Downstream Impacts of Reservoir Sediment
Desilting Operation between Taiwan and
Japan
Chi-Bin Chen, Chan-Chun Yao, Tsang-Jung Chang, Fong-Zuo Lee and Yutaka Hayashi
Abstract
Reservoir sedimentation problem is a vital issue in recent years due to reservoir active storage is going to be 2/3 of design capacity, especially in Taiwan. Therefore, several sediment desilting countermeasures are presented to deal with sedimentation problem. The sediment bypass tunnel, excavation, sediment replenishment and hydraulic desilting operation are major strategies for reservoir sediment management. However, the downstream environmental impact becomes to be a new issue when reservoir desilting operation is implemented. Therefore, this study compares the field investigation items and results after sediment releasing from reservoir between Taiwan and Japan. The investigation items include bed material and water quality in Taiwan as same as in Japan. Based on field study results, reservoir desilting operation seems to be not obviously affect water quality, especially on dissolved oxygen item. It means that the reservoir desilting operation of empty flushing in Japan and turbidity current venting in Taiwan does not significantly impact downstream water environmental conditions normally on water quality items. However, the released sediment from Taiwan is classified to silt and clay, from Japan is classified to sand and gravel. Therefore, there is not significantly changing of downstream river bed in Taiwan. But, the public water supply is constrained when reservoir desilting is operated.
Keywords: Reservoir sedimentation, sediment desilting countermeasures, water quality, dissolved oxygen
1 General instructions
In recent years, the issues related to sustainable operation and storage reservation of existing reservoirs are essentially important. The loss of active reservoir volume due to sedimentation has been estimated to be higher than the increase of reservoir capacity by construction. An effective reservoir sediment desiltation strategy is a vital challenge. Turbidity current venting is an optional countermeasure for reservoir desilting operation. If the turbidity current is generated and travelled through a reservoir, successful operation of a sluicing outlet to vent turbidity current depends on accurate prediction of turbidity current movement (Lee et al., 2014, 2018).
In Taiwan, the modification of the existing powerhouse penstock as a venting tunnel for venting the turbid water was a major project task to improve the sluicing capacity in Shihmen reservoir, especially for turbidity current venting operation. The Shihmen reservoir has a natural drainage area of 762.4 km2. It is formed by the Shihmen dam located at the upstream reach of the Dahan River flowing westward to the Taiwan Strait. The Shihmen dam completed in 1963 is a 133 m high embankment dam with six spillways, one bottom outlet, two power plant intakes and two flood diversion tunnels. The elevations of the spillway crest, bottom outlet, power plant intake and flood diversion tunnel are EL.235 m, EL.169.5 m, EL.173 m and EL.220 m, respectively. The design discharge of six spillways, one bottom outlet, two power plant intakes and two flood diversion tunnels are 11,400 m3/s, 34 m3/s, 137.2 m3/s and 2,400 m3/s, respectively. With a design water level of EL.245 m, the reservoir pool has 16.5 km in length and the surface area of the water has 8.15 km2. The initial storage capacity was 0.31109 m3, and the active storage was 0.25109 m3. Due to a lack of desilting works, most of the incoming sediment particles had settled down rapidly along the reservoir since the dam was commissioned. Therefore, one of the two penstocks at the powerhouse was modified in 2012. It was operated for the first time during Typhoon Soulik in 2013 to release abundant sediments to the downstream river (Lai et al., 2015).
Corresponsively in Japan, we collect data from downstream river of Kurobe river which adapt empty flushing strategy for sedimentation management of Dashidaira dam and Unazuki dam. We compare downstream investigation items between Taiwan and Japan and discuss the item difference. The annual rainfall in Kurobe river basin is about 2400mm, the average river slope at mountainous area is about 1/100 and total collapse area is about 5% of catchment. At the beginning, Sennindani and Koyadaira dam were built without flushing channel at 1940 and 1936, respectively. Therefore, these two dams lost almost 90 % reservoir capacity at 2008. Based on these experiences, flushing channel was adopted to prevent sedimentation at Dashidaira dam and Unazuki dam at 1985 and 2001, respectively. The average capacity-inflow ration of Dashidaira and Unazuki is about 100 and reservoir life is about 20 year. It means that very large sediment needs to be flushed and catchment possesses much water quantity to flush sediment.
Based on operation condition, inflow discharge must large enough to possess enough power for flushing sediment. According rainfall and inflow discharge record, the average inflow discharge of Dashidaira dam would rise to an average value, 200 m3/s, from May to August. Therefore, classify inflow discharge to decide flushing discharge can be done. The flow discharge over 250m3/s can flush sediment that had deposited in the reservoir. Moreover, according to the monitoring of water quality, when flushing discharge is more than 250m3/s, the suspended solid (SS) and dissolved oxygen (DO) in the water can still maintain the living of aquatic animal. According to the operation rule, if DO is less than 2 ppm, the fish would die. Therefore, there are three rules to stop the flushing operation
even the flushing objective does not reach. First of all is inflow discharge small than 130m3/s and second is DO less than 4 ppm.
2 Results and Discussion
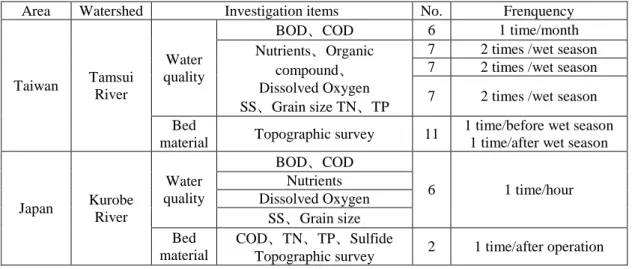
Based on field survey, the essential items of BOD, COD, nutrients, dissolved oxygen, SS and grain size of water quality are investigated in Taiwan and Japan (KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO., INC., 2018 ; Northern Region Water Resources Office, 2014). Although the survey frequency is different between Taiwan and Japan, it seems that the mentioned items of water quality are important for downstream impacts due to reservoir sediment desilting operation. However, due to released sediment is classified to silt and clay of Shihmen reservoir, the organic compound is investigated. This is different from released sediment in Japan, which is classified to sand and gravel. In addition, the field investigation period is during typhoon events in Taiwan, the safety is concerned and field data is difficult to sample due to extreme wind and heavy rainfall. Therefore, the feasibility of observation instruments are suggested to apply at hot spots.
On bed material part, the essential items of COD、TN、TP、sulfide and topographic survey are investigated in Japan. However, the essential item is topographic survey in Taiwan. The TN and TP are investigated in water quality items. The main reason is that there is a drinking water supply at the downstream of Shihmen reservoir. Therefore, the TN and TP is more important in water quality. Compare to Taiwan, the main water supply is for irrigation in the downstream of Kurobe River. That is the main difference between Taiwan and Japan.
表 1 Downstream investigation difference between Taiwan and Japan
Area Watershed Investigation items No. Frenquency
Taiwan Tamsui River Water quality BOD、COD 6 1 time/month Nutrients、Organic compound、 Dissolved Oxygen SS、Grain size TN、TP
7 2 times /wet season 7 2 times /wet season 7 2 times /wet season Bed
material Topographic survey 11
1 time/before wet season 1 time/after wet season
Japan Kurobe River Water quality BOD、COD 6 1 time/hour Nutrients Dissolved Oxygen SS、Grain size Bed material COD、TN、TP、Sulfide
Topographic survey 2 1 time/after operation
Acknowledgement
Many thanks to KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO., INC. for data exchange, Sinotech Foundation for Research & Development of Engineering Sciences & Technologies for funding support and all authors for their contribution to this research.
References
Fong-Zuo Lee, Jihn-Sung Lai, Yih-Chi Tan and Chia-Chi Sung (2014). Turbid Density Current Venting through Reservoir Outlets. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, Vol. 18, No.2, pp. 694-705. Jihn-Sung Lai, Fong-Zuo Lee, Ching-Hsien Wu, Yih-Chi Tan and Tetsuya Sumi (2015). Sediment
bypass tunnels of the Shihmen Reservoir in Taiwan. International workshop on Sediment bypass tunnels, ETH Zurich, Switzerland.
Northern Region Water Resources Office (2014). Impacts on the downstream river ecology and improve strategies by the operation of flood control and sediment desiltation of Shimen Reservoir. Technical report, National Chung Hsing University
Fong-Zuo Lee, Jihn-Sung Lai, Wen-yi, Chang and Yih-Chi Tan (2018). Assessments of Induced Disaster on Woody Debris and Turbidity Current Venting in a Reservoir. 14th APRU Multi-Hazards Symposium, Canberra, Australia.
KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO., INC. (2018). Reservoir desilting operation of Dashidaira dam and Unazuki dam.
Authors (Text style: Authors Address)
Chi-Bin Chen, Chan-Chun Yao
Sinotech Foundation for research and Development of Engineering Sciences and Technologies
Tsang-Jung Chang
Department of Bioenvironmental Systems Engineering, National Taiwan University (NTU), Taiwan
Fong-Zuo Lee (corresponding Author)
Hydrotech Research Institute, National Taiwan University (NTU), Taiwan Email: windleft@gmail.com
Yutaka Hayashi