1
行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫成果報告
類神經網路於震測圖型的強健性之辨認
The Study of Neur al Networ ks for Robust Recognition of Seismic Patter ns
計畫編號:NSC 89-2213-E-009-101
執行期限:88 年 8 月 1 日至 89 年 7 月 31 日
主持人:黃國源 交大資訊科學系 kyhuang@cis.nctu.edu.tw
一、中文摘要 多層的感知器的類神經網路被訓練後 當成分類器,而應用於震測圖型的強健性 之辨認。利用多層感知器的強健性的訓練 原理被探討。在實驗上有三類震測圖型被 用於分析:即亮點、尖滅、與水平反射的 圖型。每一類震測圖型被抽取七個與平 移、旋轉、大小均不產生變化的 Moments 作特徵值。 訓練用的圖型集合包含沒有雜訊的、 低雜訊的、和被分類錯誤的震測圖型。測 試用的圖型集合包含各種不同程度的震 測圖型。 剛開始的時候,吾人利用無雜訊與低 雜訊的震測圖型來訓練多層的感知器。在 訓練收斂後,此一網路被應用於有雜訊的 測試的震測圖型之分類。吾人選取一些有 更高雜訊而且被分類錯誤的測試用的震 測圖型加入訓練的圖型。多次反覆此種分 類與訓練。此種重新訓練能夠在更高階段 有效地增強神經網路的強健性。 最後吾人在每一訓練階段所得的神經 網路應用於實際上的 Mississippi canyon 的震測圖,作偵測與油氣構造有關的亮點 圖型。從實驗上,多層的感知器被證明在 震測圖型的辨認上有強健性的能力而且 辨認結果有助於震測解釋。 關鍵詞:類神經網路,多層的感知器,強 健性之辨認,Moments,震測圖型。 Abstr actThe multilayer perceptron of neural network is trained as a classifier and is applied to the robust recognition of seismic patterns. The principle of robust training using multilayer perceptron is described. Three classes of seismic patterns are analyzed in the experiment: bright spot,
pinch-out, and horizontal reflection patterns. Seven moments that are invariant to translation, rotation, and scale, are employed for feature generation of each seismic pattern. The training set includes noise-free, low noisy, and misclassified seismic patterns. The testing set includes seismic patterns with various noise levels. The multilayer perceptron is initially trained with the training set of noise-free and low noisy seismic patterns. After convergence of training, the network is applied to the classification of the testing set of noisy seismic patterns. Some misclassified testing seismic patterns with higher noise level are selected and added to the training set for retraining. Repeat the classification and the training through several steps. The retraining can significantly improve the robustness of the network in higher steps. Finally we apply the network at each training step to the real seismic data at Mississippi canyon, the bright spot pattern can be detected. From experiments, the multilayer perceptron is shown to have the capability of robust recognition of seismic patterns and the recognition results are encouraged to the seismic interpretation.
Keywor ds: Neural networks, multilayer
perceptron, robust recognition, moments, seismic patterns. 二、緣由與目的 類神經網路之研究,在國內外均極受 重視,其應用之領域更是相當的廣泛。近 年來,類神經網路已被廣泛的應用於地球 物理的圖型識別(Aminzadeh et al., 1994; Dysart and Pulli, 1990; Huang, 1999, 1997; Huang et al., 1987, 1989, 1992; Johnston,
2
1993; Kemp et al., 1992; McCormack et al., 1993; Michael and Smith, 1992; Schmidt and Hadsell, 1992; Poulton et al., 1989, 1992; Veezhinathan et al., 1991; Wang and Huang, 1993; Wang and Mendel, 1992; Yang and Huang, 1991),而且類神經網路 也被應用於增強影像圖型(Gupta et al., 1990; Gonzalez and Woods, 1993)與中文 字(Huang et al., 1997)的強健性的辨認。 在此吾人提出應用類神經網路於模 擬的震測圖型 與實際上在 Mississippi canyon 的震測圖上亮點圖型偵測的強健 性之辨認。所研究的類神經網路 model 為 多 層 的 感 知 器 Multilayer perceptron(MLP) (Rumelhart et al., 1986)。
三、結果與討論
(1) The principle of robust training and recognition is described. The two-layer perceptron has the capability of robust recognition. Using the misclassified patterns in the retraining, the new classification regions can accommodate those patterns into the correct class.
(2) Seven moments that are invariant to translation, rotation, and scale, are employed for feature generation of each seismic pattern and useful in the seismic recognition. (3) The analyzed seismic patterns are bright spot, pinch-out, and horizontal reflection patterns. The two-layer perceptron is used in the robust training and recognition of simulated seismic patterns in several steps and the recognition results are improved. Then applying the network of each step to real seismic data at Mississippi canyon, the bright spot pattern is detected.
(4) The distance between each testing seismic pattern and noise-free class pattern is calculated in the feature space. The selection of the misclassfied patterns into the training set must be closer to the noise-free class pattern. If the new training set can not get the convergence of the training of the network and the less number of error patterns, then we must select other
misclassified patterns into the training set for retraining.
(5) Selection of a few misclassified seismic patterns into the training set for retraining of the network can greatly reduce the number of error seismic patterns in the next classification.
(6) In the recognition of seismic patterns, we adopted Hopfield net (Huang et al., 1989), Fukushima's neocognitron (Huang and Liaw, 1992), and this paper's multilayer perceptron (MLP). The Hopfield net has a convergence problem if the training patterns are not orthonormal (Lippman, 1987). Fukushima's neocognitron is too complex in the design of the training subpatterns and the calculations of many hidden layers in the hierarchical recognition processes. Multilayer perceptron (MLP) accompanied with 7 invariant moments is convenient in the design of training patterns, and has the robust capability in seismic pattern recognition. 四、成果自評 研究內容與原計畫相符程度: 100% 達成預期目標情況: 100% 研究成果的學術或應用價值: 建立類神經 網路於震測圖型辨認之系統,及幫助探 油震測解釋 是否適合在學術期刊發表: 是 主要發現或其他有關價值: 可用於中文字 的強健性的辨認 五、參考文獻
Aminzadeh, F., Katz, S., and Aki, K., 1994, Adaptive neural nets for generation of artificial earthquake precursors: Inst. Electr. Electron. Eng., Geoscience and Remote Sensing, GE-32, 1139-1143. Dobrin, M. B., and Savit, C. H., 1988,
Introduction to geophysical prospecting: 4th ed., McGraw-Hill.
Gonzalez, R. C. and Woods, R. E., 1993, Digital Image Processing: Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., Reading,
3
Massachusetts.
Gupta, L., Sayeh, M. R., and Tammana, R., 1990, A neural network approach to robust shape classification: Pattern Recognition, 23, 563-568.
Hu, M. K., 1962, Visual pattern recognition by moment invariants: IRE Trans. Info. Theory, vol.IT-8, 179-187.
Huang, K. Y., Yen, H. T., and Han, C. S., 1997, Neural networks for robust recognition of printed Chinese characters: Computer Processing of Oriental Languages, 10, 425-442.
Huang, K. Y., 1999, Neural networks for seismic principal components analysis: IEEE Trans. on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol.37, No.1, 1999, 297-311. Johnston, D. H., 1993, Seismic attribute
calibration using neural networks: 63rd Ann. Internat. Mtg., Soc. Explor. Geophys., Expanded Abstracts, 250-253. Lippmann, R. P., 1987, An introduction to
computing with neural nets: IEEE ASSP Mag., 4, 4-22.
McCormack, M. D., Zaucha, D. E., and Dushek, D. W., 1993, First-break refraction event picking and seismic data trace editing using neural networks: Geophysics, 58, 67-78.
Poulton, M., Sternberg, B., and Glass, C., 1992, Location of subsurface targets in geophysical data using neural networks: Geophysics, 57, 1534-1544.
Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E. and Williams, R. J., 1986, Learning internal representations by error propagation, in Rumelhart, D. E., and McClelland, J. L., Eds., PDP, Vol. 1: M.I.T. Press, 318-362.
Wang, L. X. and Mendel, J. M., 1992, Adaptive minimum prediction-error deconvolution and source wavelet estimation using Hopfield neural networks: Geophysics, 57, 670-679.
Envelope Thresholding Peaks of seismogram Compress data in time direction Input seismogram
Fig. 1. Preprocessing of seismic data.
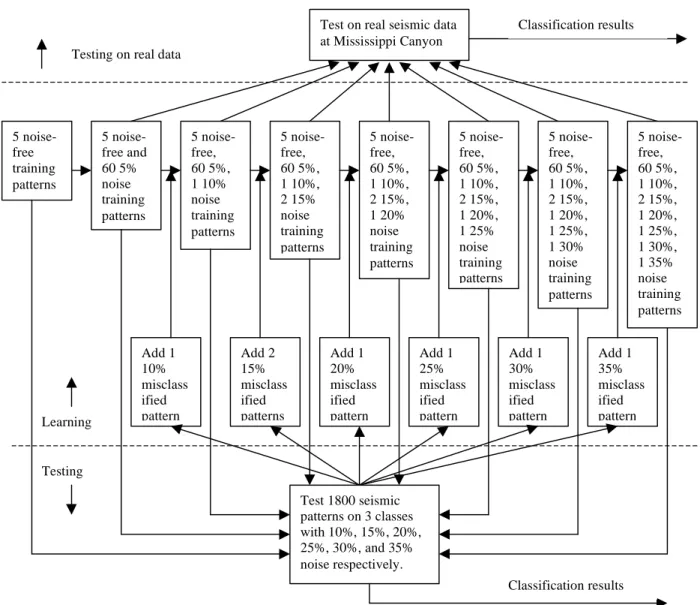
f1 f2 ••• f7 Wk j Wj i • • • i k j Input nodes Hidden nodes Output nodes • • •
4 5 noise-free training patterns Add 1 10% misclass ified pattern 5 noise-free, 60 5%, 1 10% noise training patterns 5 noise-free and 60 5% noise training patterns 5 noise-free, 60 5%, 1 10%, 2 15% noise training patterns 5 noise-free, 60 5%, 1 10%, 2 15%, 1 20% noise training patterns 5 noise-free, 60 5%, 1 10%, 2 15%, 1 20%, 1 25% noise training patterns 5 noise-free, 60 5%, 1 10%, 2 15%, 1 20%, 1 25%, 1 30% noise training patterns 5 noise-free, 60 5%, 1 10%, 2 15%, 1 20%, 1 25%, 1 30%, 1 35% noise training patterns Add 2 15% misclass ified patterns Test 1800 seismic patterns on 3 classes with 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 30%, and 35% noise respectively. Add 1 20% misclass ified pattern Add 1 25% misclass ified pattern Add 1 30% misclass ified pattern Add 1 35% misclass ified pattern Learning Testing Classification results Test on real seismic data
at Mississippi Canyon
Classification results
Testing on real data
Fig. 3. Training and testing of robust recognition by two-layer perceptron. Table 1. Performance of testing 1800 patterns of 3 classes
(600 testing patterns for each class).
# of total error patterns # of iterations of network Step 1 468 512 Step 2 412 388 Step 3 279 373 Step 4 46 606 Step 5 33 800 Step 6 29 1031 Step 7 15 2186 Step 8 5 1430