The development of Rasch model to analyze the ranking of
elimination system with double repechage
Ho, Pi-Yen
Yau, Han-Dau
Graduate Institute of Sports Training Science, National College of P. E. & Sports,
250, Wen-Hua 1
stRoad, Kueishan 333 Taoyuan, Taiwan, ROC.
E-Mail: yauhd@hotmail.com
AbstractThe purpose of this study was to estimate the performances of elimination
system with double repechage by using Many-Facet Rasch model. The subjects
were the women players of Athens 2004 Olympic Judo Game (- 48 kg, extra-light).
In the measurement design, the elimination system with double repechage included
‘facet’ and ‘hierarchical’ factor; there were two repechage matches in addition to the
main elimination matches. This study used an estimate elimination matches’ model
by the design of Yau’s development in 2004, the losing of 1/16 hierarchical anchored
at -0.43; the scoring model was 3 points model and anchored at -0.33. the result of
estimation in this research was successful, estimated potential was almost equal to the
competition result ranking, the only deficit was an disorder appeared to one player; in
further analysis, this result could be accept because the winning percent was the same
and the competitor include the gold medal, so that the unreasonable higher estimation
could be happen. However, limited by the hierarchical factor, there were players with
high estimate potential did not get good ranking. In conclusion, our method quantized
the ranking of Olympic judo elimination system with double repechage successfully.
Keywords: facet, ranking, Rasch model, the elimination system with double repechage,
Introduction
Performance is the important priority indicates on ports science research, for example, within the events like swimming and track& field, the objective records could be used in academic purpose. However, some kinds of competition, final performances were the results that judged by ranking. Ranking was the ordinal scales,it could not used to parametric statistics,for instance, it would result in mistake that the ranking used to be the indicate for multiple regression analysis. In some situation, many sports science research take the winning percent or winning points to be the effect indicates, but, ‘winning percent or points’ only was the assessments for objects, without comparison within objects, in other words, there is not a standard between objects. From Yau’s(2003b) research had improved that “Rasch model had converted (a logistic transformation) ranking of ordinal data (performance) into an approximately equal-interval number line (linear continuum or scale representing the variable), it could offer more information and precisely competition results.”
The system of competition
There are two main kinds of competition system: round matches and elimination matches. All the competitors had to participate once at least in the round matches system, it seems more fair than elimination matches system. In further, in elimination system competition, if the competitors lose one time, that means he was eliminated. From another point, there were lees request of facility and human recourses in the elimination system, but the final result would be unfair and depended on fortune more.
1. Double Elimination Matches means if the competitor loses one time, he would join another single eliminate matches.
2. Double Round Matches means there are two round match system, and the competitors is less, but had more competition time.
3. Rank Ordering Matches means the purpose of competition was for ranking. Like the world table tennis championship.
4. Challenge Tournaments means the system was classified by skill, the superior must accept the challenge from lower level.
5. Combination Tournaments means that tournaments combine two systems, ex: elimination matches first, then round matches; or group round matches first, then round matches. 6. Page System means single elimination matches was the main component, if the
competitor defeated by champion, he got the chance to join another single elimination matches, this method was design for who has the ability to achieve silver.
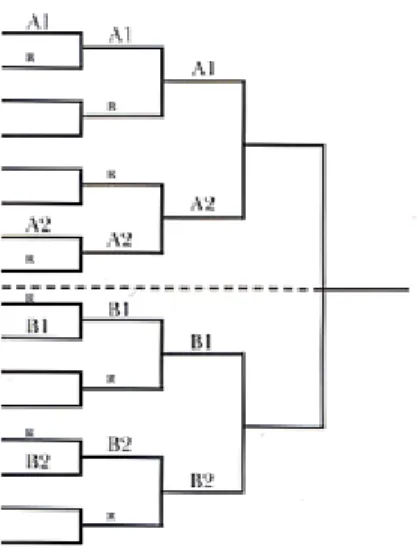
Figure 1 The elimination system with double repechage
All contestants defeated by the group winners A1, A2, B1 and B2 will take part in the repechage of their respective pools according to the elimination system. Their final contest will be against the loser of the final of each receptive other table. The winners of these two contests are placed « third », the losers are placed « fifth ». The « seventh » are the losers of the final repechage fights.
Purpose
performance in the Olympic judo competition system.
Thurstone (1927) had point out the paired comparisons method for social value analysis, in 1952, Bradley and Terry build the paired comparisons method theory formula. Further more, Davidson and Beaver (1977) had expanded the Bradley-Terry model; allow the contest result to be the drawn game. The Rasch measurement model could promote the level of quantification. Linacre(1995)had indicate :Bradley-Terry model could use the Rasch model convert into:
In the Bradley-Terry model, if the n& m was equal (drawn game), the formula could not be establish. Davidson and Beaver (1977) had add a parameter ν, established the Davidson-Beaver model:
Matthews and Morris used the Davidson-Beaver model to study the effect of pain control in 1995. Linacre used the Rasch model to present the effect of equal and ranking by the following formulas:
From the results of these research, we can understand Rasch model could applied on ‘paired comparisons’, in other words, the competition system of fighting sports could build linear logarithmic model by the level parameter (effects or components), so that, theoretically, the ranking competition system in this research was also the ‘paired comparisons’, could evaluate the judo contest performance in the ranking system by linear logarithmic Rasch model.
Linacre(1997) used the Winsteps (Rasch model software) to improve the paired-comparison assessment, original data was 1977 Venice chess championship (round matches), there were 11 players, table records as follow: winner ‘1’, loser ‘0’, drawn game ‘D’. From the point of assessment: the raw data are independent subjects (each participants had only link to each other one time on each topic), therefore, there shall 726 link points in the whole data base (repeat model), but only 110 link points in paired-comparison model, deficiency was 85% (616 link points). For assessment, round matches was the lowest limited design for potential estimate, each topics has only one time to link to each other. Rasch model was Bn-Bm=log(Rn/Rm);the difficulty at the same competition was Do, estimate the ability of player n was B’n, B’n-Do=log(Rn/Rm), so the player m was B’n ,B’m-Do= log(Rm/Rn). In that, B’n-B’m=2log(Rn/Rm)=2Bn-Bm, from this formula we can understand that home team and visiting team repeated scaling in round matches, we shall add 0.5 parameter to adjust the score.
competition. Based on this conclusion, Davidson-Beaver model had been applied on paired comparison medical pain control research(Matthews& Morris, 1995)、study the effect of Rasch model on equal and ranking method (Linacre, 1995) and another research had used the Winsteps method to evaluate the players’ ability in 1977 Venice chess championship(round matches). In Linacre’s extreme score study (1999), he pointed out that paired comparison was a variable and strong method, extreme score could be adjusted by Bayesian process, it advocated that use the parameter 0.33 to adjust in extreme score adjustment.
eliminate the disarray phenomenon.
Yau did a further research (2002a), made use of one-step Vertical equating method to provide precisely calibration ability for all group round matches competitors. This method could solve the problem of potential evaluation in group round matches. Even more, through the linear logistic Rasch model to evaluate the performance or ranking contests to complete the estimate of ranking competition by Hierarchical model (Yau, 2003a), and the purpose of this study is analysis the ranking of elimination matches’ evaluation, the foundation was the mathematics estimate of elimination matches (paired matches’ number ), the parameter 2 of exponent ( n
2
) for weighted in hierarchical, converting the result (ranking) into Rasch scale (logit) and a revision of adjust value, make the estimate potential could fit with the competition results.Methods:
Subjects were the 2004 Athens Olympic games female judo players, women-48kg extra-light class (figure 1). As far as examination design be concerned, the Olympic judo competition system has facet factor and hierarchical factor; for this reason, establish the calibration standard for players ability in this class, by Yau’s(2004) elimination matches estimate model. And then, we except could get a reasonable proficiency, make the examination ability according to contest results, finally, reach the purpose of this study, quantizing the ranking of Olympic judo competition.
results from prescribed rules), if the players potential ability was not according to the ranking of contest results, we would analysis the situation of paired contests(competitors) and discuss the reason why inconformity.
Results:
1. To assess the potential of elimination matches system
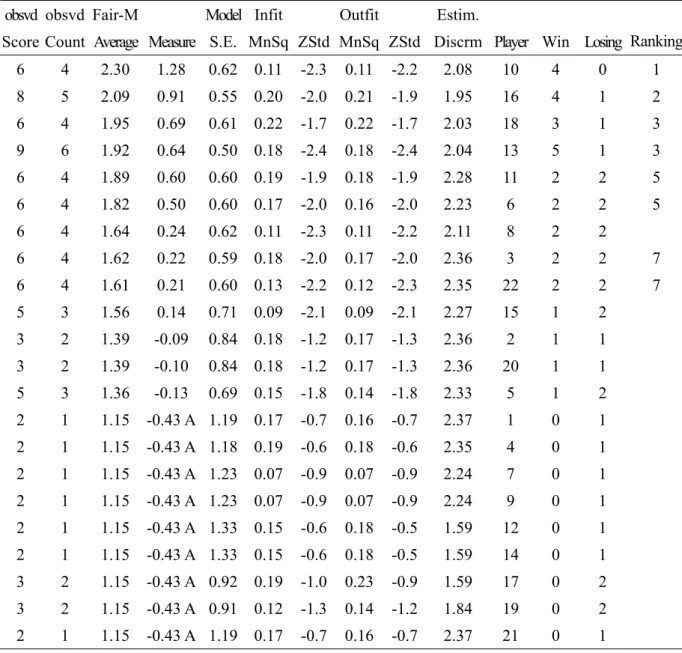
Table 1. Estimation results of 2004 Athens Olympic women judo performance, -48kg extra-light class obsvd obsvd Fair-M Model Infit Outfit Estim.
Score Count Average Measure S.E. MnSq ZStd MnSq ZStd Discrm Player Win Losing Ranking
6 4 2.30 1.28 0.62 0.11 -2.3 0.11 -2.2 2.08 10 4 0 1 8 5 2.09 0.91 0.55 0.20 -2.0 0.21 -1.9 1.95 16 4 1 2 6 4 1.95 0.69 0.61 0.22 -1.7 0.22 -1.7 2.03 18 3 1 3 9 6 1.92 0.64 0.50 0.18 -2.4 0.18 -2.4 2.04 13 5 1 3 6 4 1.89 0.60 0.60 0.19 -1.9 0.18 -1.9 2.28 11 2 2 5 6 4 1.82 0.50 0.60 0.17 -2.0 0.16 -2.0 2.23 6 2 2 5 6 4 1.64 0.24 0.62 0.11 -2.3 0.11 -2.2 2.11 8 2 2 6 4 1.62 0.22 0.59 0.18 -2.0 0.17 -2.0 2.36 3 2 2 7 6 4 1.61 0.21 0.60 0.13 -2.2 0.12 -2.3 2.35 22 2 2 7 5 3 1.56 0.14 0.71 0.09 -2.1 0.09 -2.1 2.27 15 1 2 3 2 1.39 -0.09 0.84 0.18 -1.2 0.17 -1.3 2.36 2 1 1 3 2 1.39 -0.10 0.84 0.18 -1.2 0.17 -1.3 2.36 20 1 1 5 3 1.36 -0.13 0.69 0.15 -1.8 0.14 -1.8 2.33 5 1 2 2 1 1.15 -0.43 A 1.19 0.17 -0.7 0.16 -0.7 2.37 1 0 1 2 1 1.15 -0.43 A 1.18 0.19 -0.6 0.18 -0.6 2.35 4 0 1 2 1 1.15 -0.43 A 1.23 0.07 -0.9 0.07 -0.9 2.24 7 0 1 2 1 1.15 -0.43 A 1.23 0.07 -0.9 0.07 -0.9 2.24 9 0 1 2 1 1.15 -0.43 A 1.33 0.15 -0.6 0.18 -0.5 1.59 12 0 1 2 1 1.15 -0.43 A 1.33 0.15 -0.6 0.18 -0.5 1.59 14 0 1 3 2 1.15 -0.43 A 0.92 0.19 -1.0 0.23 -0.9 1.59 17 0 2 3 2 1.15 -0.43 A 0.91 0.12 -1.3 0.14 -1.2 1.84 19 0 2 2 1 1.15 -0.43 A 1.19 0.17 -0.7 0.16 -0.7 2.37 21 0 1
We has chose the evaluation of elimination system model develop by Yau in 2004: Rasch multi-scoring model with multi facets, mathematical design was three facets, scoring model was 3 points model, winner got 2 points and loser got 1 point, anchor exam value was -0.33 and used 0.55 for weighting. Players never won any matches (players No. 1, 4, 7, 9, 12, 14, 21 lose one time, N0. 17 and 19 lose two times), set up the anchor exam value was -0.43. the exam results were as table 1.
First, the top six players estimation potential were: 1.28、0.91、0.69、0.64、0.60、0.50, according to contest results. Secondly, player No.8 potential value 0.24 was higher than player No.7 potential value 0.22、0.21 who has the same ranking with the former, need to analysis the reason why inconformity in further.
2. The analysis of contest results:
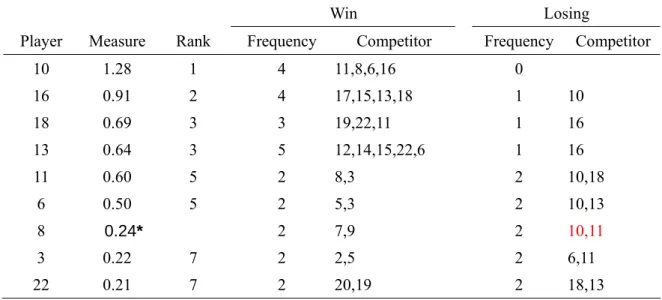
Analysis the contest results of the top 9 players screening from table 1, calculate the win or losing frequency into table 2 as below.
Table 2. Top 9 of -48kg extra-light in 2004 Athens Olympic women judo performance
Win Losing
Player Measure Rank Frequency Competitor Frequency Competitor
As far as win or losing frequency and percentage be concerned, it was according to ranking approximately, secondly we should exam the competitors’ potential then we could evaluate the self potential. Player No.13 rank third who won 5 matches, losing one time; the winning percentage was 0.83, his estimated potential was lower, come from the different of competitors’ potential. Players No. 11、6、8、3 and 22 were win two matches, losing two times, the winning percentage was 0.50, however, player N0. 11、6 and 8, the three players estimated potential were higher than gold metal player(who’s exam potential was 1.28) obviously. Analysis of competitors, Players No.11 and 6 who have same ranking (fifth) were lose to gold and bronze, so their estimated exam potential were highest at five players who had same winning percentage (0.50), player No.8 had lose to gold and fifth, his estimated exam potential was medium in five players had the some winning percentage (0.50), and then, player No. 3 had lose to two fifth players, and player No. 22 had lose to two bronze, so their estimated exam potential were under the bottom.
Discussion:
addition to an elimination match, there were two repechage should be take on. The main purpose was maintain the first two characteristics, the anchor value was -0.43, scoring model was 3 points model and set the anchor value -0.33. This design had much advantage to contest estimated results; the only deficiency was produce a disorder estimated potential value. Making a further analysis of this result, it could be accept because the winning percentage was equal, and his competitor include gold metal player, that’s why the over-valuation appeared, on the other hand, because the hierarchical character of the competition system, although this player had higher estimated potential but still could not get good place. In conclusion, our method quantized the ranking of Olympic judo elimination system with double repechage.