行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫 成果報告
獨立董事與財務報表重編:財務專家之影響
研究成果報告(精簡版)
計 畫 類 別 : 個別型
計 畫 編 號 : NSC 99-2410-H-151-009-
執 行 期 間 : 99 年 08 月 01 日至 100 年 07 月 31 日
執 行 單 位 : 國立高雄應用科技大學財經與商務決策研究所
計 畫 主 持 人 : 李文智
計畫參與人員: 碩士班研究生-兼任助理人員:張玉欣
博士班研究生-兼任助理人員:吳政仲
其他-兼任助理人員:謝孟欣
報 告 附 件 : 出席國際會議研究心得報告及發表論文
公 開 資 訊 : 本計畫可公開查詢
中 華 民 國 100 年 10 月 31 日
中文摘要: 根據美國會計總局(General Accountability Office, GAO)於
2002、2006 年研究調查報告指出,自 1997 年至 2005 年 9 月
間,公司發生財務報表重編的頻率逐年增加,重編公司占上市
公司之家數由 1997 年的 0.89%成長至 2002 年的 3.7%,至 2005
年已達 6.8%,且發現財務報表重編公司之平均規模有逐年上升
的趨勢。
而企業重編財務報表之事件往往對資本市場造成極大之衝
擊,就美國而言,過去研究指出,證券市場在重編宣告後之累
積異常報酬大約下跌 4%至 12%,且財務報表重編會使得投資
人對管理當局之能力、誠信及企業盈餘品質產生高度疑慮,擴
大資訊不對稱之程度,進而提高企業之資金成本(Dechow,
Sloan, and Sweeney 1996;Anderson et al. 2002;Hribar and
Jenkins 2004)。
沙氏法案要求公司審計委員會具有財務專家,但因外界壓
力,將非會計專業背景之財務專家納入。DeFond et al. (2005)針
對此一問題研究,實證發現市場對於指派會計專業背景之財務
專家進入審計委員會有顯著正向反應。
本文主要發現如下:本文發現獨立董事的設置,確實可抑制
財務報表重編事件的發生;而財務報表重編金額變動幅度,則
會隨著獨立董事專業背景之不同而有顯著差異。
英文摘要: According to the research reports of U. S. General Accountability
Office (GAO) on American companies, the frequency of
restatements is increasing rapidly from 1997 to 2005, and the
median size of restatements firms also increased sharply during the
period.
The announcements of restatements generally have significant
effects on share price. For example, previous literature document
that the cumulative abnormal returns of announcements of
restatements are about 4% to12%. In addition, the restatements will
lead to the loss the investors’ confidence on the financial
statements and integrity of managers/directors, broaden the
information asymmetry, and further lead to the increase of cost of
capital (Dechow, Sloan, and Sweeney 1996;Anderson et al.
2002;Hribar and Jenkins 2004).
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) requires public companies
disclose whether they have a financial expert on their audit
committee. In addition, because it is controversial whether SOX
should define financial experts narrowly to include primarily
accounting financial experts (as initially proposed) or more broadly
to include nonaccounting financial experts (as ultimately passed),
DeFond et al. (2005) investigate the response of capital market and
find a positive market reaction to the appointment of accounting
financial experts assigned to audit committees but no reaction to
nonaccounting financial experts assigned to audit committees.
The empirical evidence shows that there exists a significantly
negative relationship between independent directors and
restatements. We also find that the expertise of independent
directors has different effects on the magnitude of restatements.
中文摘要
根據美國會計總局(General Accountability Office, GAO)於 2002、2006 年研究調
查報告指出,自 1997 年至 2005 年 9 月間,公司發生財務報表重編的頻率逐年增加,
重編公司占上市公司之家數由 1997 年的 0.89%成長至 2002 年的 3.7%,至 2005 年
已達 6.8%,且發現財務報表重編公司之平均規模有逐年上升的趨勢。
而企業重編財務報表之事件往往對資本市場造成極大之衝擊,就美國而言,過
去研究指出,證券市場在重編宣告後之累積異常報酬大約下跌 4%至 12%,且財務
報表重編會使得投資人對管理當局之能力、誠信及企業盈餘品質產生高度疑慮,擴
大資訊不對稱之程度,進而提高企業之資金成本(Dechow, Sloan, and Sweeney 1996;
Anderson et al. 2002;Hribar and Jenkins 2004)。
沙氏法案要求公司審計委員會具有財務專家,但因外界壓力,將非會計專業背
景之財務專家納入。DeFond et al. (2005)針對此一問題研究,實證發現市場對於指派
會計專業背景之財務專家進入審計委員會有顯著正向反應。
本文主要發現如下:本文發現獨立董事的設置,確實可抑制財務報表重編事件
的發生;而財務報表重編金額變動幅度,則會隨著獨立董事專業背景之不同而有顯
著差異。
關鍵詞:公司治理、財務報表重編、獨立董事、機構投資人
Abstract
According to the research reports of U. S. General Accountability Office (GAO) on
American companies, the frequency of restatements is increasing rapidly from 1997 to
2005, and the median size of restatements firms also increased sharply during the period.
The announcements of restatements generally have significant effects on share price.
For example, previous literature document that the cumulative abnormal returns of
announcements of restatements are about 4% to12%. In addition, the restatements will
l
e
a
d
t
o
t
he
l
os
s
t
he
i
nve
s
t
or
s
’
c
onf
i
de
nce
on
t
he
f
i
na
nc
i
a
l
s
t
a
t
eme
nt
s
and
i
nt
e
gr
i
t
y
of
managers/directors, broaden the information asymmetry, and further lead to the increase
of cost of capital (Dechow, Sloan, and Sweeney 1996;Anderson et al. 2002;Hribar and
Jenkins 2004).
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) requires public companies disclose whether they
have a financial expert on their audit committee. In addition, because it is controversial
whether SOX should define financial experts narrowly to include primarily accounting
financial experts (as initially proposed) or more broadly to include nonaccounting
financial experts (as ultimately passed), DeFond et al. (2005) investigate the response of
capital market and find a positive market reaction to the appointment of accounting
financial experts assigned to audit committees but no reaction to nonaccounting financial
experts assigned to audit committees.
The empirical evidence shows that there exists a significantly negative relationship
between independent directors and restatements. We also find that the expertise of
independent directors has different effects on the magnitude of restatements.
Keywords: corporate governance, restatements, independent directors, institutional
investors
一、緣由與目的
根據美國會計總局(General Accountability Office, GAO)於 2002、2006 年研究調
查報告指出,自 1997 年至 2005 年 9 月間,公司發生財務報表重編的頻率逐年增加,
重編公司占上市公司之家數由 1997 年的 0.89%成長至 2002 年的 3.7%,至 2005 年
已達 6.8%,且發現財務報表重編公司之平均規模有逐年上升的趨勢。
而企業重編財務報表之事件往往對資本市場造成極大之衝擊,就美國而言,過
去研究指出,證券市場在重編宣告後之累積異常報酬(cumulative abnormal returns,
CAR)大約下跌 4%至 12% (Dechow et al. 1996;Anderson and Yohn 2002;Palmrose et
al. 2004)。且財務報表重編會使得投資人對管理當局之能力、誠信及企業盈餘品質
產生高度疑慮,擴大資訊不對稱之程度,進而提高企業之資金成本(Dechow et al.
1996;Anderson et al. 2002;Hribar and Jenkins 2004)。而在國內部份,有關企業重編
對於資本市場之影響的文獻並不多見,但以聯華電子於 2005 年 12 月中應證管會要
求重編 2002、2003 年與 2004 年財務報表之事件為例,重編訊息揭露當日即引起相
當大的震撼,盤中股價下跌達 6.42%,且自 2005 年 9 月 26 日至 12 月 30 日止該公
司的累積異常報酬達-22%,聯華電子報表重編事件雖僅為個案,但仍可明顯看出企
業重編報表之影響不小。
沙氏法案要求公司審計委員會應由獨立董事組成,並要求公司揭露審計委員會
中是否具有財務專家。關於財務專家之定義,沙氏法案草案原以具有會計專業背景
者為限,但立法過程中各方意見紛至沓來,以致於沙氏法案最終版本放寬財務專家
之資格,亦將非會計專業背景之財務專家納入。DeFond et al. (2005)針對此一問題,
採取事件研究法之形式,針對 702 個委任外部董事進入審計委員會之宣告進行研
究,並進一歩檢測市場對於審計委員會中加入會計及非會計類財務專家之訊息宣告
是否有不同之反應。實證發現市場對於指派會計專業背景之財務專家進入審計委員
會有顯著正向反應;但對於指派非會計類的財務專家則無反應,這可能因為市場認
為具會計專業之獨立董事更能扮演監督之角色。
綜合財務報表重編與獨立董事相關文獻(例如 Abbott, Parker, and Peter 2004﹔
Chin and Chi 2009 等),我們發現探討獨立董事與財務報表重編關聯性之研究並不多
見,且過去相關研究大多來自美國之證據,亦即所謂英美法系(或稱習慣法系)國
家的資料。至於獨立董事與財務報表重編在大陸法系(或稱成文法系)國家(例如
台灣)之關聯性為何?缺乏相關實證證據,本文使用台灣資料,正可填補文獻之匱乏。
其次,過去研究極少提供有關”
純會計專業背景”
與”
非會計專業背景”財務專家其背
景之差異是否影響監督職能發揮,而在財務報表重編之議題方面,相關研究更是付
之闕如,而這正是本計畫的一大特點。此外,有關機構投資人、董監質押比例等公
司治理變數與財務報表重編之關聯性為何?目前並無定論,故本計畫亦加入相關重要
公司治理變數一併探討。目前正值我國積極推行獨立董事制度之際,卻面臨獨立董
事人才不足之問題,本研究之證據,可供學術界及主管機關參考,具有極高的政策
意涵。
具言之,本研究希望完成以下的研究目的:
(1)在沙氏法案討論過程中,有關財務專家之認定,引起熱烈討論,本計畫探討”
純會計專業背景”
與”
非會計專業背景”
財務專家與財務報表重編之關聯性之差異,為
過去文獻所無,本文之實證結果正可填補文獻之匱乏;且目前正值我國積極推行獨
立董事等相關公司治理制度之際,藉由探討獨立董事之專業背景與公司財務報表重
編之關聯性,能提供具體政策意涵,可做為未來制定相關政策及配套措施之參考。
(2)過去探討獨立董事與財務報表重編關聯性之研究並不多見,且這些研究皆使
用習慣法國家之資料。有關獨立董事專業背景與財務報表重編在成文法國家之關聯
性為何?缺乏相關實證證據。本計劃之研究結果可填補相關文獻之匱乏。
(3)本計劃同時探討獨立董事、獨立董事專業背景等獨立董事特性及機構投資人
持股比例、董監質押比例、董監事持股比例等重要公司治理變數與公司財務報表重
編之關聯性,可顯示上述重要公司治理變數共同運作下之影響以及相對效果,能填
補目前學術文獻之不足,提供學術界、實務界參考。
二、結果與討論
我們發現有關獨立董事專業背景與財務報表重編關聯性之研究並不多見,且這
些研究皆使用習慣法國家之資料。至於獨立董事與財務報表重編在成文法國家之關
聯性為何?缺乏相關實證證據。且過去研究並無進一步探討”純會計專業背景”與”
非會計專業背景”
財務專家與財務報表重編之關聯性,因此,本文從這個角度切入,
探討獨立董事之專業背景與公司財務報表重編事件之關聯性。在財務報表重編事件
方面,本研究進一步從發生可能性及重編變動金額兩種角度進行探討。有關本計劃
之研究結果進一步說明如下:
本研究探討獨立董事之專業背景與公司財務報表重編事件之關聯性。在財務報
表重編事件方面,本研究進一步從發生可能性及重編變動金額兩種角度進行探討。
本文選取 2006 年至 2009 年之資料,以台灣上市上櫃公司為研究對象。而由於產業
性質之不同,樣本排除金融、保險、證券與管理股票,而非曆年制公司或資料有遺
漏值之公司亦予排除。本研究相關財務資料係取自台灣經濟新報社資料庫。
首先,在財務報表重編發生可能性部份,在不考慮獨立董事之專業背景下,無
論獨立董事變數係使用虛擬變數或以公司獨立董事人數佔總董事人數比率做為代理
變數,實證結果均顯著為負,顯示獨立董事之存在可抑制財務報表重編之發生,支
持假說 1a 的論述。其次,本文進一步考慮獨立董事之專業背景是否對財務報表重編
發生可能性有不同影響,實證結果仍然發現獨立董事之存在可抑制財務報表重編之
發生,但會計背景獨立董事變數並不顯著,亦即會計背景獨立董事對財務報表重編
發生可能性並無增額影響。
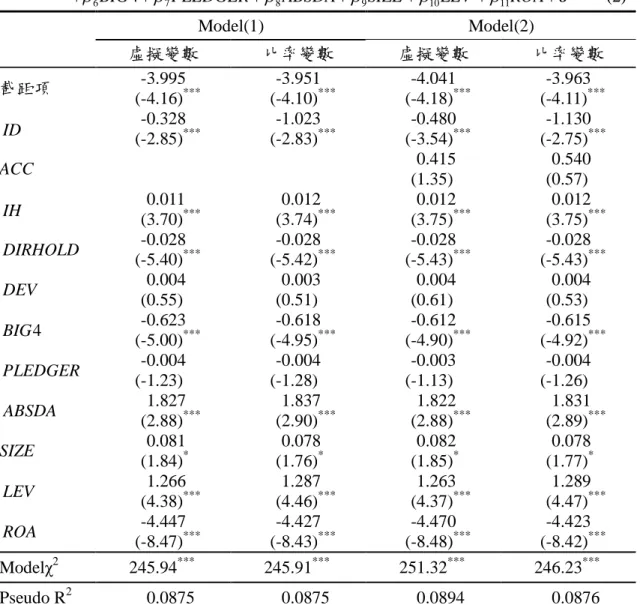
表 1 是否重編 Logistic 迴歸結果(n=4,780)
0 1 2 3 4 5
4
RESTATE
ID
IH
DIRHOLD
DEV
BIG
6
PLEDGER
7ABSDA
8SIZE
9LEV
10ROA
(1)
0 1 2 3 4 5
RESTATE
ID
ACC
IH
DIRHOLD
DEV
6
BIG
4
7PLEDGER
8ABSDA
9SIZE
10LEV
11ROA
(2)
Model(1)
Model(2)
虛擬變數
比率變數
虛擬變數
比率變數
截距項
-3.995
(-4.16)
***-3.951
(-4.10)
***-4.041
(-4.18)
***-3.963
(-4.11)
***ID
-0.328
(-2.85)
***-1.023
(-2.83)
***-0.480
(-3.54)
***-1.130
(-2.75)
***ACC
0.415
(1.35)
0.540
(0.57)
IH
0.011
(3.70)
***0.012
(3.74)
***0.012
(3.75)
***0.012
(3.75)
***DIRHOLD
-0.028
(-5.40)
***-0.028
(-5.42)
***-0.028
(-5.43)
***-0.028
(-5.43)
***DEV
0.004
(0.55)
0.003
(0.51)
0.004
(0.61)
0.004
(0.53)
4
BIG
-0.623
(-5.00)
***-0.618
(-4.95)
***-0.612
(-4.90)
***-0.615
(-4.92)
***PLEDGER
-0.004
(-1.23)
-0.004
(-1.28)
-0.003
(-1.13)
-0.004
(-1.26)
ABSDA
1.827
(2.88)
***1.837
(2.90)
***1.822
(2.88)
***1.831
(2.89)
***SIZE
0.081
(1.84)
*0.078
(1.76)
*0.082
(1.85)
*0.078
(1.77)
*LEV
1.266
(4.38)
***1.287
(4.46)
***1.263
(4.37)
***1.289
(4.47)
***ROA
-4.447
(-8.47)
***-4.427
(-8.43)
***-4.470
(-8.48)
***-4.423
(-8.42)
***Modelχ
2245.94
***245.91
***251.32
***246.23
***Pseudo R
20.0875
0.0875
0.0894
0.0876
註1:RESTATE:虛擬變數,若公司發生財務報表重編者設為1,否則為0;ID:獨立董事變數,本研究 分別使用虛擬變數及比率之設定進行測試。在虛擬變數設定部份,若公司設有獨立董事,則ID 為1,否則為0;在比率設定部分,ID為公司獨立董事人數佔總董事人數比率;ACC: 會計專業 背景獨立董事變數,本研究分別使用虛擬變數及比率之設定進行測試。在虛擬變數設定部份, 若公司獨立董事具會計專業背景,則ACC為1,否則為0;在比率設定部分,ACC為公司具會 計專業之獨立董事人數佔董事總人數之比率;IH:機構投資人持股比率;DIRHOLD:董(監)事持 股比率;DEV:控制股東所有權與控制權偏離程度;BIG4:虛擬變數,若公司簽證會計師為四大 事務所者設為1,否則為0;PLEDGER:董監持股質押比例;ABSDA:經期初資產總額平減之裁 決性應計數的絕對值;SIZE:公司規模;LEV:負債比率;ROA:資產報酬率另一方面,本文進一步探討獨立董事、獨立董事的專業背景與財務報表重編金
額變動幅度間之關聯性。在不區分獨立董事之專業背景下,無論獨立董事變數係使
用虛擬變數或以公司獨立董事人數佔總董事人數比率做為代理變數,實證結果均顯
著為正,顯示獨立董事與財務報表重編金額變動幅度呈顯著正相關,與假說 1b 的預
期相反。其次,我們進一步考慮獨立董事之專業背景是否對財務報表重編金額變動
幅度有不同影響,實證結果發現,無論兩個獨立董事變數係使用虛擬變數或以公司
獨立董事人數佔總董事人數比率做為代理變數,實證結果均發現獨立董事與財務報
表重編金額變動幅度呈顯著正相關,與先前的結果一致,但與假說 1b 的預期相反;
但我們發現會計背景獨立董事變數在兩種變數設定下皆顯著為負,顯示會計背景獨
立董事對財務報表重編金額變動幅度有顯著負向之增額影響,可降低財務報表重編
金額變動幅度,支持假說 2b 的論述。
綜合上述,本文發現獨立董事的設置,確實可抑制財務報表重編事件的發生;
而財務報表重編金額變動幅度,則會隨著獨立董事專業背景之不同而有顯著差異。
過去財務報表重編相關研究大多來自美國之證據,亦即所謂英美法系(或稱習
慣法系)國家的資料。至於獨立董事與財務報表重編在大陸法系(或稱成文法系)
國家(例如台灣)之關聯性為何?缺乏相關實證證據,本文使用台灣資料,正可填補
文獻之匱乏。其次,過去研究並無探討”
純會計專業背景”
與”
非會計專業背景”
財務
專家其背景差異與財務報表重編之關聯性,而這正是本計畫的最大特點。目前正值
我國積極推行獨立董事制度之際,卻面臨獨立董事人才不足之問題,本研究之證據,
可供學術界及主管機關參考,具有極高的政策意涵。
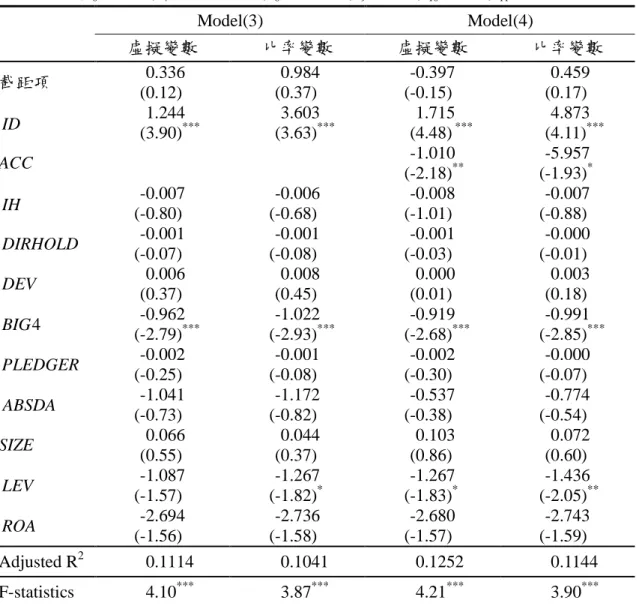
表 2 重編金額變動絕對值迴歸結果(n=248)
0 1 2 3 4 5
4
ABSRES
ID
IH
DIRHOLD
DEV
BIG
6
PLEDGER
7ABSDA
8SIZE
9LEV
10ROA
(3)
0 1 2 3 4 5
ABSRES
ID
ACC
IH
DIRHOLD
DEV
6
BIG
4
7PLEDGER
8ABSDA
9SIZE
10LEV
11ROA
(4)
Model(3)
Model(4)
虛擬變數
比率變數
虛擬變數
比率變數
截距項
0.336
(0.12)
0.984
(0.37)
-0.397
(-0.15)
0.459
(0.17)
ID
(3.90)
1.244
***3.603
(3.63)
***1.715
(4.48)
***4.873
(4.11)
***ACC
-1.010
(-2.18)
**-5.957
(-1.93)
*IH
-0.007
(-0.80)
-0.006
(-0.68)
-0.008
(-1.01)
-0.007
(-0.88)
DIRHOLD
-0.001
(-0.07)
-0.001
(-0.08)
-0.001
(-0.03)
-0.000
(-0.01)
DEV
0.006
(0.37)
0.008
(0.45)
0.000
(0.01)
0.003
(0.18)
4
BIG
-0.962
(-2.79)
***-1.022
(-2.93)
***-0.919
(-2.68)
***-0.991
(-2.85)
***PLEDGER
-0.002
(-0.25)
-0.001
(-0.08)
-0.002
(-0.30)
-0.000
(-0.07)
ABSDA
-1.041
(-0.73)
-1.172
(-0.82)
-0.537
(-0.38)
-0.774
(-0.54)
SIZE
0.066
(0.55)
0.044
(0.37)
0.103
(0.86)
0.072
(0.60)
LEV
-1.087
(-1.57)
-1.267
(-1.82)
*-1.267
(-1.83)
*-1.436
(-2.05)
**ROA
-2.694
(-1.56)
-2.736
(-1.58)
-2.680
(-1.57)
-2.743
(-1.59)
Adjusted R
20.1114
0.1041
0.1252
0.1144
F-statistics
4.10
***3.87
***4.21
***3.90
*** 註 1:ABSRES:經重編前損益平減之重編損益變動數,其絕對值;ID:獨立董事變數,本研究分別使 用虛擬變數及比率之設定進行測試。在虛擬變數設定部份,若公司設有獨立董事,則 ID 為 1, 否則為 0;在比率設定部分,ID 為公司獨立董事人數佔總董事人數比率;ACC: 會計專業背 景獨立董事變數,本研究分別使用虛擬變數及比率之設定進行測試。在虛擬變數設定部份, 若公司獨立董事具會計專業背景,則 ACC 為 1,否則為 0;在比率設定部分,ACC 為公司具 會計專業之獨立董事人數佔董事總人數之比率;IH:機構投資人持股比率;DIRHOLD:董(監) 事持股比率;DEV:控制股東所有權與控制權偏離程度;BIG4:虛擬變數,若公司簽證會計師 為四大事務所者設為 1,否則為 0;PLEDGER:董監持股質押比例;ABSDA:經期初資產總額 平減之裁決性應計數的絕對值;SIZE:公司規模;LEV:負債比率;ROA:資產報酬率三、計劃成果自評
我們發現有關獨立董事專業背景與財務報表重編關聯性之研究並不多見,且這
些研究皆使用習慣法國家之資料。至於獨立董事與財務報表重編在成文法國家之關
聯性為何? 缺乏相關實證證據。且過去研究並無進一步探討”
純會計專業背景”與”
非會計專業背景”
財務專家與財務報表重編之關聯性,因此,本文從這個角度切入,
探討獨立董事之專業背景與公司財務報表重編事件之關聯性。在財務報表重編事件
方面,本研究進一步從發生可能性及重編變動金額兩種角度進行探討。有關本計劃
之研究結果進一步說明如下:
首先,在財務報表重編發生可能性部份,在不考慮獨立董事之專業背景下,無
論獨立董事變數係使用虛擬變數或以公司獨立董事人數佔總董事人數比率做為代理
變數,實證結果均顯著為負,顯示獨立董事之存在可抑制財務報表重編之發生,支
持假說 1a 的論述。其次,本文進一步考慮獨立董事之專業背景是否對財務報表重編
發生可能性有不同影響,實證結果仍然發現獨立董事之存在可抑制財務報表重編之
發生,但會計背景獨立董事變數並不顯著,亦即會計背景獨立董事對財務報表重編
發生可能性並無增額影響。
另一方面,本文進一步探討獨立董事、獨立董事的專業背景與財務報表重編金
額變動幅度間之關聯性。在不區分獨立董事之專業背景下,無論獨立董事變數係使
用虛擬變數或以公司獨立董事人數佔總董事人數比率做為代理變數,實證結果均顯
著為正,顯示獨立董事與財務報表重編金額變動幅度呈顯著正相關,與假說 1b 的預
期相反。其次,我們進一步考慮獨立董事之專業背景是否對財務報表重編金額變動
幅度有不同影響,實證結果發現,無論兩個獨立董事變數係使用虛擬變數或以公司
獨立董事人數佔總董事人數比率做為代理變數,實證結果均發現獨立董事與財務報
表重編金額變動幅度呈顯著正相關,與先前的結果一致,但與假說 1b 的預期相反;
但我們發現會計背景獨立董事變數在兩種變數設定下皆顯著為負,顯示會計背景獨
立董事對財務報表重編金額變動幅度有顯著負向之增額影響,可降低財務報表重編
金額變動幅度,支持假說 2b 的論述。
綜合上述,本文發現獨立董事的設置,確實可抑制財務報表重編事件的發生;
而財務報表重編金額變動幅度,則與獨立董事的專業背景具有顯著關聯。
過去財務報表重編相關研究大多來自美國之證據,亦即所謂英美法系(或稱習
慣法系)國家的資料。至於獨立董事與財務報表重編在大陸法系(或稱成文法系)
國家(例如台灣)之關聯性為何?缺乏相關實證證據,本文使用台灣資料,正可填補
文獻之匱乏。其次,過去研究並無探討”
純會計專業背景”
與”
非會計專業背景”
財務
專家其背景差異與財務報表重編之關聯性,而這正是本計畫的最大特點。目前正值
我國積極推行獨立董事制度之際,卻面臨獨立董事人才不足之問題,本研究之證據,
可供學術界及主管機關參考,具有極高的政策意涵。
本計劃之實證結果預計將投稿至學術研討會及學術期刊,並預期針對財務報表
重編及公司治理等相關議題進行更深入之探討。
四、參考文獻
中文部分
高蘭芬,2002,『董監事股權質押之代理問題對會計資訊與公司績效之影響』,成功大學會
計學研究所未出版之博士論文。
陳瑞斌、許崇源,2005,『公司治理與權益資金成本之關聯性研究』,第十四屆會計理論與
實務研討會,中華民國台北。
林宜勉、呂惠民與盧其群,2006,會計師審計品質與財務報表重編之關聯性,2006 會計理
論與實務研討會。
薛敏正、林嬋娟與林秀鳳,2008,董事會特性與財務報告重編,交大管理學報,第二十八
卷,第 2 期 (12 月):73-103。
陳宏姿,2001,『董監事結構與企業財務績效關聯之研究』,政治大學會計學研究所未出版
之碩士論文。
翁淑育,2000,『台灣上市公司股權結構.核心代理問題及公司價值之研究』,輔仁大學金融
研究所未出版之碩士論文。
楊麗弘,2000,『台灣上市公司股權結構與經營績效研究-由董監事持股質押效果論之』,
長庚大學管理學研究所未出版之碩士論文。
葉銀華、李存修及柯承恩 , 2000,公司治理與評等系統,台北:商智文化。
英文部分
Abbott, L. J., S. Parker, and G. F. Peters. 2004. Audit committee characteristics and restatements.
Auditing: A Journal of Practice & Theory 23(Mar): 69-87.
Admati, A. R., P. Pfleiderer
,
and
J
.
Zechner
.
1994.
“
Lar
ge
Shar
ehol
der
Act
i
vi
s
m,
Ri
s
k
Shar
i
ng,
and
Fi
nanc
i
a
l
Ma
r
ket
Equi
l
i
br
i
um”
.
J
our
nal
of
Pol
i
t
i
ca
l
Economy
102(
6)
:1097-1130.
Agrawal, A., and G. N. Mandelker.1990. Large Shareholders and the Monitoring of Managers:
The Case of Anti-takeover Charter Amendments. Journal of Financial & Quantitative
Analysis 25: 143-161.
Agrawal, A., and S. Chadha. 2005. Corporate governance and accounting scandals. Journal of
Law and Economics 48 (Oct): 371-406.
Aier, J. K., J. Comprix, M. T. Gunlock, and D. Lee. 2005. The financial expertise of CFOs and
accounting restatements. Accounting Horizons 19(Sep): 123-135.
Anderson, K. L., and T. L. Yohn. 2002. The effect of 10-K restatement on firm value, information
as
ymmet
r
i
e
s
,
a
nd
i
nves
t
or
s
’
r
e
l
i
ance
on
ea
r
nings. Working paper, Georgetown University.
Bathala, C. T., K. P. Moon, and R. P. Rao. 1994. Mangerial Ownership, Debt Policy, and the
Impact of Institutional Holdings: An Agency Perspective ,Financial Management 3;38-50。
Bhagat
,
S.
,
and
B.
Bl
ack,
1996,
“
The Uncertain Relationship between Board Composition and
Bhoj
r
a
j
,
S.
a
nd
P
.
Sengupt
a
,
2003,
“
Ef
f
e
ct
of
Cor
por
at
e
Gover
nance
on
Bond
Ra
t
i
ngs
a
nd
Yi
e
l
ds
:
The Role of Institutional Investors and Outside Directo
r
s
”
,
J
our
na
l
of
Bus
i
nes
s
76(
3)
,
pp.
455-475.
Brickley, James A., Lease, Ronald C. and Smith, Jr., Clifford W. (1988), "Ownership Structure
and Voting on Antitakeover Amendments," 20 Journal of Financial Economics 267.
Chen,
Y.
,
and S.
Hu,
2001,
“
The
Cont
r
ol
l
i
ng Sha
r
ehol
der
’
s
Pe
r
s
onal
St
ock Loan and Fi
r
m
Per
f
or
manc
e”
,
Wor
ki
ng
Pa
per
,
Nat
i
onal
Tai
wan
Uni
ver
s
i
t
y
.
Chin, C. L.. and H. Y. Chi. 2009. Reducing restatements with increased industry expertise.
Contemporary Accounting Research 26 (3): 729-765.
Choy, H. L., F. A. Gul. 2008. Restatements and Auditors' Reputational Costs. SSRN Working
Paper.
Cl
aes
s
ens
,
S.
,
S.
Dj
ankov
,
and
L.
H.
P
.
Lang,
2000,
“
The
Separ
a
t
i
on
of
Owner
s
hi
p
a
nd
Cont
r
ol
i
n
Ea
s
t
As
i
an
Cor
por
a
t
i
on
”
,
J
our
na
l
of
Fi
nanc
i
al
Economi
cs
58,
pp.
81-112.
Davi
ds
on I
I
I
,
Wal
l
ac
e
N.
,
Bi
a
o Xi
e
,
and We
i
hong Xu,
2004,
“
Ma
r
ket
Reac
t
i
on t
o Vol
unt
ar
y
Announc
ement
s
of
Audi
t
Commi
t
t
e
e
Appoi
nt
ment
s
:
The
Ef
f
ect
of
Fi
nanc
i
a
l
Exper
t
i
s
e”
,
Journal of Accounting and Public policy 23, pp. 279-293.
De
Angel
o,
L.
,
1986,
“
Accounting Numbers as Market Valuation Substitutes: A study of
Management
Buyout
s
of
Publ
i
c
St
ockhol
der
s
”
,
The
Account
i
ng
Revi
ew
61,
pp.
400-420.
Dec
how,
P
.
M.
,
Sl
oan,
R.
,
and Sweeney
,
A.
(
1996)
,
“
Ca
us
es
and Cons
equenc
es
of
Ear
ni
ngs
Manipulation: An Analysis of F
i
r
ms
Subj
ec
t
t
o Enf
or
cement
Ac
t
i
ons
by t
he
SEC,
”
Contemporary Accounting Research, 13(1), 1-36.
DeFond, M. L., and J. Jiambalvo. 1991. Incidence and circumstances of accounting errors.The
Accounting Review 66 (Jul): 643-655.
DeFond, M.L., R. N. Hann, and
X.
Hu,
2005,
“
Doe
s
t
he
Ma
r
ket
Val
ue
Fi
nanc
i
al
Exper
t
i
s
e
on
Audi
t
Commi
t
t
e
es
of
Boar
ds
of
Di
r
ec
t
or
s
?”
,
J
our
nal
of
Ac
c
ount
i
ng Res
ea
r
ch 43,
pp.
153-193.
Fac
ci
o,
Mar
a
,
a
nd Lar
r
y H.
P
.
Lang,
2002,
“
The
ul
t
i
mat
e
owner
s
hi
p of
we
s
t
e
r
n Eur
ope
an
cor
por
a
t
i
ons
.
”J
our
nal of Financial Economics 65: 365-395.
Fos
ber
g,
R.
H.
1989.
“
Out
s
i
ded i
r
e
ct
or
s
and ma
nagement
moni
t
or
i
ng”
.
Akr
on Bus
i
nes
s
a
nd
Economic Review20:24-32.
General Accounting Office. 2002. Financial statement restatements: trends, market impacts,
regulatory responses, and remaining challenges. Washington D.C. GAO-03-138.
General Accounting Office. 2006. Financial statement restatements: update of public company
trends,
market
impacts,
and
regulatory
enforcement
activities.
Washington
D.C.
GAO-06-678.
Grossman, S., a
nd
O.
Ha
r
t
,
1988,
“
One-Share, One-Vot
e
,
and
t
he
Mar
ket
f
or
Cor
por
a
t
e
Cont
r
ol
”
,
Journal of Financial Economics 20, pp. 175-202.
He
r
mal
i
n,
B.
,
and
M.
We
i
s
bach.
1991.
“
The
Ef
f
ect
s
of
Boar
d
Compos
i
t
i
on
and
Di
r
ec
t
I
ncent
i
ves
on
Fi
r
m
Per
f
or
mance
.
”
Fi
nanci
al
Management 20(4):101-112.
Hribar, P., and N. T. Jenkins. 2004. The effect of accounting restatements on earnings revisions
and the estimated cost of capital. Review of Accounting Studies 9 : 337-356.
Jarrell, G. A. and A. B. Poulsen.1987. "Shark repellents and stock prices: the effects of
antitakeover amendments since 1980". Journal of Financial Economics 19 (1):127--168.
J
ens
e
n,
M.
,
and
R.
Ruba
ck,
1983,
“
The
Mar
ket
f
or
Cor
por
at
e
Cont
r
ol
:
The
Sc
i
ent
i
f
i
c
Evi
denc
e”
,
Journal of Financial Economics 11, pp. 5-50.
J
ens
e
n,
M.
,
a
nd
W.
H.
Me
c
kl
i
ng,
1976,
“
The
or
y
of
t
he
Fi
r
m:
Manager
i
a
l
Behavi
or
,
Agency
Cos
t
and
Owner
s
hi
p
St
r
uc
t
ur
e”
,
J
our
nal
of
Fi
nanc
i
a
l
Economi
cs
3,
pp.
305-360.
Jian, Jiu-Young, and Yu-Me
i
Che
n,
2005,
“
The
Ef
f
ec
t
s
of
Audi
t
i
ng
Qua
l
i
t
y
and
of
I
ndepe
ndent
Di
r
ec
t
or
s
and
Super
vi
s
or
s
on
t
he
I
nt
er
e
s
t
Cos
t
of
Ne
wl
y
I
s
s
ued
Cor
por
at
e
Bonds
”
,
Wor
ki
ng
Paper:National Yunlin University of Science and Technology.
Karpoff, Jonathan, Malatesta, Paul and Walkling, Ralph.1996. "Corporate Governance and
Shareholder Initiatives: Empirical Evidence," 42 Journal of Financial Economics 365.
Khanna
,
T.
,
and
K.
Pa
l
e
pu,
1998,
“
Emer
gi
ng
Mar
ket
Bus
i
ne
s
s
Gr
oups
,
For
ei
gn
I
nt
e
r
medi
ar
i
es
,
and
Cor
por
a
t
e
Gover
nance
”,
Wor
ki
ng
Pape
r
,
Har
var
d
Bus
i
ne
s
s
Sc
hool
.
Kinney, W.R., Jr. and L. S. McDan
i
e
l
.
1989.
“
Char
act
e
r
i
s
t
i
cs
of
Fi
r
ms
Cor
r
e
ct
i
ng
Pr
evi
ous
l
y
Re
por
t
ed
Qua
r
t
er
l
y
Ea
r
ni
ngs
.
”
J
our
na
l
of
Ac
count
i
ng
a
nd
Economi
cs
11:71-93.
Kl
e
i
n,
A.
(
2002)
,
“
Audi
t
Commi
t
t
e
e
,
Boa
r
d of
Di
r
ect
or
Char
act
e
r
i
s
t
i
c
s
,
and Ear
ni
ngs
Management
,
”
J
our
nal
of
Account
i
ng
and Economics, 33(3), 375-400.
La Porta, R., F. Lopez-de-S
i
l
ane
s
,
A.
Shl
ei
f
er
,
and
R.
W.
Vi
s
hny
,
1998,
“
Law a
nd
Fi
nance”
,
Journal of Political Economy 106, pp. 1113-1155.
La Porta, R., F. Lopez-de-Si
l
a
ne
s
,
a
nd A.
Shl
e
i
f
er
,
1999,
“
Cor
por
a
t
e
Owner
s
hi
p ar
ound the
Wor
l
d”
,
J
our
na
l
of
Fi
nance
54,
pp.
471-517.
Mc
Conne
l
l
,
J
.
,
and
H.
Ser
vaes
,
1990,
“
Addi
t
i
ona
l
Evi
dence
on
Equi
t
y
Owner
s
hi
p
a
nd
Cor
por
a
t
e
Va
l
ue
”
,
J
our
na
l
of
Fi
na
nc
i
a
l
Economi
cs
27,
pp.
595-612.
Palmrose, Z. V., V. J. Richardson, and S. Scholz. 2004. Determinants of market reactions to
restatement announcements. Journal of Accounting and Economics 37 (Feb): 59-89.
Richardson, S., I. Tuna, and M. Wu. 2002. Predicting earnings management: the case of earnings
restatements. Working paper, University of Pennsylvania and University of Science and
Technology.
See
t
ha
r
ama
n,
A.
,
Gul
,
F.
A.
,
and
Lynn,
S.
G.
2002
“Li
t
i
gat
i
on
Ri
s
k
and
Audi
t
Fee
s
:
Evi
de
nce
from UK Firms Cross-Li
s
t
ed
on
US
Mar
ket
s
.
”
J
our
nal
ofAccounting and Economics33:
91-115.
Shl
e
i
f
er
,
A.
,
and R.
Vi
s
hny
,
1986,
“
Lar
ge Shar
ehol
der
s
a
nd Cor
por
at
e
Cont
r
ol
”
,
J
our
nal
of
Political Economy 94, pp. 461-488.
―――――
and
―――――,
1997,
“
A
Sur
vey
of
Cor
por
at
e
Gover
na
nc
e”
,
J
our
nal
of
Fi
nanc
i
a
l
Economics 52, pp. 737-783.
Stanley, J. D., and F. T. DeZoort. 2007.Audit firm tenure and financial restatements: An analysis
of industry specialization and fee effects Journal of Accounting and Public Policy 26:
131-159.
Xi
e
,
B.
,
W.
N.
Davi
ds
on,
a
nd P
.
J
.
Dada
l
t
,
2003,
“
Earnings Management and Corporate
Gover
na
nc
e
:
The
Rol
e
of
t
he
Boar
d
a
nd
t
he
Audi
t
Commi
t
t
ee
”
,
J
our
na
l
of
Cor
por
a
t
e
Fi
nanc
e
9, pp.295-316.
國科會補助專題研究計畫項下出席國際學術會議心得報告
日期:
年
月
日
一、參加會議經過
此次在補助下,學生得以參加2010 International Conference on Material and
Manufacturing Technology (ICMMT 2010)國際研討會,首先對此學生表達感謝之意。
學生前往中國大陸重慶參與這個國際研討會,所發表的論文為Manufacturing
process planning to Evaluation on Failure Causes for Lithography Machine: Analytic
Hierarchy Process,該Session形式為發表人發表15-20分鐘、評論人5分鐘,之後再由與
會人員發問,雖然此非學生第一次在此種國際會議場合以英文簡報,心中之緊張還是
計畫編號
NSC
99-2410-H-151-009-計畫名稱
獨立董事與財務報表重編:財務專家之影響
出國人員
姓名
吳政仲
服務機構
及職稱
國立高雄第一科技大學管理研究
所財務金融組博士班研究生
會議時間
99 年 9 月 17 日至
99 年 9 月 19 日
會議地點
中國大陸重慶
會議名稱
(中文) 2010 年材料與製造技術國際會議
(英文) 2010 International Conference on Material and Manufacturing
Technology (ICMMT 2010)
發表論文
題目
(英文) Manufacturing process planning to Evaluation on Failure Causes
for Lithography Machine: Analytic Hierarchy Process
會人員的諸多寶貴的意見,在整個會議過程也受到教授的諸多指導,實是獲益良多。
二、與會心得
此次的研討會,成員來自世界各地的先進,除了可了解現今財務研究趨勢與潮流
外,聽取知名學者的評論意見亦是一大收穫,他們於評論時不但匯總該研究議題的來
龍去脈,而且其評論意見不多但往往一針見血,非常值得研究後輩學習。當然,參加
學術會議的過程中,認識一些國際學者對於自己往後研究之路也是一大助益。
三、建議
參與如此的國際研討會,除了獲悉研究發展趨勢外,另可增進自己的國際觀,有
助於激勵自己於日後應精益求精,提昇學術研究能力。而國科會支持參與重要國際會
議並與國際學術接軌的政策,值得肯定,希望國科會本著支持與鼓勵學術發展,能夠
持續補助出國參加研討會,增加學生國際學術交流機會也提升國際觀。
四、攜回資料名稱及內容
1.大會手冊
2.會議論文摘要電子檔
國科會補助專題研究計畫項下出席國際學術會議心得報告
日期:
年
月
日
一、參加會議經過
此次在補助下,學生得以參加2011 International Conference on Information and
Education Technology(ICIET 2011)國際研討會,首先對此學生表達感謝之意。
學生前往中國大陸貴陽參與這個國際研討會,所發表的論文為A Study of
Synchronous and Bucket Trading Behavior of Institutional Investors,該Session形式為發表
計畫編號
NSC
99-2410-H-151-009-計畫名稱
獨立董事與財務報表重編:財務專家之影響
出國人員
姓名
吳政仲
服務機構
及職稱
國立高雄第一科技大學管理研究
所財務金融組博士班研究生
會議時間
100 年 1 月 26 日
至
100 年 1 月 28 日
會議地點
中國大陸貴陽
會議名稱
(中文) 2011 年資訊與教育技術國際會議
(英文) 2011 International Conference on Information and Education
Technology(ICIET 2011)
發表論文
題目
(英文) A Study of Synchronous and Bucket Trading Behavior of
Institutional Investors
國際會議場合以英文簡報,心中之緊張還是不言可喻,但終究還是順利完成,評論人
的意見也還算在意料之中,感謝評論人及與會人員的諸多寶貴的意見,在整個會議過
程也受到教授的諸多指導,實是獲益良多。
二、與會心得
參加此國際學術研討會,讓學生認識各國學者及研究生,並自其中找尋自已有興
趣Section參加,訓練聽力及以英文發表論文之能力,瞭解現今各領域之最新發展及可
討論研究之議題,自其中可獲取未來可進一步思考之研究方向,並瞭解世界各國在研
究什麼。
三、建議
在國際研討會以英文發表論文是台灣學生的缺點,國科會應多補助學生參與國際
學術研討會之經費,讓學生在經費充裕下可出席國際會議,擴展其國際觀。
四、攜回資料名稱及內容
1.大會手冊
2.會議論文摘要電子檔
Manufacturing process planning to Evaluation on Failure
Causes for Lithography Machine : Analytic Hierarchy Process
Po-Sheng Ko
1,aCheng-Chung Wu
2,b1
415 Chien-Hung Road, Kaohsiung, 807, Taiwan
2
2, Juoyue Rd., Nantz District Kaohsiung, 811, Taiwan
a
psko@cc.kuas.edu.tw
bwu_0110@yahoo.com.tw
Abstract
This study conducted hierarchical analysis on the evaluation item of the stability index of the lithography machine, and established a set of evaluation mechanism for failure prediction, in order to provide references and indicators of troubleshooting for lithography machine. The results showed, when the lithography machine is out of order, the possible failure causes are mainly be found based on the past experiences. Moreover, engineers’skills in maintenance of lithography machine should be also considered. It is clear that, technology-centered is the current trend in today's semiconductor technology processing. In the weight analysis of rating index for complexity in broken Wafer, the most important problem is the lithography machine error due to failure in its components. Good design and configuration of semiconductor lithography process in the early stage can enhance the rapid maintenance of lithography machine in case of malfunctioning effectively. For timely maintenance, maintaining the organization stringency needs to be improved.
This study also found that, under the good configuration of maintenance system, adequate information is closely associated a good system. As for lithography process in semiconductor industry, the complexity of broken Wafer is first considered. Thus, the overall lithography process of semiconductor relies on engineers’ experience. More specifically, a quick error interpretation and repair are required in field maintenance. As in a competitive market of semiconductor processing with high-tech and high-cost, a timely maintenance in the lithography machine is urgent and requested.
Keywords: lithography machine, failure analysis, Analytic Hierarchy Process
1. Introduction
Under globalization of IT and severe competition, how to reduce production costs and production cycle is an important factor for semiconductor wafer fabrication. Usually, wafer fabrication can be divided into several areas, which are thin film, lithography, etching, diffusion, ion implantation and chemical mechanical polishing (Xiao, 2001). In IC design, the design of logic circuits varies with different product specifications. Therefore, before designing the IC specifications, IC circuit diagram should be designed and the photo-mask should be produced based on their functions. Generally, the semiconductor processing can be divided into pre-operation process, wafer growth, FEOL and BEOL. Lithography, which is a technology that transfers the designed patterns from the photo-mask or demagnifying photo mask onto the photo resist of wafer surface. It includes three main steps: photo
ITRS (2002) pointed out that optical lithography is still the main force of lithography process, it is estimated that it is not going to be replaced any time in the near future. There are two major challenges to the development of optical lithography, including: 1) how to overcome the physical limitations to optical lithography; 2) the need to develop a new post-optical lithography, and apply it into mass production processes. Therefore, in order to achieve these goals, in addition to applying the process with a smaller line width in the design of electronic components, high-density is also needed. Also, for a smaller line width and higher yield rate, the increasingly progress of process technology increases its difficulties at the same time. So the control of lithography process is also the bottleneck, which inhibits the process technologies to be more precise.
As a result, the lithography times, or the quantity of photo masks needed in a process are used to show the difficulty level of this process. Whether the density of components in the whole semiconductor industry could continue to a smaller line width depends on the success in lithography development. In wafer fabrication, as the rapid development of semiconductor technology, how to break through the limits of optical lithography has been the R&D goal to large manufacturers. Photolithography is no doubt the core, which plays a critical role in the entire IC process. Also because of the yield rate in lithography processing, which is important to IC process, many studies have conducted in-depth research on the prevention and detection of the problems in lithography process.
Based on the traditional probability theory, Leang and Spanos (1997) conducted the diagnostic analysis of the machine by gathering actual operation information in lithography processing, in order to find out the probability of failure cause combination, and specific failure in some failure causes. Through the calculation of conditional probability, the probability of possible failure cause was obtained when some failures occurred. However, using Bayes' Theorem for diagnosis was labor-intensive and time-consuming. Moreover, based on the diagnostic system with historical data and training, it could only predict the failure cause which have had occurred. However, for those never occurred before, it tended to lose the diagnosis capacity. Therefore, probability theory as the fault diagnosis for lithography process is not a good diagnostic system.
If the yield rate in lithography process could be enhanced, the yield rate of the entire IC process would be enhanced as well. If there are positioning errors in the exposure imaging layers of lithography, iterated errors would occur due to the machine itself, as well as the process environment and wafer manufacturing. In the semiconductor processing, regardless of the reasons, defect rate would like to occur. If the yield rate could beraised,each IC’sproduction costcould be reduced, thus enhancing the competitiveness. Hence, each waferplant’scapacity isdetermined by the yield rate of the same product. As the product with fewer defects is another evaluation index, the problems ignored in the past are now affecting the circuit, thus resulting in a lower yield rate, and increasing impact of defect.
As seen, the importance of lithography in wafer fabrication is undoubted. The machine dispatching, material selection, performance evaluation and improvement, as well as scheduling of lithography process have been discussed and studied. However, there were scanty studies on the
lithography machines is very important to the entire production, if the failure cause could be found quickly and repaired timely when problems occur, the capacity of lithography process could be greatly improved, thus enhancing the productive efficiency of wafer.
2. Problem Statement
The stability of machine plays an important role in lithography processing. In fact, the yield rate of machine, which is affected by many factors, is the core of the lithography processing. Past researches mostly emphasized on random effects or environment affecting the wafers, the stability of the machine itself was seldom studied and discussed.
In fact, the stability of machine is the important factor affecting the lithography processing. If the machine is shutdown or faulted, the resulting impact would be significant. Moreover, in order to maintain the completion of machine and smooth operation, it is required to interpret the failure correctly, so as to estimate the possibility of repair. If the machine malfunctions, it is important to use the corresponding technical feasibility to determine the order of repair, and make the machine to resume online quickly without interrupt. Thus, how to appropriately arrange the machine configuration is an important issue for good lithography processing. Also, lithography process plays a major role in the IC process, as it involves the manufacturing technology of a higher level and requires a long production time, it accounts for 40% to 50% of the entire wafer fabrication time (Xiao, 2001). Therefore, optical lithography has been the improvement focus of lithography process.
Therefore, ensuring the stability of machine is an important issue to the stability of lithography processing. This study discussed each impact index of stability based on the iterated error of the machine itself, which determined the quality of photo mask transfer printing patterns. Additionally, AHP was conducted on the evaluation item of index for machine stability, in order to integrate the findings of past researches. As there are various failure causes in lithography machine, this study mainly aimed at the major causes in wafer fabrication, for some detailed causes without impact on machine’soperationare assumed not the failure causes.
3. Methodology
Expert system is one of the common methods for fault diagnosis in process. Kramer (1987) used fuzzy inference to construct an expert system based on rule bank, which was applied to fault diagnosis in chemical factories, achieving a good diagnostic result. However, expert systems may be limited to rule bank, it cannot find the faults that has never occurred before, lack learning and forecast ability (Petti et al., 1992), and is time-consuming of knowledge acquisition (Gupta and Rao, 1994). When the rule bank continued to expand, it was easy to see contradiction between the rules, thus it is not easy to manage (Surma and Braunschweig, 1996). All the extending problems have constrained the development of fault diagnosis in expert system.
Therefore, upon the theoretical basis of expert system, coupled with actual experiences in on-site maintenance, this study proposed a more specific, effective and efficient analysis for interpreting and identifying machine fault. Specifically, the causes affecting or resulting in failure of lithography machine are
of index for fault identification, it not only could provide valuable reference information for maintenance engineers, but also connect the insufficient data link at the same time, in order to provide more specific problem-solving technologies and coping directions. Eventually, the difficulties in troubleshooting of lithography machine for wafer fabrication can be solved effectively, thus enhance the production efficiency of wafer.
2.1 Data Resource
This study aimed to discuss the data resource of main failure causes and corresponding technical information of lithography machine in the semiconductor industry. The data were collected from on-site experiences of maintenance engineers with at least 5 years of seniority in the case company and the industry. The data included the actual maintenance and troubleshooting cases of lithography machine.
The subjects of this study were the maintenance engineers of lithography machine in the semiconductor industry, with many years of experiences in troubleshooting and on-site maintenance, and have accumulated experience equivalent to experts. Along with technical exchanges and daily discussions with colleagues, they fully recognize the importance of troubleshooting and maintenance of lithography machine. Therefore, this study organized the past performance data of engineers and the case company, in order to establish a referential index for troubleshooting and coping directions.
2.2 Hierarchy construction
This study used AHP solve the possible problems of machine failures in the semiconductor wafer lithography process, based on the on-site maintenance of engineers, past experiences of the case company on repair, and past studies. Based on expert survey, this study constructed the analysis framework for AHP as follows.
Based on the expert survey, the main criteria of machine failure evaluation in wafer lithography process include: ME repair and resume capacity, broken wafer complexity, possibility of ME scheduled work resumption and other related factors. The evaluation indexes include: ME repair manpower, ME repair techniques, ME repair experience, ME fault interpretation error, EIO of ME debugging, misoperation of master device, EIO of accessory installation, machine age, EIO of machine, failure in machine parts, inadequate cleaning, inadequate lubrication, proper system maintenance, sufficient repair information, rigorous maintenance organization, good design and configuration of machine system, training of maintenance personnel, decision-making error, staff deployment error, loose system of maintenance organization, poor maintenance facilities, natural errors (human or objects), and special maintenance organizations and cultural structures.
4. Result Discussion
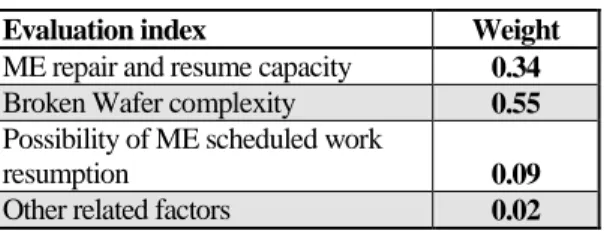
4.1 Evaluation criteria analysis
In the weight analysis on evaluation criteria (see Table 1), this study found that, for failure evaluation in lithography machine and lithography processing in semiconductor industry, the primary consideration is the broken wafer complexity (weight = 0.55). At the beginning of a broken wafer, fault interpretation is needed, which would affect the overall wafer production. Thus, the experience of maintenance work relies on in the overall semiconductor lithography processing. The analysis on criteria evaluation also supports this argument.
shows that the failure is due to the machine itself, the evaluation of ME repair and resume capacity should be done next.
Table 1 Weight of evaluation index for criteria Evaluation index Weight ME repair and resume capacity 0.34 Broken Wafer complexity 0.55 Possibility of ME scheduled work
resumption 0.09
Other related factors 0.02
The purpose is to ensure that, when the broken wafer complexity can be interpreted as failure in lithography machine, on-site maintenance engineers have enough capability to carry out troubleshooting. Otherwise, the overall defect rate would increase fast, which would be a very significant loss to semiconductor manufacturing company. Moreover, it is a challenge to the repair and resume capacity of the on-site maintenance engineer on ME. If a timely shutdown and maintenance are not conducted, or fail to identify the failure cause and overcome it in time, resulting in stoppage of the production line, it would be a great loss to semiconductor manufacturing companies.
In the criteria evaluation of other detailed items, this study found that, for a failure evaluation in lithography machine, the impacts from the possibility of ME scheduled work resumption (weight = 0.09) and other related factors are very small (weight = 0.02). This also shows that, in the semiconductor lithography processing, if machine has failure, the primary work is to repair and then resume work, the conditions to be considered are time efficiency and efficiency. As to whether it is necessary to conduct evaluation on the possibility of ME scheduled work resumption, although it should be considered in troubleshooting, it is only a contingent condition. Both defect rate and shutdown would lead to great loss in semiconductor manufacturing companies. Shutdown is not allowed except for necessary reasons or the failure cause is the main critical part.
The weight of other relevant factors in criteria analysis is only 0.02, this also strongly supports that the time efficiency is needed in semiconductor manufacturing company advanced in this study. In other words, unless it is absolutely necessary to consider other factors, semiconductor manufacturing companies only require a fast fault interpretation and repair. This is also consistent with the analysis of evaluation indexes. Therefore, the maintenance engineers should emphasize on quality rather than quantity. However, this study suggested that it is not the best policy in the long run. In the competitive semiconductor processing era that involves high-tech and high costs, although zero defect rate is a desired goal for all companies, it is less attractive than time efficiency. Thus, it is obvious that desire for time efficiency is urgent in the maintenance of lithography machine.
5. Conclusion
5.1 Conclusions
To ensure the stability of lithography machine is the most important issue for current semiconductor processing. Because once the machine malfunctions, it may like to cause stock pile in the lithography processing area, thus unable to reach a balanced production line. If a set of diagnostic system is built, it could
troubleshooting in lithography machine.
Objectively, the enhancement of failure evaluation on lithography machine depends on a good machine system, as well as a good design and configuration of maintenance equipment. Also from the view of practical experience, over-dependency on the experience of existing staff is sufficient at this stage, but there may be restrictions on the company's future development, which may be the possible directions worth considering for breakthrough or improvement. In the weight analysis on evaluation index for criteria, this study found that, the primary consideration for semiconductor industry in lithography process is the broken wafer complexity. In other words, fault interpretation is needed once a broken wafer occurs, this process would affect the overall wafer production. Thus, the experience of maintenance work relies on in the overall semiconductor lithography process. If a timely shutdown and maintenance are not conducted, or fail to identify the failure cause and overcome it in time, resulting in stoppage of the production line, it would be a great loss to semiconductor manufacturing companies.
6. References
[1] Fan, C. M., Guo, R. S., Chen,A.,Hsu,K.C.and Wei,C.S.“DataMining and FaultDiagnosisBased on Wafer Acceptance Test Data and In-Line Manufacturing Data.”,2001 IEEE International Semiconductor Manufacturing Symposium, 171-174 (2001).
[2] Gupta,M.M.and Rao,D.H.“Case-Based Reasoning Applying PastExperienceto New Problems.”,
Information Systems Management, 10(2), 77-80 (1994).
[3] ITRS, International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductor: 2001, Yield Enhancement (2002).
[4] Kramer,M.A.“Malfunction DiagnosisUsing Quantitative Models with Non-Boolean Reasoning in Expert Systems.”,AIChE Journal, 33(1), 130-140 (1987).
[5] Leang, S. and Spanos, C. J. “A General Equipment Diagnostic System and Its Application on PhotolithographicSequences.”,IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 10(3), 329-343 (1997).
[6] Petti,T.F.,Klein,J.and Dhurjati,P.S.“DiagnosticModelProcessor׃Using Deep Knowledge for Process FaultDiagnosis.”,AIChE Journal, 36(4), 565-575 (1992).
[7] Spanos, C. J., Guo, H. F., Miller, A. and Levine-Parrill,J.“Real-Time Statistical Process Control Using Tool Data.”,IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 5(4), 308-318 (1992).
[8] Surma,J.and Braunschweig,B.“Case-Based Retrieval in Process Engineering׃Supporting Design by Reusing Flowsheets.”,Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 9(4), 385-391 (1996).