The Study of Academic Research Trends in the Patent Related Fields in
Taiwan
Rong-Jer Lai 1, Chih-Yung Chen 2
1 National Kaohsiung University of Applied Sciences, Taiwan
2 Kaohsiung Motor Vehicles Office, Directorate General of Highways, Taiwan
Correspondence author email: E-mail : rjlai@cc.kuas.edu.tw
Abstract
This study investigates the patent related theses and dissertations from the universities in Taiwan until the academic year 2007. First, the research trends are analyzed by the life cycle model of the annual published works, and then the cluster analysis is carried out based on the similarities among the keywords set for each thesis or dissertation. Finally, the evolution of research trends is explored from the social, economic and industrial development perspectives.
The result shows that the development of Taiwan’s patent related researches can be divided into three stages: (1) beginning stage before 1994: The majority of subjects are on the aspect of law, such as modification of patent system, infringement and licensing. (2) introduction stage from 1995 to 1999: Besides legal issues, the subjects include management of intellectual property and application of patent analysis. (3) growth stage since 2000: The patent related researches have been intensified in a remarkable manner, and the topics cover the legal, management, commercial, financial, and engineering aspects.
On the whole, the patent related researches from the universities in Taiwan deal with the management and legal issues more than others. The continuous patent related studies in the engineering field just appear at the growth stage, and still remain in a small scale, which indicates the academics requires more efforts on the upstream of patent process.
Key words:Intellectual Property; Patent-related Issues; Trend Study; Life Cycle Model; Cluster Analysis
1. Introduction
From the historical viewpoint, the patent system in Taiwan began in 1899. Taiwan was annexed to Japan in 1895 according to the Treaty of Shimonoseki, and when Japan became the 18th member of Paris Convention for the
Protection of Industrial Property in 1899, the laws regarding patent, trademark and copyrights were promulgated and enforced in Taiwan at the same time. In August 1945 Japan lost the war, and her military in Taiwan must surrender to Generalissimo Chang Kai-shek (1887~1975) by the General Order No. 1 issued by General Douglas MacArthu (1880~1964), Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers. In October 1945 China ruled over Taiwan, and whatever legislation of China was applied on the island. The era of Temporary Ordinance for Rewarding Industrial Technologies, the patent law of China at that time, began until the end of 1948. On January first, 1949 the new Patent Law was put in force in Taiwan, not long before the Nationalist government lost the civil war in China and fled to Taiwan in September 1949. The Patent Law, which specifies three kinds of patent, i.e. invention, new utility model and new design, has been modified many times since then, and influenced to a certain degree by the systems of Japan and USA.
From the beginning of 1970s, the industrial structure of Taiwan has changed gradually from labor-intensive to technology-intensive. In accordance with the statistics from Taiwan Intellectual Property Office (TIPO), the cumulative patent applications amount to 1.26 millions during the period between 1984 and 2008 [1]. In spite of the global financial crisis there were still 78,425 applications filed in 2009, compared with 83,613 applications in 2008 [2]. On the other hand, the patent statistics report from USPTO in 2009 [3] shows that Taiwan ranks as No. 6 by geographic origin with respect to the utility patents granted, and about 40 % of them, i.e. 30,588 patents are granted between the years 2005 and 2009. When taking patent as a measure, it could be said that Taiwan is a land of innovation.
In 1999 the Fundamental Science and Technology Act was promulgated in Taiwan, by which the intellectual property rights and results derived from the projects subsidized, commissioned, or funded by the government may be conferred, in whole or in part, to the executing research and development units for ownership or licensing for use [4]. Since then the technology innovations from the universities, research institutes or organizations may be offered for the industry in the way of industry-academy collaboration, licensing and technology transfer, or strategic alliance. The universities in Taiwan, no matter they are public or private, make every effort to prosecute patents, so that 23 universities are recorded on the list of Top 100 domestic non-personal applicants in 2009 [5], which reveals the significance of intellectual property rights has dramatically changed for the academics of Taiwan. Similar development of the relationship between universities and industry also happened in the USA after the Bayh-Dole Act was enacted in 1980 [6].
The university always plays a key role in the aspects of knowledge creation and technology innovation due to her functions as education, research and service suppliers. What the patent related researches from the universities in Taiwan look like in the past decades, and how about their interrelation with the social, economic and industrial development are worthy to study with respect to the vigorous activities of technology innovation in Taiwan. Hence, in this study the patent related theses and dissertations from the universities in Taiwan until the academic year 2007 will be investigated. First of all, the research trends are analyzed by the life cycle model of the annual published works, the distinct stages of which are introduction, growth, maturity, and decline [7], and then the cluster analysis is carried out based on the similarities among the keywords set for each thesis or dissertation. Finally, the evolution of research trends is explored from the social, economic and industrial development perspectives.
2. Material and method
The theses and dissertations that contain the term “patent” within either the title or the keywords are searched out through the Electronic Theses and Dissertations System from National Central Library in Taipei [8]. 923 pieces of published works are found until the academic year 2007, but only 909 of them are counted after pruning away the repeat and the content irrelevant ones. Then, based on the number of annual publications the development of patent related researches is studied and divided into different stages following the life cycle model. Further, the similarity among the theses and dissertations is measured by the keywords reset for each publication (as stated below), and the cluster analysis is carried out with the aid of the software SPSS [9]. For this study it is the average linkage method of hierarchical clustering to be applied [10, 11].
Usually, the keywords in a scientific publication are proposed by the author(s) to denote the issues and connection she/he/they deal(s) with. Within the scope of this study the keywords put forward by the original
authors sum up to 2411 terms. Because many of them are synonyms on the one side, and a similarity matrix of large dimensions is adverse for the cluster analysis on the other side, the original keywords are merged into 148 terms in advance. In other words, for the measurement of similarity not the original keywords are used directly, but the 148 ones, of which 1 to 6 terms would be taken as attributes for each publication.
To measure the likeness of published works, Jaccard similarity coefficient is used [12]. Suppose any two works called Ti and Tj with corresponding keyword sets, say X and Y, then the degree of similarity between Ti and
Tj will be taken as the value of the number of the same terms (i. e. size of intersection) divided by the number of
the total terms (i.e. size of union) that appear in both keyword sets in the following form:
Sim(Ti, Tj)=
X
∩
Y
/X
∪
Y
(1)The value of Jaccard similarity coefficient lies between 0 (completely different) and 1 (entirely the same). For example, if T1:(A1,A2,A3), T2:(A1,A3,A5,A10), T3:(A1,A4,A5,A7,A8) and T4:(A5,A6,A9) denote four different publications T1~T4 with their corresponding keywords in terms of A1~A10, then, the degrees of similarity between T1 and the others read like:
Sim(T1, T2)=
X
∩
Y
/X
∪
Y
=A
1 A
,
3
/A
1
,
A
2
,
A
3
,
A
5
,
A
10
=2/5=0.4, Sim(T1, T3)=X
∩
Y
/X
∪
Y
=A
1
/
A
1
,
A
2
,
A
3
,
A
4
,
A
5
,
A
7
,
A
8
=1/7=0.14, and Sim(T1, T4)=X
∩
Y
/X
∪
Y
=φ
/A
1
,
A
2
,
A
3
,
A
5
,
A
6
,
A
9
=0/6=0, respectively.That is to say, T1 and T2 are more similar than T1 and T3, and between T1 and T4 it is completely different.
3. Results
Figure 1 shows the statistics of the patent related theses and dissertations published until the academic year 2007. The earliest one dated in 1975. The peak with 164 publications appears in 2006, next to it is the year 2005 with 152 publications, and at the third place is the year 2007. The publications during these three years sum to around half of the total records. Since the academic year begins in September and ends in the next August, almost all the works are published during the period between June and August, but several publications are somehow delayed, like those shifted into the year 2008 as shown in Figure 1.
1 2 4 3 1 4 2 7 2 3 3 4 12 8 13 12 17 24 45 83 95 120 152 164 121 7 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 1975 1982 1985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008
year
N
o.
of
publ
ic
at
ions
Figure 1: Statistics of the patent related theses and dissertations published in Taiwan
The development of the patent related researches is divided into three stages as follows: the beginning stage before 1994, during this period there are less than 10 publications annually; the introduction stage between 1995 and 1999, for this duration the yearly publications are below 20; and the growth stage since 2000, when the universities in Taiwan intensify the researches in the patent related fields, so that the annual publications increase rapidly and reach the peak in 2006. It is noted that the published works reduced remarkably in 2007 compared with those in 2006. Whether it means the recession of research activity begins is still indefinite to answer, as far as the statistics is concerned.
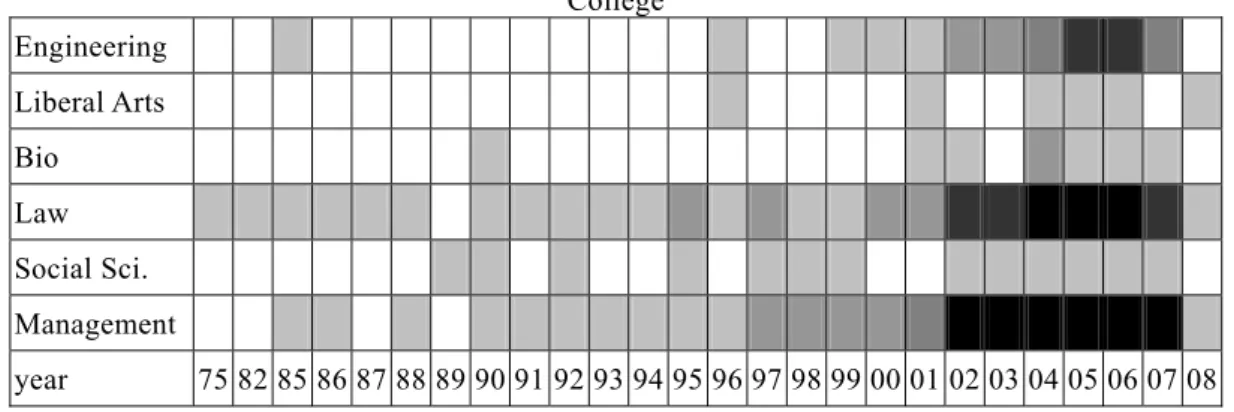
Besides, after classification of the published works by category of the source, it is found that 469 publications, i.e. 52% of total records, belong to college of management, 269 (about 30% of the whole) to college of law, and 122 to college of engineering. Additional analysis based on the annual distribution in Figure 2 shows that the patent related researches in Taiwan start from college of law during the beginning stage, and main participators joining during the introduction stage come from college of management. From the growth stage on the participators are diversified, including the involvement of the colleges of liberal arts, bio and social sciences, particularly those from college of engineering. Although the researches are not limited to the legal, management and engineering aspects, the issues of management play a dominant role with respect to the quantity of publications.
College Engineering Liberal Arts Bio Law Social Sci. Management year 75 82 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 Note: The shade indicates the number of publications. The darker shade means the more publications.
Figure 2: Distribution of the publications by category of the source
The result of cluster analysis based on the above mentioned Jaccard similarity coefficient indicates that the publications could form itself into 6 groups. The distribution of the publications by source and the topics concerned within each group are shown in Table 1 briefly. Further description of each group will be stated as follows.
Group I is composed of 116 publications, and main participants come from colleges of management and law. The topics concerned are:
(1) intellectual property management system for business, organization and university, including the establishment of management system, strategy of marketing, planning of R & D, patent strategy, patent around, defense tactics to patent troll, human resource management, laboratory management, review and reward system for the patent proposal etc., and their effects on the intellectual property management system. At the university level, the issues further include the effect of technology transfer on the application of R & D, the relationship between the academic research and technology development, and the interaction between the high-tech industries and the university etc.,
(2) patent abuse and compulsory licensing of the patents that are taken as industrial standards, including the case study of patent infringement between Philips Electronics and CD-R/CD-RW manufacturers, and (3) patent licensing, including drafting of licensing contract, licensing strategy, patent pool, royalty,
technology transfer, and legal issues resulted from the restricted competition, such as violation against the fair trade law or antitrust law.
Group II contains 409 publications, mainly from colleges of management and engineering. The related topics are:
(1) patent analysis, through which the patents about specific technology or product such as lithium battery, TFT-LCD and so on are searched out and analyzed to demonstrate the technology status and the development trends. The theories involved are text mining, social network analysis, co-citation approach based on bibliometrics, logistic and Gompertz models, and rough set theory,
(2) R & D of specific technology or product, e.g. heat sink, backlight module, and disc brake for bicycle with the aid of patent information before the initiation of work,
(3) development of automatic retrieval and classification system of patent documents in order to grasp the patents effectively and quickly,
4.2.3 Growth stage since 2000
During this period not only the quantity of patent related researches increases rapidly, but also the scope extends widely. The key points are the patent analysis, management of intellectual property, and assessment of intangible assets. The new issues include the systematic methods of technology innovation, automatic retrieval and classification system of patent documents, R & D of specific technology or product, patent abuse and compulsory licensing and so on. Most works about systematic methods of technology innovation, automatic retrieval and classification system of patent documents, and R & D of specific technology or product come from college of engineering, and could be ascribed to the stage of innovation and R&D along the patent process.
5. Conclusions
The development of the patent related researches in Taiwan can be divided into the stages of beginning, introduction and growth after the life cycle model. During the beginning stage before 1994, the major research subject is on the legal aspect, such as modification of patent system, infringement and licensing. For the introduction stage from 1995 to 1999, besides legal issues the research subjects include management of intellectual property and application of patent analysis. In 2000 the growth stage began, and the researches on the patent related issues have been intensified in a remarkable manner, the topics cover the legal, management, commercial, financial, and engineering aspects. The publications in the academic year 2007 reduce significantly, but it is still indefinite to say this means the recession of research activity in this respect.
On the whole, the patent related researches from the universities in Taiwan deal with the management and legal issues more than others. The continuous patent related studies from the engineering field just appear at the growth stage, and still remains in a small scale, which indicates the academics requires more efforts on the upstream of patent process.
Reference
[1] TIPO, Annual statistics report 2008, published on June 12th, 2009. [2] TIPO, Annual statistics report 2009, published on May 5th, 2010.
[3] USPTO, Patents By Country, State, and Year - Utility Patents (December), online available: http://www.uspto.gov/web/offices/ac/ido/oeip/taf/cst_utl.htm, 2009.
[4] Fundamental Science and Technology Act, Article 6, Paragraph 1, Laws & Regulations Database, Taiwan, online available: http://law.moj.gov.tw/Eng/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?PCode=H0160028, 2005.
[5] TIPO, Top 100 domestic applicants in terms of corporate bodies, published on March 31st, 2010.
[6] Demain A.L., The Relationship between Universities and Industry: The American University Perspective, Food technol. biotechnol. 39 (3) 157–160, 2001.
[7] Industry Life Cycle, in: K. Hillstrom, L.C. Hillstrom (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Small Business, Gale Cengage, eNotes.com, online available: http://www.enotes.com/small-business-encyclopedia/industry-life-cycle, 2002.
[8] Electronic Theses and Dissertations System, National Central Library, Taipei. [9] SPSS Taiwan Co..
[10] Kantardzic M., Data Mining, John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey, 2003.
[11] Chow W.S., Multivariate Statistical Analysis: with Application of SAS/STAT, BestWise Co., Taipei, 2002. [12] Jain A.K., Dubes R.C., Algorithms for Clustering Data, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 1988.
[13] Intellectual Property Court Organization Act Article 2, online available: http://jirs.judicial.gov.tw/eng/FLAW/FLAWDAT0201.asp?lsid=FL042719
[14] Central Bank of Taiwan, Balance of payments on the royalties and license fees, 2009.
[15] TIPS, Background of Project, online available: http://www.tips.org.tw/body.asp?Sno=BCCB, 2010.
[16] TIPS, List of certificated corporations, online available: http://www.tips.org.tw/body.asp?Sno=BGCD, 2010. [17] Department of Statistics, Ministry of Education, Taiwan, online available:
http://www.edu.tw/files/site_content/B0013/overview05.xls
[18] Patent Guider, Learning Tech Co., http://www.learningtech.com.tw/en/html/analysis.htm. [19] Patent Pilot, Apex Information Co., http://www.apexi.com.tw/product/patent_pilot.html.