 號 : MOST 106-2320-B-041-003- 執 行 期 間 : 106年08月01日至107年07月31日
執 行 單 位 : 嘉藥學校財團法人嘉南藥理大學藥學系(含碩士班)
計 畫 主 持 人 : 劉淑芬
計畫參與人員: 學士級-專任助理:陳儷英
報 告 附 件 : 出席國際學術會議心得報告
中 華 民 國 107 年 10 月 16 日
中 文 摘 要 : 血管鈣化在患有動脈粥樣硬化、慢性腎病、糖尿病和高血壓的患者 中普遍存在,是心血管疾病發病率和死亡率增加的強而有力的獨立 預測因子。血管鈣化是一種活躍的細胞介導過程,類似於成骨作用 和骨質疏鬆症,形成機制是受到調控骨骼鈣化的基因所影響。近年 來關於心血管鈣化調控機制的研究主要集中在成骨細胞去分化、基 質囊泡、細胞外基質分解和礦化以及細胞凋亡等方面。黃腐醇是啤 酒花和啤酒中具有生物活性的異戊烯化類黃酮在傳統醫學中長期用 作鎮靜劑和抗微生物劑。最近的研究更確定黃腐醇可改善部分新陳 代謝症候群指標,讓人們開始關注到黃腐醇對心血管和代謝疾病的 保護作用。然而,黃腐醇在血管鈣化中的作用尚未有人研究。因此
,在本研究中,我們使用β-glycerophosphate誘導的大鼠血管平滑 肌細胞鈣化的體外模型來評估黃腐醇對血管鈣化的作用和機制。實 驗中使用大鼠血管平滑肌細胞培養於含有10 mM β-
glycerophosphate、100 nM insulin、50 μg/ml ascorbic acid與 10 mM sodium pyruvate的10% DMEM培養液中培養,經過14天後與對 照組相比,β-GP組顯著地增加大鼠血管平滑肌中的ALP活性和鈣含 量,並進一步由von Kossa和Alizarin Red S染色測定證實可形成多 細胞結節和鈣離子沉積。透過西方墨點法和免疫細胞化學螢光染色 確定成骨細胞分化標誌物和信息傳導途徑的蛋白質表現。我們的數 據顯示,經β-GP培養14天後血管平滑肌細胞的確有礦物化的現象產 生,而黃腐醇卻可以濃度相關性地降低β-GP誘導的成骨細胞分化和 VSMC的鈣化,包括ALP活性,鈣含量和成骨細胞分化標記BMP-2、
Runx-2、Pit-1與active β-catenin等蛋白質的表現以及礦化結核 的形成。此外,黃腐醇顯示出可以抑制β-GP誘導的ROS產生、細胞 凋亡和caspase 3和-9的蛋白質表現,這些是已知會造成血管鈣化的 因素。因此,本研究顯示黃腐醇可能在預防鈣化相關血管疾病中起 作用, 需要進一步的動物研究來證實這些新發現。
中 文 關 鍵 詞 : 血管鈣化、黃腐醇、血管平滑肌細胞、 β-連環蛋白、runt 相關轉 錄因子2
英 文 摘 要 : Vascular calcification (VC) is prevalent in patients with atherosclerosis, chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension, is a strong independent predictor of increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. VC is an active, cell-regulated process. Recent studies on the regulatory mechanism of cardiovascular calcification have been focused osteogenic dedifferentiation, matrix vesicles, extracellular matrix degradation & mineralization and cell apoptosis. Xanthohumol (XN), a bioactive prenylated
flavonoid in hops (Humulus lupulus L.) and beer, has long been used in traditional medicine as a sedative and
antimicrobial agent. More recently, attention has been devoted to the protective effects on the cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. However, the role of xanthohumol in VC is still unclear. In this study, an in vitro model of rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) calcification induced by β-glycerophosphate (β-GP) are used to identify
the effect and mechanisms of XN on VC. Methods: Incubation of VSMCs with β-GP for 14 days induced an osteoblast-like morphological change. The mineralization was visualized by Von Kossa and Alizarin red staining. Alkaline phosphatase activity (ALP) and calcium content were also detected. The protein expression of osteoblastic differentiation markers and signaling pathways were determined by western blot and immunocytochemistry. Results: Our data showed that
xanthohumol concentration-dependently reduced β-GP-induced osteoblastic differentiation and calcification of VSMCs including ALP activity, calcium content and bone
morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), sodium-phosphate cotransporter Pit-1 and β-catenin expression as well as the formation of
mineralized nodule. Furthermore, xanthohumol was shown to inhibit the β-GP-induced ROS production, apoptosis and protein expressions of caspase 3 and -9, which are known contributors to vascular calcification. Therefore, this study indicates that xanthohumol may have a role in
prevention of calcification-associated vascular diseases.
Further animal studies are needed to substantiate these novel findings.
英 文 關 鍵 詞 : vascular calcification, xanthohumol, vascular smooth muscular cell, β-catenin, Runt-related transcription factor 2
科技部補助專題研究計畫成果報告
(□期中進度報告/■期末報告)
黃腐醇對於大鼠血管鈣化之影響及其相關機轉研究
計畫類別:■個別型計畫 □整合型計畫
計畫編號:MOST 106-2320-B-041-003-
執行期間:106 年 08 月 01 日至 107 年 07 月 31 日
1
執行機構及系所:嘉藥學校財團法人嘉南藥理大學 藥學系 (含碩士班)
計畫主持人:劉淑芬 共同主持人:
計畫參與人員:陳儷英
本計畫除繳交成果報告外,另含下列出國報告,共 1 份:
□執行國際合作與移地研究心得報告
■出席國際學術會議心得報告
□出國參訪及考察心得報告
中 華 民 國 107 年 10 月 12 日
中文摘要
血管鈣化在患有動脈粥樣硬化、慢性腎病、糖尿病和高血壓的患者中普遍存在,是心血管疾病發病率 和死亡率增加的強而有力的獨立預測因子。血管鈣化是一種活躍的細胞介導過程,類似於成骨作用和 骨質疏鬆症,形成機制是受到調控骨骼鈣化的基因所影響。近年來關於心血管鈣化調控機制的研究主 要集中在成骨細胞去分化、基質囊泡、細胞外基質分解和礦化以及細胞凋亡等方面。黃腐醇是啤酒花 和啤酒中具有生物活性的異戊烯化類黃酮在傳統醫學中長期用作鎮靜劑和抗微生物劑。最近的研究更 確定黃腐醇可改善部分新陳代謝症候群指標,讓人們開始關注到黃腐醇對心血管和代謝疾病的保護作 用。然而,黃腐醇在血管鈣化中的作用尚未有人研究。因此,在本研究中,我們使用β-glycerophosphate 誘導的大鼠血管平滑肌細胞鈣化的體外模型來評估黃腐醇對血管鈣化的作用和機制。實驗中使用大鼠 血管平滑肌細胞培養於含有 10 mM β-glycerophosphate、100 nM insulin、50 μg/ml ascorbic acid 與 10 mM sodium pyruvate 的 10% DMEM 培養液中培養,經過 14 天後與對照組相比,β-GP 組顯著地增加大鼠血 管平滑肌中的 ALP 活性和鈣含量,並進一步由 von Kossa 和 Alizarin Red S 染色測定證實可形成多細胞 結節和鈣離子沉積。透過西方墨點法和免疫細胞化學螢光染色確定成骨細胞分化標誌物和信息傳導途 徑的蛋白質表現。我們的數據顯示,經β-GP 培養 14 天後血管平滑肌細胞的確有礦物化的現象產生,
而黃腐醇卻可以濃度相關性地降低β-GP 誘導的成骨細胞分化和 VSMC 的鈣化,包括 ALP 活性,鈣含 量和成骨細胞分化標記 BMP-2、Runx-2、Pit-1 與 active β-catenin 等蛋白質的表現以及礦化結核的形成。
此外,黃腐醇顯示出可以抑制β-GP 誘導的 ROS 產生、細胞凋亡和 caspase 3 和-9 的蛋白質表現,這些 是已知會造成血管鈣化的因素。因此,本研究顯示黃腐醇可能在預防鈣化相關血管疾病中起作用, 需 要進一步的動物研究來證實這些新發現。
中文關鍵詞:血管鈣化、黃腐醇、血管平滑肌細胞、 β-連環蛋白、runt 相關轉錄因子2
Abstract
Vascular calcification (VC) is prevalent in patients with atherosclerosis, chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension, is a strong independent predictor of increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. VC is an active, cell-regulated process. Recent studies on the regulatory mechanism of cardiovascular calcification have been focused osteogenic dedifferentiation, matrix vesicles, extracellular matrix degradation & mineralization and cell apoptosis. Xanthohumol (XN), a bioactive prenylated flavonoid in hops (Humulus lupulus L.) and beer, has long been used in traditional medicine as a sedative and antimicrobial agent. More recently, attention has been devoted to the protective effects on the cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. However, the role of xanthohumol in VC is still unclear. In this study, an in vitro model of rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) calcification induced by β-glycerophosphate (β-GP) are used to identify the effect and mechanisms of XN on VC. Methods: Incubation of VSMCs with β-GP for 14 days induced an osteoblast-like morphological change. The mineralization was visualized by Von Kossa and Alizarin red staining. Alkaline phosphatase activity (ALP) and calcium content were also detected. The protein expression of osteoblastic differentiation markers and signaling pathways were determined by western blot and immunocytochemistry. Results: Our data showed that xanthohumol concentration-dependently reduced β-GP-induced osteoblastic differentiation and calcification of VSMCs including ALP activity, calcium content and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), sodium-phosphate cotransporter Pit-1 and β-catenin expression as well as the formation of mineralized nodule.
Furthermore, xanthohumol was shown to inhibit the β-GP-induced ROS production, apoptosis and protein expressions of caspase-3 and -9, which are known contributors to vascular calcification. Therefore, this study indicates that xanthohumol may have a role in prevention of calcification-associated vascular diseases.
Further animal studies are needed to substantiate these novel findings.
Key words: vascular calcification, xanthohumol, vascular smooth muscular cell, β-catenin, Runt-related
transcription factor 2
一、前言
血管鈣化 (Vascular calcification) 是指鈣和磷礦物質在血管壁上的異常沉積。血管鈣化的現象在粥 狀動脈硬化、高血壓、糖尿病血管疾病、衰老和慢性腎臟疾病中是常見的 (Yiu et al., 2015),並且是心 血管疾病和相關死亡的重要危險因子 (Lanzer et al., 2014)。據估計,動脈壁礦物化是目前受到心血管疾 病 (cardiovascular disease, CVD) 影響的病人中佔大多數的原因 (Sage et al., 2010)。尤其是慢性腎病族 群所特異性的廣泛性血管鈣化已經被視為心臟血管疾病主要的原因 (Moe et al., 2005)。慢性腎病本身的 尿毒物質以及鈣磷失調等問題,甚至於含有鈣磷酸鹽結合劑及活性維他命D的臨床使用都有可能促進以 及造成血管的鈣化問題,加重心臟血管以及腦血管疾病並發症的可能性。最近的一些醫學研究發現,
早期粥狀動脈硬化患者的血管中出現血管鈣化現象,其發生與心腦血管疾病的進展密切相關。第二型 糖尿病則是另一個受影響的群體。由此可以預見的是未來十年,血管鈣化和心血管疾病的頻率也會隨 之增加 (Shao et al., 2010)。因此抑制血管鈣化是降低心血管發生率及死亡率的有效方法。
Wnt/β-Catenin 訊 息 傳 遞 路 徑 在 造 骨 細 胞 新 生 作 用 (osteoblastogenesis) 與 血 管 鈣 化 (vascular calcification) 上扮演著種要角色 (Lee et al., 2012)。Wnt訊息傳遞路徑主要分為兩種類型: Canonical和 non-Canonical,只有Canonical Wnt路徑需透過β-catenin來傳遞訊息,Canonical Wnt/β-catenin路徑被認為 與造骨細胞分化過程較相關(Lin & Hankenson, 2011)。在Canonical Wnt/β-catenin路徑中,Wnt會結合在 穿膜受體Frizzled(Fzd)和co-receptor LRP5/6上,接著會活化細胞內Dishevelled(DVL)來抑制glycogen synthase kinase 3β(GSK3β)的磷酸化,進而抑制β-catenin的降解。β-catenin是這個訊息調控路徑下游 非常重要的一個調控者,在正常情形下,細胞質中游離態的β-catenin會經由proteosome-dependent之機 轉降解。當GSK3β使β-catenin在細胞中穩定下來後會堆積於細胞質並且進入細胞核與TCF/LEF 結合,
共同去調控目標基因,進行轉錄作用 (Takada et al., 2009; Lin & Hankenson, 2011)。在研究中顯示,當 β-catenin和TCF/LEF結合後,會活化Runx2啟動子上的基因轉錄,Runx2也會與TCF/LEF形成複合物,
這個複合物會與骨骼發育重要調節者之一的FGF18 (fibroblast growth factor) 的啟動子 (promoter) 結 合,進而促進FGF18表現。在造骨前驅細胞和骨髓基質幹細胞中也發現,當Canonical Wnt/β-catenin路 徑被活化後,會增加Runx2的轉錄活性,進而促使造骨細胞分化,增加骨形成 (Glass et al., 2005)。另 外,其他的研究也指出Wnt/β-catenin路徑被活化後,會活化Runx2等基因轉錄,使成骨細胞中的ALP表 現增加而增加血管上鈣的沉積而促使動脈血管鈣化 (Shao et al., 2010; Lee et al., 2012)。
在高磷作用下所負載產生的活性氧屬 (reactive oxygen species, ROS) 也被認為是血管鈣化期間血 管平滑肌細胞成骨轉化的下游介質。在分離的線粒體中,高磷可以調節線粒體膜電位,這在ROS的生 成中是很重要 (Montes et al., 2010)。Byon等人證實H2O2可以增加小鼠血管平滑肌中Runx2轉錄因子的 表現和活性,並使細胞轉化為成骨表現型和增加鈣化。他們還確認Runx2反應依賴於PI3K/AKT/Runx2 信號 (Byon et al., 2008)。最近,Zhao等人使用牛主動脈平滑肌細胞暴露於β-glycerophosphate (-GP)的 模型,顯示ROS生產在成骨轉換過程中是重要的。-GP是有機磷酸鹽供體,透過ALP的作用導致磷酸 鹽升高,並且在該研究中促進平滑肌細胞譜系標誌物的下調,成骨標誌物的增加和ROS的生成量增加 了3倍。透過投與SOD不但減少ROS的形成也顯著降低鈣沉積 (Zhao et al., 2011)。除此之外,磷酸鹽可 由血管平滑肌細胞表面的運轉體(cotransporter, Pit1)進入細胞,增加線粒體膜電位與線粒體ROS,並 且活化NF-κB的路徑,進一步刺激及調控成骨細胞的基因表現 (Msx2 and Runx2) 和血管礦化,使血管 的平滑肌細胞表現出類似成骨細胞的功能而造成血管中層的鈣化 (Al-Aly, 2011)。
高磷可能促進血管基質鈣化的另一種機制是通過刺激血管平滑肌細胞凋亡(Apoptosis-dependent
matrix mineralization)。 生長停滯特異性基因6(Gas6)的下調可能是一個重要的基礎機制,在磷酸鹽 誘導的人類主動脈血管平滑肌細胞鈣化期間,Gas6及其受體Ax1表現均降低 (Son et al, 2006)。Gas6-Axl 存活途徑跟血管細胞的成骨分化有關,其抗細胞凋亡作用透過Bcl-2介導的PI3K-AKT途徑實現; 磷酸化 使Bcl-2去活化和活化促凋亡蛋白Bcl-2相關的死亡啟動子,導致caspase-3活化和細胞凋亡 (Son et al, 2007)。在動物試驗中,高磷飼養的小鼠動脈中層發現平滑肌細胞會脫落並伴隨礦物沉積 (Pai et al., 2010)。此外,兒科透析患者的鈣化血管表現出廣泛的平滑肌細胞凋亡 (Shroff et al., 2008)。
黃腐醇是啤酒花 (Humulus lupulus L.) 和啤酒中具有生物活性的異戊烯化類黃酮,在傳統醫學中長 期用作鎮靜劑和抗微生物劑。其他的藥理活性還包括抗癌、抗氧化及肝保護等作用。後來陸續有動物 實驗證實黃腐醇可透過改善肝臟與循環膽固醇和MCP-1濃度以降低動脈膽固醇含量來改善ApoE缺陷 小鼠的動脈粥樣硬化斑塊形成、高膽固醇血症和肝脂肪變性 (Doddapattar et al., 2013)。除此之外,也 透過抑制膽固醇酯轉移蛋白減少動脈粥樣硬化區域的膽固醇積累積 (Hirata et al., 2017)。在最近一項以 餵食實驗鼠高脂食物的動物實驗中發現黃腐醇具有降膽固醇、降血糖,改善部分新陳代謝症候群指標,
並減少體重增加幅度 (Miranda et al., 2016),這是首次研究發現,有一種成份可以同時改善多種健康問 題,未來還需要更多研究,才能了解這種成份在人體是否安全,是否也一樣能產生效果。低密度脂蛋 白(LDL)的氧化被認為在動脈粥樣硬化中發揮中心作用。黃腐醇具有清除超氧化物的能力,在抑制 LDL氧化的實驗中顯示黃腐醇具有很高的抗氧化活性 (Schemppet al., 2010)。與α-tocopherol併用時,黃 腐醇完全抑制銅介導的LDL氧化。根據這些發現,黃腐醇可以保護人類LDL免於氧化 (Miranda et al., 2000 )。由於黃腐醇可以調節脂質代謝,因此能預防心血管疾病如粥狀動脈硬化。除了其直接的抗氧化 活性,黃腐醇還誘導細胞的防禦機制克服化學品 (Plazar et al., 2007) 或手術誘發的氧化壓力 (Dorn et al., 2013 )。黃腐醇最近也被證實濃度依賴性地抑制PDGF-BB誘導的血管平滑肌細胞增殖與遷移。在小 鼠股動脈袖套模型中測試,黃腐醇顯著降低新內膜形成。結論顯示黃腐醇在體外可以抑制PDGF-BB誘 導的血管平滑肌細胞增殖和遷移以及體內新內膜形成 (Liu et al., 2017)。基於以上這些因素,我們預期 黃腐醇可能具有預防和改善動脈粥樣硬化發展的前途性藥物。幾項研究已經確定了黃腐醇對心血管系 統的保護作用,然而黃腐醇是否會影響血管鈣化與對抗氧化壓力對血管細胞所造成的損傷的研究仍然 相當罕見,因此,本計畫目的在評估黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)抑制血管鈣化的潛力及藉此深入了解其分子 機制。
二、研究方法
1. 鈣化平滑肌細胞培養 (Mineralization of vascular smooth muscle cells):
(1) 大鼠血管平滑肌細胞從 Sprague-Dawley rats (200-250 g) 的胸主動脈(aorta)獲得,在無菌環境 下將周圍多餘的結締組織及脂肪組織除去,並用無菌的 PBS 溶液清洗數次。處理乾淨後,將 其剪成較小的碎片平鋪在 T-25 培養瓶 (flask) 並加入 6 ml 細胞培養液 (10% DMEM),置於 5%
CO2、95% O2、37℃恆溫及飽和水蒸氣的培養箱內培養。之後,平均每三天更換一次細胞培養 液。當細胞長至 80% ~ 90% 匯合狀態 (confluence) 時,即可進行繼代培養,實驗所使用的為 3~6 代的細胞。
(2) 誘發細胞鈣化: 將 104個細胞/1 ml 置於六孔細胞培養盤中培養 (day 0),以 10% DMEM 培養 待細胞長至八分滿 (day 7),細胞改用含 10 mM β-glycerophosphate、100 nM insulin、50 μg/ml ascorbic acid 與 10 mM sodium pyruvate 的 10% DMEM 繼續培養,每 2 天更換一次藥物及培養 液,繼續培養 7 天 (day 14)。
2. 細胞存活率 (MTT assay):
藥物處理後的細胞將 medium 抽出,加入 500 l 之酸化 isopropanol 溶解盤底紫色結晶 formazan,
10 分鐘後,將上清液抽取 200 μl 至 96 孔盤中,測量 540nm (OD540) 和 630nm (OD630) 的吸光值,將每 一組之 (OD540-OD630) 值和控制組之值比較後即可計算其給藥後的細胞存活率。
3. 鹼性磷酸酶活性測定 (Alkaline phosphatase activity assay):
將 104個平滑肌細胞/ml 置於六孔細胞培養盤中培養 (day 0),以 10% DMEM 培養待細胞長至八 分滿 (day 7),細胞改用含 10 mM β-glycerophosphate 的 10% DMEM 繼續培養,投與不同濃度的黃腐醇 (xanthohumol),每 2 天更換一次藥物及培養液,培養 7 天後 (day 14) 進行細胞內鹼性磷酸酶活性試驗。
首先將 well 內的培養液移除,細胞層用 PBS 輕洗 3-4 次,接著加入含有 0.1% Triton X–100 的 lysis buffer 打破細胞,加入 reaction solution 於 37°C 避光反應 1 小時後,再加入 1 M NaOH 終止反應,測量 405nm 吸光值。利用 bicinchoninic acid protein(BCA)assay 來做蛋白質定量,在 37°C 反應 1 小時後,加入 1 M NaOH 終止反應,測量 540 nm 吸光值。
4. 細胞礦物化染色法 (Alizarin Red S & Von Kossa staining)
將 104個平滑肌細胞/ml 置於六孔細胞培養盤中培養 (day 0),以10% DMEM培養待細胞長至八分 滿 (day 7),細胞改用含10 mM β-glycerophosphate的10% DMEM繼續培養,投與不同濃度的黃腐醇 (xanthohumol),每2天更換一次藥物及培養液,培養7天後 (day 14) 進行血管細胞礦物化染色試驗。在 培養終止時,首先將培養盤內的培養液移除,細胞層用PBS輕洗3-4次,接著利用70%冰乙醇固定細胞 層,於4°C反應1小時,固定後接著以二次水清洗3-4次,吸乾孔內液體後緩慢加入1% Alizarin Red S solution,在室溫下反應60分鐘後觀察顏色深淺並拍照。Alizarin Red S染色法可染出造骨細胞所堆積 的bone nodules礦物質沉積,利用染色結果的顏色深淺來判斷礦物化程度的高低。為了定量其礦物化程 度,待拍照後加入10% cetylpyridinium chloride solution 反應30 min,測量其540 nm吸光值。
5. 細胞鈣沉積含量測定 (Quantification of calcium deposition in aortas)
將 104個平滑肌細胞/ml 置於六孔細胞培養盤中培養 (day 0),以10% DMEM培養待細胞長至八分 滿 (day 7),細胞改用含10 mM β-glycerophosphate的10% DMEM繼續培養,投與不同濃度的黃腐醇 (xanthohumol),每2天更換一次藥物及培養液,培養7天後 (day 14) 進行血管細胞鈣含量測定。細胞以 0.6 N HCl去鈣化 (decalcified) 24小時,使用calcium kit 測量HCl上清液的鈣含量。
6. 免疫螢光染色(Immunofluorescence staining):
將 105個平滑肌細胞/ml 置於六孔細胞培養盤中培養 (day 0),以10% DMEM培養待細胞長至八分 滿,細胞改用含10 mM β-glycerophosphate的10% DMEM,投與不同濃度的黃腐醇 (xanthohumol),反應 48小時後細胞以PBS洗滌,去除PBS後加入10%formalin在4℃固定10分鐘,10分鐘後以PBS洗6次,然後 加入0.3% Triton X-100於室溫下作用15分鐘,接著加入適量blocking buffer (1% BSA)於室溫下作用1小 時,以稀釋過的primary antibody均勻覆蓋在4℃作用隔夜,去除醫及抗體後再加上secondary antibody於 室溫下作用1小時,之後以PBS 沖洗,即可封片。再以共軛焦電子顯微鏡觀察。
7. 西方墨點法 (Western blotting) :
將1 x 106個平滑肌細胞種於10公分培養盤並培養於含10 mM β-glycerophosphate的10% DMEM中,
投與不同濃度的黃腐醇 (xanthohumol),待反應特定時間後將細胞以PBS洗二次後,加入lysis buffer作用 15分鐘後,收集細胞並以13,000 rpm,4℃離心取上清液,可儲存於-80℃待日後使用。蛋白質濃度 以”Bio-Rad DC Protein Assay”測量。依據一般流程進行跑膠和轉漬,之後將稀釋好的Primary antibody 均勻覆蓋在PVDF membrane上4 ℃作用隔夜,之後再以washing buffer洗一小時去除多餘的抗體。再將 Secondary antibody稀釋到合適濃度,均勻倒在PVDF membrane上室溫反應1小時。最後再以washing buffer洗60分鐘,則加入ECL 1分鐘,待略乾後壓片、洗片即可完成。
8. 細胞凋亡檢測 (Apoptosis detection): Annexin V/PI 的雙染法
將 104個平滑肌細胞/ml 置於六孔細胞培養盤中培養,以10% DMEM培養待細胞長至八分滿,細 胞改用含10 mM β-glycerophosphate的10% DMEM,投與不同濃度的黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)作用72小時 後,將培養液、及利用trypsin打下的細胞全部收集在一起後離心(1,200 rpm,4℃,5分鐘)。倒掉上清
液後加入1 ml PBS將沈澱的細胞沖散,然後用相同轉速再次離心。倒掉上清液後加入300 l 4℃之PBS,
然後逐次少量的加入99.9% 的酒精700 l以固定細胞,在4℃放置隔夜。接著離心、去除上清液後加入 PBS 570 l、10 g/ml的 RNase 2 l及0.5% 之Trixton X-100 30 l在37℃下作用1小時,接著離心並去除 上清液後加入PBS 600 l和10 mg/ml之PI 2 l在4℃下染色30分鐘後即可利用流體細胞分析儀(Coulter Epics XL-MCL,Beckman Coulter)測定細胞生長週期。另外,可藉Annexin V/PI 的雙染法偵測細胞凋 亡的情況。
9. 細胞內活性氧屬 (ROS) 的含量測定:
細 胞 內 ROS 是 以 螢 光 顯 微 鏡 來 觀 測 特 定 probe 的 氧 化 來 評 估 。 使 用 的 probe 是 2’7’- dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA, Molecular Probes, Leiden, The Netherlands)。在60 mm的 dish中種下5x105個細胞,使之貼附整晚,接著在含10 mM β-glycerophosphate的10% DMEM中投予不同 濃度的黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 作用72小時候,分別用10 M的H2DCFDA、10 M DHE和25 M CMFDA 在37 oC下染細胞30分鐘,接著以PBS沖洗並收集細胞,並用flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson and Co., Franklin Lakes, NY) 分析螢光強度。
10. 統計分析 (Statistical analysis)
所有實驗數據均以平均值 ± 標準誤 (Mean ± S.E.) 及百分率 (%)表示。實驗數據的比較,除有特 別標示外,均採用Student's t-Test評估對照組與給藥組間之差異。當 p 值小於0.05時,表示於統計學上 有顯著差異。
三、結果
1. 黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 對大鼠血管平滑肌生長的影響
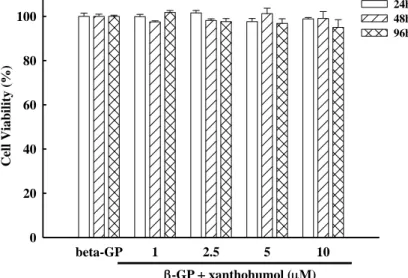
為了瞭解黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 對血管平滑肌是否具有毒殺作用或是影響其生長,實驗中使用 MTT assay來觀察大鼠血管平滑肌細胞在不同濃度的黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) (1~10 μM) 的直接作用下 是否受到影響。將控制組的吸光值當作100%,藉由測得其他組別的吸光值可以間接得知其細胞生長是 否受到影響。由實驗結果得知,黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)直接作用24~96小時後,濃度1~10 μM對於細胞存 活率並沒有抑制作用【Fig. 1】,因此我們取黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 1、2.5、5及 10 μM的濃度進行以下 的細胞實驗。
beta-GP 1 2.5 5 10
Cell Viability (%)
0 20 40 60 80 100
24hr 48hr 96hr
-GP xanthohumol (M)
2. 黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 對於ALP活性的影響
在誘發細胞鈣化的培養液中,可以使血管平滑肌細胞分化為類成骨細胞,並且分泌代表成骨細 胞分化之標的酵素ALP。因此以ALP活性試驗確認平滑肌細胞分化為類成骨細胞的現象以及黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 對於細胞鈣化之影響。由ALP活性試驗的結果顯示,大鼠血管平滑肌細胞經誘發細 胞 鈣 化 培 養 液 培 養 14 天 的 細 胞 確 實 具 有 ALP 活 性 (β-GP 組 ) , 而 投 予 不 同 濃 度 的 黃 腐 醇 (xanthohumol) 的組別與β-GP組相比之下,ALP活性皆有明顯下降的現象產生【Fig. 2】。
Fig. 1 Effects of xanthohumol on the cell proliferation of VSMCs. Cells were seeded in 96-well plates for 24 h, and then treated with indicated concentration of xanthohumol for another 24, 48, 72 and 96 h. Then cell proliferation was determined by MTT method.
Each value represents the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, with triplicate determinations in each experiment.
CTL β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
ALP Activity (IU/mg protein)
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
-GP + xanthohumol
##
*
**
**
*
(M)
Fig. 2 xanthohumol suppressed the β-GP-induced increases in ALP activity in cultured rat VSMCs.
ALP activity was measured using an ALP assay kit. Each value represents the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, with triplicate determinations in each experiment. ##p<0.01 versus control group;
*p<0.05, **P<0.01 compared to β-GP alone.
3. 黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 對於平滑肌細胞之骨礦物化作用的影響
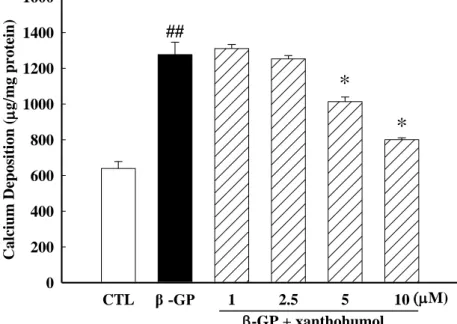
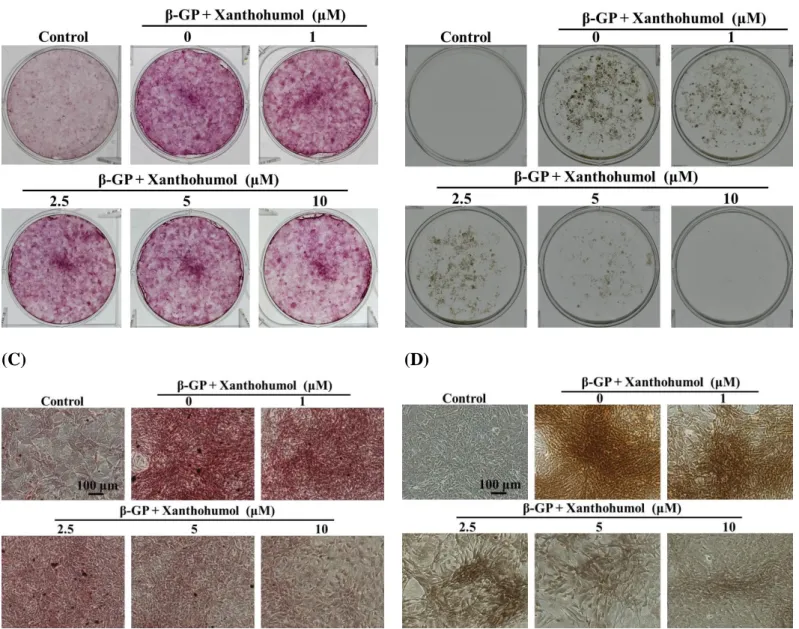
如【Fig. 2】所示,黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 可以有效的減少ALP活性,接下來為測試黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 對於平滑肌細胞分化為類成骨細胞之骨礦物化作用的影響。由【Fig. 3】可以知道黃 腐醇 (xanthohumol) 可以有效的減少細胞鈣沉積;我們分別運用礦物化染色法 Alizarin Red S 與 Von Kossa染色 (可將磷 酸 鈣 染 成 黑 色 ~茶 褐 色 )可染出類成骨細胞所堆積的bone nodules礦物質 沉積,於可見光下觀察骨礦物化染色結果。實驗結果顯示,經骨誘導培養液培養14天的組別的確有 礦物化的現象產生,而投與不同濃度的黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 的組別可以抑制平滑肌細胞的礦物化
【Fig. 4】。
CTL β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
Calcium Deposition (g/mg protein)
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600
-GP + xanthohumol
##
*
*
M)
Fig. 3 Xanthohumol inhibits β-GP-induced calcification in VSMCs. Calcification was induced by the addition of β-glycerophosphat (β-GP). Calcium contents were measured and normalized by the protein content of cell lysates. Each value represents the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, with triplicate determinations in each experiment. ##p<0.01 versus control group; *p<0.05 versus β-GP group.
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
Fig. 4 Xanthohumol inhibits β-GP-induced calcification in VSMCs. Confluent VSMCs were incubated with calcification medium in the indicated concentration of α-mangostin for 14 days. Calcification was induced by the addition of β-glycerophosphate (10 mM). VSMCs were stained for mineralization with Alizarin red (A), Von Kossa staining (B) and microscopic images (magnification ×100) (C, D).
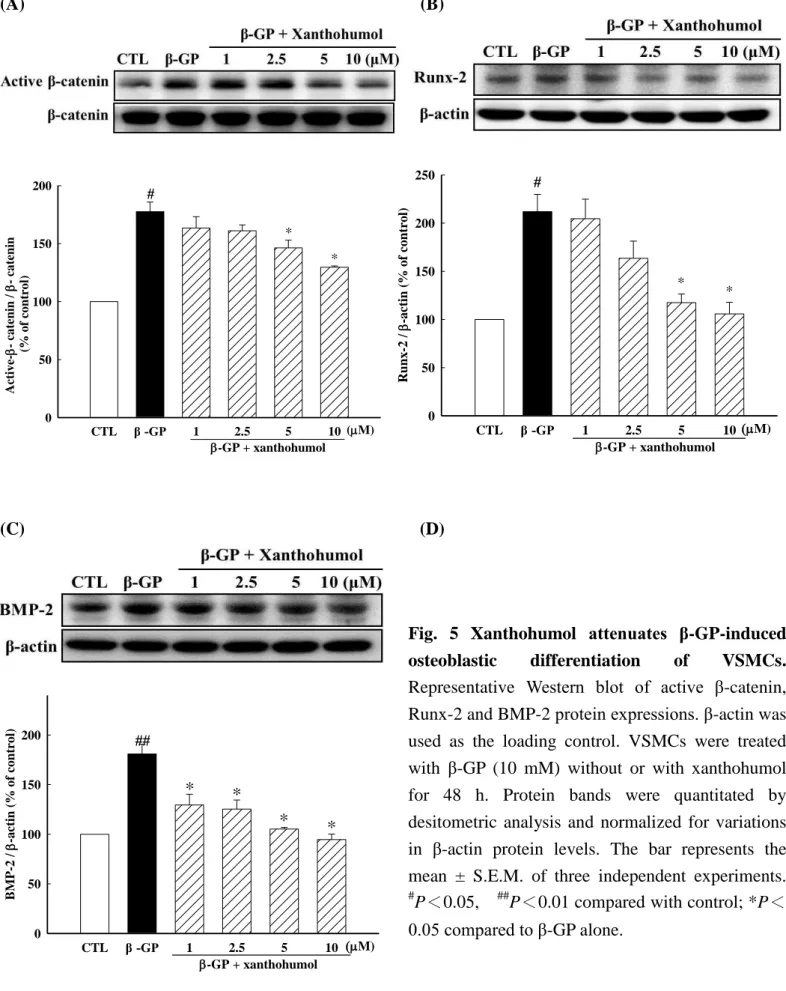
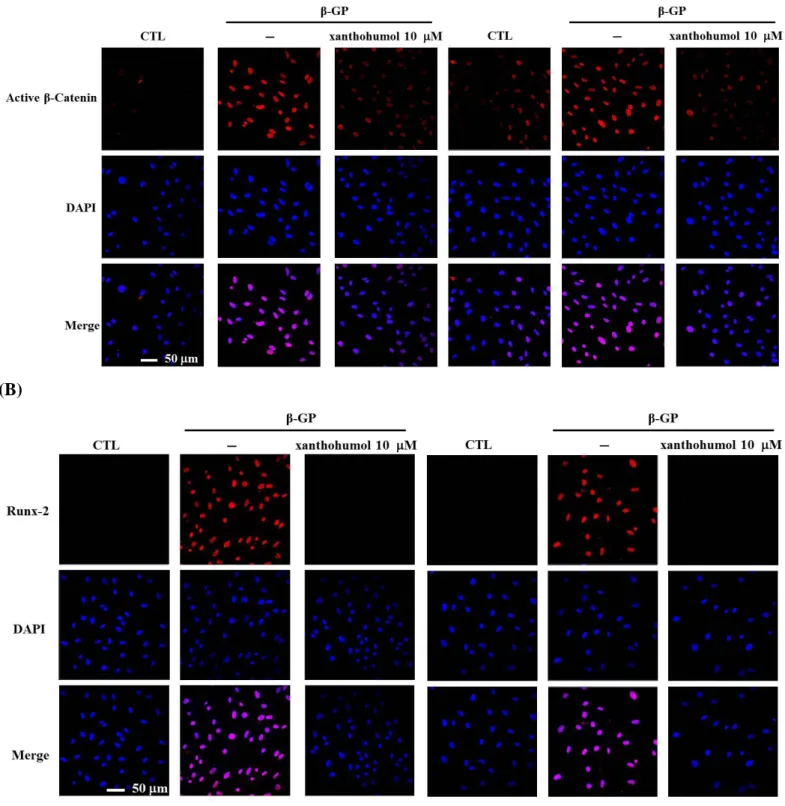
4. 黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 對血管平滑肌細胞在β-glycerophosphate 誘導下對成骨化相關蛋白的影響 過去文獻顯示在細胞與動物研究中,血管鈣化與Wnt/β-catenin訊息路徑有關。為了評估黃腐醇對於 Wnt/β-catenin路徑的影響,我們利用西方墨點法分別探討細胞內active β-catenin的表現。如【Fig. 5A】
所示,投予黃腐醇可減少細胞中active β-catenin的表現。轉錄因子Runx-2在平滑肌細胞分化為類成骨細 胞過程中扮演極重要的角色,Runx-2可由許多不同的訊息傳遞路徑所調控,包括BMP和Wnt/β-catenin 訊息傳遞路徑,藉由增加轉錄因子Runx-2的表現,可增加平滑肌細胞分化為類成骨細胞,且促進血管 鈣化。由【Fig. 5B】結果發現,加入黃腐醇後會減少細胞內轉錄因子Runx-2的表現,然後對平滑肌細 胞分化為類成骨細胞進行調控。利用免疫螢光染色法觀察,如【Fig. 6】所示,β-GP會使active β-catenin 與Runx-2的螢光表現增加,同時投予黃腐醇會使active β-catenin與Runx-2的螢光表現減少。由以上結果 顯示黃腐醇可以抑制Wnt/β-catenin訊息傳遞路徑。
當BMP與受體結合後會磷酸化和活化下游的傳遞分子如Smad1/5/8,而磷酸化的Smad1/5/8會與 Smad4形成一個複合物 (Co-Smad),接著Co-Smad會轉移到細胞核內成為一個轉錄因子,或是調節 Runx-2和其他相關基因的表現。在實驗上,為了進一步確認黃腐醇對於BMP/Runx-2訊息傳遞路徑的影 響,利用西方墨點法評估黃腐醇對細胞中的BMP-2蛋白質表現的影響。結果發現,在黃腐醇的存在下,
細胞中的BMP-2的蛋白質表現明顯減少【Fig. 5C】。
(A) (B)
CTL β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
Active-- catenin /- catenin (% of control) 0 50 100 150 200
-GP + xanthohumol
#
*
(M)
*
CTL β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
Runx-2 / -actin (% of control)
0 50 100 150 200 250
-GP + xanthohumol
#
* *
M)
(C) (D)
CTL β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
BMP-2 /-actin (% of control) 0 50 100 150 200
-GP + xanthohumol
##
* *
* *
M)
Fig. 5 Xanthohumol attenuates β-GP-induced osteoblastic differentiation of VSMCs.
Representative Western blot of active β-catenin, Runx-2 and BMP-2 protein expressions. β-actin was used as the loading control. VSMCs were treated with β-GP (10 mM) without or with xanthohumol for 48 h. Protein bands were quantitated by desitometric analysis and normalized for variations in β-actin protein levels. The bar represents the mean ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments.
#P<0.05, ##P<0.01 compared with control; *P<
0.05 compared to β-GP alone.
(A)
(B)
Fig. 6 Effect of xanthohumol on active β-catenin and Runx-2 expressions in rat VSMCs. VSMCs were treated with β-GP (10 mM) without or with xanthohumol (10 M) for 48 h. Cells were subjected to immunofluorescence staining for β-catenin (A, red) or Runx-2 (B, red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
Scale bars, 50 m.
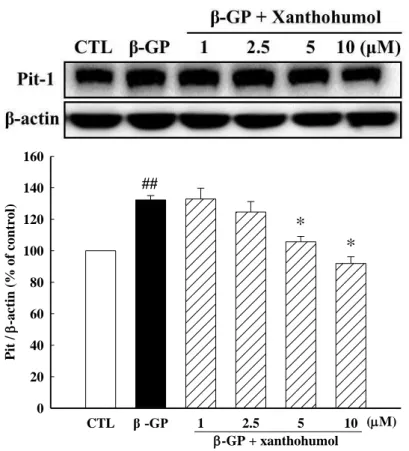
5. 黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 對Pit-1/ROS/PI3K/AKT路徑的影響
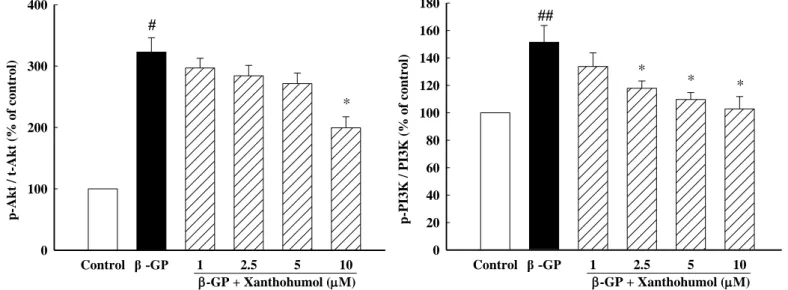
先前已有研究證實磷酸鹽可由血管平滑肌細胞表面的運轉體 (cotransporter, Pit1) 進入細胞後,增 加線粒體膜電位與線粒體ROS,並且活化PI3K/AKT的路徑,進一步刺激及調控成骨細胞的Runx-2基因 表現和血管礦化,使血管的平滑肌細胞表現出類似成骨細胞的功能而造成血管中層的鈣化 (Al-Aly, 2011). 為了評估黃腐醇對於Pit-1/ROS/PI3K/AKT/Runx-2路徑的影響,我們利用西方墨點法分別探討細 胞內Pit-1、AKT、PI3K等蛋白質的表現與細胞ROS的生成量。如【Fig. 7】所示,投予黃腐醇可減少細 胞中Pit-1的表現。另外,加入黃腐醇後會減少細胞內ROS的生成【Fig. 9】,推論黃腐醇或許可減少磷酸
鹽由血管平滑肌細胞表面的運轉體 (cotransporter, Pit-1) 進入細胞,進而減少ROS的生成。
在高磷作用下所負載產生的活性氧屬 (reactive oxygen species, ROS) 也被認為是血管鈣化期間血 管平滑肌細胞成骨轉化的下游介質。Byon等人證實H2O2可以增加小鼠血管平滑肌中Runx-2轉錄因子的 表現和活性,並使細胞轉化為成骨表現型和增加鈣化。他們還確認Runx-2反應依賴於PI3K/AKT/Runx-2 信號 (Byon et al., 2008)。由【Fig. 8】結果發現,加入黃腐醇後可減少細胞內p-PI3K/PI3K relative density 的表現量。在下游的Akt的蛋白質表現上,如【Fig. 8】所示,10 M黃腐醇可抑制p-Akt/Akt relative density 的表現量。由以上結果顯示黃腐醇可以抑制PI3K-AKT訊息傳遞路徑。
CTL β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
Pit / -actin (% of control)
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
-GP + xanthohumol
##
*
*
(M)
Fig. 7 Xanthohumol attenuated the expression of sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter, Pit-1.
VSMCs were treated with β-GP (10 mM) without or with xanthohumol for 48 h. β-actin was used as the loading control.Protein bands were quantitated by desitometric analysis and normalized for variations in β-actin protein levels. The bar represents the mean ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments. ##P<0.01 compared with control; *P<0.05 compared to β-GP alone.
Control β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
p-Akt / t-Akt (% of control)
0 100 200 300 400
-GP + Xanthohumol (M)
#
*
Control β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
p-PI3K / PI3K (% of control)
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
-GP + Xanthohumol (M)
##
* *
*
Fig. 8 Xanthohumol attenuated β-GP-induced phosphor-PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Representative Western blot of p-Akt, Akt, p-PI3K and PI3K protein expressions. VSMCs were treated with β-GP (10 mM) without or with xanthohumol for 48 h. Protein bands were quantitated by desitometric analysis and normalized for variations in β-actin protein levels. The bar represents the mean ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 compared with control; *P<0.05 compared to β-GP alone.
Control β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
DCFH-DA Fluorescence intensity (% of control)
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
-GP + xanthohumol
##
*
(M)
*
*
Fig. 9 Xanthohumol attenuates β-GP-induced ROS production. Production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was measured by DCFH-DA. The bar represents the mean ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments.
##P<0.01 compared with control; *P<0.05 compared to β-GP alone.
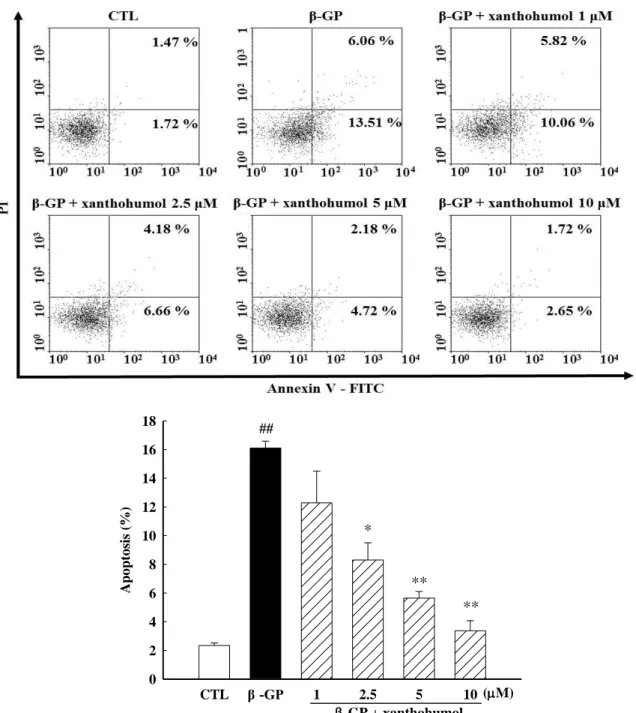
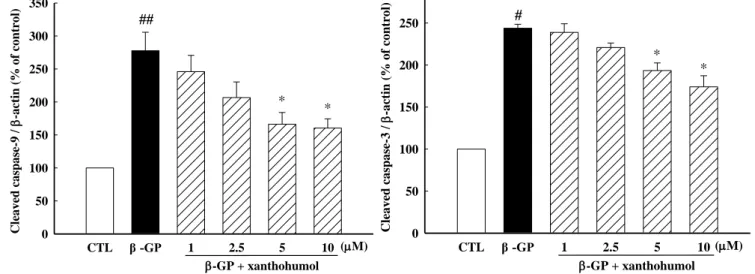
6. 黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 對細胞程式凋亡及相關蛋白的影響
根據研究顯示,細胞凋亡的活化會產生血管鈣化。為了進一步評估黃腐醇對細胞凋亡及相關蛋白 的影響,我們先用annxein V 和PI雙染搭配流式細胞儀進行分析偵測細胞凋亡率。細胞給予β-GP與不同 濃度的xanthohumol作用72小時後,進行染色與分析。由【Fig. 10】結果顯示,β-GP組可引起明顯之細 胞凋亡現象 (P<0.01),加入黃腐醇後可以有效地減少β-GP 引起之細胞凋亡現象。進一步利用西方墨 點法觀察細胞 caspase-3 和 caspase-9 之蛋白質表現量,由【Fig. 11】結果顯示,β-GP組可明顯活化細 胞內caspase-3 和 caspase-9,但 在5 M或10 M黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)作用下可以有效抑制caspase-3 和 caspase-9的活化 (P<0.05)。以上結果顯示黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 或許透過抑制細胞凋亡來防止磷 酸鹽誘導血管平滑肌細胞鈣化的現象。
CTL β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
Apoptosis (%)
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
-GP + xanthohumol
##
*
**
**
(M)
Fig. 10 Xanthohumol suppresses β-GP-induced apoptosis. Cells were cultured with or without β-GP in the presence or absence of different concentrations of xanthohumol for 3 days. Apoptosis rates of VSMCs were determined by flow cytometry following Annexin V-FITC and Propidium Iodide (PI) staining. The bar represent the mean ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments. ##P<0.01 compared with control; *P<0.05,
**P<0.01 compared to β-GP alone.
CTL β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
Cleaved caspase-9 / -actin (% of control)
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350
-GP + xanthohumol
##
* *
(M) CTL β -GP 1 2.5 5 10
Cleaved caspase-3 / -actin (% of control) 0 50 100 150 200 250
-GP + xanthohumol
#
*
*
(M)
Fig. 11 Xanthohumol suppresses -GP-induced activation of caspases. Representative Western blot of caspase-3 and -9. Protein bands were quantitated by desitometric analysis and normalized for variations in β-actin protein levels. The bar represent the mean ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments. #P<0.05, ##P
<0.01 compared with control; *P<0.05 compared to β-GP alone.
四、討論
血管鈣化是老年人、粥狀動脈硬化、高血壓和糖尿病患者中最常被發現的病理變化。血管平滑肌 細胞可以轉分化為合成/成骨細胞樣表現型,從而促進血管鈣化的發生。本研究主要目的為探討黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 對血管平滑肌細胞分化為類成骨細胞之影響,並進一步研究所涉及的作用機轉為何。我 們利用大鼠胸主動脈血管平滑肌細胞以β-glycerophosphate誘發的血管鈣化之細胞實驗模式。由實驗結 果我們發現黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)可抑制成骨細胞分化標記BMP-2、β-catenin和Runx-2的蛋白質表現。
另外,加入黃腐醇後會減少細胞內ROS的生成,透過PI3K/AKT路徑減少Runx-2轉錄因子的表現和活 性。這些發現第一次證明黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)可以透過阻斷BMP/β-catenin和PI3K/AKT訊息傳遞路徑 抑制成骨細胞分化的標記和鈣化表現。因此,黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)為具有潛力的植物化學成分可用來 預防心血管疾病。
幾種成骨細胞表現型基因已被認為是成骨細胞分化的標誌物,例如ALP和Runx-2 (Liu et al., 2016)。
實驗結果顯示黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)在β-glycerophosphate誘導的大鼠血管平滑肌細胞分化模型中顯著 抑制BMP-2和Runx-2表現並減少Alizarin Red S 與Von Kossa染色,表明黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)可以抑制 成骨細胞分化和礦化基質的產生。轉錄因子Runx-2在血管鈣化過程中扮演極重要的角色,Runx-2會受 到許多訊息傳遞路徑的調控,包括BMP和Wnt/β-catenin訊息傳遞路徑 (Zhan et al., 2014)。藉由活化轉 錄因子Runx-2,可增加成骨細胞分化相關蛋白質的產生,包括有collagen type Ι、ALP和OCN等。在我 們的研究結果中,黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)可以有效的抑制Runx-2蛋白質的表現。
Wnt信號在血管鈣化中具有關鍵作用 (Rong et al., 2014)。 Wnt/β-catenin訊息路徑的活化可以增加 BMP-2的表達並刺激血管平滑肌細胞分化為類成骨細胞。血管鈣化是血管平滑肌細胞轉化成成骨細胞 的活性過程的一部分。 在這項研究中,我們嘗試調查黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)和Wnt/β-catenin訊息路徑之 間的關係。Wnt訊息傳遞路徑主要分為兩種類型: Canonical和non-Canonical,只有Canonical Wnt路徑需 透過β-catenin來傳遞訊息 (Gao et al., 2014)。Canonical Wnt/β-catenin路徑被認為與造骨細胞分化過程較 相關。在Canonical Wnt/β-catenin路徑中,Wnt會結合在穿膜受體Frizzled(Fzd)和co-receptor LRP5/6上,
接著會活化細胞內Dishevelled(DVL)來抑制glycogen synthase kinase 3β(GSK3β)的磷酸化,進而抑 制β-catenin的降解。β-catenin是這個訊息調控路徑下游非常重要的一個調控者,在正常情形下,細胞質 中游離態的β-catenin會經由proteosome-dependent之機轉降解。當GSK3β使β-catenin在細胞中穩定下來後 會堆積於細胞質並且進入細胞核與TCF/LEF 結合,共同去調控目標基因,進行轉錄作用 (Hill et al., 2005)。在研究中顯示,當β-catenin和TCF/LEF結合後,會活化Runx2啟動子上的基因轉錄,Runx2也會 與TCF/LEF形成複合物,這個複合物會與骨骼發育重要調節者之一的FGF18 (fibroblast growth factor) 的 啟動子(promoter)結合,進而促進FGF18表現。結果顯示投予黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)可減少細胞中Active
β-catenin的表現,顯示黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)可以抑制Wnt/β-catenin訊息傳遞路徑。
我們假設黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)可以透過阻斷BMP和Wnt/β-catenin訊息傳遞路徑抑制成骨細胞分 化的標記和鈣化表現。 β-GP暴露活化Wnt/β-catenin路徑並抑制胞質內β-catenin的降解。 因此,更多的 游離β-catenin可以進入細胞核並激活BMP基因,其隨後誘導BMP-2的高表現。 BMP-2刺激活化Runx-2 的轉錄作用。此外,黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 抑制β-catenin的表現,並且還引起隨後的下游BMP-2被抑制,
進而抑制Runx-2。在這項研究中,我們不能確定黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 和BMP-2與Wnt受體之間的關 係。此外,Wnt信號通路的作用是廣泛和複雜的。 我們需要進一步研究以確認黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 是否通過此途徑影響其他病理過程。黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)對BMP和Wnt/β-catenin路徑的影響是有希望 成為新的治療靶標以防止血管系統的鈣化。
血管鈣化與細胞凋亡有密切相關。根據先前的研究報告指出發炎的過程會促使蛋白酶分解細胞外 基質,會導致血管平滑肌細胞釋放裝載有ALP和annexin 2 (Anx 2) 的基質小泡,而提高他們的鈣化潛 力。這些基質小泡起源是未知的,它們可能起源於質膜起泡或透過融合多泡體 (multivesicular bodies, MVBs) 與質膜來釋放。因為這些基質小泡釋放的結果能夠比細胞凋亡過程中釋放的凋亡小體更具有礦 化能力增強細胞鈣化的作用(Shanahan CM, 2013)。Caspase為細胞凋亡過程中非常重要的媒介,普遍以 未活化狀態(inactive form)存在於細胞質,必須藉由其他蛋白酶(proteases)、其他caspases或自行水解成 活化態(active form),隨後才得以進行細胞凋亡的工作。當細胞受到細胞外或細胞內的壓力及傷害時,
像是:放射性輻射、缺氧、藥物、DNA damage等,會使粒線體膜電位下降。而此路徑中最重要的是Bcl-2 家族,其中Bcl-2位於粒線體膜的外層,調控細胞的存活,另外會促使 Cytochrome C從粒線體的 intermembrane space釋放到細胞質中,與Apaf-1和Caspase-9結合刺激形成apoptosome,之後ATP進而活 化Caspase-9的複合物,Caspase-9也促使下游的caspase活化,最後誘導走向細胞凋亡。在西方墨點法中,
我們發現β-GP可以促使caspase-9 與 caspase-3蛋白質活化,我們發現細胞凋亡蛋白Cleaved Caspase-9 與 Cleaved Caspase-3會隨著黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)濃度的增加,降低其蛋白表現量,在流式細胞儀分析 中,發現投予黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)會抑制 β-GP 引起的血管平滑肌細胞走向程序性凋亡。總結以上結 果可得知,黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)可能藉由抑制caspase-9 和 caspase-3活化而降低 β-GP 引起在血管平 滑肌細胞中引起的細胞凋亡來改善細胞鈣化的作用。
在這項研究中,實驗證實黃腐醇於體外試驗中可以有效地減少大鼠胸主動脈血管平滑肌細胞以 β-glycerophosphate 誘發的血管鈣化現象並透過抑制血管平滑肌細胞分化為類成骨細胞和減少鈣過量 沉積與抑制細胞凋亡來防止磷酸鹽誘導血管平滑肌細胞鈣化的現象。然而,這些體外研究數據仍需要 利用臨床前動物模型進一步驗證。
五、參考文獻
Al-Aly Z. Phosphate, oxidative stress, and nuclear factor-κB activation in vascular calcification. Kidney Int.
2011 May;79(10):1044-7.
Byon CH, Javed A, Dai Q, Kappes JC, Clemens TL, Darley-Usmar VM, McDonald JM, Chen Y. Oxidative stress induces vascular calcification through modulation of the osteogenic transcription factor Runx2 by AKT signaling. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:15319–15327.
Doddapattar P, Radović B, Patankar JV, Obrowsky S, Jandl K, Nusshold C, Kolb D, Vujić N, Doshi L, Chandak PG, Goeritzer M, Ahammer H, Hoefler G, Sattler W, Kratky D. Xanthohumol ameliorates atherosclerotic plaque formation, hypercholesterolemia, and hepatic steatosis in ApoE-deficient mice.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013 Oct;57(10):1718-28.
Dorn, C.; Massinger, S.; Wuzik, A.; Heilmann, J.; Hellerbrand, C. Xanthohumol suppresses inflammatory response to warm ischemia–reperfusion induced liver injury. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 94, 10–16.
Gao Y., Song C., Hui L., et al. Overexpression of RNF146 in non-small cell lung cancer enhances proliferation and invasion of tumors through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(1).
e85377.
Glass DA 2nd, Bialek P, Ahn JD, Starbuck M, Patel MS, Clevers H, Taketo MM, Long F, McMahon AP, Lang RA, Karsenty G. Canonical Wnt signaling in differentiated osteoblasts controls osteoclast differentiation. Dev Cell. 2005 May;8(5):751-64.
Hill T. P., Später D., Taketo M. M., Birchmeier W., Hartmann C. Canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling prevents osteoblasts from differentiating into chondrocytes. Developmental Cell. 2005;8(5):727–738.
Hirata H, Uto-Kondo H, Ogura M, Ayaori M, Shiotani K, Ota A, Tsuchiya Y, Ikewaki K. Xanthohumol, a hop-derived prenylated flavonoid, promotes macrophage reverse cholesterol transport. J Nutr Biochem.
2017 Sep;47:29-34.
Lee KM, Kang HA, Park M, Lee HY, Choi HR, Yun CH, Oh JW, Kang HS. Interleukin-24 attenuates β-glycerophosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by inhibiting apoptosis, the expression of calcification and osteoblastic markers, and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Nov 9;428(1):50-5.
Lin GL, Hankenson KD. Integration of BMP, Wnt, and notch signaling pathways in osteoblast differentiation.
J Cell Biochem.0 2011 Dec;112(12):3491-501.
Liu R, Heiss EH, Schachner D, Jiang B, Liu W, Breuss JM, Dirsch VM, Atanasov AG. Xanthohumol Blocks Proliferation and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Vitro and Reduces Neointima Formation in Vivo. J Nat Prod. 2017 Jul 28;80(7):2146-2150.
Liu Y, Lin F, Fu Y, Chen W, Liu W, Chi J, Zhang X, Yin X. Cortistatin inhibits calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by depressing osteoblastic differentiation and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Amino Acids. 2016 Nov;48(11):2671-2681.
Miranda CL, Elias VD, Hay JJ, Choi J, Reed RL, Stevens JF. Xanthohumol improves dysfunctional glucose and lipid metabolism in diet-induced obese C57BL/6J mice. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016 Jun 1;599:22-30.
Miranda, C.L.; Stevens, J.F.; Ivanov, V.; McCall, M.; Frei, B.; Deinzer, M.L.; Buhler, D.R. Antioxidant and prooxidant actions of prenylated and nonprenylated chalcones and flavanones in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3876–3884.
Moe SM, Reslerova M, Ketteler M, O'neill K, Duan D, Koczman J, Westenfeld R, Jahnen-Dechent W, Chen NX. Role of calcification inhibitors in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Kidney Int. 2005 Jun;67(6):2295-304.
Montes de Oca A, Madueño JA, Martinez-Moreno JM, Guerrero F, Muñoz-Castañeda J, Rodriguez-Ortiz ME, Mendoza FJ, Almaden Y, Lopez I, Rodriguez M, Aguilera-Tejero E. Highphosphate- induced calcification is related to SM22α promoter methylation in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2010; 25:1996–2005.
Pai AS, Giachelli CM. Matrix remodeling in vascular calcification associated with chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010; 21:1637–1640.
Plazar, J.; Žegura, B.; Lah, T.T.; Filipič, M. Protective effects of xanthohumol against the genotoxicity of benzo(a)pyrene (BaP), 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline (IQ) and tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BOOH) in HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2007, 632, 1–8.
Rong S., Zhao X., Jin X., et al. Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease is induced by bone morphogenetic protein-2 via a mechanism involving the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2014;34(6):2049–2060.
Sage AP, Tintut Y, Demer LL. Regulatory mechanisms in vascular calcification. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010 Sep;7(9):528-36.
Schempp H, Vogel S, Hückelhoven R, Heilmann, J. Re-evaluation of superoxide scavenging capacity of xanthohumol. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 1435–1444.
Shao JS, Cheng SL, Sadhu J, Towler DA. Inflammation and the osteogenic regulation of vascular calcification:
a review and perspective. Hypertension. 2010 Mar;55(3):579-92.
Shroff RC, McNair R, Figg N, Skepper JN, Schurgers L, Gupta A, Hiorns M, Donald AE, Deanfield J, Rees L, Shanahan CM. Dialysis accelerates medial vascular calcification in part by triggering smooth muscle cell apoptosis. Circulation. 2008; 118:1748–1757.
Son B, Kozaki K, Iijima K, Eto M, Nakano T, Akishita M, Ouchi Y. Gas6/Axl-PI3K/Akt pathway plays a central role in the effect of statins on inorganic phosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007; 556:1–8.
Son BK, Kozaki K, Iijima K, Eto M, Kojima T, Ota H, Senda Y, Maemura K, Nakano T, Akishita M, Ouchi Y. Statins protect human aortic smooth muscle cells from inorganic phosphate-induced calcification by restoring Gas6-Axl survival pathway. Circ Res. 2006; 98:1024–1031.
Takada I, Kouzmenko AP, Kato S. Wnt and PPARgamma signaling in osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis.
Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009 Aug;5(8):442-7.
Yiu AJ, Callaghan D, Sultana R, Bandyopadhyay BC. Vascular Calcification and Stone Disease: A New Look towards the Mechanism. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2015;2(3):141-164.
Zhao MM, Xu MJ, Cai Y, Zhao G, Guan Y, Kong W, Tang C, Wang X. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote p65 nuclear translocation mediating high-phosphate-induced vascular calcification in vitro and in vivo. Kidney Int. 2011; 79:1071–1079.
Zhan JK, Tan P, Wang YJ, Wang Y, He JY, Tang ZY, Huang W, Liu YS. Exenatide can inhibit calcification of human VSMCs through the NF-kappaB/RANKL signaling pathway. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014 Nov 19;13:153.
科技部補助專題研究計畫出席國際學術會議心得報告
日期:107 年 10 月 2 日
一、 參加會議經過
此次參加第 18 屆世界基礎與臨床藥理學大會是經由台灣藥理學會網站公告後得知,
由於此會議在日本京都舉行因此可以趁機和亞洲的藥理學者與藥師們相互討論交 流。此次會期自 7 月 1 日 ~ 6 日在京都著名的國立京都國際會館 (kyoto international conference center)舉行。主辦單位除了早上與下午的學術專題報告外,特別於中午午 餐時段安排了壁報展示 (poster presentation),提供與會學者進行壁報討論,提供餐點 讓學者在輕鬆愉悅的心情下進行學術交流。本次大會安排了 4 天 Poster Session 的時 段,由於此次張貼的內容是關於血管鈣化,因為被歸類 Cardiovascular System。在這 5 天中我和許多國際學者相互討論交流研究心得,藉由主題演講、專題討論、 臨床 病例研討等活動進行交流。 對於促進世界藥學與藥理學界的往來及提昇彼此學術的 水平扮演了重要的平台工作。
計畫編號 MOST-106-2320-B-041-003
計畫名稱 黃腐醇對於大鼠血管鈣化之影響及其相關機轉研究 出國人員
姓名 劉淑芬 服務機構
及職稱 嘉南藥理大學藥學系/教授 會議時間 107 年 7 月 1 日至
107 年 7 月 6 日 會議地點 日本 京都
會議名稱 (英文) 18th World Congress of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (WCP2018 KYOTO)
發表題目 (英文) Xanthohumol attenuates beta-glycerophosphate-induced vascular calcification by inhibiting osteoblastic differentiation
附件六
二、 與會心得
本次大會中的 opening Lectures 是邀請到 2018 諾貝爾生理與醫學獎得主-日本免疫學 家 Tasuku Honjo 教授,他的演講主題是 ”Future of cancer immunotherapy by PD-1 blockade” 最令人印象深刻。在演講中 Tasuku Honjo 教授指出,癌症每年導致數百萬 人的死亡,是人們面臨的最大挑戰,而他的研究方向則是透過活化人體本身的免疫 系統來攻擊腫瘤細胞,並建立了一個革命性的癌症治療方式。免疫力的發展是為了 保護我們的身體免受外來顆粒的侵害,包括細菌和病毒。雖然負責獲得性免疫的效 應細胞(主要是 T 細胞和 B 細胞)能夠區分自身和非自身,但由於不完美的中樞耐 受性,它們有時會攻擊身體的組織。開發了幾種免疫檢查點來限制這些細胞的過度 活化。最重要的免疫檢查點之一是程序性細胞死亡-1(PD-1),其主要在活化的淋巴 細胞上表達。由於其配體 (PD-Ligands, PD-Ls) 在體內廣泛表達並影響對自身和外源 抗原的反應,因此控制 PD-1 / PD-L 相互作用可以控制多種免疫相關疾病,如自身免 疫疾病、病毒感染,和癌症。目前,PD-1 / PD-L1 阻斷策略已經應用於臨床癌症治療,
提供了 PD-1 信號是人類癌症免疫逃逸的主要因素之一的證據。 PD-1 阻斷在癌症免 疫療法中的顯著功效,有望通過 PD-1 信號調節控制其他免疫疾病。在這場演講中,
Tasuku Honjo 教授總結了 PD-1 的歷史,隨後的基礎研究以及它們在臨床中的應用。
他與研究團隊於 1992 年發現了一系列可能參與程式性細胞死亡的 cDNA,其中,第
一個基因被命名為 PD-1(programmed cell death protein 1) ,後來發現 PD-L1 會抑制 T
細胞的功能,並發現在腫瘤細胞中 PD-L1 的 mRNA 濃度增高,進一步研發出來的抗
癌藥物 PD-1 抑制劑 Opdivo (nivolumab) 與 Keytrud (pembrolizumab) 已於 2014 年
在日本與美國通過上市,全球開始掀起一股癌症免疫療法的新浪潮。
三、 發表論文全文或摘要
Background: Vascular calcification is highly correlated with cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. It is characterized by phenotype transition from vascular smooth muscles (VSMCs) to osteoblast-like cells. Xanthohumol is the most abundant prenylated flavonoid in hops. Several studies have identified the protective effects of xanthohumol on the cardiovascular and metabolic systems; however research on the effect and mechanisms of xanthohumol on vascular calcification is still quite rare. Therefore, we used beta-glycerophosphate to induce calcification in rat VSMCs to determine the effects of xanthohumol on osteoblastic differentiation and VSMCs mineralization in vitro. Methods:
Incubation of VSMCs with beta-glycerophosphate for 14 days induced an osteoblast-like morphological change. The mineralization was visualized by Von Kossa and Alizarin red staining. Alkaline phosphatase activity (ALP) and calcium content were also detected. The protein expression of osteoblastic differentiation markers and signaling pathways were determined by western blot and immunofluorescence. Results: Our results showed that xanthohumol significantly attenuated the osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization of VSMCs due to decreased ALP activity, calcium content and sodium-phosphate cotransporter Pit-1, Runx2, beta-catenin, and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) protein expressions. Furthermore, xanthohumol inhibited beta-glycerophosphate-induced protein expressions of MMP-9 and p-ERK1/2, which are known contributors to vascular calcification. Conclusion: Xanthohumol attenuated vascular calcification by suppressing osteoblastic differentiation markers and calcification phenotype through the blockade of BMP-2/Smad1/5/8 and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways. The present study will show for the first time that xanthohumol can act as a potential phytochemical in preventing or treating calcification-associated vascular diseases.
四、 建議
參加這次的學會時與一些其他國家的相關研究領域學者進行討論,感到獲益匪淺,
獲得一些改進的建議對自己的研究有所幫助,很感謝科技部經費補助,希望將來能 有機會能再參與類似的國際會議。建議校方及國內相關學會,能秉持禮尚往來,促 進交流的原則,於國內舉辦藥理及藥學專業學術研討會時,也能主動積極地邀請世 界專業團體來台參與相關的學術研討會,以擴大交流的品質及範圍。對於提升本校 的國際聲譽與學術地位應有幫助。
五、 攜回資料名稱及內容
大會議程手冊與摘要書本
六、 其他
106年度專題研究計畫成果彙整表
計畫主持人:劉淑芬 計畫編號:106-2320-B-041-003- 計畫名稱:黃腐醇對於大鼠血管鈣化之影響及其相關機轉研究
成果項目 量化 單位
質化
(說明:各成果項目請附佐證資料或細 項說明,如期刊名稱、年份、卷期、起 訖頁數、證號...等)
國
內 學術性論文
期刊論文 0
研討會論文 1 篇
前往日本京都參加18th World Congress of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (WCP2018 KYOTO)。發表方式: poster presentation,論文題目: Xanthohumol attenuates beta-glycerophosphate- induced vascular calcification by inhibiting osteoblastic
differentiation。摘要如下:
Background: Vascular calcification is highly correlated with
cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. It is characterized by phenotype transition from vascular smooth muscles (VSMCs) to
osteoblast-like cells. Xanthohumol is the most abundant prenylated flavonoid in hops. Several studies have identified the protective effects of xanthohumol on the cardiovascular and metabolic systems; however research on the effect and mechanisms of
xanthohumol on vascular
calcification is still quite rare.
Therefore, we used beta- glycerophosphate to induce calcification in rat VSMCs to determine the effects of xanthohumol on osteoblastic differentiation and VSMCs
mineralization in vitro. Methods:
Incubation of VSMCs with beta- glycerophosphate for 14 days induced an osteoblast-like morphological change. The
mineralization was visualized by Von Kossa and Alizarin red
staining. Alkaline phosphatase activity (ALP) and calcium content were also detected. The protein expression of osteoblastic differentiation markers and
signaling pathways were determined by western blot and
immunofluorescence. Results: Our results showed that xanthohumol significantly attenuated the osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization of VSMCs due to decreased ALP activity, calcium content and sodium-phosphate cotransporter Pit-1, Runx2, beta- catenin, and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) protein
expressions. Furthermore, xanthohumol inhibited beta- glycerophosphate-induced protein expressions of MMP-9 and p-ERK1/2, which are known contributors to vascular calcification. Conclusion:
Xanthohumol attenuated vascular calcification by suppressing osteoblastic differentiation
markers and calcification phenotype through the blockade of BMP-
2/Smad1/5/8 and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways. The present study will show for the first time that xanthohumol can act as a potential phytochemical in preventing or treating
calcification-associated vascular diseases.
專書 0 本
專書論文 0 章
技術報告 0 篇
其他 0 篇
智慧財產權 及成果
專利權 發明專利 申請中 0
件
已獲得 0
新型/設計專利 0
商標權 0
營業秘密 0
積體電路電路布局權 0
著作權 0
品種權 0
其他 0
技術移轉 件數 0 件
收入 0 千元
國 外
學術性論文
期刊論文 0
研討會論文 0 篇
專書 0 本
專書論文 0 章
技術報告 0 篇
其他 0 篇
智慧財產權 及成果
專利權 發明專利 申請中 0
件
已獲得 0
新型/設計專利 0
商標權 0
營業秘密 0
積體電路電路布局權 0
著作權 0
品種權 0
其他 0
技術移轉 件數 0 件
收入 0 千元
參 與 計 畫 人 力
本國籍
大專生 0
人次
碩士生 0
博士生 0
博士後研究員 0
專任助理 1
(1)第一個月培養大鼠胸主動脈血管平滑 肌細胞 (primary culture) 與採購實驗 藥品及實驗所需物品。
(2)前三個月進行細胞存活率、Alkaline phosphatase activity assay、Calcium deposition、細胞礦物化染色法
(Alizarin Red S & Von Kossa staining)。
(3)然後四個月再進行西方墨點法實驗
,測定黃腐醇 (xanthohumol) 對細胞鈣 化指標BMP-2, Runx2, MMP-2 & MMP-9等 蛋白質表現與BMP-2/Smad1/5/8、
Wnt/β-catenin等相關路徑的活化和已 知於加速血管鈣化上扮演重要角色之轉 錄因子Runx2表現之影響。
(4)以三個月時間進行細胞凋亡相關實驗 (Annexin V/PI 的雙染法 & caspase- 3/-9 activity)、細胞內活性氧屬 (ROS) 的含量測定與西方墨點法分析 Bax、Bcl-2、caspases,探討黃腐醇 (xanthohumol)對細胞凋亡的影響。
(5)最後的月份為整理實驗數據與繪圖
非本國籍 大專生 0