行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫 成果報告
產業需求導向之科技校院數位設計專業實務課程發展與驗
證研究--數位出版產業需求導向之科技校院數位設計專業
實務課程發展與驗證研究(子計畫三)
研究成果報告(精簡版)
計 畫 類 別 : 個別型 計 畫 編 號 : NSC 98-2511-S-003-035- 執 行 期 間 : 98 年 08 月 01 日至 99 年 07 月 31 日 執 行 單 位 : 國立臺灣師範大學圖文傳播系(所) 計 畫 主 持 人 : 廖信 共 同 主 持 人 : 戴孟宗、馬立懿 報 告 附 件 : 出席國際會議研究心得報告及發表論文 處 理 方 式 : 本計畫可公開查詢中 華 民 國 99 年 09 月 20 日
摘要
隨著數位出版逐漸成為下一波出版主流趨勢,傳統出版產業人才的培育也必 須配合產業轉型,以加速出版產業之數位化,有鑑於此,本研究以數位出版產業 為對象,探討數位出版產業從業人員所需具備之專業能力,以供傳統出版人員轉 型時之參考。研究首先採用文獻探討方式,以瞭解數位出版產業之現況,再透過 層級結構問卷發送,以 Fuzzy AHP 層級分析法建構完整能力層級、指標。研究 結果顯示:(1)數位版產業主要之職務可分為行銷企劃人員、內容製作人員、程 式設計工程師三項。(2)數位出版從業人員所應具備之專業能力,共包含 4 大主 要構面,7 項能項目及 32 個能力指標。(3)數位出版產業對專業能力之需求, 能力構面上,以「系統開發」能力權重值最高,而能力指標中以「瞭解數位檔案 加密方式」權重值最高,同時也最為數位出版從業人員所需要。 關鍵詞:數位出版從業人員、專業能力、能力指標、模糊層級分析法Abstract
This study explores what professional competencies that digital publishing industry employees must possess. The result is for traditional publishing employees’ reference when they have to make changes. In this study, a literature review was conducted to collect information on the current development of digital publishing industry. Through the Analytic Hierarchy Process (FAHP) questionnaires, this study constructs a complete competence hierarchy and indicators. At the end, conclusions were reached as follows :( 1) The main occupations in the digital publishing industry are marketing planners, content writers and programmers. (2) The professional competencies people in digital publishing must possess can be categorized into 4 dimensions, 7 competence categories and 32 competence indicators.(3) Considering the demand for professional competencies in digital publishing industry, System Development Competence Dimension is weighted the most. Among competence indicators, “knowing how to encrypt digital files” is most required by digital publishing employees.
Keywords:Digital publishing, Employee, Professional Competence,
壹、 緒論
一、研究背景與動機 隨著現代人閱讀的時間越來越少,坐在電腦前的時間越來越長,很少有人 能夠將一本書完完整整地讀下來,傳統圖書出版的市場影響力在未來 5 至 10 年 內 會 逐 年 降 低 , 未 來 五 到 七 年 內 圖 書 出 版 的 模 式 將 會 產 生 極 大 的 變 化 (Tian,2007),而所有形式的出版品都將因為新數位資訊媒體的發展而重新定義 (Harrison,2000)。Frank Romano(2006)報告預測了從 2005 年到 2015 年,數 位印刷將占到全球印刷總量的 30%左右。到 2015 年,中國將成為世界最重要的 印刷市場,它的市場價值將達到 27 億歐元。到了 2015 年,48%的書會是以數位 化的隨選列印方式存在。此外諸如產品的授權收入、周邊產品之販售、虛擬商品 的營收等比例也越來越高,皆為過去傳統經營方式帶來極大變化。 「挑戰 2008:國家發展重點計畫」(經濟部,2008)執行成果報告中指出, 在 2002 年時,國內尚無數位內容核心人才的養成培育,產業極缺人才,人才來 源多為業界彼此挖角居多,多數參與本地市場開發或國際代工專案。時至今日, 人才培訓工作日益重要,必須加強發掘、匯聚創意人才及施予創作商品化輔導等 各項措施,並加強原創人才培育。 有鑑於上述之背景描述,可發現數位出版的工作需要由具有專業知識、受過 專業訓練之人員團隊合作進行(Kenney,2000),但目前從事數位出版之相關工作 者,所受之教育仍為各大專院校傳統傳播科系所各別培養,因此其所具備之能力 是否足以達到數位出版產業之需求亦值得加以探討。 那福忠(2007)根據 Joe Webb 之預測指出,從 2005 年到 2017 年,全世界 期刊與書的出版,將走向小型化,且自由個人工作者人數將大幅增加,因此對數 位出版從業人員而言,獨立工作已是不可避免的趨勢,文字、圖像、影像、及語 音整合之數位實務能力,將是數位出版從業人員皆需具備之能力。 藉由瞭解新的科技技術及新工作流程,可評估未來產業界對職場人力及所應 具備能力之需求 Schmidt(2008),因此,本研究從產業調查著手,透過探討目前 數位出版產業對專業能力之需求,主要研究目的如下: 一、探討數位出版產業之工作職務內容。 二、探討數位出版產業對專業能力之需求。 三、發展符合數位出版產業需求之專業能力指標。 四、探討產業需求之專業能力與現今數位出版課程之相對應情形。貳、 文獻回顧
一、我國數位出版產業發展現況 全球數位出版產業正值蓬勃發展之際,目前流通在臺灣市場上的數位出版商 品形式大致為光碟、電子資料庫、電子書與電子雜誌、電子報、行動內容等,雖 然總體產值上有成長,但由於大眾對數位出版品的接受度還是不夠全面,因此能 真正從這些數位出版商品中獲利的業者並不多,如何拓展數位出版品在臺灣的市 場仍是業者需要努力的關鍵(王祿旺,2008)。 根據經濟部投資業務處(2007)統計顯示,2008 年台灣數位出版產值可占 所有出版通路產值 20%以上,可替出版公司節省超過 10%的資源,並降低 20% 的成本,數位出版的直接與間接產值,已超過新台幣四百億元。數位出版為數位 知識經濟的核心產業,當它結合網路媒體科技之時,將形成台灣數位知識體系, 創造無比龐大的商機。 二、數位出版從業人員工作內涵 在中華民國圖書發行協進會與聯合線上 udn 數位閱讀網與共同舉辦的「2008 數位出版行動年」論壇「數位出版人才哪裡找?」中,與談人認為,數位出版人 才除了專業技能、熱愛熟悉網路新媒體、新科技外,還必須具備創造閱讀的能力 (在不同載具上的閱讀形式)、想像力和能溝通的跨界能力。 而杜麗琴(2008b)在「數位出版的人才需求」演講中針對遠流智慧藏公司 發展情形列出「數位出版人的六項基本能力」為:數位應用的能力、鑑賞文/圖/ 影/音的能力、邏輯組織的能力、解決問題的能力、自學的能力、溝通的能力。 其中「數位應用的能力」為數位出版從業人員所需能力之首要條件。時報數位傳 播呂宗熹(2008)則表示強大資料處理能力最為數位出版人才所應具備,其他如 說故事的能力、網路工具使用能力、網頁製作能力、flash 製作能力 和文字、聲 音、影像多媒體素材整合的能力皆相當重要。 印刷工業研究中心技術輔導組(2005)指出印刷產業要永續發展經營,需培 植印刷、資訊、網路等技術人才,並累積印刷產業領域知識(Domain Knowledge)、 獨門知識(Know How)以及整合資訊及網路技術。陳薇后(2004)認為網路編 輯所需要具備的專業技術能力有熟悉電子商務的技術、金流、物流能力與網頁編 輯能力,網頁編輯能力包括使用網頁編輯軟體、具備網頁版面的視覺搭配概念、瞭解網路使用者的使用習慣等。 台北市雜誌商業同業公會(2006)針對數位出版產業現況及群聚需求進行調 查時發現,產業界對數位出版人才之需求以企劃人才最為需要,其次為資訊研發 及美編設計人才。洪淑惠(2006)研究台灣圖書出版業美術編輯專業職能,發現 「編輯設計執行能力」最為重要,其餘為「編排設計創意」、「電腦繪圖排版軟體 之應用」。 資策會(2004)在「數位內容學院課程及培訓需求調查報告」中列出數位出 版流程的五個階段,分別為前製期、製作期、出版發行期、加值應用期、行銷期, 經整理上述文獻資料,將數位出版流程的五個階段與其工作內容、人力需求整理 如圖 1 所示: 圖 1 數位出版製作流成及對應人才 資料來源:本研究整理修改自課程及培訓需求調查報告,資策會(2004),台北: 經濟部工業局。 經整理各國出版人員能力之要求,以及數位出版從業人員之工作內容,本研 究將數位出版從業人員之能力分為出版規劃能力、圖文創作能力、介面設計能 力、多媒體製作能力、程式設計能力、數位發行能力、數位著作權管理能力等七 項。 前製期 1.主題規劃 2.劇情腳本 設定 3.素材原創 (文字、影音) 製作期 1.文字、影音素 材整合編輯 (e-Editor) 2.載體設計 3.數位列印 4.數位版權管 理(DRM) 出版發行 1.電子書 2.電子雜誌 3.電子報 4.其他 行銷期 加值應用 1.數位典藏 2.數位學習 3.專屬網站 建置 4.其他 1.市場行銷 2.產品發行 1.製作人 2.創作者 3.撰稿人 4.專案經理 5.產品企劃 1.藝術指導 2.執行製作 3.動畫師 4.攝影師 5.音效師 6.多媒體工程 師 1.出版社 2.網路服務提 供者 3.應用軟體提 供者(ASP) 4.政府機構 5.個人 1.研發工程師 2.網頁設計師 3.網站工程師 4.測試人員 5.多媒體工程 師 1.行銷企劃 2.銷售人員 3.客服人員 4.法務人員
參、 研究設計
一、研究架構 為達成研究目的,本研究透過文獻探討與模糊層級分析法,據以規劃研究架 構,如圖 3 所示。首先透過文獻探討以瞭解數位出版產業之現況,透過產業現況 整理出數位出版產業之工作內涵與能力構面,再透過模糊層級分析,獲得產業界 對數位出版從業人員能力內涵及其各項指標之相對權重,最後確立數位出版從業 人員專業能力之相對重要程度。 圖 2 研究架構圖 二、研究方法 本研究以問卷調查法為主,以文獻探討與專家問卷審查進行題項之調整 後,所得之指標構面與項目為基礎,發展「數位出版從業人員之專業能力」結 構式層級調查問卷,其專業能力層級如圖 4 所示。 張美娟(2001)認為採用 Fuzzy AHP 可處理較難量化的研究問題,例如尚 未成熟的新興產業經營策略問題、社會科學面向之資源分配優先順序問題等。 而目前國內數位出版產業仍屬商業模式尚未非常成熟之階段,因此本研究問卷 採 Fuzzy AHP 模糊層級分析法進行,利用三角模糊數、群體整合、模糊排序、 層級串連求得各專業能力間之權重。 問卷以九點量表之比較型態(9:1 到 1:9),依次進行同層指標間兩兩成 對比較。依所獲得資料,建立成對比較矩陣,導入模糊數等觀念加以處理,最 後獲得各因素間相對比較權重值,建立數位出版從業人員專業能力層級分析。 模糊數的應用,Buckley (1985) 是使用梯形模糊數,但由於實際應用中, 專業能力構面 數 位 出 版 產 業 現 況 專 業 能 力 指 標 專業能力項目 出版規劃能力 圖文創作能力 介面設計能力 多媒體製作能力 程式設計能力 數位發行能力 數位著作權管理能力 編輯企劃 內容製作 系統開發 整合發行梯形模糊數的計算較為繁雜,實用性也較低。為了簡化運算,Fuzzy AHP 將梯 形模糊數簡化為三角模糊數,以三角模糊數來表示與整合專家意見。本研究使 用之三角模糊數A~=(l,m,r)L−R ,其隸屬函數 ~(X) A μ ,如圖 3 所示。 圖 3 三角模糊數隸屬函數 該三角模糊數 A~的隸屬函數亦可以下列數學式來表示: 三、研究對象 (一)產業界部份 本研究以「2007 出版年鑑」所列出之「數位出版類」公司,為問卷發 放之對象。2007 出版年鑑中所列出之數位出版公司共計 46 家,因此本問卷 共計發送 46 份,回收 34 份,回收率 74%,扣除無效問卷 4 份,有效問卷為 30 份。調查期間從九十八年三月二十二日至九十八年四月十日。 (二)學校部份 本研究選擇九十八學年度曾於各大科技校院及大專院校開設數位出版 課程之教師進行問卷之填答,問卷共計發放 15 份,回收 11 份,回收率 73%。 問卷調查期間從九十九年四月十二日至三十日。 l , m, r, 1 ~
μ
1 1 − − m x l≤x≤m, m r x r − − m≤x≤r, 0 , otherwise.u
Ã圖 4 數位出版從業人員專業能力整體層級架構圖
數
位
出
版
從
業
人
員
專
業
能
力
瞭解數位攝影方式 瞭解影像掃瞄方式 瞭解影音剪輯方式 瞭解影音錄製方式 瞭解平面媒體製作方式 內 容 製 作 整 合 發 行 能力項目 圖文創作能力 網頁設計軟體操作 設計內容整合 瞭解「使用者介面」設計原理 瞭解不同閱讀器介面 畫面樣式(ex:工具列、按鈕)設計 數位發行能力 多媒體製作能力 瞭解智慧財產權規範 瞭解數位檔案加密方式 瞭解數位版權管理方式 數位著作權管理 出版規劃能力 瞭解開發平台軟體 瞭解多媒體程式語言 資料庫系統管理 Metadata 設計 程式設計能力 能力指標 介面設計能力 編 輯 企 劃 系 統 開 發 瞭解各式電子出版品規格 出版載具規劃 字型規劃 版面規劃 製作物外包規劃 產品創新能力 分鏡繪製 電腦繪圖軟體操作 動畫製作軟體操作 瞭解數位檔案格式轉換方式 瞭解印前作業規格 色彩管理 瞭解發行通路 瞭解數位出版電子商務系統 數位出版品檔案管理 能力構面肆、 資料分析與討論
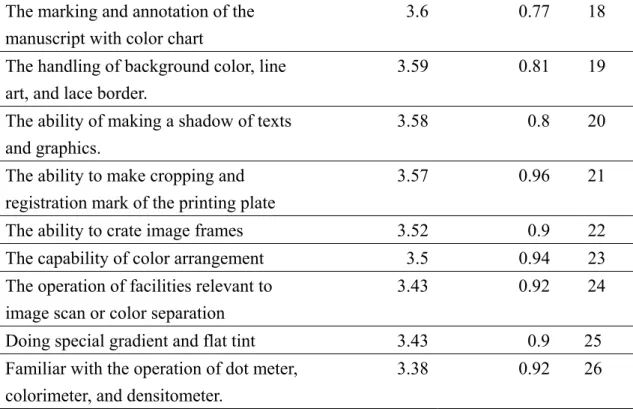
一、問卷填答者基本資料分析 根據本研究所回收之問卷,其中男性填答者所佔比例較高(60%),年齡多 集中於 30 至 40 歲之間(57%),學歷普遍為大學以上(90%),多有 5 年左右從 事出版工作之年資。在公司類別部份,由於此選項為複選題,在比例上將有部分 比例將重複計算,其中以電子書製作類型最多(25%),電子期刊製作(23%)、 數位出版加值服務(23%)類型亦屬多數。 二、權重調查結果 經整理出之數位出版從業人員專業能力指標有 4 大構面、7 大項目及 32 項 指標,透過專家問卷審查的意見修改,並藉由語意尺度表進行各層面指標的成對 比較,以求取各層級指標間之權重後,各層面指標之一致性檢定及權重說明如下: (一)能力構面 針對專業能力的 4 大構面,經由統計分析後各層面權重及排序如表 1 所示。 其中以「系統開發」能力(權重值 0.270)最高,其他依序為「內容製作」能力 (權重值 0.262)、「整合發行」能力(權重值 0.244)以及「編輯企劃」能力(權 重值 0.223)。 表 1 數位出版從業人員專業「能力構面」模糊權重 能力構面 三角模糊數幾何平均 模糊權重值 權重 排序 編輯企劃 1.048 1.242 1.415 0.220 0.216 0.233 22.3% 4 內容製作 1.304 1.522 1.504 0.274 0.265 0.248 26.2% 2 系統開發 1.241 1.577 1.677 0.260 0.274 0.277 27.0% 1 整合發行 1.175 1.407 1.464 0.246 0.245 0.242 24.4% 3 C.I.=0.063; R.I.=0.90; C.R.=0.07< 0.1 註:C.I.為一致性指標;R.I.為隨機性指標;C.R.為一致性比率。 (二)能力項目 由於「內容製作」能力構面及「整合發行」能力構面所包含之能力內涵較多, 因此在「內容製作」能力構面下又分有 3 項能力項目;在「整合發行」能力構面下分有 2 項能力項目,其權重說明如下: 1.內容製作構面 「內容製作」指標構面下之 3 項能力項目,經統計後各項目權重如表 2 所 示,其中以「多媒體製作能力」(權重值 0.524)最為重要。 表 2 數位出版從業人員專業「內容製作」之能力項目模糊權重 能力項目 三角模糊數幾何平均 模糊權重值 權重 排序 圖文創作能力 0.882 0.965 1.072 0.242 0.231 0.228 23.4% 3 介面設計能力 0.879 1.008 1.146 0.241 0.241 0.244 24.2% 2 多媒體製作能力 1.888 2.204 2.484 0.517 0.528 0.528 52.4% 1 C.I.=0.050; R.I.=0.58; C.R.=0.09< 0.1 2. 整合發行構面 「整合發行」指標構面下之 2 項能力項目,經統計後各項目權重如表 3 所 示,以「數位著作權管理能力」(權重值 0.598)最為重要。 表 3 數位出版從業人員專業「整合發行」之能力項目模糊權重 能力項目 三角模糊數幾何平均 模糊權重值 權重 排序 數位發行能力 1.070 1.138 1.206 0.407 0.401 0.397 40.2% 2 數位著作權管理能力 1.559 1.700 1.833 0.593 0.599 0.603 59.8% 1 C.I.=0; R.I.=0.00; C.R.=0< 0.1 (三)能力指標 1.出版規劃能力 「出版規劃能力」項目下共有 6 項指標,經由統計分析後各指標權重及排 序如表 4 所示,其中以「字型規劃」(權重值 0.304)最為重要。 表 4 數位出版從業人員專業「出版規劃能力」之能力指標模糊權重 能力指標 三角模糊數幾何平均 模糊權重值 權重 排序 瞭解各式電子出版品規格 1.507 1.848 2.266 0.193 0.190 0.198 19.4% 2 出版載具規劃 1.324 1.557 1.801 0.169 0.160 0.157 16.2% 4 字型規劃 2.349 3.040 3.401 0.300 0.313 0.297 30.4% 1
版面規劃 0.892 1.113 1.362 0.114 0.115 0.119 11.6% 5 製作物外包規劃 1.338 1.671 2.024 0.171 0.172 0.177 17.3% 3 產品創新能力 0.408 0.481 0.596 0.052 0.050 0.052 5.1% 6 C.I.=0.027; R.I.=1.24; C.R.=0.02< 0.1 2.圖文創作能力 「圖文創作能力」項目下共有 6 項指標,經由統計分析後各指標權重及排 序如表 5 所示,其中以「動畫製作軟體操作」(權重值 0.201)最為重要。 表 5 數位出版從業人員專業「圖文創作能力」之能力指標模糊權重 能力指標 三角模糊數幾何平均 模糊權重值 權重 排序 分鏡繪製 1.399 1.756 2.115 0.195 0.195 0.193 19.4% 2 電腦繪圖軟體操作 1.260 1.626 1.975 0.176 0.180 0.180 17.9% 3 動畫製作軟體操作 1.432 1.810 2.230 0.199 0.201 0.203 20.1% 1 瞭解數位檔案格式轉換方式 0.637 0.766 0.972 0.089 0.085 0.089 8.7% 6 瞭解印前作業規格 1.153 1.446 1.728 0.161 0.160 0.158 15.9% 5 色彩管理 1.297 1.615 1.953 0.181 0.179 0.178 17.9% 3 C.I.=0.005; R.I.=1.24; C.R.=0.004< 0.1 3.介面設計能力 「介面設計能力」項目下共有 5 項指標,經由統計分析後各指標權重及排 序如表 6 所示。其中以「網頁設計軟體操作」(權重值 0.401)最為重要。 表 6 數位出版從業人員專業「介面設計能力」之能力指標模糊權重 能力指標 三角模糊數幾何平均 模糊權重值 權重 排序 網頁設計軟體操作 2.248 2.753 3.236 0.397 0.404 0.402 40.1% 1 設計內容整合 0.637 0.762 0.910 0.112 0.112 0.113 11.2% 5 瞭解「使用者介面」設計原理 0.844 1.032 1.286 0.149 0.152 0.160 15.3% 3 瞭解不同閱讀器介面 0.724 0.811 0.937 0.128 0.119 0.116 12.1% 4 畫面樣式(ex:工具列、按鈕)設計 1.212 1.450 1.679 0.214 0.213 0.209 21.2% 2 C.I.=0.010; R.I.=1.12; C.R.=0.008< 0.1
4.多媒體製作能力 「多媒體製作能力」項目下共有 5 項指標,經由統計分析後各指標權重及 排序如表 7 所示,其中以「瞭解影像掃瞄方式」(權重值 0.293)最為重要。 表 7 數位出版從業人員專業「多媒體製作能力」之能力指標模糊權重 能力指標 三角模糊數幾何平均 模糊權重值 權重 排序 瞭解數位攝影方式 1.475 1.827 2.211 0.276 0.285 0.288 28.3% 2 瞭解影像掃瞄方式 1.499 1.900 2.308 0.281 0.296 0.301 29.3% 1 瞭解影音剪輯方式 0.787 0.863 0.995 0.147 0.134 0.130 13.7% 4 瞭解影音錄製方式 0.782 0.831 0.924 0.146 0.130 0.120 13.2% 5 瞭解平面媒體製作方式 0.799 0.995 1.231 0.150 0.155 0.160 15.5% 3 C.I.=0.015; R.I.=1.12; C.R.=0.013< 0.1 5.程式設計能力 「程式設計能力」項目下共有 4 項指標,經由統計分析後各指標權重及排 序如表 8 所示,其中以「瞭解開發平台軟體」(權重值 0.363)最為重要。 表 8 數位出版從業人員專業「程式設計能力」之能力指標模糊權重 能力指標 三角模糊數幾何平均 模糊權重值 權重 排序 瞭解平台開發軟體 1.851 2.178 2.503 0.368 0.356 0.366 36.3% 1 瞭解多媒體程式語言 1.601 2.112 2.202 0.318 0.345 0.322 32.8% 2 資料庫系統管理 0.922 1.063 1.221 0.183 0.174 0.178 17.8% 3 Metadata 設計 0.660 0.769 0.921 0.131 0.126 0.134 13.0% 4 C.I.=0.012; R.I.=0.90; C.R.=0.01< 0.1 6.數位發行能力 「數位發行能力」項目下共有 3 項指標,經由統計分析後各指標權重及排 序如表 9 所示。其中以「瞭解發行通路」(權重值 0.346)最為重要。 表 9 數位出版從業人員專業「數位發行能力」之能力指標模糊權重 能力指標 三角模糊數幾何平均 模糊權重值 權重 排序 瞭解發行通路 1.028 1.188 1.349 0.338 0.347 0.353 34.6% 1 瞭解數位出版電子商務系統 1.049 1.144 1.249 0.344 0.334 0.327 33.5% 2
數位出版品檔案管理 0.968 1.090 1.222 0.318 0.319 0.320 31.9% 3 C.I.=0.025; R.I.=0.58; C.R.=0.043< 0.1 7.數位著作權管理能力 「數位著作權管理能力」項目下共有 3 項指標,經由統計分析後各指標權 重及排序如表 10 所示,其中以「瞭解數位檔案加密方式」(權重值 0.513) 最為重要。 表 10 數位出版從業人員專業「數位著作權管理能力」之能力指標模糊權重 能力指標 三角模糊數幾何平均 模糊權重值 權重 排序 瞭解智慧財產權規範 0.723 0.864 1.012 0.184 0.194 0.202 19.3% 3 瞭解數位檔案加密方式 2.030 2.293 2.548 0.517 0.514 0.509 51.3% 1 瞭解數位版權管理方式 1.176 1.305 1.450 0.299 0.292 0.289 29.4% 2 C.I.=0.004; R.I.=0.58; C.R.=0.006< 0.1 三、層級串連 依據以上各層級要素間的權重計算之後,接著進行整體層級權重的計 算,以排序出各能力指標之需求先後順序。其中以「瞭解數位檔案加密方式」 能力指標之權重值(12.5%)最高,其餘整體層級權重分析結果其權重值與 權重排序如下表 11 所示。 表 11 能力指標層級串連排序 能力構面 權重值 能力指標 權重值 層級串連 總權重值(%) 排序 編輯企劃 0.223 瞭解各式電子出版品規格 0.194 4.3% 19 出版載具規劃 0.162 3.6% 24 字型規劃 0.304 6.8% 11 版面規劃 0.116 2.6% 30 製作物外包規劃 0.173 3.9% 23 產品創新能力 0.051 1.1% 32 內容製作 0.262 分鏡繪製 0.194 5.1% 14 電腦繪圖軟體操作 0.179 4.7% 18
動畫製作軟體操作 0.201 5.3% 13 瞭解數位檔案格式轉換方式 0.087 2.3% 31 瞭解印前作業規格 0.159 4.2% 20 色彩管理 0.179 4.7% 17 網頁設計軟體操作 0.401 10.5% 2 設計內容整合 0.112 2.9% 29 瞭解「使用者介面」設計原理 0.153 4.0% 22 瞭解不同閱讀器介面 0.121 3.2% 28 畫面樣式(ex:工具列、按鈕) 設計 0.212 5.6% 12 瞭解數位攝影方式 0.283 7.4% 9 瞭解影像掃瞄方式 0.293 7.7% 8 瞭解影音剪輯方式 0.137 3.6% 25 瞭解影音錄製方式 0.132 3.5% 27 瞭解平面媒體製作方式 0.155 4.1% 21 系統開發 0.270 瞭解平台開發軟體 0.363 9.8% 3 瞭解多媒體程式語言 0.328 8.9% 4 資料庫系統管理 0.178 4.8% 15 Metadata 設計 0.130 3.5% 26 整合發行 0.244 瞭解發行通路 0.346 8.5% 5 瞭解數位出版電子商務系統 0.335 8.2% 6 數位出版品檔案管理 0.319 7.8% 7 瞭解智慧財產權規範 0.193 4.7% 16 瞭解數位檔案加密方式 0.513 12.5% 1 瞭解數位版權管理方式 0.294 7.2% 10 四、大專院校數位出版課程專業能力培育情形 透過表12之結果顯示,目前所開設之數位出版課程內容中,僅有18項能力 指標與業界需求「相符」,且未有「很相符」之指標,另有14項業界所需之專業 能力項目未能與課程內容相符,其中多項產業需求高之能力項目,學校課程皆未 能與其相符,顯示目前國內大專院校及技職校院所開設之課程內容,與業界仍有
差異。 表12 數位出版課程與專業能力之對應情形 相符之能力指標 平均數 產業需求排序 1.設計內容整合能力 3.82 29 2.瞭解印前作業規格 3.73 20 3.瞭解平面媒體製作方式 3.55 21 4.版面規劃能力 3.55 30 5.瞭解數位出版電子商務系統 3.45 6 6.瞭解發行通路 3.45 5 7.瞭解數位檔案格式轉換方式 3.36 31 8.瞭解智慧財產權規範 3.36 16 9.瞭解各式電子出版品規格能力 3.27 19 10.瞭解不同閱讀器介面 3.27 28 11.數位出版品檔案管理能力 3.27 7 12.電腦繪圖軟體操作能力 3.27 18 13.產品創新能力 3.27 32 14.瞭解影像掃瞄方式 3.18 8 15.出版載具規劃能力 3.18 24 16.瞭解數位攝影方式 3.09 9 17.瞭解數位版權管理方式 3.09 10 18.字型規劃能力 3.09 11 19.色彩管理能力 2.91 17 20.瞭解數位檔案加密方式 2.91 1 21.製作物外包規劃能力 2.82 23 22.瞭解使用者介面設計原理 2.73 22 23.畫面樣式設計能力 2.64 12 24.網頁設計軟體操作能力 2.64 2 25.分鏡繪製能力 2.45 14 26.瞭解影音錄製方式 2.36 27 27. Metadata 設計能力 2.18 26 28.瞭解影音剪輯方式 2.18 25 29.動畫製作軟體操作能力 2.09 13 30.資料庫系統管理能力 2.09 15 31.瞭解多媒體程式語言 2.09 4 32.瞭解開發平台軟體 2.09 3
五、研究發現 透過文獻之整理與層級分析問卷調查,本研究獲致研究發現如下: (一)數位出版從業人員非全為傳統出版業之背景轉型 本次問卷發放之數位出版公司主管,多非傳統傳播、印刷、文學科系學 歷背景,反而以 IT 專長背景者較多,因此可以發現隨著數位印刷技術的進 步、及多媒體設計軟體的不斷開發,傳統出版產業從業人員所應具體的專業 能力及 know how 已經產生了變化。文獻資料亦顯示目前負責數位出版品開 發營運、行銷推廣、動畫設計、程式開發的人也大多不是來自出版業,但具 備良好的彈性與溝通能力,以及對內容的想像力使得公司得以順利運作。 因此在數位出版品的製作過程中,需仰賴大量的資訊科技,並透過程式 設計工程師與多媒體設計師之溝通合作,才能生產出符合消費者閱讀使用需 求之數位出版品,與傳統出版人員所需之專業能力已大符不同。 二、數位出版品製作過程所需能力與文獻探討之差異 透過問卷本研究發展出數位出版從業人員專業能力層級架構,問卷分析 結果以「系統開發」能力權重值最高,而在文獻中,台北市雜誌商業同業公 會 2006 年所進行之「數位出版人才需求」調查則為「企劃」人才需求最高, 其次為「資訊研發」人才,探究其中原因,本研究認為科技與軟體之快速發 展為主要之因素。 2007 年 Amazon.com 所研發之 kindle 熱銷前,數位出版一直處於「雷聲 大雨點小」之境,然隨著近兩年無線網路逐漸普及,以及微軟推出之 Windows 7 觸控介面,成功地與各種多媒體功能加以結合,衍生激盪出許多數位生活 的新體驗與其他豐富多樣的創新應用,種種科技的進步也讓數位出版產業對 於人才的需求,已不僅只於「企劃」階段,後面所含括之技術開發部份,更 需仰賴大量系統開發人才之協助,以加速數位出版產業之發展。 根據台灣數位出版聯盟(2010)最新公布之「電子書產業問卷調查」(圖 5),其中轉檔與系統規格之問題分列前二、三名,而缺乏數位出版人才亦位 居第五,顯示隨著時間的改變,數位出版產業對能力之需求也隨之產生變化。 因此具備「系統開發」能力,並且熟悉網路媒體、科技資訊,在數位出版品 製作過程中仍是相當重要的。
5 6 7 7 9 11 12 14 15 17 30 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 其他 電子書侵蝕紙本市場 電子書容易被盜版 缺少公共版權的電子書 不知如何定價 工作流程改造 公司內缺乏數位出版人才 拆帳比例眾說紛紜 系統規格不清楚 轉檔成本太高 缺乏電子版權 圖 5 出版公司在數位出版領域所面臨最大之挑戰統計圖 資料來源:電子書產業問卷調查,台灣數位出版聯盟(2010),台北。
伍、 結論與建議
一、結論 (一)數位出版產業之工作職務內容 目前國內數位出版公司之主要之職務有行銷企劃人員、內容製作人員、程式 設計工程師三項,而視公司類型不同有文案、翻譯、電子商務等不同工作職務, 此外隨著工作型態的改變,個人工作室之數量也逐日增加,目前數位出版公司也 常將部分影音拍攝、美術設計或翻譯等案件,委外交由相關合作公司進行。 (二)數位出版產業對專業能力之需求 研究發現產業界對數位出版從業人員之專業能力需求以「瞭解數位檔案加密 方式」之權重值最高,相較於傳統出版業,數位出版物在現今網路傳輸檔案方便 且快速的情況下,其檔案的流通安全性及合法性皆相當受到數位出版產業所重 視,而隨著數位版權管理(Digital Rights Management)技術不斷提升,數位出 版從業人員也應不斷充實相關能力。 (三)數位出版產業從業人員職務與能力指標之對應情形 根據本研究經問卷調查所發展之專業能力指標,將其與數位出版從業人員職 務分佈情形,將兩者間對應如下所示: 1. 行銷企劃人員: (1)瞭解發行通路、(2)瞭解數位出版電子商務系統、(3)數位出版品檔案管 理、(4)瞭解數位版權管理方式、(5)字型規劃、(6)瞭解智慧財產權規範、 (7)瞭解各式電子出版品規格、(8)製作物外包規劃、(9)出版載具規劃、(10) 版面規劃、(11)產品創新能力。 2.內容製作人員: (1)網頁設計軟體操作、(2)瞭解影像掃瞄方式、(3)瞭解數位攝影方式、(4) 畫面樣式(ex:工具列、按鈕)設計、(5)動畫製作軟體操作、(6)分鏡繪製、 (7)色彩管理、(8)電腦繪圖軟體操作、(9)瞭解印前作業規格、(10)瞭解「使 用者介面」設計原理、(11)瞭解平面媒體製作方式、(12)瞭解影音剪輯方 式、(13)瞭解影音錄製方式、(14)瞭解不同閱讀器介面、(15)設計內容整 合、(16)瞭解數位檔案格式轉換方式。3.程式設計工程師: (1)瞭解數位檔案加密方式、(2)瞭解開發平台軟體、(3)瞭解多媒體程式語 言、(4)資料庫系統管理、(5) Metadata 設計。 (四)產業需求之專業能力與現今數位出版課程之相對應情形 本次研究共發展出32項能力指標,然而經調查開設出數位出版相關課程教 師之意見後,有18項能力指標與業界需求「相符」,依序為:1.設計內容整合 能力;2.瞭解印前作業規格;3.瞭解平面媒體製作方式;4.版面規劃能力;5. 瞭解數位出版電子商務系統;6.瞭解發行通路;7.瞭解數位檔案格式轉換方 式;8.瞭解智慧財產權規範;9.瞭解各式電子出版品規格能力;10.瞭解不同 閱讀器介面;11.數位出版品檔案管理能力;12.電腦繪圖軟體操作能力;13. 產品創新能力;14.瞭解影像掃瞄方式;15.出版載具規劃能力;16.瞭解數位 攝影方式;17.瞭解數位版權管理方式;18.字型規劃能力。 另有14項業界所需之專業能力項目未能與課程內容相符,依序為:1.瞭解 開發平台軟體;2.瞭解多媒體程式語言;3.資料庫系統管理能力;4.動畫製作 軟體操作能力;5.瞭解影音剪輯方式;6. Metadata設計能力;7.瞭解影音錄 製方式;8.分鏡繪製能力;9.網頁設計軟體操作能力;10.畫面樣式設計能力; 11.瞭解使用者介面設計原理;12.製作物外包規劃能力;13.瞭解數位檔案加 密方式;14.色彩管理能力。 其中多項產業需求高之能力項目,學校課程皆未能與其相符,顯示目前國 內大專院校及技職校院所開設之課程內容,與業界之需求仍有差異。
國科會補助專題研究計畫成果報告自評表
請就研究內容與原計畫相符程度、達成預期目標情況、研究成果之學術或應用價
值(簡要敘述成果所代表之意義、價值、影響或進一步發展之可能性)
、是否適
合在學術期刊發表或申請專利、主要發現或其他有關價值等,作一綜合評估。
1. 請就研究內容與原計畫相符程度、達成預期目標情況作一綜合評估
5
達成目標
□ 未達成目標(請說明,以 100 字為限)
□ 實驗失敗
□ 因故實驗中斷
□ 其他原因
說明:
2. 研究成果在學術期刊發表或申請專利等情形:
論文:
5
已發表 □未發表之文稿 □撰寫中 □無
專利:□已獲得 □申請中
5
無
技轉:□已技轉 □洽談中
5
無
其他:(以 100 字為限)
3. 請依學術成就、技術創新、社會影響等方面,評估研究成果之學術或應用價
值(簡要敘述成果所代表之意義、價值、影響或進一步發展之可能性)(以
500 字為限)
隨著數位出版逐漸成為下一波出版主流趨勢,傳統出版產業人才的培育也必須配合產業轉 型,以加速出版產業之數位化,因此本研究以數位出版產業為對象,探討數位出版產業從 業人員所需具備之專業能力,以供傳統出版人員轉型時之參考。研究首先採用文獻探討方 式,以瞭解數位出版產業之現況,再透過層級結構問卷發送,並輔以實地訪談方式,利用 Fuzzy AHP 層級分析法建構完整能力層級、指標。 研究發現數位出版從業人員職務與能力指標之對應情形,其中行銷企劃人員以「瞭解發行 通路」能力最為需要;內容製作人員以「網頁設計軟體操作」能力最為需要;程式設計工 程師以「瞭解數位檔案加密方式」能力最為需要。2010 國科會補助出席國際學術會議報告
99 年 08 月 18 日 報告人姓名 廖信 服務單位 及職稱 國立台灣師範大學圖文傳播學系 副教授 會議時間 6/2/2010-6/5/2010 會議地點 Hawaii, USA 會議名稱 Hawaii International Conference on Social Science
發表論
文題目 The Study of the Competency for Pre-press Professionals
報告內容:
一、參加會議經過 夏威夷國際研討會是以社會科學為主題的研討會,可以見到各式各樣與社 會、人相關的研究議題。參與這次會議的學者大約有200 多人。 本人的發表被安排在6/3 下午 2:40 - 4:10,在發表期間有多位與會的學者前 來詢問本人的研究主題及內容,並交換了些彼此的研究心得。圖一、圖二為參加 此次研討會之留影。 圖一 圖二二、參加會議心得 此次研討會除了發表自己的研究成果之外,也藉由研討會觀摩別人的 研究議題與方法,而從觀摩他人的研究中也發現有趣的議題,例如喬治亞州 政府對未婚懷孕少女的輔導與安置,並藉由這樣的輔導機制成功的協助少女 重新進入社會。對於個人日後的研究方向多所啟發,參與此次研討會個人收 穫頗豐。 同時,感謝國科會對於本人參加此次研討會經費上的補助,讓本人有 此次的學習之旅。 三、建議事項 無 四、攜回資料 研討會論文集光碟片一片 五、論文內容
The Study of the Competency for Pre-press Professionals
Shin Liao, Ph.D. Associate Professor, Department of Graphic Arts Communication,National Taiwan Normal University
162, Hoping E. RD., Taipei, 10610, Taiwan, sliao@ntnu.edu.tw
Abstract
The objective of this research is to explore the competency for pre-press
professionals under the circumstance of rapid revolution and change of technology in the printing industry. The literature reviews collected in the beginning of this research identified a few of skills, knowledge, somewhat goodwill or attitude, of the pre-press professional as the competency. A survey was also conducted through members of the Association of the Taipei Printing Industry. The total 287 questionnaire were sent out for investigation, and 107 out of them were returned and valid. The rate of feedback is nearly equal to 37%. The competency for pre-press professionals were finally
categorized into 26 items in the research; more importantly, the 3 items among them--the ability to precisely set both plate-making and finished size, the skill of layout, including setting running head, running page, corner line and cutting line, the understanding of color cast in fixing a manuscript – are most essential for pre-press professionals and highly valued by the printing industry.
Keyword: printing industry, pre-press professional, competency
Introduction
With the rapid development and revolution of technology, the process and procedure of the printing has been tremendously changed toward digitalization. Especially in the pre-press process, digital prepress technology has become less cost intensive, more efficient and reliable, and as the knowledge and skill required to use the new hardware and especially software have become more widespread within the labor force, digital automation has been introduced to almost every part of the process. This circumstance has come out an issue of how to manage the workflow to gain efficiency and quality in the entire production of digital printing.
To deeply explore the competency of pre-press professionals will be the key to success in managing workflows of production in the modern printing industry. The pre-press is the first process of production. Employees, who are actually responsible for the production (e.g. layout), usually have to attend to part of pre-press in order to complete the process without errors. Managers can be benefited from understanding capabilities of their labor force well to assign task, allocate responsibility and implement job training. According to the report from the Industrial Development Bureau of Taiwan Ministry Economic Affairs (2006), 12 companies have accepted the Bureau’s help to upgrade color-control techniques and to integrate work-flows
through digitalization. All evidences show that competency of pre-press professionals change. Since the competency of professionals has been changeable along with the technological and economic development, its scopes and contents need be updated too (Lee, 2003). The identification of the competency in this research is based on the principle of adjusting with the integration of new technique and printing job.
The purposes of this research are mainly to explore the current development of the modern printing industry and to understand the professional competency of the pre-press industry.
Terminologies:
Competency: the condition or quality of being competent when someone fulfill the job, including of ability, skill, knowledge, and somewhat goodwill.
printing industry: pre-press, press, post-press. Prepress is the term used in the printing and publishing industries for the processes and procedures that occur between the creation of a print layout and the final printing. The prepress procedure includes the manufacture of a printing plate, image carrier or form, ready for mounting on a printing press, as well as the adjustment of images and texts or the creation of a high-quality print file. The pre-press professional means someone who is fully responsible and specially trained for pre-press tasks.
Literature Review
The Current Printing Industry:
Since the labor force, especially pre-press professionals is the key to success in managing a printing business, in the era of knowledge based economy, we can foresee that the digital automation will become the main stream in the printing industry. Not only were work forces replaced by the automation of machines quickly, but also white-collar employees felt threatened with such a volatile environment of management.
Huang (2001) pointed that digitalization has made it possible that processes of printing, including of pre-press, press, and post-press, can be fully coordinated without any impedance. The International Cooperation for Integration of 6 Processes in Prepress, Press and Postpress (abbreviated as CIP4), formed by many printing suppliers and educational groups, strived to set up a standard format of file transfer and data sharing for the integration of the printing industry. Therefore, printing techniques, graphic arts and graphic communications are formed into one technology. With the mature of CIP4 application, all files can be inter-operated cross platform through machines supplied by those members, so as to avoid the repetition of file inputs, reduce errors and get high-quality products. (Liao, 2006)
At the same time, the electronic commerce and internet also facilitate the
integration of the printing industry. As a result, a company can greatly gain efficiency from customers’ inputs to final printing by digital automation, mainly in the reduction of production costs and the enhancement of performance without errors.
The Pre-press Workflow:
In current Taiwan printing industry, the pre-press process can be mainly
typesetting graphic and text. The facilities of graphic input include of the plotter plate, digital camera, photo CD, handy scanner, flatbed scanner, desktop scanner, and cylinder scanner. The text input is usually done by typing directly from a keyboard, or scanning from the manuscript and then transferred into the electronic file by text recognition of some software (Chang, 2000). The client-server network can serve well in the assembly of files among computers. The Color Electronic Prepress System (CEPS), which edits graphics and texts and then makes into four color separation screens for the plate-making use, becomes the main operation system of pre-press process (Ho, 1995). The digital instrument of pre-press output, based on the Postscript language, interprets through the Raster Image Processor (RIP) to screen data and then outputs by layout software (Cheng, 2001). The facilities of pre-press output include of electronic files for multi-media publication and network communication, the screen plate machine, computer to plate ( CTP) machine, the proof machine, and the digital press machine for customizing products (Hsieh, 2000).
Color Management System (CMS) is coordinated by a set of software and
hardware to maintain the consistency of color through the procedures of pre-press (Lo, 1998). The core elements of CMS are calibration, characterization, and conversion, following the specification of International Color Consortium (ICC) (Lee, 1999).
Professional Competency:
A profession is a vocation founded upon specialized educational training, the purpose of which is to supply disinterested counsel and service to others, for a direct and definite compensation, wholly apart from expectation of other business gain. The scholar Chia (1979) made a definition of profession which should covers abundant knowledge, excellent capability, service and devotion.
The competency is the condition and quality of doing something well or
effectively. The competency does not mean only the personal technique or skill but a kind of ability to make the job efficiency and success by fully utilizing knowledge, perception, and expertise (Chu & Chen, 1999). Lee (1999) also explained that the competency is the performance of personal knowledge, operation skill and good attitude to execute the job effectively.
Wu (2007), quoting from Darlling-Hammond, stated that the profession is composed of expertise, technique, mission and responsibility. Professionalism is the process of enhancing those elements to be qualified with service, independence, and uniqueness.
Chen(2001) defined that the competency is the behavior or real performance of implementing a job through the personal knowledge, skill, and goodwill.
Hong(1997) divided the competency into the dominant and recessive ability. Generally speaking, profession, management, and personal relationship are relevant to dominant abilities. Intellectual wisdom and personal value belong to recessive
abilities.
According to above statements, this research generalized that the competency for the professional is the condition and quality of utilizing knowledge, technique, and goodwill for someone who is devoted to a special-trained job. As a result,
professionals with the competency will be highly respected in society through their join into the group, service and independence.
Method
Questionnaire and Validity:
Literature review and survey method were used to conduct this research. According to literature review, prepress professional competence were defined. A questionnaire was developed to investigate how important the competences were ranked. A five points Likert scale from 5 to 1was equivalent to strongly agree, agree, no ideas, disagree and strongly disagree. The questionnaire was reviewed by five respect scholars and professionals from the field of graphic communication to check questionnaire’s content validity.
Samples:
The target samples of this research included managers, leaders, or executives with the experience of management in the printing operation from the Association of Taipei Printing Industry. The 287 questionnaires in total were sent, and 115 out of them were returned. After removing 8 invalid copies, 107 questionnaires were effective. The return rate is 37%.
Reliability:
Cronbach’s α is used to test the internal consistency among participants. The αvalue is 0.966, which means the answers to the questionnaire among participants reaching high reliability.
Results
The Description Data:
This study has collected 107 valid questionnaires. The description data of the participants are described as the following:
1. Sex—
72 out of 107 participants are male and 35 are female. The percentage of male is equal to 67.28%, and females 32.71%.
2. Age—
14 out of 107 participants are grouped into the age from twenty to twenty nine, 18 from thirty to thirty nine, 41 are from forty to forty nine, 24 are from fifty to fifty nine, and 10 above or equal to sixty.
As a result, the percentage of people of age from twenty to twenty nine years is equal to 13.08%, from thirty to thirty nine 16.82%, from forty to forty nine 38.31%, from fifty to fifty nine 22.42%, and above or equal to sixty 9.43%. 3. Seniority—
9 out of 107 participants belong to the group with the seniority of less than 5 years, 13 between five and ten years, 10 between eleven and fifteen years, 26 between sixteen and twenty years, and 17 between twenty one and twenty five years, 14 between twenty six and thirty years, and 18 more than and equal to thirty one years.
As a result, the percentage of the group with seniority less than five years is equal to 8.41%, between five and ten 12.14%, between eleven and fifteen 9.34%,
between sixteen and twenty 24.29%, between twenty one and twenty five 15.88%, between twenty six and thirty 13.08%, and more than and equal to thirty one 16.82%.
4. Educational Level—
11 out of 107 participants belong to the group with junior high school educational level, 31 are senior or vocational high school, 53 are under-graduate or college, and 12 are graduate level.
As a result, the percentage of the group with junior high school educational level is equal to 10.3%, senior or vocational high school 29%, under-graduate or college 49.5%, and graduate 11.2%.
5. Working Department—
20 out of 107 participants belong to the group people working in the department of pre-press, 14 press, 2 post-press, 2 logistics, 39 sales, and 30 others.
As a result, the percentage of the group working in the department of pre-press is equal to 18.69%, press 13.08%, post-press 1.86%, logistics 1.86%, sales 36.44%, and others 28.03%.
Independent Variables
Category Quantity Percentage(%)
sex male 72 67.28 female 35 32.71 age 20~29 14 13.08 30~39 18 16.82 40~49 41 38.31 50~59 24 22.42 ≧60 10 9.34 seniority <5 years 9 8.41 5~10 years 13 12.14 11~15 years 10 9.34 16~20 years 26 24.29 21~25 years 17 15.88 26~30 years 14 13.08 ≧31 years 18 16.82
education junior high school 11 10.3 senior or vocational high school 31 29 under-graduate or college 53 49.5 graduate 12 11.2 department Pre-press 20 18.69 press 14 13.08 Post-press 2 1.86 logistics 2 1.86 sales 39 36.44 others 30 28.03
Table 1. The Data Distribution of the Sample
The Rankt of the Competency for Pre-press Professionals:
We have mentioned the adoption of Likert’s five-level scaling method in the questionnaire to measure the importance of competency. We assign points to each
level, and 5 points means very important, 4 points important, 3 neither important nor unimportant, 2 unimportant, and 1 very unimportant.
Content of Competency Mean Standard Deviation
Ranking
The ability to precisely set both plate-making and finished size
4.16 0.82 1 The skill of layout, including setting
running head, running page, corner line and cutting line
4.07 0.79 2
The understanding of color cast in fixing a manuscript
3.98 0.91 3 The ability of composition to present
texture materials in graphic form on paper or printing medium
3.91 0.84 4
The setting of columns to begin page layout
3.89 0.91 5 The execution of blocking out color
pictures
3.77 0.82 6 The skills of character manipulation, such
as handling color tint, reversing, rotation, and transformation
3.77 0.87 7
The adjustment of color tone for images and pictures
3.76 0.73 8 The adjustment of color cast of images
and pictures
3.75 0.75 9 The capability of page layout 3.73 0.76 10 The recognition of printing techniques,
including of offset and gravure press.
3.71 0.88 11 The manipulation of texts, especially in
the size, font, and typeface.
3.67 0.82 12 The adjustment of sharpness and softness
of graphics.
3.67 0.73 13 The capability of composing texts and
graphics in plates of color printing
3.67 0.84 14 The understanding of software and
hardware of compositors
3.66 0.96 15 The execution of repairing of pictures 3.65 0.79 16
The understanding of the principle of color separation and reproduction
The marking and annotation of the manuscript with color chart
3.6 0.77 18 The handling of background color, line
art, and lace border.
3.59 0.81 19 The ability of making a shadow of texts
and graphics.
3.58 0.8 20 The ability to make cropping and
registration mark of the printing plate
3.57 0.96 21 The ability to crate image frames 3.52 0.9 22 The capability of color arrangement 3.5 0.94 23 The operation of facilities relevant to
image scan or color separation
3.43 0.92 24 Doing special gradient and flat tint 3.43 0.9 25 Familiar with the operation of dot meter,
colorimeter, and densitometer.
3.38 0.92 26
Table 2. The Importance of Competency of Pre-press Professionals According to table 2, we can see that the ability to precisely set both
plating-making and finished size is the most important from the point of view of the printing industry, then the second comes the skill of layout, setting running head, running page, corner line and cutting line, and the third the understanding of color cast in fixing a manuscript.
Quantity Kendall’s W Chi-square D.F. P-value 107 0.089 238.137 25 0.0000
Table 3. Kendall’s W Test Statistics
From table 3, Kendall's coefficient of concordance W, equal to 0.089, and
P=0.0000<0.05, shows that 107 respondents’ opinions toward 26 items of competency reach ranking consistency.
The Comparison among Managers:
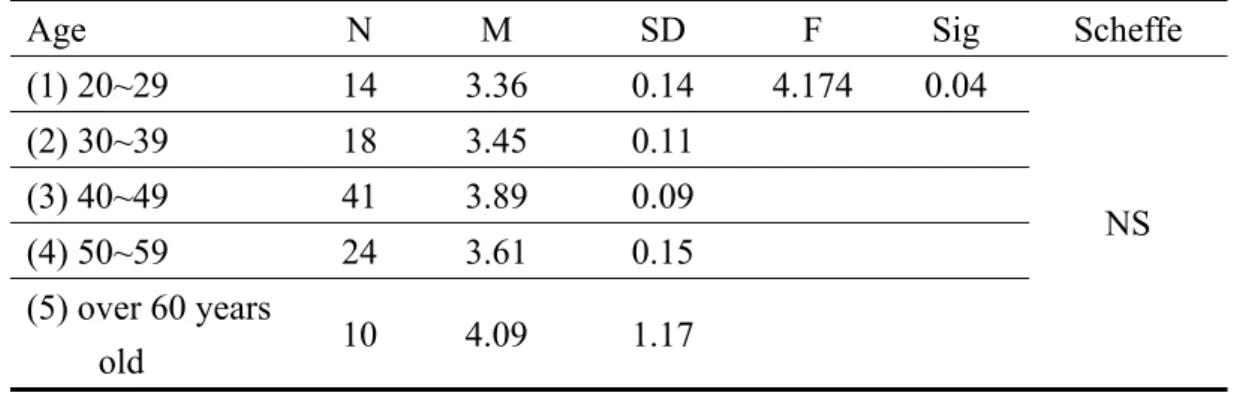
The multi-variance analysis was adopted to exam whether managers’ attributions affect their rating of the competence. The results indicated that managers’ sex (F=1.38, P=0.17) and seniority (F=0.671, P=0.673) do not affect managers to rate the
was used to exam how the age and education level affect competences rating. The results showed that there is no difference among age groups (Table 5); however, managers with high school degree and junior high school degree do have different rating on the importance of competence (Table 6). Overall, most managers in this study rate the professional competences consistently except mangers with junior high degree.
I.V. D.V. N M SD F P Rating of the importance of
professional competence sex 107 3.67 0.62 1.38 .170 seniority 107 3.68 0.58 0.671 .673 age 107 3.68 0.332 4.174 .04* education 3.62 0.61 3.474 .019*
Table 4: Multi-variance analysis
Age N M SD F Sig Scheffe (1) 20~29 14 3.36 0.14 4.174 0.04 NS (2) 30~39 18 3.45 0.11 (3) 40~49 41 3.89 0.09 (4) 50~59 24 3.61 0.15 (5) over 60 years old 10 4.09 1.17
Table 5: Scheffe post hoc test on age groups
Education level N M SD F Sig Scheffe (1) Junior high school 11 3.30 0.53 3.474 0.019 2>1 (2) High school 31 3.94 0.60
(3) Undergraduate 53 3.67 0.60 (4) Graduate 12 3.57 0.70
Conclusion
Although managing the printing business in such a volatile environment of digital automation is a challenge for a lot of managers or executives, they can still promote the competency for the entire company step by step. The key will be the truly understanding the competency of labor force.
This research identifies 26 items of competency for prepress professionals and concludes that the ability to precisely set both plate-making and finished size, the skill of layout, including setting running head, running page, corner line and cutting line, the understanding of color cast in fixing a manuscript are the most essential and highly valued by managers in the printing industry.
A company running toward the digitalization will succeed by providing a good training for labor force, re-allocating the workflow of production, and gaining the competency of organization.
Reference
Chen, S.Y.(2001). The study of performance evaluation indicators for digital prepress enterprise. Unpublished master’s thesis, National Taiwan Normal University, Taiwan.
Chen, D.H.(2001). The research of supply-demand influencers between specialized architecture and construction subject courses in Vocational High School and basic human resource for the construction industry. Unpublished master’s thesis, Chung Hua University, Taiwan.
Chia, F.M.(1979). Introduction to Education. Wu-Nan Book Press: Taipei, Taiwan. Chu, Y.S. & Chen, Y.C.(1999). Explore the importance of general education from the
development history of vocational education in Taiwan. Journal of Shu-Te University, Taiwan, 1(1), 257-265.
Field, J. N. (ed.) (1980). Graphic Arts Manual. N.Y. : Arno Press , Mustards Publishing Corp.
Ho, C.I.(1995). New Knowledge of computer prepress. ARCO Infocom Press: Taiwan. Hong, J.C.(1997). Competence transform: Did rolling stone gather moss? Journal of
Occupation and Training, 15(2), 59-63.
Hsieh, W.C.(2000). A Study of Professional Fundamental Competence Possessed by Vocational High School Graduate Majoring in Printing in Taiwan. Unpublished
master’s thesis, National Taiwan Normal University, Taiwan.
Hung, L.C.(2001). The Study of Graphic Communications Technical Development in Taiwan. Unpublished master’s thesis, National Taiwan Normal University, Taiwan.
Industrial Development Bureau, Ministry of Economic Affairs, Taiwan. (2006). Project of Developing High Valued Printing Industry. Results of the
implementation Report of Industrial Development Bureau Project 2006 (Report NO.:PG9503-0259).
Lee, C.C.(2003). Building the benchmark of professional competence of Taiwan vocational high school: Students from printing department as an example, Journal of Chinese Association of Graphics Science & Technology 2003 (CAGST), 191-211.
Lee, L.S.(1999). Guidelines for the Selection of Task Analysis Strategy: Perspective on Technology and Vocational Training. Shih-Da University Press: Taipei, Taiwan.
Liao, S.(2006). Importing digital working flow (CIP3/4) into Printing Industry. Journal of Printing Technology, 22(4), 83-92.
Lo, M.C.(1998). The core technology of the color management system. Taiwan Printing Industry Association the 50th Annual Report, special issue, 282-288. Wu, L.Y.(2006). A Study on the Needs of the Professional Knowledge and
Competence of Teachers for the Classes of Mental Retardation in Senior High School. Unpublished master’s thesis, National Pingtung University of Education, Taiwan.
98 年度專題研究計畫研究成果彙整表
計畫主持人:廖信 計畫編號: 98-2511-S-003-035-計畫名稱:產業需求導向之科技校院數位設計專業實務課程發展與驗證研究--數位出版產業需求導向 之科技校院數位設計專業實務課程發展與驗證研究(子計畫三) 量化 成果項目 實際已達成 數(被接受 或已發表) 預期總達成 數(含實際已 達成數) 本計畫實 際貢獻百 分比 單位 備註(質 化 說 明 : 如 數 個 計 畫 共 同 成 果、成 果 列 為 該 期 刊 之 封 面 故 事 ...等) 期刊論文 1 1 100% 廖 信 、 潘 怡 臻 (2010.05)。數位出 版從業人員專業能力 之研究。教育資料與 圖書館學,47(3), 371--397 。 ISSN 1013-090X。(TSSCI) (NSC: 98-2511-S-003-035) 研究報告/技術報告 0 0 100% 研討會論文 1 1 100% 篇 論文著作 專書 1 1 100% 數位出版產業之專業 能力需求與學校培育 現況/ 廖信著. 初版. --臺北縣深坑鄉:揚智 文化, 2010.09, ISBN 978-957-818-970-6 (平裝) 申請中件數 0 0 100% 專利 已獲得件數 0 0 100% 件 件數 0 0 100% 件 技術移轉 權利金 0 0 100% 千元 碩士生 3 3 100% 博士生 0 0 100% 博士後研究員 0 0 100% 國內 參與計畫人力 (本國籍) 專任助理 0 0 100% 人次 期刊論文 1 1 100% 國外 論文著作 研究報告/技術報告 0 0 100% 篇研討會論文 1 1 100%
Liao, Shin & ; Yi-Chen Pan (2010.06). Professional Abilities of the Employees Working in Digital Publishing Industry. The 3rd International Conference on Information Sciences and Interaction Sciences Proceedings (ICIS 2010).71--76. Chengdu, China. ISBN: 978-1-4244-7385-4 (IEEE, EI Accepted) (NSC: 98-2511-S-003-035) 專書 0 0 100% 章/本 申請中件數 0 0 100% 專利 已獲得件數 0 0 100% 件 件數 0 0 100% 件 技術移轉 權利金 0 0 100% 千元 碩士生 0 0 100% 博士生 0 0 100% 博士後研究員 0 0 100% 參與計畫人力 (外國籍) 專任助理 0 0 100% 人次 其他成果
(
無 法 以 量 化 表 達 之 成 果 如 辦 理 學 術 活 動、獲得獎項、重要 國際合作、研究成果 國際影響力及其他協 助產業技術發展之具 體效益事項等,請以 文字敘述填列。) 本研究透過瞭解數位出版從業人員之專業能力,提出建議以作為傳統出版人員 轉型之方向,並提供出版產業人才培育及相關單位課程安排之參考。 成果項目 量化 名稱或內容性質簡述 測驗工具(含質性與量性) 0 科電腦及網路系統或工具 0 教材 0 舉辦之活動/競賽 0 研討會/工作坊 0 電子報、網站 0 處 計 畫 加 填 項 目 計畫成果推廣之參與(閱聽)人數 0