Using ICT with Competence Indicators for the Learning of Mathematics
全文
(2) teaching. materials. for. students. of. factors.. different. requirements. In the development concept of. It is estimated that a student requires fifty. blending information into teaching in each course,. thousand times of enhancement to truly learn a skill. they hope to integrate the materials into proper. [5]. As teachers are unable to provide so many times. categories. The Separating-Grade Detailed Item. of enhancement, teaching machines are required as a. (SGDI) is viewed as the index of knowledge map and. result. Machines can provide materials, interact with. the Information and Communication Technologies. students and provide immediate response to students’. (ICT) are used to manage the knowledge. ICT, and in. answers according to the sequence of teaching. particular the desktop computer, are now a part of. materials. If students answer correctly, they can. teaching and learning culture in classroom [2][3]. The. continue learning.. interest in ICT in school is unequivocal support for. opportunities to operate the machines can be regarded. the value of computers in educational settings and a. as enhancement to behaviors.. Acquiring correct answers and. political commitment to the creation of a knowledge economy. The main goal of this study is to propose. 1.1.2 Information Processing Theory. feasible categorization method of learning resources and design the application system of digital teaching materials that cross the borders of different editions. Gagné made use of the viewpoint of cognitive. of textbooks for the use of teachers when blending. psychology to explain the human behavior [6]. It is a. information into teaching and help students from. kind of learning to explore learning procedures in the. getting lost in the Internet.. view of information management and interpret human “learning and memory” as “information management” with changes generated during the. 1.1 Pedagogy Review. procedures.. According to Gagné’s idea, three. principles help learning: y Analyze the components of final task to. 1.1.1 Programmed Instruction. perform teaching activities. y Ensure that each component element is. Skinner thought that enhanced training is the main. skilled.. mechanism of organism learning procedure [4]. When. stimulation. repeats. and. causes. y Arrange component elements in order to. proper. responses, the response stimulation is controlled. The. ensure that final task can be acquired.. main point is: the teaching materials are divided into. The ultimate goal of teaching is to have potential. many small units and evaluation is made after each. of students fully developed. To achieve such a goal,. small unit right away and response is given after the. planning in teaching is required. A planned teaching. evaluation. The advantage is that it conforms to the. has to adopt scientific design principle, that is, to. principle of individual teaching; feedback is obtained. verify the importance of teaching goals and. right away after reaction to form the responsive. emphasize the description of form in nature. When. learning situation; reparation of teaching materials. making teaching design, one shall base it on analysis. goes from ease to difficulty to maintain learning. of level tasks. At establishment of teaching activities. motives and to exclude interference of external. and learning design stage, the internal conditions of 2.
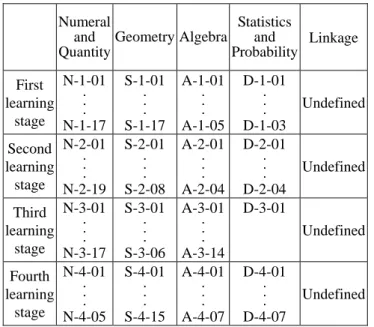
(3) learners and external situation outside learning have. learning moving and self-orientation learning of. to be noticed to obtain the best learning results.. learners, that is, to assist learners in developing their. Evaluation measures, standards and tools are to be. own learning scaffold.. determined to measure students’ performances and conduct teaching evaluation.. 1.2 SGDI - Index in Knowledge Map 1.1.3 Scaffolding Instruction Vygotsky. (1978). thought. “learning. 1.2.1 Learning Areas and Competence Indicators. leads. development”. Scaffolding accounts for how a more knowledgeable partner can assist the cognitive. The major features of the Grade 1-9 Curriculum. development of a less able one [7][8][9]. Good. which is implemented gradually from 2001 are to. learning should transcend the developed zone. The. bring up the "lifelong learning" ability of students.. best teaching and evaluation are in the zone of. The competence indicators in learning area of. proximal development (ZPD). By means of leading. mathematics are divided into four stages: the first. through the possible developed zone, the students. learning stage for grade 1-3, the second for grade 4-5,. obtain a temporary support [10]. The framework of. the third for grade 6-7, and the fourth for grade 8-9.. self learning scaffold assists the learners to. The mathematics contents have five subjects:. understand the meaning and purpose of the learn. numeral and quantity; geometry; algebra; statistics. contents [11]. The focus of learning is transferred. and probability and linkage. The competence. from the teachers to the students [12].. indicators of the learning stages are shown in Table 1.. Some feasible scaffold behaviors in teaching. Table 1. The competence indicators of the learning stages in mathematical area. include: providing relevant examples, assistant counseling and posing questions. Scaffold behaviors are divided into the following links: y Building. scaffolds:. circling. the. Numeral Statistics and Geometry Algebra and Linkage Quantity Probability. current. learning themes and building conceptual. First N-1-01 . . learning . stage N-1-17 Second N-2-01 . . learning . stage N-2-19. frames under “near development area.” y Entrance into situations: guiding students into certain question situations. y Independent exploration: making students explore independently.. Third N-3-01 . . learning . stage N-3-17 Fourth N-4-01 . . learning . stage N-4-05. y Cooperative learning: group negotiation and discussions. y Evaluation of effects: evaluation of learning effects includes self-evaluation by students and learning evaluation by learning groups of individuals. The final goal of scaffold teaching is to achieve 3. S-1-01 . . . S-1-17 S-2-01 . . . S-2-08 S-3-01 . . . S-3-06 S-4-01 . . . S-4-15. A-1-01 . . . A-1-05 A-2-01 . . . A-2-04 A-3-01 . . . A-3-14 A-4-01 . . . A-4-07. D-1-01 . . . D-1-03 D-2-01 . . . D-2-04 D-3-01. Undefined. Undefined. Undefined D-4-01 . . . D-4-07. Undefined.
(4) The competence indicators are arranged in three codes. The first is the theme; the second the stage and the third serial number, representing indicator serial number under the subcategory. For example: N-1-06 indicates the understanding of Nine-to-Nine Multiplication (N: the numeral and quantity, 1: first learning stage, 06: the sixth competence indicator).. Actual Level of Development 3-n-01. ZPD 3-n-02. Level of Potential Development 3-n-03. Figure 1. ZPD and the indicators of SGDI. From the ZPD theory, it shows that the student. The SGDI of competence indicators represents. develops two concepts, real level of development and. the relation for learning order. It also represents the. potential level of development. If someone has. level that the materials are easy or difficult. The. learned the ability with the SGDI, the next SGDI. system will select the SGDI of the grade 1-9. becomes the ZPD.. curriculum as the classified item, in accordance with it to establish the knowledge indexed map. Thus, the. 2. The System Architecture. other teachers also conveniently use the learning elements. The system uses the SGDI for the. 2.1 The Design of the System. classification of the learning and evaluating elements, such as the index of the knowledge map. Table 2 shows the learning progression with the SGDI.. The computer as a partner providing feedback and assistance might provide support to young learners. Table 2. The learning progression with competence indicators and SGDI (Grade 3) Competence Indicator. SGDI. [13]. The system provides a temporary support (the scaffolds) to help the students develop their. N-1-01. N-1-02. ....... N-1-16. N-1-17. self-scaffolding as the capability of the learner. 3-n-01. 3-n-02 3-n-08. ....... 3-n-12 3-n-14. 3-n-14 3-n-16. advanced. It is based on the SGDI of the competence indicators in Grade 1-9 Curriculum to build knowledge index map for the convenient use of teaching elements by teachers. Figure 2 shows the. 1.2.2 Learning Elements as External Knowledge. learning flow chart for three-grade students. Students are dependent on the sequence of SGDI for advanced learning. The teaching elements that teachers upload. From. the. related. documents. of. knowledge. are divided with SGDI to avoid the complication. management, it shows that learning elements are. from detailed categories of teaching materials of. regarded as external knowledge. And the information. programmed instruction. It helps teachers upload. technology could be applied for the external. teaching elements in yearly detailed items. To realize. knowledge management to preserve, reuse, share and. the control on learning procedures, the system has. reproduce. Figure 1 shows the relation between ZPD. two parts, the first one is learning elements and the. and the indicators of SGDI.. other is the evaluation elements. Students have to do two things—to browse learning elements and take 4.
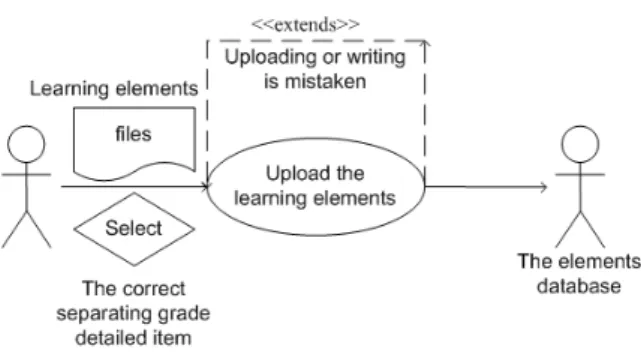
(5) after they enter the system, the system. tests.. provides students with teaching material list based on their learning conditions.. Students. select one of the teaching materials and the system will transmit the elements to the monitor of student’s computer. y Accepting evaluation: For students, after they Figure 2. The learning flow chart for three-grade. enter the system, the system provides students. students. with evaluation list based on their learning conditions.. 2.2 The Function of System Modules. Students. click. to. accept. evaluation and the system provides students with questions in random order.. Students. The system is designed for two types of users:. have to complete all the questions in fifteen. teachers and students. The function of system. minutes or they have to start from the. modules is shown as figure 3.. beginning again. y Checking learning conditions: For students, they click to check learning conditions and the system responds them to the computer screen. Figure 4 shows the teachers use SGDI to stores the learning elements in the learning database based. Figure 5 is the teacher inquiring some of the learning elements. Figures 6-7 show an example of the learning elements.. Figure 3. The use case of the whole system functions y Entering the system: For all of the users, add the account, then use it. y Uploading the learning elements: For teachers, store it in the learning database based on the SGDI.. Figure 4. Uploading the learning elements. y Uploading the evaluating elements: For teachers, store it in the evaluating database based on the SGDI. y Inquiring. any. elements:. Inquiring. any. elements by means of the SGDI. y Browsing learning elements: For students, 5.
(6) 3. Method and Result 3.1 Subjects and Design Forty participants are randomly selected male and female three-grade students enrolled in elementary school. The test instrument is the Mathematical Achievement Test. There are twenty-five questions in numeral. It examines the numeral for three-grade students. The cognitive level includes knowledge, realization, application and analysis. The applied. Figure 5. The teacher inquires some of the elements. category includes addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and mixed situation in the case of money, measurement,. time. and. statistical. table.. The. reliability is .80, the concurrent validity compared with “Mathematical Ability Develop Test” is .77. The experiment is the one-group pretest-posttest design. The performing procedure has pretest, using the system for a month, and then posttest.. 3.2 Result and Discussion The original scores are transferred into percentage. Figure 6. The learning element for students. scores and the descriptive statistics of experimental results are shown in Table 3.. Table 3. Means and Standard Deviations of Pretest and Posttest Pretest Posttest M 63.9 73.4 SD 21.57 18.11 The results were analyzed by the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) of randomized block design that the system is considered as an independent variable, whereas the score of mathematical achievement test. Figure 7. The learning element. is dependent variable defined in the section of experimental design. ANOVA is used to uncover the direct effect of one or more independent variables on 6.
(7) the dependent variable. The key statistic is the F-test. ability on their own. Therefore, this study infer that. of difference of group means. The analysis of. using nine-year ability index yearly detailed item as. ANOVA shows that the result is significant ( Table. the control of teaching material categorization and. 4).. learning progress are feasible. It proposes concrete suggestions on current use of teaching resource. Table 4. The summary table of ANOVA SS df MS F SSb.subject 27571.69 39 SSw.subjects 5121.50 40 SSb.treatment 1757.81 1 1757.81 20.38** SSresidual 3363.69 39 86.25 SSt 32693.19 79 **F.99(1, 39) = 7.32, p < .01. network. From research on effects of remedy teaching on junior high school students with poor performance in English, students with low academic achievements can improve their achievement after taking remedy teaching. At the moment, each city/county is aggressively building teaching resource websites with the main consideration for teachers to blend the information into their teaching. If students. Table 4 shows the difference of the score of. use. mathematical achievement test between pretest and. the. learning. system. after. classes. into. consideration, they can also improve their academic. posttest. The students spend approximately a month. achievements. Using yearly detailed items to. reading and training the materials and elements. The. categorize learning elements helps teachers upload. statistical result is significant (F1,39 = 20.38**, p <. and acquire teaching materials and it is as well as a. 0.01). The system benefits students a lot in. simple mechanism of learning procedure control for. calculation ability which should be derived from the. students when they study on their own.. smoothness training on numeral. It also helps students improve in mathematical application ability. From the above tables show that:. References. Teaching of mathematical concept might not be a field where computer system can develop. The. [1] International Society for Technology in Education. elements provided by the system can not complete. (ISTE),. teaching of mathematical concept. Improvement of. [2] L. Plowman and C. Stephen, “A ‘benign addition’?. of the evaluation elements are application questions. Research on ICT and pre-school children”,. and solving more application questions helps students Feasible. learning. technology. 2000.. the training of the system and pressure of time. Most. questions.. educational. standards for students”, Eugene, OR: Author,. students’ calculation ability might be pushed under. solve. “National. Journal of Computer-Assisted Learning, Vol. 19,. resource. Issue 2, pp.148-164, 2003.. categorization method is established in order to build. [3] R. Luckin, D. Connolly, L. Plowman and S. Airey,. the networked learning environment.. “Children’s interactions with interactive toy technology”, Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, Vol. 19, pp.165-176, 2003.. 4. Conclusions and Future Research. [4] B. F. Skinner, “Programmed instruction revisited”, Phi Delta Kappan, Vol. 68, pp.103-110, 1986.. The system helps students improve mathematical. [5] B. F. Skinner, “The technology of teaching”, New 7.
(8) York: Appleton-Century- Crofts, 1968. [6] R. M. Gagné and M. P. Driscoll, “Essentials of Learning for Instruction”, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1975. [7] L. S. Vygotsky, “Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes”, M. Cole, V. JohnSteiner, S. Scribner, E. Souberman, (Eds.). Cambridge, MA; Harvard University Press (Original work published 1935), 1978. [8] L. S. Vygotsky, “Thought and Language” The MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass. 1986. [9] D. J. Wood, J. S. Bruner and G. Ross, “The role of tutoring in problem solving”, Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, Vol. 17, Issue 2, pp.89-100, 1976. [10] A. S. Palincsar and A. L. Brown, “Reciprocal teaching. of. comprehension-. comprehension-. fostering. monitoring. and. activities”,. Cognition and Instruction, Vol. 1, Issue 2, pp.117-175, 1984. [11] M. C. Wang and S. T. Peverly, “The self-instructive process in classroom learning context”, Contemporary Education Psychology, Vol. 11, pp.370-404, 1986. [12]. M.. H.. Bickhard,. “Constructivism. and. Relativisms: A shopper’s guide”, Science & Education, Vol. 6, pp.29-42, 1997. [13] T. W. Chan and A. B. Baskin, “Learning companion systems”, In Intelligent Tutoring Systems: at the Crosssroads of Artificial Intelligence and Education (eds. C. Frasson & G. Gauthier), Ablex, Norwood, pp.7-33, 1990.. 8.
(9)
數據
相關文件
• Among the learning objectives for ELEKLA, the language development strategies, literary competence development strategies and attitudes specific to language and literature
• Among the learning objectives for ELEKLA, the language development strategies, literary competence development strategies and attitudes specific to language and literature
The indicators for assessment of child learning experiences evaluate children’s learning performance from the curriculum perspective, while the indicators for the Domain of
Based on “The Performance Indicators for Hong Kong Schools – Evidence of Performance” published in 2002, a suggested list of expected evidence of performance is drawn up for
stating clearly the important learning concepts to strengthen the coverage of knowledge, so as to build a solid knowledge base for students; reorganising and
* 2 Learning contents to be replaced by the learning elements covered in the enriched TEKLA curriculum starting from 2016/17 school year... The enriched
Learning elements of the knowledge contexts at junior secondary level in the TEKLA Curriculum Guide was enriched to give students a broad and balanced. foundation on
• elearning pilot scheme (Four True Light Schools): WIFI construction, iPad procurement, elearning school visit and teacher training, English starts the elearning lesson.. 2012 •