【附錄12】
The Construction of Mystery-Seeking Motive Theory
in Internet Behavior
CHIN-MOU CHENG, RONG-JYUE FANG, RONG-LAIN HO
College of Humanities and Society, Fooyin University
151, Chinhsueh Rd., Ta-liao, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Department of Industrial Technology Education
National Kaohsiung Normal University
116, Ho Ping 1Rd., Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
so003@mail.fy.edu.tw, fang@mail.stut.edu.tw, her5621@yahoo.com.tw, http://www.nknu.edu.tw/
Abstract: - Surfing on the Internet is an indispensable behavior of our daily life. This article aimed at the
construction of mystery-seeking motive theory (MSMT) related to the Internet behavior. The researchers intended to explore motives and hidden factors, especially the locus of internal and external control attribution and sensation-seeking perspectives through investigating the related papers. In recent years, many papers related to Internet addiction pop up like mushroom and bamboo shoots after rain. Most of them stressed unduly the negative or problematic behavior but rarely mentioned the positive exploration. Hence, to visit scenic spots and to understand the truth, the researchers ambitiously devoted themselves to constructing the motive theory and to explaining network behavior, hoping to unearth its implication on the general technology education. Study group discovered that the motive theory concerning network behavior was based on inquiring and searching of related data. After clarification, the questionnaire for the empirical study was composed. There were 574 students selected as the testing samples from four universities. The results showed that the MSMT had a great mysterious extent from beginning to end, and also obtained the interaction with one another among flow experience, peak phenomena, and Internet addiction. We established MSMT for the instruction of general technology education. If teachers could handle the information of network learning and explore the truth to solve the problem, then students would enhance their on-line learning and pursue truths. Finally, several suggestions were proposed: to compile a more rigid questionnaire; to spread the MSMT; to occupy the status of general technology education; to keep track of more understanding of similar studies.
Key-Words: -MSMT, Internet behavior, Flow experience, Peak phenomenon, Internet addiction, General
technology education, Locus of control, Sensation-seeking
1 Introduction
All people searched for the mysterious experience, such as „visiting quietly scenic spots‟, „inquiring about the secret boundary,‟ and so on. To fulfill the curious mind of human nature, people inquire the outcome, truth and the causes of everything. Especially in the virtual reality, the world is mystical. The general psychology concerned some kind of motivation hidden behind any behavior. This article concerned users‟ behavior of network from the motive viewpoint, and wanted to construct a theory of the motivation. The network users face the searchable process of virtual reality; they actually want to seek something mystery, and look up to come to light. The motive theory hidden behind these behaviors is important, including self-attribute, self-efficacy, hierarchy of needs, and sensation seeking [1].We search for information by network related with motive, seeking diligently precise balance [11]. This article focused the motive theory
on self-attribute and sensation seeking, because they were effective to search a mystery and had a scale to measure motive. Simultaneously, we aimed the motive theory with an applicable domain at general technology education.
Self-attribute motive theory showed that one faced the situation, such as network, to inquire about the reasons of reflecting on success or failure in the disposition, and the internal-controller turned causes to internal attribute and the external-controller turned causes to external attribute. The network users meet the setback and conflict in the realistic environment; they can actually obtain compensation, satisfactory or achievement in a network situation. The sensation seeking motive theory emphasized that a person with high needs of the stimulating experience was more like loved novelties deeper , taking more risks than a person with low needs. [22].
We consult the related research materials of Internet addiction for nearly six years, and may mainly discover four items of the motive ingredient
about Internet addiction: individual psychological factor, situation factor, social interaction factor, and personal behavior factor[3]. The research materials of Internet addiction aimed mostly in terms of addicting behaviors at negative or morbid state and questionable behavior. This article directed the immersing network into positive development and the meaning of peak experience. And the common network user or the computer game player who faces the virtual reality may also discover these factors. Now in the network world with fast conveniences, the users want to inquire about and satisfy the curious mind, and receive the unique attractive intensity of network connotation and stimulate, and seek the high level of psychological demand and pursue a new satisfaction of network. Especially in the net coffee situation, the computer games or electrical toy and pleasant sensation of obtaining the treasure, the users just like the demand of self-realization to satisfy “virtual peak experience”. The general network user, even in individual significant behavior, tries to produce immersing experience or peak phenomena with all his heart. Therefore, we inquire into the network behavior of students to seek its mystery process, and want to understand the truth in view of items as follows.
1. Students who face the daily network situation have psychological factors with inspiring something mysterious, and getting involved in self-attribution and sensational orientation of motivation for the self-realization with the peak phenomenon.
2. Students who face the virtual reality control a mystery-seeking process trying to evade the face-to-face social interaction for simulating interpersonal relationship. They transform themselves and adjust their moods for seeking the special conscious experience of network.
3. Students who face the setback and conflict of realistic society are unable to obtain the psychological need, and their psychological defense mechanism often seek to compensate the similar satisfactory feeling of self-realization through the network situation.
4. The peak phenomenon is a satisfaction of self-realization need, and it possibly produces in the network situation resembling to attain the peak experience of an ordinary life situation.
5. The entire process of the mystery-seeking phenomenon has several stages, and appears possibly to have the tendency of addicting to network, flow experience and peak phenomena from stimulate- seeking with motive control to seek compensation and satisfaction through the mystery-seeking process of the daily situation.
6.In general technology education, the students are enabled to have the macroscopic field of vision, multiple viewpoints and broad mind to achieve the goal which they learn thoroughly to understand the truth and the true meaning of life via the Internet. We hope to construct the mystery-seeking motive theory of the Internet for promoting students‟ healthy behavior.
2 Theory and hypotheses development
The purpose of this article was to construct the theory of mystery-seeking to interpret the behavior of Internet addiction via searching for the related literature. We reviewed deliberatively the network behavioral documents, then analyze real diagnosis to verify the mystery-seeking motive theory through the result of surveying questionnaires. It was shown that the on-line mystery-seeking behavior was significant and could deduce to other behavior. We explored further to understand the special meaning of this theory on general technology education.
2.1 On-line mystery-seeking phenomenon
Now we access the network to seek mysterious phenomena in developing information technology, and inquire the virtual reality into the hot topic of discussion. It meant that using special equipment to let a person feel personally the situation experiences in computer software simulation. The virtual reality is a 3D three-dimensional space which is produced by the computer, and the user may carry on the conversation with this spatial thing , and operate partial thing with the user's free will in virtual space. Then he had a suitable feeling of participation and infusion, and could result in a phenomenon of peak experience which was originally a manner situation that the psychologist A. Maslow (1908-1970) indicated in achieving a satisfactory situation of the self- actualization need. The virtual peak experience is to satisfy the need of self-realization through the network like attaining the peak experience on the ordinary life situation. The flow experience of Internet addiction which the users play in the net route and want to stop the involuntary phenomenon but cannot. There were the problematic Internet to use[4] and pathological using Internet [7] from stimulates-seeking the performance to the dependent feeling of network [13], and exploring the relation between sensation seeking and Internet addiction [19]. The flow experience was a intrinsic enjoying experience as the similar peak experience, and respected intensely and highly joyful enjoying the time of spiritual pleasure [16]. The pleasure of flow meant that was decided by intrinsic motive whichwas filled possibly in the active process with joyful stimulus and a bad miss. When the master of computer game created good results in game process, his consciousness and cognitive condition had some special states of subjective self-transcendence, dedicating focal investment of narrow point [17]. The motive of behavior urged users to use search engine to pick up the information for understanding the truth [12].In other words the on-line users always enjoyed unconsciously and were addicted to the Internet.
Flow theory was used in the network research in recent years, and confirmed that the using network behavior had a flow phenomenon. The translated name of “flow” is diverse, such as smooth experience, fascinating and charming[21], current immersing in network [10], the interactive satisfaction of network game, and turning one's thought toward a loved thing. No matter what the translated name was, “flow” demonstrated the positive peak experience of on-line motive and the negative galloping phenomenon.
2.2 Suppositions of mystery-seeking theory
By inquiring the related literature, we may induce several suppositions as follows:A. When using network, the external controller of motive self-attribution is more favorable in seeking compensation and producing flow experience in the network situation than the internal controller.
The internal controller handles everything himself and attributes his success to endeavor and on the other hand failure to negligence. The external controller accepts failure fate with resignation; he can‟t handle everything and attribute his success to luck or an opportunity and failure to the evil environment. The network users depend on the strength of intrinsic drives order instead of external factors, and want to do whatever they like, thus resulting in flow experience [5]. They are involuntary
to the network situation and immersing
unconsciously to network for compensating unsatisfactory need in the realistic environment.
B. In the network situation, the more one seeks compensation, the more one enables to obtain the flow experience and peak phenomenon.
The flow experience of network and reading experience are the same feeling. When the users immerse completely themselves in network, they lose self-awareness. They usually pay attention to the self- image in daily life, but in the immersing situation they evacuate temporarily with the self-defense [2]. They can‟t obtain satisfaction of psychological need in the real life situation, and often transform need into the network virtual situation to compensate for satisfaction.
C. In the process of network search, the self-efficacy affects the flow experience.
Immersing in the network, one accepts the skill and challenge to face the higher and more complex level. One attains a self-harmony by flow experience, and infuses consciousness into action. The master of network indulges himself heartily in an activity, and usually achieves a impossible duty which he never realized the challenge for surpassing process of former activity, and the feelings let him even more affirm his self-efficacy and urge him to verify diligently the new skill [6]. One could continue diligently to obtain this flow feeling [5]. Immersed in the browsing condition of network, the users interact with machines to enjoy continuously and lose self-determination, and strengthen actually self-efficacy[15].
D. The better one has strong sensation-seeking, the better one obtains the peak phenomenon.
When people carry on the activity, they feel completely investing their attention into the situation, filter out all unrelated perception, and they enter into the flow condition. Flow is a temporary and subjective experience, and the reason indicates that one wants to engage continually in some kind of activity[20].
When one is absorbed completely in network game it means that he has a whole concentration and enjoyment. The effect of flow experience lets the user more intensify the process than the result and time factors [9]. Flow is a kind of subjective experience of man-machine interaction, and the special characteristic of game and exploration. In the period of man-machine interaction, Internet users could sense the subjective joy and infusion. Their special characteristic of playing a game may result in
positive mood, satisfaction and further
exploration[20], obtaining the peak phenomenon.
2.3 Research model and hypotheses
Based on the development of basic motive theories mentioned above, we offer the following model as shown in Figure 1.
MSMT
Figure 1 Research model
According to this research model, we offer the hypotheses concerning the mystery-seeking person in the network behavior.
H1: There is a positive relationship among locus of control and flow experience, Internet addiction and peak phenomena. locus of control sensation-seeking flow experience Internet addiction peak phenomenon
H2: There is a positive relationship among sensation-seeking and flow experience, Internet addiction and peak phenomenon.
H3: There is a positive relationship between flow experience and Internet addiction.
H4: There is a positive relationship between Internet addiction and peak phenomenon.
H5: There is a positive relationship between flow experience and peak phenomenon.
3 Methodology
3.1 Content analysis
The content analysis is deduced from the related articles, periodicals and network materials.. In view of on-line behavior mentioned above, we illustrate the origin, process and result of mystery-seeking motive. And efforts are made to make a bridge of connection between mystery-seeking theory and general technology education to explain the meaning and application in general technology education.
3.2 Survey
3.2.1 Instrument
As to the measuring tool, the authors had woven a "Network Technology and Health Caring Questionnaire (NTHCQ)" covering 34 items. This questionnaire was derived from five scales for reference and revision: (1) Rotter‟s internal and external control scale[18]; (2) Zukerman‟s Sensation Seeking Scale;(3) Students Using Network Technology Questionnaire [3]; Using Network Behavior Scale [8]; and Peak Experience Rating of Self-realization[3]. Participants respond to these items on a four-point or two-point Likert-type scale ranging from Strongly Disagree to Strongly Agree. NTHCQ covers five subscales of Internet addiction (items4-12), flow experience (items 13-20), locus of control (items 21-25), sensation-seeking (items 26- 29), and peak phenomenon (items31-34).
3.2.2
ParticipantsParticipants came mainly from four universities in Taiwan : Fooyin University, National Kaohsuing Normal University, Mindao Institute of Management, and Lingtong University. The principle of sampling depended on teaching convenience and simple random rule. The total of sampling subjects was 574.
4 Results
According to 574 subjects responding to items in NTHCQ, factor analysis and research hypotheses were examined in order.
The results with Cronbach‟s α coefficient of Internet addiction(items 4-12), flow experience (items 13-20), locus of internal or external control (items 21-25), sensation-seeking (items 26- 29),and peak phenomenon (items31-34) covering five subscales were 0.52, 0.81, 0.49, 0.41 and 0.67, respectively. Subscales carry on the validity test of construction by a main axle fact or analysis, and the result could explain the total variation weighs.
The hypotheses are examined and analyzed, and tables are listed as follows:
Table 1 correlations
Pearson locus seeking flow peak addict
locus -.042 .004 .118** -.072
seeking -.042 .031 -.160** .085*
flow .004 .031 .020 .393**
peak .118** -.160** .020 -.143**
addict -.072 .085* .393** -.143**
*Correlation is significant at the .05 level (2-tailed) **Correlation is significant at the .01 level (2-tailed)
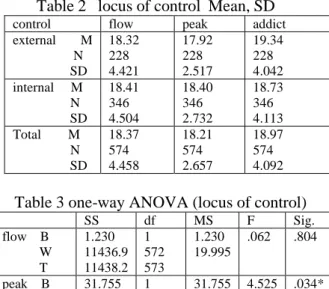
Table 2 locus of control Mean, SD
control flow peak addict
external M N SD 18.32 228 4.421 17.92 228 2.517 19.34 228 4.042 internal M N SD 18.41 346 4.504 18.40 346 2.732 18.73 346 4.113 Total M N SD 18.37 574 4.458 18.21 574 2.657 18.97 574 4.092
Table 3 one-way ANOVA (locus of control)
SS df MS F Sig. flow B W T 1.230 11436.9 11438.2 1 572 573 1.230 19.995 .062 .804 peak B W T 31.755 4013.74 4045.49 1 572 573 31.755 7.017 4.525 .034* addict B W T 50.075 9546.53 9596.61 1 572 573 50.075 16.690 3.000 .084
There is a positive relationship between locus of control and peak phenomenon(r=.118), but there is not significant difference among locus of control and flow experience(r=.004), Internet addiction(r=-.072) (see Table 1). Then by using one-way ANOVA, we can discover a significant difference between locus of control and peak phenomenon, and the internal controller is more manageable than external controller to achieve the peak phenomenon(see Table 2, 3). It is different that the user of network can immerse himself in flow experience according to the order of his intrinsic drives and non-external factor [5]. Thus, H1 is supported partially.
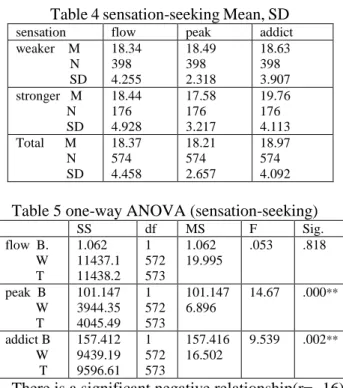
Table 4 sensation-seeking Mean, SD
sensation flow peak addict
weaker M N SD 18.34 398 4.255 18.49 398 2.318 18.63 398 3.907 stronger M N SD 18.44 176 4.928 17.58 176 3.217 19.76 176 4.113 Total M N SD 18.37 574 4.458 18.21 574 2.657 18.97 574 4.092
Table 5 one-way ANOVA (sensation-seeking)
SS df MS F Sig. flow B. W T 1.062 11437.1 11438.2 1 572 573 1.062 19.995 .053 .818 peak B W T 101.147 3944.35 4045.49 1 572 573 101.147 6.896 14.67 .000** addict B W T 157.412 9439.19 9596.61 1 572 573 157.416 16.502 9.539 .002**
There is a significant negative relationship(r=-.16) between sensation-seeking and peak phenomenon, and there is a significant positive relationship between sensation-seeking and Internet addiction, but there is not a significant difference between sensation-seeking and flow experience[14]. Then by using one-way ANOVA, we can discover a significant difference among sensation-seeking and peak phenomenon, Internet addiction, and the sensation weaker is much easier than stronger to achieve peak phenomenon; and the sensation stronger is much easier than weaker to addict to Internet(see Table 4, 5). We can infer that the participants(N=398) of sensation weaker in network are more than sensation stronger(N=176) (Table 4 ).The inequality between sensation weaker and stronger brings forth errors. So the sensation weaker who converges the stimulate-seeking is much easier than stronger to achieve peak phenomenon, and the sensation stronger who has a tendency of Internet addiction is much easier than weaker to addict to Internet. Thus H2 is supported partially.
The flow experience is a kind of the subjective man-machine experience of interaction. In the man-machine interactive period, one has the special characteristic of exploring a game and may result in the positive mood and satisfaction with subjective and joyful sensation, and initiate a plan to inquire further into the game [20].
From Table 1, there is a significant positive correlation(r=.393) between flow experience and Internet addiction, and H3 is really supported. It demonstrated that the deeper flow experience the more obvious Internet addiction.
From Table 1, there is a significant negative correlation(r=-.143) between Internet addiction and peak phenomena, and H4 is not supported. It demonstrated that the more tendency of Internet addiction the easier not to achieve the peak phenomenon. Students addicted to Internet or net coffee forgot to return home, affecting their quality of life, the health in mind and body, and never achieve to peak phenomenon.
From Table 1, there is no significant correlation (r=.020) between flow experience and peak phenomena, and H5 is really not supported. It demonstrated that the flow experience is unequal to the peak phenomenon.
5 Conclusions and Suggestions
We inquired into the network motive hidden behind the behavior to construct the mystery-seeking motive theory(MSMT) through the related literature analysis and survey method concerning the start, process and result stage of mystery-seeking to achieve the research goal. In order to confirm MSMT, we developed NTHCQ with 34 items, and assessed the mystery-seeking motive of Internet behavior.
Through the data analysis of 574 participants by SPSS 14.0 software for Window, it was indicated that the hypotheses 1, 2 were supported partially, hypotheses 3 was supported wholly, and hypothesis 4, 5 were not supported. There was a positive relationship between locus of control and peak phenomenon, but there was not positive relationship among locus of control and flow experience, Internet addiction. There was a negative relationship between sensation-seeking and peak phenomenon, and there
was a positive relationship between
sensation-seeking and Internet addiction, but there was not a significant difference between sensation-seeking and flow experience. And there was a positive relationship between flow experience and Internet addiction, and a significant negative correlation between Internet addiction and peak phenomenon, and there was no significant correlation between flow experience and peak phenomenon.
According to our further investigation, the MSMT could apply on general technology education, and design a program of general curriculum and teaching on technology education for college students.
The implication of this study on general education is to inquire about the truth of on-line behavior, and to establish a macroscopic field of teaching and learning vision. The general education originated from the western liberal education, and it cultivated
the general talented persons, regardless of the geometry, astronomy, music, language and so on, they need to understand thoroughly. It was a cognitive problem concerning the changing from the ancient to modern and the relation between heaven and earth, and had the basic technological literacy, and it was relative to professional education. The professional education emphasized the importance of expert training, and the general education focused a vast learning on self-control. The professional education moved towards to specialization and diversification, and the general education enabled the students to integrate view of technical real things and perform the series of reorganization to achieve the harmony between nature and humanity. In other words, the general education enabled the learners to obtain the macroscopic field of vision, the open mind, the basic literacy of widely experience through the teaching process. Therefore, the general technology education let the student cognitively accept not only the professional education, but also understand the manner of basic literacy, longing for the perfect personality and healthy spirituality in order to promote the technological blessing and life meaning. The focus of constructing MSMT is to apply this mystery-seeking motivation to general technology education. The objectives of general technology education cover three domains: cognitive thinking, affection, and psychomotor. Students should inspire their rational thought and moral judgment, and when they faced moral questions, they could make the keen judgment and correct choice. Then they could enhance their life quality, integrating the life meaning with the value viewpoint. They could understand sincerely the relation between modern civilization and individual duty, and receive continually the wisdom to find the mission of future. The general technology education would guide the students to display their ability and expression, communication, synthesis, analysis, understanding, and critique. The teachers of general technology education should plan appropriately a course according to their academic specialty to let the students obtain the core specialized domain of language ability, creative thinking, future career planning, and could be good at expressing their creative and critical thinking ability.
The suggestions of this article are to establish a rigorous questionnaire or scale with high reliability and validity to examine the truth of students‟ on-line behavior; to define explicitly the special nouns, such as flow experience, peak phenomenon, Internet addiction, etc.; to apply SMST to promote effectively the Internet behavior on technological literacy and to develop a macroscopic field of vision; and to
research into the application of SMST in technical education with quantitative and qualitative methods.
References:
[1] Chang, Chun-hsing (1991). Modern psychology,. Taipei: East-Chinese publishing Company. [2]Chen, H., Wigand, R., and Nilan, M. (1999),
Exploring Web Users' Optimal Flow Experiences,
Computers in Human Behavior, 15 (5), 585-608
[3]Cheng Chin-mou (2003). Indicators of network addiction and the model of Internet counseling in college students. Research article of FooYin Uui. [4]Caplan, S. E. (2002) Problematic Internet use and
psychosocial well-being: development of a theory- based cognitive-behavioral measure instrument.
Computers in Human Behavior, 18, 553-575.
[5]Csikszentmihalyi, M. & Csikszentmihalyi, I. (1988).Optimal experience Psychological studies
of flow consciousness.N.Y:Cambridge Uni.Press.
[6]Csikszentmihalyi, M. & LeFevre, J.(1989). Optimal experience in work and Leisure. Journal
of Personality and Social Psychology, 56(5),
815-822.
[7]Davis, R. A. (2001) A cognitive-behavioral model of pathological Internal use. Computer in Human
Behavior, Vol.17. Issue 2.
[8]Fang, T.W. (2002). Emotional regulation, identity, and interpersonal relationship of Internet addiction tendency. Poster presented at the 110th APA Annual Convention, Chicago IL.USA.
[9]Ghani, A. J. & Deshpande, P. S. (1994) .Task characteristics and the experience of optimal flow in human-computer interaction. The Journal of
Psychology, 128(4), 381-391.
[10]Greenfield, D. N. (1999) .The nature of internet
addiction: Psychological factors in compulsive internet use. Paper presented at the 1999 meetings
of the American Psychological Association, Boston, Massachusetts, August, 20, 1999.
[11]Kuo, Feng-Yang (2004). An investigation of effort–accuracy trade-off and the impact of self-efficacy on Web searching behaviors,
Decision Support Systems, 37, Issue: 3, 331-342.
[12]Liaw, Shu-Sheng; Huang, Hsiu-Mei (2003) An investigation of user attitudes toward search engines as an information retrieval tool,
Computers in Human Behavior, 19, 6, 751-765.
[13]Lin, S. J., & Tsai, C. C. (2002). Sensation seeking and Internet addiction. Computers in
Human Behavior, 18, 411-426.
[14]Lavin,M.(1999) Sensation seeking and collegiate vulnerability to Internet school adolescents.
Computers in Human Behavior, 18, 411-426
[15]Novak, T. P., Hoffman, D. L. (2005) Thinking Style, Task Congruence, and Performance: New
Measures of Task-Specific Experiential and Rational Cognition. Internet Retailing. Vanderbilt. [16]Privette, Gayle (1983). Peak experience, peak
performance, and flow: A comparative analysis of positive human experience. Journal of Personality
and Social Psychology, 45, 1361-1368.
[17]Privette, Gayle, & Bundrick, Charles M. (1991). Peak experience, peak performance, and flow: Correspondence of personal descriptions and theoretical constructs. Journal of Social Behavior
and Personality, 6, 169-188
[18]Rotter, J. B. (1990). Internal versus external control of reinforcement: a case history of a variable.American Psychologist, 45, 489–493. [19]Tsai, Chin-Chung & Lin, Sunny (2001). Analysis
of attitude toward computer networks and internet
addiction of Taiwanese adolescents.
Cyberpsychology & Behavior. Vol 4(3) ,373-376.
[20]Webster,J.,Trevino, K. L. & Ryan, L.(1993).The dimensionality and correlates of flow in human-computer interactions. Computers in
Human Behavior, 9(4), 411-426.
[21]Young, K. S. (1999). Cyber disorders: The mental health concern for the new millennium.
Cyberpsychology & Behavior. Vol 2(5), 475-479.
[22]Zucherman, M., (1979) Sansation-seeking:
Beyond the optimal level of arousal. Hillsadle,