行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫 期中進度報告
膜過濾結垢機制及預防之研究--總計畫(2/3)
期中進度報告(精簡版)
計 畫 類 別 : 整合型 計 畫 編 號 : NSC 95-2221-E-002-386- 執 行 期 間 : 95 年 08 月 01 日至 96 年 07 月 31 日 執 行 單 位 : 國立臺灣大學化學工程學系暨研究所 計 畫 主 持 人 : 李篤中 處 理 方 式 : 期中報告不提供公開查詢中 華 民 國 96 年 05 月 28 日
行政院國家科學委員會補助專題研究計畫成果報告
※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※
※ ※
※ 膜過濾結垢機制及預防之研究-總計畫 ※
※ ※
※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※
計畫類別:□個別型計畫 ■整合型計畫(重點研究群計畫) 計畫編號:NSC 95-2221-E002-386 執行期間:95 年 8 月 1 日至 96 年 7 月 31 日 計畫主持人:李篤中 教授-子計畫一 共同主持人:黃國楨 教授-子計畫二 王大銘 教授-子計畫三 鄭東文 教授-子計畫四 莊清榮 教授-子計畫五 吳容銘 助理教授-子計畫六 本成果報告包括以下應繳交之附件: □赴國外出差或研習心得報告一份 □赴大陸地區出差或研習心得報告一份 □出席國際學術會議心得報告及發表之論文各一份 □國際合作研究計畫國外研究報告書一份 執行單位:國立台灣大學 化學工程學系 中華民國96 年 5 月 31 日
行政院國家科學委員會補助專題研究計畫成果報告
膜過濾結垢機制及預防之研究-總計畫
Study on Fouling Mechanisms and Prevention of Membrane Filtration
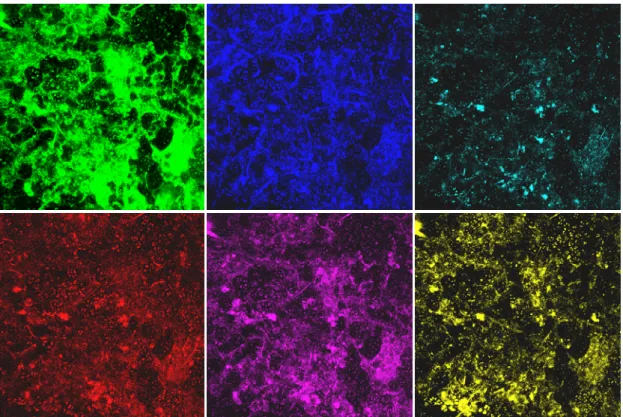
計畫編號 :NSC 95-2221-E002-386 執行期間 :95 年 8 月 1 日至 96 年 7 月 31 日 執行單位 :國立台灣大學 化學工程學系 計畫主持人:李篤中 教授 近年來,隨著生物技術、精密陶瓷、材料科學、電子工業及奈米產業等尖端高科技產業 之快速發展,使得在精密製程上對產品純度之要求大為提昇,例如具極高價位的生技產品像 是酵素、藥用蛋白質或賀爾蒙的回收等,因此精密分離技術的重要性日益突顯。而薄膜過濾 技術是一種相當簡易的物理操作,不牽涉到熱能的需求及相的變化,並有以下的競爭優點: 沒有相間傳送及相變化的問題;可以連續分段分離各種不同物質;能源需求低,對熱敏感產 品相當適合;可操作在室溫,不需再做任何處理;以及可同時完成分段,純化及濃縮等目的; 因此是近半世紀發展最快速的分離技術之一。 過濾速度常是過濾性能的重要指標。在過濾過程中之濾速衰減現象,主要是因為溶質或 粒子於濾材表面的吸附、流體力學特性、或是化學變化而發生的結垢現象(fouling)。薄膜過濾 技術的效率與操作穩定性受其結垢行為所影響,因此如何預防或延緩結垢的發生,是本整合 計畫的重要課題。本年度所完成的研究成果依各子計畫說明如下: (1) 薄膜生物顆粒反應器新程序之開發及機制 在本年計畫中,我們以第一年計畫中建立之技術針對生物膠羽、好氧顆粒、生物膜 活/ 死菌及生物間質(EPS)分佈進行測量,及量測其氧濃度之內部動態變化,最後建立分佈與動態 變化之關連性,以發展探測生物絮聚體結構及輸送程序之關鍵技術。 在薄膜生物顆粒反應器中,由於懸浮液中的顆粒具生物性,所產生的生物絮聚體薄膜結 垢與其他膜過濾結垢比較,兩者的內部結構有所不同,因此成功探測生物絮聚體結垢層內的 結構是薄膜生物顆粒反應器的關鍵技術之一。本研究以共軛焦雷射掃瞄電子顯微鏡針對生物 絮聚體結構進行影像切片分析(圖1),並且重建生物絮聚體 3D 計算網格,應用計算軟體計算 生物絮聚體內流態分佈,推導出生物結垢層內孔洞分佈與透過率之間的關係。孔洞越大,透 過率也越大,懸浮液通過結垢層時較易通過孔洞大的區域。雖然生物結垢層是影響濾速的重 要因素之一,然而若有適當方法改變所產生的結垢層結構,使其主要由大孔洞構成,因可改 進過濾速度或反應速率。
Fig. 1 CLSM images scanned at 5 μm above membrane surface. Top view of fouling layer of image size 100 μm x 100 μm. Green: proteins, β-D-glucopyranose polysaccharides (blue), α-D-glucopyranose polysaccharides (light
blue), red: total cells, purple: dead cells, yellow: lipids.
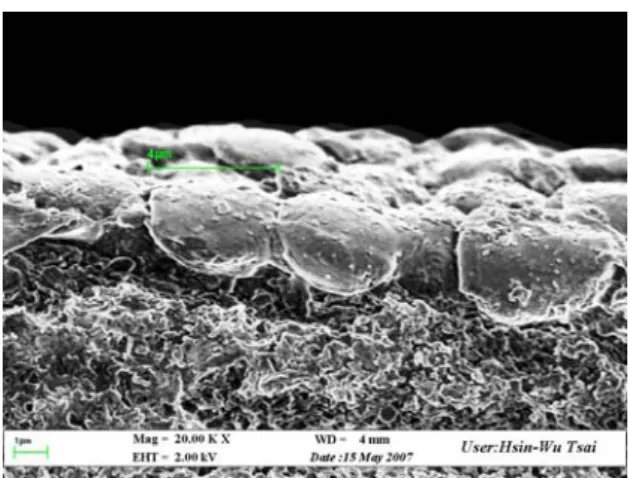
(2) 多相掃流微過濾結垢機制之研究及其在生化分離上之應用 在眾多提升掃流微過濾之過濾速度的方法中,若將氣泡通入過濾渠道,則會增強濾面上 的剪應力,降低固體粒子的附著機率;而且程序簡單、成本低廉,所以是優先的選擇之一。 研究結果顯示:增加氣泡速度會有效減少濾餅量,但是濾餅的結構會變得較為緻密。經由對 濾餅性質的深入分析發現:氣泡之尺寸分布是影響濾餅量、過濾比阻、甚至穩定濾速的重要 因素。在固定掃流速度下,提高掃流速度會使氣泡之平均直徑變小,但是分佈變廣。所存在 的小氣泡,會造成粒子堆積較為緊密,過濾比阻因而提高。而在相同的通氣速度下,提高掃 流速度會使得氣泡尺寸分布變小,因此亦會使得粒子堆積較緊密,過濾比阻提高。將濾餅量 與平均過濾比阻同時考慮後發現:在低掃流速度下,通入氣體對穩定濾速幾乎沒有影響;而 在高掃流速度時,通入氣體反而會降低穩定濾速,通入氣體時的穩定濾速只有未通氣時的 3/4,而氣體速度亦對濾速沒有顯著影響。 為了解粒子在濾膜上的堆積結構,將達到穩態的濾餅以SEM 觀察,如圖 2 所示。其操作 條件為 us=0.2 m/s,ΔP=50 kPa, ug=0.02 m/s。由圖中可以看出:在通氣的情況下,粒子的堆 積結構相當緻密,故可以預期將有較高的平均過濾比阻。
Fig. 2 The side view of filter cake at uL =0.2 m/s, uG =0.02 m/s and ΔP =50 kPa. (SEM x 20,000) (3) 無機膜過濾蛋白質溶液之結垢現象與濾速回復 對於奈米薄膜而言,電性對過濾影響很大,除了超過濾中的擴散及對流項外,電位差項 在奈米系統中更顯重要,因此奈米過濾之操作需同時要考慮到篩選效應(sieving effect)效益與 帶電效應(charge effect)之影響,本研究選用無機薄膜以連續式掃流過濾操作就溶液性質、薄 膜特性及操作參數等對管式無機薄膜蛋白質溶液過濾實驗並探討在不同操作條件、溶液性質 下對濾速與結垢現象的影響以尋求提升濾速之操作方式。在液體速度與溶質濃度之影響方 面,在低液體速度時會產生比較大的濃度極化層,因此當壓力增加時這層濃度極化層會被壓 的更緊密,而造成濾速逐漸趨緩。在液體速度較高時,所產生之剪切力已足夠帶走膜面上可 移除之濃度極化阻力,因此濾速會隨壓力增加而有一線性增加。而由於該膜之孔洞與溶質大 小差異均很大,所以具有完全阻隔的效果,因此改變不同濃度對其濾速並無太大的影響。 在溶液 pH 值之影響方面,液體速度較高時,由結果發現在 pH=4.9 時濾速為最低,這是 因為該 pH 值為 BSA 之等電點,此時 BSA 不帶電因此容易互相聚集成更大的分子也因為少了與 膜面互相的排斥力,因此更易於吸附於膜面上形成結垢造成濾速降低。然而液體速度較低且 一樣在 pH=4.9 時,濾速並不會在隨著壓力上升而增加,造成這個現象的原因有可能是在等電 點時 BSA 在膜面上已經形成一層緊密的極化層,因此當壓力再增加時會使這層極化層被壓縮 的更緊密,造成孔隙度下降及過濾比阻增加,而提早達到一極限濾速。 在曝氣之影響方面,曝氣可以有效的提升濾速,也因為隨壓力增加濾速有趨緩的現象, 所以在曝氣後濾速提升的程度會隨壓力增加而增加。 (4) 低結垢過濾膜之製備及其防垢機制之探討 結垢是造成膜過濾操作過程中濾速衰減的主因,會導致操作成本增加及膜壽命減短,進 而限制了膜過濾技術的實用性。因此,如何避免或減緩結垢的產生,成為膜過濾相關研究最 主要的課題,本子計劃提出之目的即是希望能發展適當的製膜技術及改質方法,製備出低結 垢過濾膜,並對其產生防垢效果的機制加以探討。 在 第 一 年 的 計 畫 中 已 成 功 利 用 蒸 氣 誘 導 式 相 分 離 結 合 溼 式 法 製 備 出 高 連 通 性 的 polysulfone 及 PVDF 微過濾膜,可控制其平均孔徑在 0.1 μm 至 0.8 μm 之間,其孔隙度高於 相同平均孔徑的商業膜。本年度的目標則是建立電漿改質的技術及尋找適當的操作條件來改 質所製備出的polysulfone 及 PVDF 微過濾膜,來提高膜的親水性及降低蛋白質的吸附性;也
會建立臭氧改質PVDF 高分子的技術,再用改質過的高分子製膜,並評估膜的親水性及蛋白 質的吸附性,並比較兩種改質方法的差異。 現在已完成電漿改質技術的建立,利用氧氣電漿可成功將PVDF 膜之親水性提高,可將 對水的接觸角由110o降至30o,目前正在評估其對蛋白質的吸附性、過濾效能、及結垢程度。 另外也完成臭氧活化PVDF 技術的建立,也可利用活化後的 PVDF 接枝其它分子,目前正進 一步探討改質後PVDF 的製膜程序,來製備出親水的 PVDF 微過濾膜。 (5) 膜電性評估及其對膜結垢之影響 本研究首先量測不同 pH 值下牛血清蛋白之界達電位,等電點約在 pH=4.9,於 pH=4 時其 界達電位約為 10mV,而於膜材方面,本研究選用 PC 薄膜及較疏水之 PTFE 薄膜分別進行實驗, 比較膜面蛋白質附著現象,於 pH=4 時 pC 膜界達電位約為-20mV,故 BSA 與 PC 膜材間應有 很明顯之靜電吸引作用,該蛋白質於膜面吸附關係如圖 3 之 SEM 分析所示,可看出在低蛋白 質濃度下該膜面的吸附似由小顆粒蛋白質團所聚集而成,且吸附量並不多,吸附發生只限於 膜面某些區域,並非完全佈滿於膜面上,推測是由於 PC 膜材較親水之特性所導致此現象,故 吸附後膜面之界達電位值應變化不大;在高濃度時,膜面上蛋白質則有明顯的高覆蓋率,且 被吸附的 BSA 之結構有立體現象。
Fig. 3 SEM micrographs(magnification×30000) for PC membrane (3000ppm BSA)
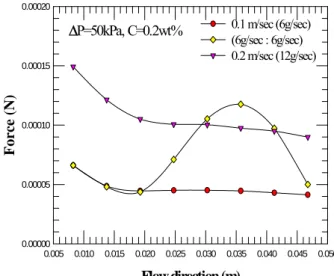
本計畫之重點在於建立膜電性量測技術,並藉以分析溶質與膜材間之靜電作用及其所導 致之膜結垢形為。本研究延伸第一年膜電性量測技術開發,首先利用同軸圓管流線電位模式 配合自行設計之管膜電性量測系統,確立了該量測技術的可行性,這技術應是目前唯一被提 出決定管膜外壁電位之量測方法。另一方面,以蛋白質於膜面附著現象,分析了溶質-溶質及 溶質-膜之間的靜電與親和性作用於膜分離中扮演角色。建立了膜材與溶質膠體粒子之界達電 位及表面能(接觸角)量測技術,可提供分析靜電與親和性作用力,有助於未來以較定量方式 微觀分析膜結垢機制。 (6) 改變掃流膜過濾之流力行為以減緩結垢之研究 在本研究中針對掃流過濾實驗所得到濾速値進行數值模擬,使用計算流力(computational fluid dynamics, CFD)軟體 Fluent,探討是否可以改變流力操作方式來改善薄膜結垢的情形、計 算過濾總阻力值和觀察計算膜面上之剪應力的變化情形(圖 4),針對分析結果提出利用側流 (side-stream)的構思,改變濾室中的流力狀態以提升剪應力(圖 4),達到減緩結垢提升濾速的
效果。圖5 是基於相同的過濾原漿的量(12 g/sec),有無側流的掃流實驗結果,發現有側流的
因此若是在傳統掃流過濾的流道中引進1 或數個側流,將可達到減緩結垢及提升濾速的結果。 本研究以CFD 成功模擬掃流過濾操作,雖然系統簡化許多,但可對膜表面進行受力分析 以及提供側流操作以減緩結垢及提升濾速是一大突破。 ΔP=50kPa, C=0.2wt% Flow direction (m) 0.005 0.010 0.015 0.020 0.025 0.030 0.035 0.040 0.045 0.050 Force (N ) 0.00000 0.00005 0.00010 0.00015 0.00020 0.1 m/sec (6g/sec) (6g/sec : 6g/sec) 0.2 m/sec (12g/sec)
Fig. 4 Force analysis on the membrane surface
Fig. 5 Cake deposition (a) with side stream. (b) without side stream.
綜合效益: 本研究計畫除可凝聚國內薄膜分離技術之研究人力外,本年度達成以下成果 1. 瞭解生物結垢層內孔洞分佈。-子計畫一 2. 比較傳統之生物反應器(MBR)及新開發之生物顆粒反應器(MGBR)其結垢物之特性。-子 計畫一 3. 分析在不同操作條件(例如:懸浮液濃度、掃流速度、過濾壓差、氣泡大小、通氣強度) 下之流態及濾面剪應力等流力特性,了解濾膜之結垢機制與濾餅性質。-子計畫二、四 4. 探討薄膜特性(種類、材質、孔徑等)對其結垢機制及分離效率的影響。-子計畫一、三 5. 在含菌體細胞、蛋白質、塩類、氣泡等多成分、多相混合物,以掃流微過濾進行分離, 並探討不同之pH 值、電解質濃度等懸浮液條件及操作條件對分離效率之影響。-子計畫二、 四 6. 從改質前後膜材特性的改變,及材料與結垢物之間的作用力關係來釐清防垢效應的主要 機制。-子計畫三 7. 分析蛋白質溶液過濾之濃度極化阻力與操作參數間之關係。-子計畫二、四 8. 分析蛋白質溶液過濾之結垢現象,建立結垢阻力與操作參數間之關係。-子計畫二、四 9. 建立蛋白質溶液之濾速與操作參數間之分析模式。-子計畫二、四 10. 建立接枝材料選擇的基準,希望日後可藉此準則,針對不同的應用狀況,設計出適用的 低結垢過濾膜-子計畫三 11. 找出提升蛋白質溶液過濾濾速之操作方式。-子計畫二、四 12. 培訓國內具有適用計算流力套裝軟體、以及具有膜組設計能力之人員。-子計畫一、六 13. 以流力方式改進現有之掃流過濾技術。-子計畫六 14. 以計算流力方式發展掃流過濾技術之模型。-子計畫六 15. 分別建立微孔道及同心圓管流之流線電位理論模式,及其膜電性量測技術,對近一步分 析膜結垢可提供重要的膜電性值,亦可對膜材製備、改質及應用時提供重要資訊。-子計畫 五 16. 由學理與實驗近一步究明微細粒子與膜材間之相互靜電作用力對過濾初段膜孔阻塞的影 響。-子計畫五 17. 由學理與實驗探究電場膜過濾之較佳操作條件,以利工程應用之參考。-子計畫五
研究群之論文發表:
Recent Publication List (2006)
Duu-Jong Lee
1. P. J. He, L.M. Shao, H.D. Guo, G.J. Li, and D. J. Lee, “Nitrogen Removal from Recycled Landfill Leachate by Ex-Situ Nitrification and In-Situ Denitrification,” Waste Management, 26, 838-845 (2006) (SCI, EI)
2. T. Tao, X. F. Peng, D. J. Lee, “Crack Dynamics of Thermally Drying Cake,” J. Ch. I. Ch. E. 36, 511-516 (2006) (SCI, EI).
3. K. Y. Show, T. H. Mao, D. J. Lee, and J. H. Tay, “The Effects of Sonication Density on Performance of Anaerobic Digestion with Different Hydraulic Retention Times,” J. Residue
Sci. Technol., 3, 51-59 (2006) (SCI).
4. P. J. He, Q.K. Cao, L. M. Shao, and D. J. Lee, “Aging of Air Pollution Control Residues from Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator: Role of Water Content,” Science Total Environ. 359, 26-37 (2006) (SCI,EI)
5. J. Chen, X.F. Peng, and D.J. Lee, “Diffusivity of Brownian Particles in Micro-channel,” J.
Colloid Interf. Sci., 296, 737-742 (2006) (SCI,EI)
6. R.M. Wu, D. J. Lee, C.Y. Chang, and J.L. Shie, “Fitting TGA Data of Oil Sludge Pyrolysis and Oxidation by Applying a Model Free Approximation of the Arrhenius Parameters,” J.
Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 76, 132-137 (2006) (工合著) (SCI, EI)
7. Z.C. Chiu, M.Y. Chen, D. J. Lee, S.T.L. Tay, J.H. Tay, and K. Y. Show, “Diffusivity of Oxygen in Aerobic Granules,” Biotechnol. Bioeng., 94, 505-513 (2006) (SCI, EI)
8. T. Tao, X.F. Peng, and D. J. Lee, “Force Exerted on Wastewater Sludge Floc During Ice Engulfment,” J. Ch. I. Ch. E., 37, 299-304 (2006) (SCI, EI)
9. P. J. He, F. Lu, L.M. Shao, X.J. Pan, and D. J. Lee, “Effect of Alkali Metal Cation on the Anaerobic Hydrolysis and Acidogenesis of Vegetable Waste,” Environ. Technol., 27, 317 (2006) (SCI, EI)
10. P. J. He, H. Zhang, L. M. Shao, D. J. Lee, “Limitation of Compliance Leaching Test for Evaluating Carbonated Air Pollution Control Residues,” J. Environ. Quality 35, 442 (2006) (SCI, EI)
11. C. Whiteley, and D. J. Lee, “Enzyme Technology and Biological Remediation: A Review,”
Enzyme Microbial Technol., 38, 291 (2006) (SCI, EI)
12. P. J. He, F. Lu, L.M. Shao, and D. J. Lee, “Oxygen Limitation in Static Respiration Activity Index Test,” J. Chem. Tech. Biotechnol., 81, 1177 (2006) (SCI, EI)
13. K. Y. Show, J. H. Tay, and D. J. Lee, “Properties of High Strength Aggregates from Clay-Amended Industrial Sludge,” J. Residuals Sci. Technol., 3, 105-115 (2006) (SCI).
14. P. J. He, F. Lu, L.M. Shao, X.J. Pan, and D. J. Lee, “Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Polysaccharide-rich Particulate Organic Waste,” Biotechnol. Bioeng., 93, 1145 (2006). (SCI, EI)
15. T. Tao, X. F. Peng, and D. J. Lee, “Interaction Between Wastewater-Sludge Floc and Moving Ice Front,” Chem. Eng. Sci., 61, 5369-5376 (2006). (SCI, EI)
16. T. Tao, X. F. Peng, and D. J. Lee, “Skin Layer on Thermally Dried Sludge Cake,” Drying
Technol., 24, 1047-1052 (2006). (SCI, EI)
17. M. R. Chang, D. J. Lee, and J. Y. Lai, “Coagulation and Filtration of Nanoparticles in Wastewater from Hsinchu Science-based Industrial Park (HSIP),” Separ. Sci. Technol., 41, 1303-1311 (2006). (SCI, EI)
18. A. Ramesh, D. J. Lee, M. L. Wang, et al., “Biofouling in Membrane Bioreactor,” Separ. Sci.
Technol., 41, 1345-1370 (2006). (SCI, EI)
19. M. Y. Chen, D. J. Lee, and J. H. Tay, “Excellular Polymeric Substances in Fouling Layer,”
Separ. Sci. Technol., 41, 1467-1474 (2006). (SCI, EI)
20. T. Tao, X. F. Peng, D. J. Lee, and J. P. Hsu, ”Micromechanics of Wastewater Sludge Floc: Force-Deformation Relationship at Cyclic Freezing and Thawing,” J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 298, 860-868 (2006). (SCI, EI) (合著)
21. D. J. Lee, J. Y. Lai, A. S. Mujumdar, ”Moisture Distribution and Dewatering Efficiency for Wet Materials, ” Drying Technol., 24, 1201-1208 (2006) (SCI, EI)
22. W. Y. SHeng, X. F. Peng, D. J. Lee, A. Su, ”Coagulation of Particles through Rapid Mixing, ”
Drying Technol., 24, 1271-1276 (2006) (SCI, EI)
23. Z. Yang, X. F. Peng, C. P. Chu, D. J. Lee, and A. Su, ”Sedimentation of Permeable Floc, ”
Drying Technol., 24, 1277-1282 (2006) (SCI, EI)
24. B. H. Chen, S. J. Lee, D. J. Lee, and L. Spinosa, ”Rheogical Behavior of Wastewater Sludge Following Cationic Polyelectrolyte Flocculation,” Drying Technol., 24, 1289-1295 (2006) (SCI, EI)
25. P. J. He, J. F. Xue, L. M. Shao, and D. J. Lee, “Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) in Recycled Leachate of Bioreactor Landfill,” Water Res., 40, 1465-1473 (2006). (SCI, EI)
26. K. Y. Show, J. H. Tay, D. J. Lee, et al., “Thermochemical Analysis in the Presintering Phase of Aggregates from Sludge-Marine Clay Mixes,” J. Materials Civil Eng. ASCE, 18, 55-60 (2006). (SCI, EI)
27. L. C. Chen, D. J. Lee, and S. S. Chou, “Charge Reversal Effects of Blanket in Full-scale Floc Blanket Clarifier,” J. Environ. Eng. ASCE, 132, 1523-1526 (2006) (SCI, EI).
28. C. H. Ting, and D. J. Lee, “Production of Hydrogen and Methane from Wastewater Sludge Using a Clostridium Strain,” Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, in press. (SCI, EI)
29. A Ramesh, D. J. Lee, and S. G. Hong, “Soluble Microbial Products (SMP) and Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) from Wastewater Sludge,” Appl. Microb. Biotechnol., 73, 219-225 (2006) (SCI, EI).
30. M. Y. Chen, D. J. Lee, Z. Yang, X. F. Peng, J. Y. Lai. “Fluorescent Staining for Study of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Membrane Biofouling Layers,” Environ. Sci. Technol., 40, 6642-6646 (2006) (SCI, EI).
31. P. J. He, Z. Xiao, L. M. Shao, J. Y. Yu, and D. J. Lee, “In Situ Distributions and Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Full-scale Landfill Layers,” J. Haz. Mat., 173, 1385-1394 (2006) (SCI, EI)
32. D. J. Lee, L. Spinosa, P. J. He, and T. B. Chen, “Sludge Production and Management Processes: Case Study in China,” Water Sci. Technol., 54(5), 189-196 (2006) (SCI, EI).
33. M. Y. Chen, D. J. Lee, J. H Tay, “Distributions of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Aerobic Granules,” Appl. Microb. Biotechnol., in press (SCI, EI)
34. S. S. Adav, M. Y. Chen, D. J. Lee, and N. Q. Ren, “Phenol Degradation by Aerobic Granules and Isolated Yeast Strain,” Biotechnol. Bioeng., in press (SCI, EI).
35. Z. P. Zheng, K. Y. Show, J. H. Tay, D. T. Liang, D. J. Lee, and W. J. Chiang, “Effect of Hydraulic Retention Time on Biohydrogen Production and Anaerobic Microbial Community,”
Process Biochem., 41, 2118-2123 (2006) (SCI, EI).
36. Z. P. Zheng, K. Y. Show, J. H. Tay, D. T. Liang, D. J. Lee, and W. J. Chiang, “Biohydrogen Production in a Granular Activated Carbon Anaerobic Fluidized Bed Reactor,” Int. J.
Hydrogen Energy, in press (SCI, EI).
37. Z. P. Zheng, K. Y. Show, J. H. Tay, D. T. Liang, D. J. Lee, and W. J. Chiang, “Rapid Formation of Hydrogen-Producing Granules in an Anaerobic Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor Induced by Acid Incubation,” Biotechnol. Bioeng., in press (SCI, EI)
38. M. R. Chang, D. J. Lee, and J. Y. Lai, “Nanoparticles in Wastewater from a Science-Based Industrial Park-Coagulation Using Polyaluminum Chloride,” J. Environ. Manag., accepted. (SCI, EI)
39. Z. Yang, X. F. Peng, M. Y. Chen, D. J. Lee, and J. Y. Lai, “Intra-layer Flow in Fouling Layers on Membranes,” J. Membrane Sci., in press. (SCI, EI).
40. J. P. Hsu, Y. L. Weng, D. J. Lee, S. J. Tseng, A. Su, and C. J. Chen, “Electrokinetic Flow in an Elliptic Microchannel Covered by Ion-Penetrable Membrane,” Colloids Surf. B, accepted. (SCI, EI).
41. P. J. He, F. Lu, L.M. Shao, X.J. Pan, and D. J. Lee, “Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Polysaccharide-rich Particulate Organic Waste,” J. Ch. I. Ch. E., accepted (SCI, EI)”
42. Z. Yang, X. F. Peng, D. J. Lee, and A. Su, “Reynolds-Number-Dependent Permeability of Wastewater Sludge Flocs,” J. Ch. I. Ch. E., in press (SCI, EI).
43. Z. C. Chiu, M. Y. Chen, D. J. Lee, C. H. Wang, and J. Y. Lai, “Oxygen Diffusion in Active Layer of Aerobic Granule Considering Steady-State and Transient Responses,” Water Res., in press (SCI, EI).
44. S. S. Adav, M. Y. Chen, D. J. Lee, and N. Q. Ren, “Degradation of Phenol by Acinetobactor Strain Isolated from Aerobic Granules,” Chemosphere, accepted (SCI, EI)
45. A Ramesh, D. J. Lee, and J. Y. Lai, “Membrane Biofouling by Extracellular Polymeric Substances or Soluble Microbial Products from Membrane Bioreactor Sludge,” Appl. Microb.
Biotechnol., in press. (SCI, EI)
46. J. F. Lu, X. F. Peng, and D. J. Lee, “Stability of Boiling on Annular Fin Surfaces,” Heat
Transfer Eng., accepted.
47. T. Tao, X. F. Peng, A. Su, A. S. Mumjudar, and D. J. Lee, “Model for Sludge Cake Drying Accounting for Developing Cracks,” Drying Technol., accepted (SCI, EI).
48. Y. Zhang, X. F. Peng, A. Su, A. S. Mumjudar, and D. J. Lee, “Drying for Porous Medium Containing Concentrations Sodium Chloride Solution,” Drying Technol., accepted (SCI, EI). 49. J. P. Hsu, S. H. Lin, S. J. Tseng, A. Su, D. J. Lee, and C. J. Chen, “Ionic Separation Efficiency
of a Novel Electric-field-assisted Membrane Module Comprising an Array of Microchannel Units,” J. Colloid Interf. Sci., in press. (SCI, EI)
50. J. P. Hsu, C. C. Ting, D. J. Lee, S. J. Tseng, C. J. Chen, and A. Su, “Residence Time Distribution for Electrokinetic Flow through a Microchannel Comprising a Bundle of Cylinders,” J. Colloid Interf. Sci., in press. (SCI, EI)
51. M. Y. Chen, D. J. Lee, J. H. Tay, and K. Y. Show, “Staining of Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Cells in Bio-aggregates,” Appl. Microb. Biotechnol., (SCI, EI) accepted.
Recent Publication List (2005-2006)
Kuo-Jen Hwang
1. Hwang, K.J., Y.C. Shie and Y.S. Lin, “Cake formation and flux decline in centrifugal filter basket,” J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Engrs., 36, 5, 517-525 (2005).
2. Hwang, K.J. and L.W. Lin, “Separation of Protein from Microbe/Protein Binary Suspension Using a Cross-Flow Microfiltration,” J. Chem. Eng. Japan, 38, 11, 894-902 (2005).
3. Hwang, K.J., S.Y. Lyu and F.F. Chen, “The Preparation and Filtration Characteristics of Dextran-MnO2 Gel Particles,” Powder Technol., 161, 1, 41-47 (2006).
4. Hwang, K.J., F.Y. Chou and K.L. Tung, “Effects of operation conditions on the performance of cross-flow microfiltration of fine particle/protein binary suspension,” J. Membr. Sci., 274, 1-2, 183-191 (2006).
5. Hwang, K.J., Y.L. Hsu and K.L. Tung, “Effect of Particle Size on the Performance of Cross-Flow Microfiltration,” Adv. Powder Technol., 17, 2, 189-202 (2006).
6. Hwang, K.J., S.F. You and T.M. Don, “Disruption Kinetics of Bacterial Cells during Purification of Poly-β-Hydroxyalkanoate Using Ultrasonication,” J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Engrs.,
37, 3, 209-216 (2006).
7. Ramesh, A., D.J. Lee, M.L. Wang, J.P. Hsu, R.S. Juang, K.J. Hwang, J.C. Liu, S.J. Tseng, “Biofouling in Membrane Bioreactor” Sep. Sci. Technol., 41, 7, 1345-1370 (2006).
8. Hwang, K.J., Y.T. Hsieh and W.T. Wang, “Cross-flow microfiltration of fine particles suspended in polymeric solution”, Sep. Sci. Technol., 41, 8, 1551-1563 (2006).
9. Hwang, K.J. and S.J. Hwang, “The Purification of Protein in Cross-Flow Microfiltration of Microbe/Protein Mixtures”, Sep. Purif. Technol., 51, 416-423 (2006).
10. Hwang, K.J. and M.T. Hong, “Effect of Slurry Rheology on the Performance of Cross-Flow Filtration,” J. Chem. Eng. Japan, 39, 7, 693-702 (2006).
11. Hwang, K.J. and K.H. Chou, “Effect of Cake Compression on the Performance of Centrifugal Dewatering,” Drying Technol., 24, 1263-1270 (2006).
12. Ho, C.D., K.J. Hwang, J.W. Tu and Y.S. Su, “The Recycle-Effect on Cool-Thermal Discharge Systems under Melt Removal and Flow Rate Variations”, International Communications in
Recent Publication List (2005-2007)
Da-Ming Wang
1. M.H. Ho, D.M. Wang, H.J. Hsieh, H.C. Liu, T.Y. Hsien, J.Y. Lai, L.T. Hou, “Preparation and characterization of RGD-immobilized chitosan scaffolds,” Biomaterials, 26, 3197-3206 (2005).
2. C.Y. Hsieh , S.P. Tsai , D.M. Wang , Y.N. Chang , H.J. Hsieh, “Preparation of gamma-PGA/chitosan composite tissue engineering matrices,” Biomaterials, 26, 5617-5623 (2005).
3. C.Y. Hsieh, H.J. Hsieh, H.C. Liu, D.M. Wang, L.T. Hou, “Fabrication and release behavior of a novel freeze-gelled chitosan/γ-PGA scaffold as a carrier for rhBMP-2,” Dental Materials 22, 622-629 (2006).
4. M.H. Ho, L.T. Hou, C.Y. Tu, H.J. Hsieh, J.Y. Lai, W.J. Chen, D.M. Wang, “Promotion of cell affinity of porous PLLA scaffolds by immobilization of RGD peptides via plasma treatment,” Macromolecular Bioscience 26, 5617-5623 (2006).
5. H.A. Tsai, C.Y. Kuo, J.H. Lin, D.M. Wang, A. Deratani, C. Pochat, K.R. Lee, J.Y. Lai, “Morphology Control of Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes via Water Vapor Induced Phase Separation,” J. Membrane Sci., 278, 390-400 (2006).
6. M.H. Ho, D.M. Wang, L.T. Hou, H.J. Hsieh, J.Y. Lai, “Preparation of cell-specific membranes for bone regeneration by peptide grafting,” Desalination, 199, 144-146 (2006). 7. M.H. Ho, D.M. Wang, L.T. Hou, C.Y. Tu, H.J. Hsieh, J.Y. Lai,“RGD immobilization on
PLLA membranes to promote biocompatibility,” Desalination ; 200, 501-502 (2006).
8. D.Y. Kang, E. Wu, D.M. Wang, “Modeling white-light-emmiting diodes with phosphor layers,” App. Phys. Lett. 89, 231102-231104 (2006).
9. C.Y. Hsieh, S.P. Tsai, M.H. Ho, D.M. Wang, C.E. Liu, C.H. Hsieh, H.C. Tseng, H.J. Hsieh, “Analysis of freeze-gelation and cross-linking processes for preparing porous chitosan scaffolds,” Carbohydr Polym, 67, 124-132 (2007).
10. S.P. Tsai, C.Y. Hsieh, Y.N. Chang YN, Wang, D.M. Wang, H.J. Hsieh, “Gamma-poly(glutamic acid)/chitosan composite scaffolds for tissue engineering applications,” Mater Sci Forum, 539-543: 567-572 (2007).
11. S.P. Tsai SP, C.Y. Hsieh, D.M. Wang, LLH Huang, J.Y. Lai , H.J. Hsieh, “Preparation and cell compatibility evaluation of chitosan/collagen composite scaffolds with amino acids as cross-linking bridges,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci. (2007)
Recent Publication List (2005-2006)
Tung-Wen Cheng
1. 鄭東文、潘帥宇、李日瑋,2005,『沉浸式薄膜過濾系統臨界濾速之探討』,化工,52(1), 50-62。
2. H. M. Yeh, T. W. Cheng and J. W. Tsai, 2006, “Sizing Agent Recovery by Membrane Ultrafiltration in Tubular-Membrane Module,” Chem. Eng. Commun., 193(6), 661-674. (SCI, EI)
3. C, D. Ho, T. W. Cheng, Y. T. Chen and J. J. Guo, 2006, “The Theoretical and Experimental Studies on the heavy Water Enrichment in Concentric-Tube Frazier-Scheme Thermal-Diffusion Columns under Flow-Rate Fractions and Plate Spacing Variation,” J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Engrs., in press.
4. T. W. Cheng and L. N. Li, 2006, “Gas-Sparging Cross-Flow Ultrafiltration in Flat-Plate Membrane Module: Effects of Channel Height and Membrane Inclination,” Sep. Purif.
Recent Publication List (2006)
Ching-Jung Chuang
1. C.J. Chuang, P.W. Wang, C.C. Hu, and K.L. Tung, (2006) “Electroosmotic Flow through Particle Beds Packed with Conditioned Sludges,” J. Water Supply: Res. and Technol.–Aqua, 55(7), 527-533 (SCI:; EI).
2. Y.L. Li, T. H. Chang, C.Y. Wu, C. J. Chuang and K. L. Tung(2006)” CFD Analysis of Particle Deposition in the Spacer- filled Membrane Module”, J. Water Supply: Res. and Technol.–Aqua, 55(7), 589-601 (SCI:; EI)
3. C. C. Hu, S. Y. Wang, C. L. Li, C. J. Chuang and K. L. Tung(2006),”Ion Exchange Adsorption and Membrane Filtration Hybrid Process for Protein Mixture Separation”, J. Chem.Eng. Jpn, 39, 1283-1290 (SCI:; EI)
Recent Publication List (2005-2006)
Rome-Ming Wu
1. S. S. Sung, D. J. Lee, and R. M. Wu, “Steady-State Solid-Flux Plot of blanket in Upflow Suspended Bed,” J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Eng., 36, 385-390 (2005). (Jul.) (SCI, EI) (0.227) 石延 平教授論文獎 (NSC 93-2214-E-032-003)
2. R. M. Wu, D. J. Lee, C. Y. Chang, and J. L. Shie, “Fitting TGA data of oil sludge pyrolysis and oxidation by applying a model free approximation of the Arrhenius parameters,” J. Anal.
Appl. Pyrol., 76, 132-137 (2006). (Jan.) (SCI, EI) (1.352) (NSC 94-2214-E-032-001)
3. R. M. Wu, M. H. Lin, H. Y. Lin, and R. Y. Hsu, “3D Simulations of Hydrodynamic Drag Forces on Two Porous Spheres Moving along Their Centerline,” J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 301, 227-235 (2006). (Sep.) (EI) (1.784) (NSC 94-2214-E-032-001)
4. K. J. Hwang and R. M. Wu, “Use of Models in the Design of Cross-Flow Microfilters for the Purification of Protein from Bio-Mixtures,” J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Eng., 38, 385-390 (2007). (Jan.) (SCI, EI) (0.227)
5. R. M. Wu, T. H. Lee, and W. J. Yang, “A Study of Water Treatment Clarifier,” Tamkang
Journal of Science and Engineering, accepted (2006). (NSC 93-2214-E-032-003)
6. R. M. Wu, K. J. Li, and S. S. Sung, “Dynamic Response of Sizes of Humic Acid-Kaolin-PACl Aggregates,” Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, accepted (2006). (NSC 93-2214-E-032-006)
7. W. J. Yang and R. M. Wu, “An Improvement of Construction and Operation of Water Treatment Clarifier,” International Journal of Transport Phenomena, submitted March. (2007) 8. K. J. Lee and R. M. Wu, “Simulation of Resistance of Cross-flow Microfiltration and Force