Appendix Ⅰ
The Relationship between the Elements of the Jones Matrix and a Waveplate
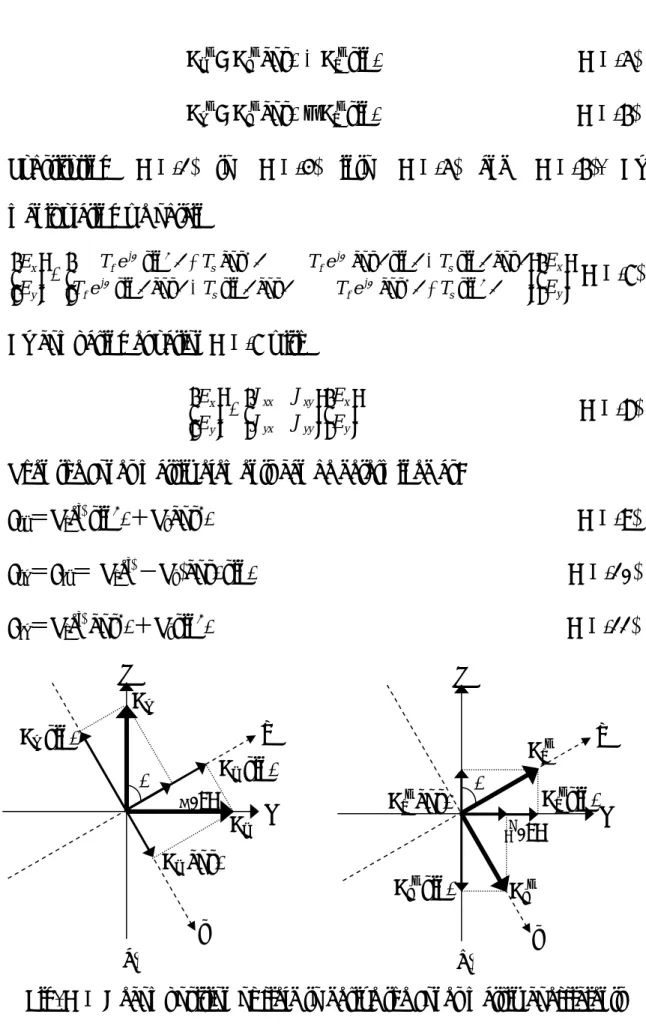
Suggest that a waveplate with retardation ∆ is orientated at the angle θ.
As shown in Fig. AⅠ(a), considering the orthogonal field components Ex and Ey impinging on a birefringence medium which has fast and slow axes (f and s) orientated at angle θ. The total field Ef, and Es along the medium axis is therefore can be expressed as [A1]:
Ef = Ex sinθ + Ey cosθ (AⅠ-1) Es = Ex cosθ - Ey sinθ (AⅠ-2) These fields propagate through the medium with different velocities and possibly different attenuation. If we assume the s component field has a zero relative phase shift with respect to the phase lead of the f component field, then the exit fields Ef’ and Es’ , as shown in Fig. Fig. AⅠ(b), are given by
Ef’ = Ef Tfejφ (AⅠ-3) Es’ = Es Ts (AⅠ-4) where φ is the phase lead ( for instance, λ/2 waveplate would have a phase lead of π ) and Tf and Ts are field amplitude transmission coefficients. With respect to the x and y axes, the output fields Ex’ and Ey’ are therefore given by
Ex’ = Es’ cosθ + Ef’ sinθ (AⅠ-5) Ey’ = Es’ cosθ – Ef’ sinθ (AⅠ-6) Substituting (AⅠ-1) to (AⅠ-4) into (AⅠ-5) and (AⅠ-6). By manipulating we obtain
⎥⎦
⎢ ⎤
⎣
⎡
⎥⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢⎢
⎣
⎡
+
−
−
= +
⎥⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢⎢
⎣
⎡
y x
s j
f s
j f
s j
f s
j f
y x
E E T
e T T
e T
T e
T T
e T E
E
θ θ
θ θ θ
θ
θ θ θ
θ θ
θ
ϕ ϕ
ϕ ϕ
2 2
2 2
' '
sin cos
cos sin cos
sin
cos sin sin
cos cos
sin (AⅠ-7)
By comparing equation AⅠ-7 with
⎥⎦
⎢ ⎤
⎣
⎥⎡
⎦
⎢ ⎤
⎣
=⎡
⎥⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢⎢
⎣
⎡
y x
yy yx
xy xx
y x
E E J J
J J E
E
' '
(AⅠ-8)
Then the Jones matrix elements can be determined as:
Jxx=Tfejφsin2θ+Tscos2θ (AⅠ-9) Jxy=Jyx=(Tfejφ-Ts)cosθsinθ (AⅠ-10) Jyy=Tfejφcos2θ+Tssin2θ (AⅠ-11)
s θ
Y
Ey sinθ
Ey cosθ
Ex sinθ
Ex cosθ Ey
Ex
Es’ Ef’
Ef’ sinθ X
Es’ sinθ
Es’ cosθ Ef’ cosθ
Y
θ
s
f f
X
(a) (b)
Fig. AⅠ Decomposition of field to derive the Jones matrix coefficients
Appendix Ⅱ
The Derivation of Power Intensity of a
Symmetric Resonator Laser Constructed of Fiber Loop Mirrors from Electrical Field
As shown in Fig. 2-6, the transmission coefficient, reflection coefficient, reflectance and transmittance from the discussion in chapter 2 can be expressed as [10]:
t = (1-2K)(1-γ)e(-α+jβ)L (2-13) jr = 2j K 1−K (1-γ) e(-α+jβ)L (2-14) R = r*r = 4 K(1-K) (1-γ)2e-2αL (2-15) T = t*t = (1-2K)2(1-γ)2e-2αL (2-16) Define the one round-trip gain parameter G as:
G= g×e(−αg+jβ)L2 (2-20) Define the one round-trip optical power transmittance coefficient of the WDM MUX and DeMUX as:
αWij =αWi×αWj (2-21) If the input amplitude of the electrical field is Ein, then we can find that the output amplitude of the electrical field Eout can be denoted as [8]:
( )2 5 5 ...
3 3+ −
−
=tt E G rrtt E G tt rr E G
Eout i j inαWij i j i j inαWij i j i j inαWij (2-22)
in Wij
j i
Wij j i
out E
G r
r
G t
E t 2 2
1 α
α
= + (2-23) Then the output power intensity can be given as:
2 2 2 2 2
1 i j Wij in
Wij j i out
out E
G r
r
G t E t
I ×
= +
= α
α (2-24)
Now we derive every term in Eq. 2-24 by substituting Eq. 2-13 to Eq. 2-16 and Eq. 2-20 into Eq. 2-24. First, the value of Ein 2 is equal to Iin. Then
* 2 2 2 2
2
2 2 1 1
1 ⎟⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
⎟ +
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
= +
+ rr G
G t t G
r r
G t t G
r r
G t t
Wij j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
α α α
α α
α (AⅡ-1)
⎟⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
⎟ +
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
= +
+ * * 2* 2
* *
*
* 2 2
2
2 2 1 1
1 r r G
G t
t G r
r
G t t G
r r
G t t
Wij j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
α α α
α α
α (AⅡ-2)
⎟⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
+ +
= +
+ 2 2 * * 2 2 * * 4 4
2 2
* 2 *
2 2 1
1 rr G r r G rr r r G
G t
t t t G
r r
G t t
Wij j j i i Wij
j i Wij
j i
Wij j j i i
Wij j i
Wij j i
α α
α
α α
α (AⅡ-3)
⎟⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
+ +
= +
+ 2 2 * * 2 2 4 4
2 2 2
2 2 1
1 rr G r r G RR G
G T
T G
r r
G t t
Wij j i Wij
j i Wij
j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
α α
α
α α
α (AⅡ-4)
From Eq. 2-20,
) * ( )
2 (g e( g j L2)(g e g j L2)
G = × −α + β × −α + β (AⅡ-5) )
)(
( ( ) 2 ( ) 2
2 g j L g j L
e g e
g
G = × −α + β × −α − β (AⅡ-6)
2 2
2
2 gL
e g
G = − α (AⅡ-7)
4 2
4
4 gL
e g
G = − α (AⅡ-8) Moreover, from Eq. 2-14,
] )
1 ( 1 2
][
) 1 ( 1 2
[ ) )(
(jri jrj = j Ki −Ki −γi e(−αi+jβ)L1 j Kj −Kj −γ j e(−αj+jβ)L3
) ) (
( 1 3 1 3
) 1 )(
1 ( ) 1 )(
1 (
4 i j i j i j L L j L L
j
ir K K K K e e
r =− − − − − − i + j +
− γ γ α α β
) ) (
( 1 3 1 3
) 1 )(
1 ( ) 1 )(
1 (
4 i j i j i j L L j L L
j
ir K K K K e e
r = − − −γ −γ −αi +αj β + (AⅡ-9)
* *
* j ( j i)
i r r r
r =
) ) (
(
*
* j 4 i j (1 i)(1 j)(1 i)(1 j) L1 L3 j L1 L3
i r K K K K e e
r = − − −γ −γ −αi +αj − β + (AⅡ-10)
From Eq. AⅡ-4 to Eq. AⅡ-10,
2 2
) ) (
(
) ) (
2 ( 2
* 2 *
2
]}
) 1 )(
1 ( ) 1 )(
1 ( 4
[
] )
1 )(
1 ( ) 1 )(
1 ( 4
{[
3 3 1
1
3 3 1
1
G
e e
K K
K K
e e
K K
K K G
r r G r
r
Wij
L L L j L j i
j i
j i
L L L j L j i
j i
j i Wij
j i Wij
j i
j i
j i
α
γ γ
γ γ α
α
α β α
α β α
+ + −
− + +
−
−
−
−
−
+
−
−
−
−
= +
2 2 ) ( ) (
) 2 (
2
* 2 *
2
]}
[
) 1 )(
1 ( ) 1 )(
1 ( 4
{
3 1 3
1
3 1
G e
e
e K
K K
K G
r r G r
r
Wij L
L j L L j
L L j i j i
j i Wij
j i Wij
j i
j i
α
γ γ α
α
β β
α α +
− +
+
−
+
−
−
−
−
= +
(AⅡ-11) Derived from Euler equation:
)) (
cos(
2 1 3
) ( )
( 1 3 1 3
L L e
ejβ L+L + −jβ L+L = β +
(AⅡ-12)
From Eq. 2-15,
) (
2 2
2 (1 )(1 ) 1 3
) 1 )(
1 (
16 i i i j j j L L
j i
j
e i
K K
K K
R
R = − −γ − −γ − α +α
)
( 1 3
) 1 )(
1 ( ) 1 )(
1 (
4 i j i j i j L L
j i
j
e i
K K
K K R
R = − − −γ −γ −α +α (AⅡ-13)
Substituting Eq. AⅡ-12, Eq. AⅡ-13 and Eq. AⅡ-7 into Eq. AⅡ-11, then ))
( cos(
2 2 2 2 1 3
2 2
* 2 *
2 2
L L e
R R g G
r r G r
ri jαWij + i j αWij = αWij i j − αgL β + (AⅡ-14) Substituting Eq. AⅡ-14, Eq. AⅡ-7 and Eq. AⅡ-8 into Eq. AⅡ-4, then
⎟⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
+ +
= +
+ − −
−
2 2
2
4 4 4 3
1 2 2
2
2 2 2 2
2 2
)) (
cos(
2
1 1 Wij i j L i j Wij L
L Wij
j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
g g
g
e g R R L L e
R R g
e g T T G
r r
G t t
α α
α
α β
α
α α
α
⎟⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
+ +
= +
+ − −
−
2 2 2 2 3
1 2 2
2
2 2 2 2
2 2
) (
)) (
cos(
2
1 1 2 2
2
L Wij
j i L
j i Wij
L Wij
j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
g g
g
e g R
R L
L e
R R g
e g T T G
r r
G t t
α α
α
α β
α
α α
α
⎟⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
− + +
= +
+ − −
−
] 1 )) (
[cos(
2 ) 1
1 ( 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 3
2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2
2
L L e
R R g e
g R
R
e g T T G
r r
G t t
L j i Wij
L Wij
j i
L Wij
j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
g g
g
β α
α
α α
α
α α
α
From the half angle formula:
2 2 cos sin2θ =1− θ
then
⎟⎟
⎟⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
+
− +
+ = − −
−
))]
2( ( [sin 4
) 1
1 (
3 1 2 2
2 2 2 2
2 2
2 2 2 2
2 2
2 2
2
L L e
R R g e
g R R
e g T T G
r r
G t t
L j i Wij L
Wij j i
L Wij
j i
Wij j i
Wij j i
g g
g
α β α
α α
α
α α
α
(AⅡ-15)
Therefore, substitute Eq. AⅡ-15 into Eq. 2-24 and we can get the output power intensity as:
L in
j i Wij
L Wij
j i
L Wij
j i
out I
L L e
R R g e
g R
R
e g T I T
g g
g
⎟⎟
⎟⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
+
− +
= − −
−
))]
2( ( [sin 4
) 1
( 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 3
2 2 2
2 2
2
α β α
α
α α
α
(2-25)