Department of Business Administration
I-Shou University
Master Thesis
Examining the Factors Affecting the Quality of
Human Resource Training: A Study on Xuan Thanh
Insurance Company in Vietnam
Advisor:
Dr.Wan-ching Chang
Co-Advisor:
Dr.Nguyen Dang Huy
Graduate Student: Dinh Duc Dat
Acknowledgements
First, I would like to express my gratitude to Dr. Wan-Ching Chang and Dr. Nguyen Dang Huy, my advisors for giving me the valuable knowledge backgrounds, feedbacks and comments before and during the time of writing this Thesis.
I also would like to thank my family for their care and kindness that go beyond the Thesis as always. Thanks my colleagues in Xuan Thanh insurance corporation and partners for giving me good conditions, supports and comments for the thesis comple-tion that would be a wonderful experience of my life. All of the mistakes in this thesis are solely my responsibility.
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to examine the factors that affect the quality of HMR training. Factor analysis (EFA) was conducted to check the validity of the struc-ture. The result indicates that training program and trainer did not have effect on the quality of HMR training. Four of five factors are predicted factors of HMR training quality, they are needs and objective of training, type of training, method of training and Assessing. Based on the findings, the recommendations were provided for XTIC and insurance industry, limitations of this study and suggested future research were also discussed.
Keywords: Human resource management, Human resource training, Insurance
Table of content
Acknowledgements ... i Abstract ... ii List of Tables ... v List of Figures ... vi Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION ... 1 1.1 Background ... 11.2 Overview of Vietnam Human resource and Xuan Thanh Insurance corporation . 1 1.2.1 Overview of Vietnam Human resource ... 1
1.2.2 Introduction of Xuan Thanh Insurance corporation (XTIC) ... 4
1.2.3 Operating results of the XTIC in the period 2010-2012 ... 4
1.3 Objectives of study ... 5
1.4 Research questions ... 5
1.5 Thesis contributions ... 6
Chapter 2 LITERATURE REVIEW ... 7
2.1 Introduction ... 7
2.2 The concept of human resources ... 9
2.2.1. The concept of human resources training ... 10
2.2.2 The need to complete the training of human resources ... 10
2.3. The methods of training of human resources ... 11
2.4 The factor of human resources training ... 14
2.4.1 Identify training needs ... 14
2.4.2 Define training objectives ... 15
2.4.3 Develop programs and selected training methods... 15
2.4.4 Estimated cost of training ... 17
2.4.5 Selection and training of instructors... 17
2.4.6 Program evaluation and training results ... 18
Chapter 3 METHODOLOGY ... 19
3.1 Introduction ... 19
3.2 Population and sample ... 19
3.3 The variables in this study ... 20
3.4 Research model and hypothesis ... 21
Chapter 4 RESULTS ... 23
4.1 Analysis of demographic ... 23
4.2 Factor and reliability analysis ... 24
4.3 Hypothesis testing ... 28 4.3.1 Hypothesis 1 ... 28 4.3.2 Hypothesis 2 ... 29 4.3.3 Hypothesis 3 ... 30 4.3.4 Hypothesis 4 ... 31 4.3.5 Hypothesis 5 ... 32 4.4. Discussion ... 33
Chapter 5 CONCLUSION AND ... 36
RECOMMENDATION ... 36
5.1 Summary ... 36
5.2 Recommendation for Xuan Thanh Insurance Corporation ... 36
5.3 Recommendation improve the quality of human resources in insurance industry 39 5.4 Research limitation and future works ... 40
References ... 41
Appendix ... 43
List of Tables
Table 4.1. Sample demographic description ... 23
Table 4.2 Factor analysis of independent variables ... 25
Table 4.3 Factor analysis of dependent variable ... 27
Table 4.4 The correlation coefficients of the variables ... 28
Table 4.5 The relationship of Needs and objectives of training and Quality of HMR training ... 29
Table 4.6 The relationship of Type of training and Quality of HMR training .... 30
Table 4.7 The relationship of Method of training and Quality of HMR training 31 Table 4.8 The relationship of Training program instructor and quality of HMR training ... 32 Table 4.9 The relationship of Assessment of training and Quality of HMR training33
List of Figures
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background
People are the critical property of the manufacturing process, the level of hu-man resources development is the key of advantage competitiveness for every busi-ness. It can be said that human play the decisive role in any business field (Debrah & Ofori, 2006). Concerned with human development will contribute to ensure the coun-try's development (Dominic & Kessy, 2009). Nowadays, human development index has become an important indicator to the development of a country.
In the trend of globalization, businesses are opening up many opportunities. The development of enterprises is also promoting country economy. However, this is a challenge for enterprises, in order to survive and compete with others in the market, they must utilize their own competitive advantages. The quality of human resources is the leading edge by human is a priceless resource (Baldwin & Holton, 2003). There-fore, training of human resources is an important task for not only enterprises but also the whole country.
Training human resources requires time and cost, but performing this work will bring advantage competitive for businesses and ensure sustainable business develop-ment. In doing so, enterprises must put the role and tasks as a important issue to the staff and workers (Mathieson, 2006). Businesses want to survive, grow and compete against other businesses; It is required to have the young, dynamic, creative, solid staff. To do that, the issue of using, management, and training must be put into the main target for the business development.
1.2 Overview of Vietnam Human resource and Xuan
Thanh Insurance corporation
1.2.1 Overview of Vietnam Human resource
During the period of industrialization to modernization, human resources are the most important factors determining the economy of the country and the survival of
the enterprise. However, in Vietnam today, many businesses have not paid proper at-tention and focus on the quality of human resources in their organizations.
And focus on the quality of human resources1 (GSO) in 2011, Vietnam's popu-lation reaches almost 88 million people (an estimated 87.84 million people). With this population, Vietnam is currently ranked the 13th in the world in terms of population and the 2nd in Southeast Asia. Regarding the workforce, the country had 51.4 million people aged 15 and older labor force, accounting for 58.5% of the total population. In which the labor force of rural areas accounted for 70.3%.(GSO, 2011).
(GSO, 2011 )Vietnam is currently ranked the 13th in the world in terms of pop-ulation meet the labor needs for businesses. Because of skilled labor is still very lim-ited in Vietnam. In total 51.4 million people, nearly 7.8 million people only have been trained, accounting for 15.4 %( GSO, 2011). The difference in quality of labor re-sources is obvious especially in rural areas and urban areas. In urban areas, labor was trained workers accounted for 30.9%, while in rural areas only 9%. This difference is too big, and has effects on the overall economic development of the country. urban areas accounted for 30.9%, while in rural areas only 9%. However, many enter-prises still complained about employee shortage. The reason is that the labor in Vi-etnam only meets the demand in terms of quantity, but it does not meet the demand for quality. This not only makes it difficult situation for businesses but also makes the self-employed workers lose employment opportunities for themselves.
According to data from the HCMC Institute of Development Studies (HIDS)2 in 2014, the labor supply in Vietnam is plentiful and greater demand for labor. However, most of the supply of labor is unskilled, while skilled labors mainly stay in big cities. Thus, it leads to the uneven distribution of quality labor across regions. Specifically, nearly 77% of workers in the working age have not been trained, it is limited to occu-pational skills and labor quality in urban areas is higher than in the rural region. On the demand side, the human resources of Vietnam now largely been allocated at the
1
General Statistics Office http://knoema.com/atlas/sources/General-Statistics-Office-of-Vietnam
2
cultural sector, where workers’ do not need high level skills and qualifications. The industrial labor force accounts for 20% and the service sector accounts for only about 26%(HIDS,2014).
According to the Ministry of Labor3, at present, the quality of employment is still very low. Specifically, unskilled in menial jobs is accounting for nearly 40% of the total employment of the country. In urban areas, the ratio is 18.1%, but in rural ar-eas account for almost 50% of total employment. Meanwhile, compared with the pre-vious year, along with the development of the economy in general and businesses in particular, the demand for human resources with high quality of service and industrial sectors increased rapidly.
Currently, businesses in Vietnam, especially foreign-owned companies, are thirst for skilled workforce. Meanwhile, the percentage of high quality workers in Vi-etnam is too little, not enough to meet the needs of businesses. Therefore, the quality of human resources training becomes extremely important issue today.
Thus, it is seen that the quality of labor force is currently still very low, while the demand for skilled labor of the company is continuously increase. This leads to the irony that while there is a large number of people looking for jobs, companies are still experiencing the shortage of skill workforce. This is one of the causes leading to grow-ing unemployment in Vietnam today.
To overcome this situation, the State and the agencies gave the solution as: Ac-tively organize short-term training schools for employees to sharpen and improve practical knowledge and skills career. Also, the state frequently bring opportunities and motivate employees to learn and improve their ability for their own benefits. This is an effort to help workers find employment opportunities for themselves, and gradu-ally overcome the weakness in the quality of labor resources of Vietnam today.
3
1.2.2 Introduction of Xuan Thanh Insurance corporation (XTIC)
4Xuan Thanh Insurance Corporation (XTIC) was established on 11/07/2011 by Decision No. 57 / GPDC7 / KDBH, formerly Insurance Corporation Thai Son (GMIC), established under decision No. 57 / GP / KDBH of the Ministry of Finance dated 21/12/2009.
After a short time in operation, XTIC has gradually affirmed its position on Vi-etnam's insurance market through the deployment of business areas such as: Receive and reinsurance; Capital investment activity; The assessment services, investigations, calculations adjusters, consideration of compensation and claim a third person; Office rental; Services for sale, repair, salvage and auto parts business; Purchase, sale and maintenance of motor vehicles and motorcycles, motorbikes, spare parts for motor ve-hicles, gasoline, lubricants; - Business services, hotels, restaurants, tourism and sports; Business investment in housing development and activities related to real estate; Pur-chase and sale of goods, trade and broker dealers.
1.2.3 Operating results of the XTIC in the period 2010-2012
In 2012, total revenues of the XTIC 2.380 billion count for 94% target. In that written premiums revenue reached 1,966 billion 4.69% growth compared to 2011, reaching 92% of the plan; insurance claim ratio 47% original. Profit before tax was 130 billion, down 4% compared to 2011, reaching 92.9% of the plan. In Group 4 com-pany the market leader in non-life insurance, general insurance joint stock comcom-pany Xuan Thanh growth rate ranks 3rd (after Bao Vietnam and PVI).
Business performance in 2012 is reflected in the accounting figures (audited by Deloitte), according to which in 2012 the accounting rate of return after tax on the to-tal assets reached 4.78%, the rate tax profit on equity (ROE) reached 17.69% (com-pared with 9.84% the result of PTI, PVI 6:39%, Bao Minh 3.97%); Earnings per share (ESP) reaches 14:28%, expected dividend of 12%.
4 Xuan Thanh Insurance Corporation Introduction website:
The size of human resources of the XTIC continued to increase through the year, which increased mainly business staff and the number of agents. Specifically, in 2011, an increase of 50 people in comparison with 2010. In 2012, an increase of 70 people compared to 2011.
Among employees, the highest proportion of employees accounted for 54.7% of total number of employees of the XTIC in 2012, whiles the proportion of technical personnel accounts for 11%, and management staff is 13.5%. This shows an imbalance in the workforce of XTIC where administrative staff accounts for a high percentage of workforce while professional employees such as insurance consultants only account for a low percentage.
The company is facing an urgent need for trained and skilled employees to improve its effectiveness and competitiveness. Therefore, companies must have specific training plan to meet the need to improve the quality of human resources.
1.3 Objectives of study
This objectives of study are to:1. Clarify of concepts and views on the training of human resources of the en-terprise and;
2. Analysis of factors affecting human resource training in XTIC 3. Propose solutions to improve the human resources training in XTIC
1.4 Research questions
● Is there any relationship between needs and objectives of training and quality of HMR training?
● Is there any relationship between financial for training and quality of HMR training?
● Is there any relationship between form of training and quality of HMR training?
● Is there any relationship between method of training and quality of HMR training?
● Is there any relationship between training coach and quality of HMR training?
● Is there any relationship between assessing of training and quality of HMR training?
1.5 Thesis contributions
This thesis will provide insights of the current situation of human resources management in XTIC. Through surveys and researches, the author will evaluate the human resources management quality of the company and propose some solutions to improve the quality of the training activity so that the firm can successfully operate in the era of world economy integration.
1.6 Thesis structure
The thesis will be divided into theoretical part, empirical part and the conclu-sion. The first chapter will be the general introduction part, provide readers some thoughts about the thesis and the motivation of this thesis study.
In the second chapter, definition of Human Resource Management will be provided, and there will be information about staff training , the meaning of staff training, what is the training process, types of training, analyze the importance and benefits of it are going to be explained.
Chapter three explains the research methodology of quantitative research, the method of data collection and the validity and reliability analysis of the re-search.
The empirical part is in chapter four, which consists of the results and data analysis, the display of data is done in forms of tables by using SPSS.
Finally, the five chapter provides a conclusion about the importance of staff training, research results and some suggestions for the improvement for the train-ing program of Xuan Thanh company.
Chapter 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Introduction
This chapter is going to provide the concept of Human Resource Management and staff training. In 2015, the human resources needed for life insurance companies is almost 350,000 people, for the non-life insurance segment is nearly 180,000 people. By 2020, the projected staffing needs will double up the number. Besides, the market needs of human resources for the operation of reinsurance and investment. The in-creasingly intensive competition within Vietnam insurance market has ring a bell to the awareness of insurance companies upon the need of a high quality workforce so that they can survive and develop ( Duong Thi Nhi, 2015 )5.
The important role of insurance has been confirmed by practical development of the economy, in which human resources are one of the dominate factors that make business success in this particular service. In Vietnam, the Insurance Business Act has many provisions consistent with international standards on content management, mon-itoring, resource management senior personnel, that have significant impact on busi-ness operations security Insurance. For the management team, executive and leader of a professional insurance business must follow the standard of insurance supervision issued by the Association of International Insurance Management (IAIS ) as well as the standards and conditions for officers and executives that are stipulated in insur-ance condition policy (ICP5) by Law on Insurinsur-ance Business in 2010 - relevance of HR (Suitability of Person).
Accordingly, the standard prescribes the authorities ask the Board members and senior management, operations chief, the key management positions, the owners meet all key criteria standards of competence, experience and suitability for the position as-sumed. Specifically, board members, senior managers are fully capable and honorable to perform their duties. Key owners must have sufficient financial capacity to fulfill its
5
Duong Thi Nhi, ( 2015) 2015 should approximate 530,000 personnel in insurance, 2015 Insurance special issue retrieved from http://tinnhanhchungkhoan.vn/bao-hiem/nam-2015-uoc-can-530000-nhan-su-bao-hiem-120371.html
role. When members on no longer meet the required standards, the authorities will have the appropriate remedial measures. The requirements for suitability and level of consideration depend on the position and their responsibilities. Insurers must report when there is a change in management positions as well as the degree of influence the suitability of these titles.
In Vietnam, corresponding to the above provisions in ICP5, the Insurance Law of Vietnam also set specific standards upon administration and workforce ability that insurance companies must meet to operate in Vietnam. Thus, we can see, the Vi-etnam's regulations on corporate governance positions in the insurance business cover almost all the content as international regulations in ICP5. However, Vietnam is still no regulations on the authorities to exchange information with other regulatory bodies in and outside the territory when necessary to inspect the standard response of the above-mentioned posts.
For a team of insurance intermediaries (including dealers and insurance bro-kers), IAIS has separate regulations in ICP18. Accordingly, the insurance intermediary activities’ is required to register with authorities and achieve professional certification as prescribed. Dealers sell more complex products will require expertise and more specialized. In addition, the insurance agent must constantly update their knowledge related to new products. The regular training for agents is also regulated, under which insurers must spend a minimum budget for training.
In Vietnam, the Insurance Law of Vietnam has many parts based on interna-tional standards of insurance activities such as administration quality, insurance stand-ards or insurance agent requirements… These regulations fully comply ICP18 issued by IAIS (2012). In particular, for insurance brokers, the provisions of Vietnam law does quite tight and specific performance standards of key personnel, deployment of the direct brokerage activities. In 2015, it is estimated that there are 530,000 people working in the insurance field in Vietnam.. Development strategy of Vietnam's insur-ance market at the period of 2011 - 2020 , it gives some forecasts about growth indica-tors of the insurance market, which is associated with human resources. By 2015, hu-man resources needed in the field of life insurance is almost 350,000 people (including
staff, staff and agency force), for non-life insurance segment is nearly 180,000 people (IAIS, 2012). By 2020, the needs of projected staffing will double up the number. Be-sides, the market also has needs for human resources in the activities of of reinsur-ance and investment. Thus, it can be said that the demand for human resources for Vi-etnam market is huge. Title standards in ViVi-etnam, as mentioned above, are defined ac-cording to international standards. However, the provisions on standards for new cur-rent key positions of quantifiable minimum number of years of experience and de-grees, professional certificates of conformity with the field expected to perform. Shortage of qualified senior personnel to undertake the key positions in Vietnam in-surer remains widespread. Therefore, the employee turnover in insurance companies, especially small and medium ones, is high as new competitors continue to participate in Vietnam insurance market and try to take high quality personnel from each other. The lack of skilled employees forces insurance companies to hire unqualified staff in order to meet the requirement of workforce number set by the law (IAIS, 2012)6
2.2 The concept of human resources
The definition of human resources refers to the common characteristics by Cole (2002). as Cole state that The number of human resources: The answer to the question is how many people are currently working in the organization and how many more will be added in the future. The growth in the number of human resources based on two elements including actual need of employees and the change in population or la-bor force due to migration. The quality of human resources include the general ele-ments of many factors like intellectual parts, qualifications, knowledge, ethics, skills, health, beauty and the capacity of employees. In the above factors, the physical and mental power is two important factors to consider for assessing the quality of human resources. Another hand, the structure of human resources is the indispensable factor when considering the assessment of human resources. Human structure present on dif-ferent aspects: Structure of the training level, ethnicity, gender, and age.
6
Insurance as Executive Committee, Board of Directors ( 2012) Strategy for development of Vietnam's insur-ance market 2011 -2020
From the above analysis, this thesis put the concept of human resources as fol-lows: Human resources is a category refers to the hidden power of the population, the ability to mobilize participation in the process of wealth creation physically and men-tally to the society in the present and in the future. Strength and ability that is ex-pressed through quantity, quality and structure of the population, especially the num-ber and quality of people eligible establishments participating in social production.
2.2.1. The concept of human resources training
Human resource training is the learning activities to help employees may per-form functions more effectively. That is the process of learning to make employees better grasp of his job, as these activities improve their learning and skills of workers to perform labor tasks more efficiently (Debrah & Ofori, 2006).
2.2.2 The need to complete the training of human resources
The overall objective of the training is to utilize current manpower and improve the efficiency of the business, by helping employees better understand the work and master his profession to adapt the work demand in the future.
As showed by Evan, Pucik, & Barsoux (2002) in the enterprise, training human resources and meaningful role given to both businesses and employees. as the business side it will improve employee productivity and business efficiency. Maintaining and improving the quality of human resources, creating a competitive advantage for busi-nesses, avoid obsolescence management. Administrators should apply management methods accordingly with changes in technology, engineering and business environ-ments. also it will solve the problems of the organization. Training human resources can help administrators solve the problems and conflicts which exist between individ-uals, departments, and managers.
For the employees, employees often face difficulty to adapt to new working en-vironment and new colleagues. Thus, job orientation program for new employees will help them quickly adapt to the new working environment business. Prepare manage-ment staff and professional employees. Training helps employees to get the skills nec-essary for promotion chances and hold manager position in the future.
It is also creating professionalism and cohesion between employees and busi-ness., help employees perform better job, especially when the employees’ performance does not meet the standard, or when employees get new jobs. Meanwhile, training will update employee skills and knowledge to employees, enable them to successfully ap-ply the changes in technology and techniques in business. Meeting the needs and aspi-rations of the employee development. Training helps improving employeefully apply the changes in tech now and proving the quality of human resources, creating a cou-ture. Training also gives employees with vision, a new way of thinking in their work, which is also the basis for promoting the creativity of employees at work.
2.3. The methods of training of human resources
Training on the job. This is a simple method of training and match different
types of labor, this method can be applied for direct labor and manufacturing with some management work. With this method the training is done by the instructor guides em-ployees on task by directing, watching apprentice then try to do the job until proficient (Gordon, 1992). The advantage of this method is that it reduces the time to train appren-tices and improve the link between employees in the organization. However, this ap-proach also has limitations. That apprentice is not systematic theory, can learn the cor-rect operation and unnecessary manipulation of their instructors, who teach without teaching skills. Also, this method does not apply for large numbers of employees.
Apprenticeship training style. With this method, employees were studying
theory in class, and then employees will be brought down to the base to work for a time under the guidance of skilled workers until the employee could do proficiency work. This method has the advantage of providing vocational trainees complete theory and practice, however, this method is time and cost-consuming for training (Mathieson, 2006).
Method mentoring and direction. This is the method to help employees learn
the necessary skills and knowledge to work by learning from mentor within the organ-ization (Harrison, 2000). This method is often used for training managerial staff. There are three common ways to perform: Mentoring by direct leaders, and Mentoring by mentor, Mentoring by experienced people. Mentoring method is done very quickly
with less time, saving training costs. Through it can study the experience of the in-structor (Mathieson, 2006). At the same time, this method has the disadvantage of only focusing on mentor. At the same time, workers may be affected by negative thoughts of the instructor.
Method rotation and transfer work. This training method trained people will
move in turn do the different jobs in the same field or different fields. With this meth-od, trained people will be able to accumulate the knowledge and different experience in the fields, so they can perform the job after the training process with higher capabil-ities (Mathieson, 2006). There are three ways of training. This method convert em-ployees to another department within the organization but remains functional and the old powers. The employee was assigned to work in the department, new areas outside their expertise.
The employee is circulated internally within their professional work. Method rotation and transfer work to help employees understand and know the different occu-pations. As a result, the experience and ability of workers will be increased substan-tially through the work rotation. However, this approach also has limitations such as workers without ability is very difficult to implement this method because of the pres-sure and demand is high, and people are trained not to study one systematic way. The advantage of this method is not require time and special equipment for training, thus saving the cost of training for business, especially for businesses that are experiencing financial difficulties. Workers quickly grasp the skills of the job and likely served business and production activities of enterprises. Bring practical workers, had recently trainees may be involved in the production, and have relationships with colleagues. However, it will not grasp the theoretical knowledge a systematic way from low to high. there may be restrictions on the qualifications of the mentor, so could lower the quality of education and the school can be affected by bad habits, no errors from the subjectivity of the mentor.
Training outside of work. With this method, the group of workers was
Organizing training class. this approach is used when employees need training
to complete a complex job. To implement this approach, enterprises should fully equipped with facilities for the training. With this training method, the course is divid-ed into two parts. First, employees will be gatherdivid-ed in a class where they learn theories necessary for their work. After completing their study at the theoretical class, employ-ees will be brought to workshop where they do practices. With this method, employemploy-ees are equipped with professional knowledge and after finishing their training, they are able to fulfill the tasks that are more challenging. The drawback of this method is that the initial outlay for open classes is very expensive, the construction of the educational complex course.
Funding employees to attend regular school,enterprises dispatching trained at-tend regular schools as vocational schools, colleges, universities ... Thus, it is clear with this approach the workers are better trained, have the association between theory and practice (Ahmad, K.Z. & Bakar, R.A., 2003). However, the limitations of this method are the high cost of funding and long studying time. Besides, this method re-quires employees to have sufficient ability to attend professional class. Therefore, this method often used to train qualified young workers.
Enterprises organized seminars for employees so that they can discuss topics under the guidance of an experienced and qualified. These seminars can be held at the enterprise or outside the enterprise. Also the seminar can be coupled with other pro-grams, thus it can provide learners with the necessary knowledge and experience to do the job (Ahmad, & Bakar, 2003). With this training method, the knowledge and skills of the employees can be updated quickly and on time, however the weakness of this method is the difficulty and the cost to hold a conference or seminar.
With the development of the existing computer, employees can update their knowledge and skills through electronic lectures on computers. This method can train many people, and can help businesses reduce training costs. However, employees must have certain knowledge of using computer in order to attend electronic class. In addi-tion, trained people can not understand the problem because there are no instructors.
This is a training method with the help of intermediaries, such as video tapes, CDs, VCDs, and especially the help of internet. With this method, people can contact with one another to discuss and exchange knowledge over a long distance without hav-ing to meet directly. This method can also allow learners to actively choose to learn with people they like to (Lindvall, M. and Rus, I., 2002). Clearly, with the devel-opment of today's information technology, especially the develdevel-opment of the Internet, the method should be adopted widely because of its convenience. However, employees must be very self-disciplined to use this method.
Training of laboratory style: Learners will be put into laboratory that simulate
the realistic experience at work. In this training method, the simulated scenarios can provide learners with experience and knowledge to handle similar situation at their workplace.
Modeling behaviors, this method is also used to assume the real-life situations, however, these plays were staged available to model the situation.
Training skills dispatch processed papers, learners will be given the papers and reports memo, reminding words of the leader and the different information so that this skill right decisions quickly.
2.4 The factor of human resources training
2.4.1 Identify training needs
The first step in the training plan is to identify the training needs. That is the de-termination of a systematic and objective about things like when, in certain parts need training, what training skills with the number of how many?
To determine training needs to conduct analyzes three main levels (Coverstone, 2003) : organizational analysis, job analysis and human analysis. These analyzes are used to draw targeted for training programs.
• For organizational analysis, the manager should find out where the training is needed and what factors affect the training. The manager should carefully con-sider the goals of organization, the result, the general trend and performance
in-dicators. The manager must also understand the limitations of the organization so that they can arrange training activity to fix these limitations.
• For job analysis, the question is about what should be taught in the curriculum so that after training, people can perform their work more effectively. The an-swer requires carefully analytical work with various methods such as interviews, questionnaires analytical work with various methods such as curriculum so that after training, people can perform their work more effectively.
• For human analysis, the question is to identify who need training for their work. Thus, the manager should compare the results of individuals, groups, or units based on job requirements. Many businesses also apply the self-assessment sys-tem to address employees who need training for their jobs.
2.4.2 Define training objectives
As the determination of the results to be achieved by training programs. Includes skills need to be trained specifically through the analysis of three factors in the determi-nation of whether or not the training needs and skill levels achieved after training.
Object selection and training is the right choice people need training to suit the needs and objectives of training, because if people choose not to train properly will cause waste of time and money while low efficiency of training and even meaningless (Cole, 2002).
The basis for accurate selection of trainees include (1) Consistent with the ob-jectives and content of training courses. (2) Effects of training for workers and job per-formance. (3) The level and learning ability of employees. (4) The demand for training and motivation of workers.
When conducting the selection should consider personnel file, evaluations con-ducted evaluation of the direct manager, the prospects of the workers to be able to make the right decision when choosing.
2.4.3 Develop programs and selected training methods
The training program is a system of courses and lessons are taught, shows the knowledge and skills that should be taught and how long training period.
Organizations should consider the selection of training programs internally or externally. The training program will be more expensive outside the internal training program.
For the enterprises themselves provide training programs require institutions to invest more time and effort (Baldwin, & Holton, 2003). When construction is notewor-thy to consider the following issues: The premise when designing a training program to note the best learning methods for inclusion in the training plan. Because learning objects are those who have been working, not continuous learning should study care-fully the characteristics of learners to offer training programs most effectively (Ki-nicki, & Kreitner, 2007) .
On the other hand, it should determine whether the training can train or not, whether they are capable of learning and motor learning. May do so by providing the audience a quiz results or simulation work and see the ability to research documents and perform skills like (Kinicki, A. & Kreitner, R. 2007) .. This work is increasingly interested businesses before construction of a training program. To assess motor learn-ing object should see the level of concentration on the job and career plan. After ensur-ing satisfy the premise of the study is to create a trainensur-ing environment to ensure the following: These people are trained to learn each part separately from the simple to the complex travel magazine, remove the contents of the training in sections until done competently. Environment finest training must have good lighting, adequate facilities to cater to the learning process ...The training program also includes the development of training materials. Contents of the document should have the effect of encouraging learning and remembering information. Such documents should give the example il-lustrated and accordingly, in addition to stating the objectives of the document and provide a summary. Finally, it should develop specific targets, although challenging, but well-trained people can achieve a higher level of results or better the thorough training materials. Should encourage people trained up common goals, record their achievements, ensuring more applicable skills of their training.Ultimately, the choice of appropriate methods of training in these methods.
2.4.4 Estimated cost of training
The cost for the training of human resources includes direct costs and oppor-tunity costs. Which direct costs include salaries for instructors, the cost to the employ-ees, the cost of materials, books, location, cost of organizing training courses, man-agement and recovery costs other service. Also opportunity costs include: The cost of not performing the work in study time, because the product costs down during practice (Guest, D. E. 1997). Training costs decide the selection of the training plan and have a huge impact on the effectiveness of the training of human resources. Therefore, train-ing costs have been carefully calculated to match the traintrain-ing objectives and financial viability of the business, proportionality between the cost of money and the results ob-tained. Simultaneously manage and timely adjust cost using training to ensure no waste and high efficiency (Gary, Dessler. 2007).
2.4.5 Selection and training of instructors
The quality of the teaching staff have a huge impact on the quality of the train-ing (Kraak, A. 2005). Based on the objectives, contents and methods of traintrain-ing and trainees can choose instructors who are officials in the enterprise concurrently payroll or outsource instructor is a lecturer of universities, colleges, centers. For the instructor is part-time officers shall have the advantage of knowledge of the actual work, the use they will cost more. However, the drawback is that they limit in updating knowledge, ability to impart knowledge is not high, interrupted the work of instructors (Kinicki & Kreitner, 2007).
For instructors hired from outside, has the advantage of their knowledge sys-tematically, always updated with new knowledge and teaching skills. But restrictions are costly, possibility knowledge of their actual work limitations than skilled workers.
Kraak (2005) suggested each instructor source has advantages and disadvantages, so that instructors can incorporate those outsourced and part-time staff to achieve the best results. After selecting the instructors should conduct training, provide them with information about the target audience and the content of training, as well as the training needed to enable them to develop the highest efficiency in the work teaching.
2.4.6 Program evaluation and training results
After the implementation of the training program should have the evaluation to draw the face done, not done, have the experience to training increasingly better im-proved.
Training programs are evaluated by criteria such as: Target training programs have done it? Strengths and weaknesses, economic efficiency by comparing the costs with the benefits that the program offers (Kraak, 2005).
Using the survey method using questionnaires, interview sample, observations or ask people to be trained to do the test ... to assess the results of the training program. The results as: Results awareness, learner satisfaction with the program, the ability to manipulate reality, the behavior change in a positive direction.
Chapter 3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Introduction
In this chapter, research methods will be introduced, the research methods of this thesis will be discussed, how the data is collected, the contents of the research will also be provided in this chapter. In the final part there will be a validity and reli-ability analysis.
There are two kinds of research methods, qualitative research and quanti-tative research. In the empirical part of this thesis, the quantiquanti-tative research methods is applied.
“Quantitative research methods is researcher to familiarize him/herself with the problem or concept to be studied, and perhaps generate hypotheses to be tested.” (Golafshani 2003, p.597). Quantitative research seeks to quantify the collected data for analyzing, and find a final course of the action. It is based on statistics, the ob-jects are large number of respondents and it is structured. In this thesis, quantita-tive method is used to gather the information from the employees of XTIC about their attitudes towards the staff training. By using quantitative research method, it is easy to have a clear and scientific view on the opinions by answering the questionnaires and analyzing with SPSS.
3.2 Population and sample
In this study, the author used non- probability sampling to do research. Snow-ball sampling is a method "is used to find objects with a specific scope are determined to be useful" (David, 2008, p. 816).
This sample is considered to be favorable and reasonable, because the answer would be easy to receive and answer the questions that do not take much time and cost. Questions will be distributed to XTIC employees; the aim of this study is to col-lect 200 respondents from different units of XTIC.
The sample size depends on research issues. A general rule is that the larger the sample size is, the more accurate the result is. However, due to financial and time limi-tation, the author will choose the sample size that satisfy the minimum standard.
3.3 The variables in this study
Based on previous study (Kinicki, & Kreitner, 2007; Kraak, 2005;Gary & Dessler, 2007); Cole, 2002), this study give out the variables and items for human re-source training as following:
Needs and objectives of training: Before training, company has the meeting to emphasis on training field. Work analytical to answer the question what should be taught in the training program. Workforce analysis is to identify who need training in business and should have a specific training. Determine the amount of training and re-structuring of learners and determine the result to be achieved by training programs
Types of training include send staff attend regular schools, training on the job with the help of supervisor and organize short time class inside company. Methods of training include case study method, lecture combined group discussions and methods of business games and plays.Training program instructor includes the training program is logical and scientific, documentation is rich, useful, and practical with actual work, instructors have high-level theoretical and practical.
Assessment of training have some items such as: training program is consistent with the objective of training, Awareness and skills of employees work improved and effective in their work and Employees feel satisfied for training programs. Quality of HMR training this factor includes quality human resources increases, labor productivi-ty is increased and company revenue and profit is raised.
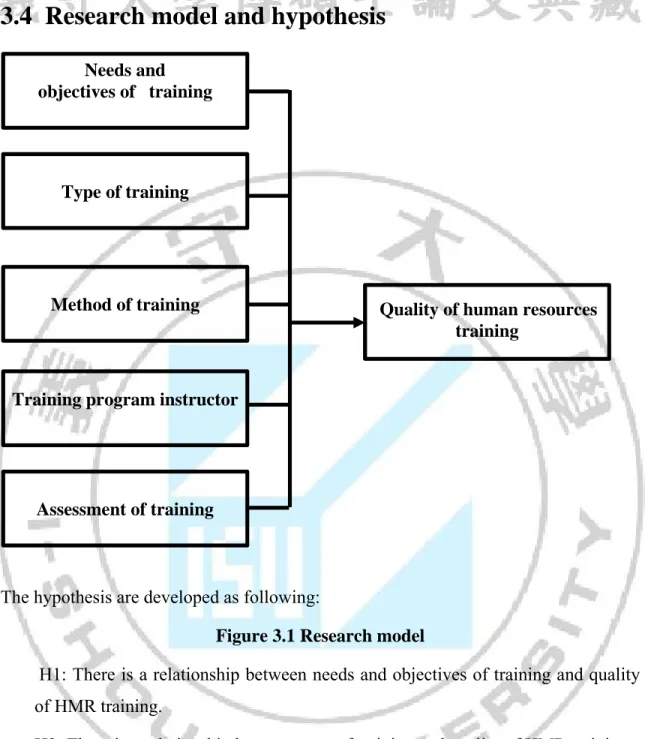
3.4 Research model and hypothesis
The hypothesis are developed as following:
Figure 3.1 Research model
H1: There is a relationship between needs and objectives of training and quality of HMR training.
H2: There is a relationship between type of training and quality of HMR training. H3: There is a relationship between method of training and quality of HMR training. H4: There is a relationship between training program instructor and quality of HMR training.
H5: There is a relationship between assessment of training and quality of HMR training? Assessment of training Type of training Method of training
Training program instructor
Quality of human resources training
Needs and objectives of training
3.5 Analysis
The study was conducted through two steps: (1) Step 1: Qualitative research by building systems development concepts / scale and the observed variables and variable calibration observations fit with reality. (2) Step 2: Quantitative Research: Using Cronbach Alpha coefficients for reliability testing closely extent that the items in ques-tion interrelated scales; Explore factor analysis (EFA) was used to test the influence factors and identify the factors considered appropriate; then using linear regression analysis to identify factors and the impact of each factor on the quality of training.
Regression model as: (Y)=f (X1,X2,X3,X4)
Chapter 4 RESULTS
4.1 Analysis of demographic
In this study, the questionnaire consists of two parts. In the first part, questions include factors affecting the training quality. The second part including personal in-formation, such as gender, age, work position and work experience. The survey was conducted in XTIC insurance company. The collected data were analyzed using SPSS software.
Total 200 questionnaires were sent to employees of public administration. After the removal of the invalid questionnaires, the remaining 170 questionnaires were in-cluded in the analysis; the valid ratio was 85%.
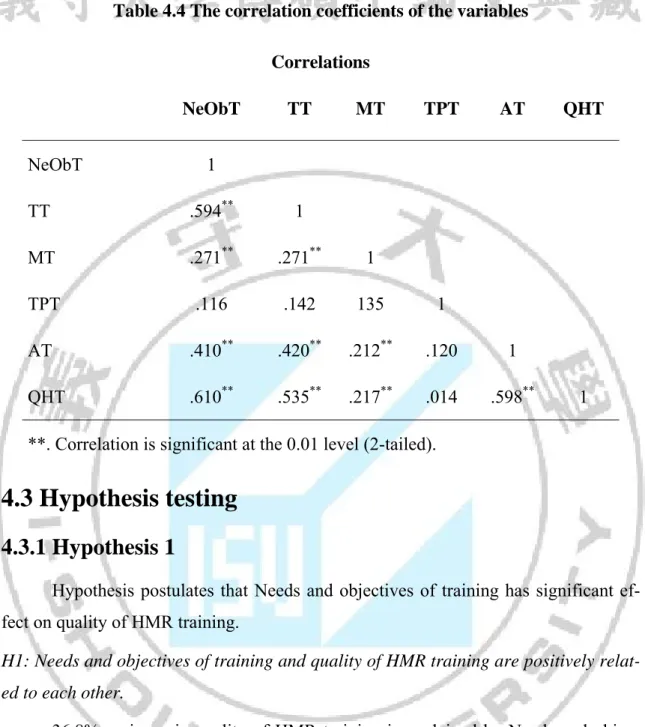
Table 4.1. Sample demographic description
Characteristic Frequency Percentage
Gender Male 89 52.4 Female 81 47.6 Total 170 100.0 Age 20 - 29 71 41.8 30 8 29a 75 44.1 Over 40 24 14.1 Total 170 100.0 Position Staff 149 87.6 Leader 21 12.4 Total 170 100.0 Experience 1 to 5 years 51 30.0
6 to 10 years 76 44.7
Over 10 years 43 25.3
Total 170 100.0
Education
High school degree 14 8.2
College degree 42 24.7
Bachelor degree 67 39.4
Master degree or higher 47 27.6
Total 170 100.0
From Table 4.1, the results showed that 89 employee are male, accounting for 52.4%, and 47.6% are female employees. Regarding to the age, 20 to 29 age group ac-counts for 41.8%. Aged 30-40 was 41.4% . Over 40 years old accounted for 14.1%.
From the results, the number of respondent was staff accounted for 87.6%, while the number of respondents currently hold leadership positions accounted for 12.4%. Regarding to work experience, the employee have 1 to 5 years experience ac-counted for 30%, from 6 to 10 years experience acac-counted for 44.7%, and over 10 years experience accounted for 25.3%.
From the aspect of education, table 4.1 shows that most of respondent have the bachelor degree: 39.5% and Master degree or higher: 27.6, while respondent who got college degree is 24.7% and the high school degree just account for 8.2%.
4.2 Factor and reliability analysis
In this study, principle component method is used for explorative factor analy-sis. Three main factors with 21 items are loaded into the system. The 17 independent items were factor analyzed. After and the result indicates that the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin value was .816 (KMO>.7), and the Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity was statistically
signif-icant at .000 level. The factor eigenvalues greater than or equal to 1.0 and variables with factor loadings greater than .5 were reported. No items of the loading factor are less than 0.5. The result of factor analysis revealed 5 dimensions, which accounted for 76.582% of the total variance. The factors were labeled as “Needs and objectives of training” (34.458%), “Type of training” (13.490%), “Method of training” (11.858%), “Training program instructor” (9.194) and “Assessment” (7.132). To test the reliabil-ity and internal consistency of each factor, the Cronbach’s alpha of each was mined. The results showed that the alpha coefficients is .898 for of each was deter-mined 76.582% of the total variance. The factors were labeled as “Needs and objec-tives of training” (34.458%), “Type of training” and 816 for “Assessing” . (Table 4.2).
Table 4.2 Factor analysis of independent variables Rotated Component Matrixa
Component 1 2 3 4 5 NOT3 .853 NOT2 .836 NOT1 .817 NOT4 .749 NOT5 .721 MT3 .882 MT2 .875 MT1 .856 TT3 .823 TT2 .822
TT1 .789 TPT2 .902 TPT3 .894 TPT1 .830 AT3 .844 AT1 .809 AT2 .796 Eigen-value 5.858 2.370 2.016 1.563 1.212 VE (%) 34.458 13.940 11.858 9.194 7.132 Cronbach uemp .898 .875 .865 .830 .816
Total variance explained=76.582; , KMO= .816, p = .000
Regarding the Quality of HMR training variable, three dependent items were factor analyzed. The result indicates that the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin value was .698 and the Bartletting” (34.458%), “Type of statistically significant at .000 level. The factor eigenvalues greater than or equal to 1.0 and variables with factor loadings greater than .5 were reported. No items of the loading factor are less than 0.5. The result of factor analysis revealed accounted for 68.004% of the total variance. The results showed that the alpha coefficients of Quality of HMR training factor is .757
Table 4.3 Factor analysis of dependent variable Component Matrixa
Component
1 Eigenvalue VE (%) Cronbach’s Alpha
QHT2 .827 2.040 68.004 .757
QHT3 .825
QHT1 .822
Total variance explained=68.004; , KMO= .698, p = .000
The result of the factor analysis is shown in Table 4.2 and table 4.3. From the result the Cronbach’s Alpha coefficients ranged from .898 to .757. No items of the loading factor are less than 0, it demonstrates that all factors were accepted and relia-ble as recommended by Nunnally (1978).
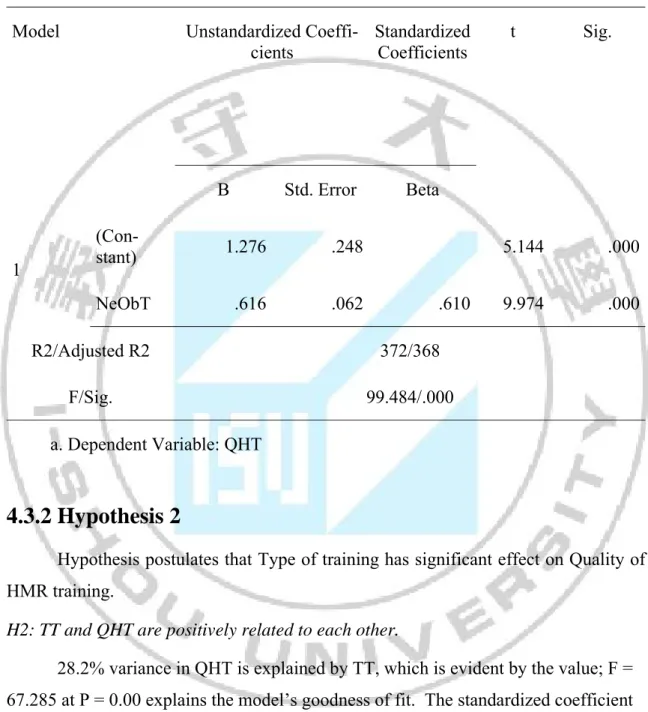
Also in the Table 4.4, it is obvious that the correlation coefficients of the varia-bles all fall within the .2 to .6 range, which demonstrates that the degree of multicol-linearity existing in the variables is acceptable and will not affect the following regres-sion analysis.
Table 4.4 The correlation coefficients of the variables Correlations NeObT TT MT TPT AT QHT NeObT 1 TT .594** 1 MT .271** .271** 1 TPT .116 .142 135 1 AT .410** .420** .212** .120 1 QHT .610** .535** .217** .014 .598** 1
**. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed).
4.3 Hypothesis testing
4.3.1 Hypothesis 1
Hypothesis postulates that Needs and objectives of training has significant ef-fect on quality of HMR training.
H1: Needs and objectives of training and quality of HMR training are positively relat-ed to each other.
36.8% variance in quality of HMR training is explained by Needs and objec-tives of training, which is evident by the value; F = 99.484 at P = 0.00 explains the model’s goodness of fit. The standardized coefficient beta (β) for organization com-mitment factor is .610 (p <0.01) is the evidence of significant positive relationship between independent and dependent variable. Therefore, on the basis of these results it can be inferred with confidence that H1 is accepted.
Table 4.5 The relationship of Needs and objectives of training and Quality of HMR training
Coefficientsa
Model Unstandardized
Coeffi-cients Standardized Coefficients t Sig. B Std. Error Beta 1 (Con-stant) 1.276 .248 5.144 .000 NeObT .616 .062 .610 9.974 .000 R2/Adjusted R2 372/368 F/Sig. 99.484/.000 a. Dependent Variable: QHT
4.3.2 Hypothesis 2
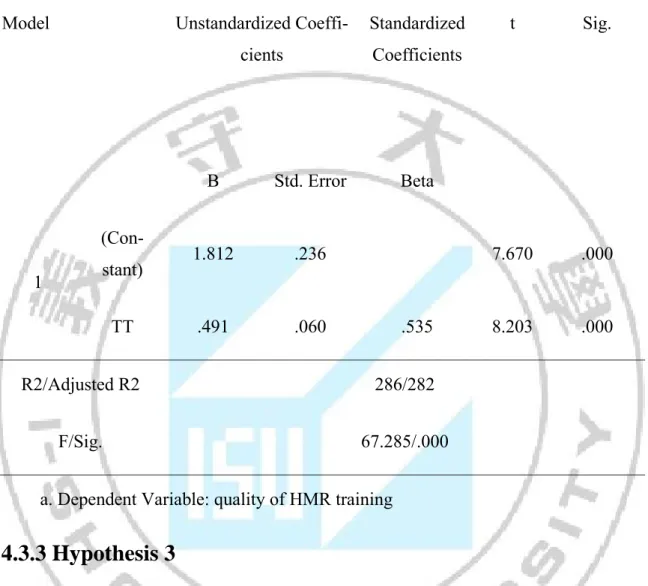
Hypothesis postulates that Type of training has significant effect on Quality of HMR training.
H2: TT and QHT are positively related to each other.
28.2% variance in QHT is explained by TT, which is evident by the value; F = 67.285 at P = 0.00 explains the model’s goodness of fit. The standardized coefficient beta (β) for organization commitment factor is .535 (p <0.01) is the evident of sig-nificant positive relationship between independent and dependent variable. There-fore, on the basis of these results it can be inferred with confidence that H2 is accepted.
Table 4.6 The relationship of Type of training and Quality of HMR training Coefficientsa
Model Unstandardized
Coeffi-cients Standardized Coefficients t Sig. B Std. Error Beta 1 (Con-stant) 1.812 .236 7.670 .000 TT .491 .060 .535 8.203 .000 R2/Adjusted R2 286/282 F/Sig. 67.285/.000
a. Dependent Variable: quality of HMR training
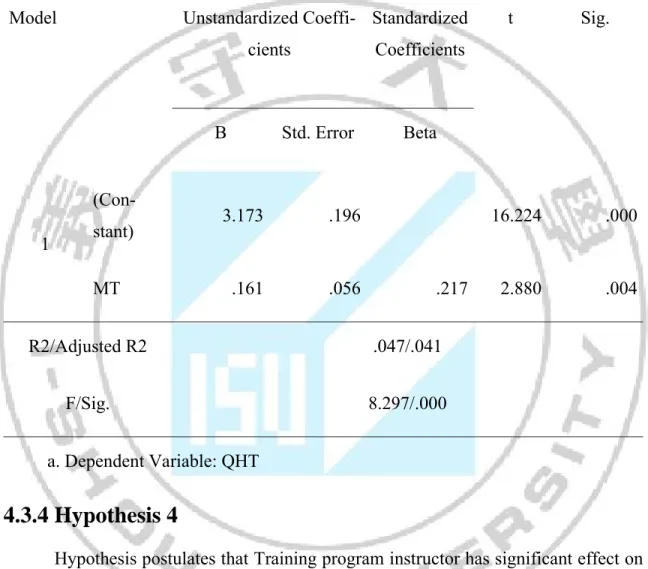
4.3.3 Hypothesis 3
Hypothesis postulates that Method of training has significant effect on Quality of HMR training
H3: Method of training and quality of HMR training are positively related to each other.
4.2% variance in Quality of HMR training is explained by type of training, which is evident by the value; F = 8.297 at P = 0.04 explains the model’s goodness of fit. The standardized coefficient beta (β) for organization commitment factor is .217 (p <0.05) is the evident of significant positive relationship between independent
and dependent variable. Therefore, on the basis of these results it can be in-ferred with confidence that H3 is accepted.
Table 4.7 The relationship of Method of training and Quality of HMR training Coefficientsa
Model Unstandardized
Coeffi-cients Standardized Coefficients t Sig. B Std. Error Beta 1 (Con-stant) 3.173 .196 16.224 .000 MT .161 .056 .217 2.880 .004 R2/Adjusted R2 .047/.041 F/Sig. 8.297/.000 a. Dependent Variable: QHT
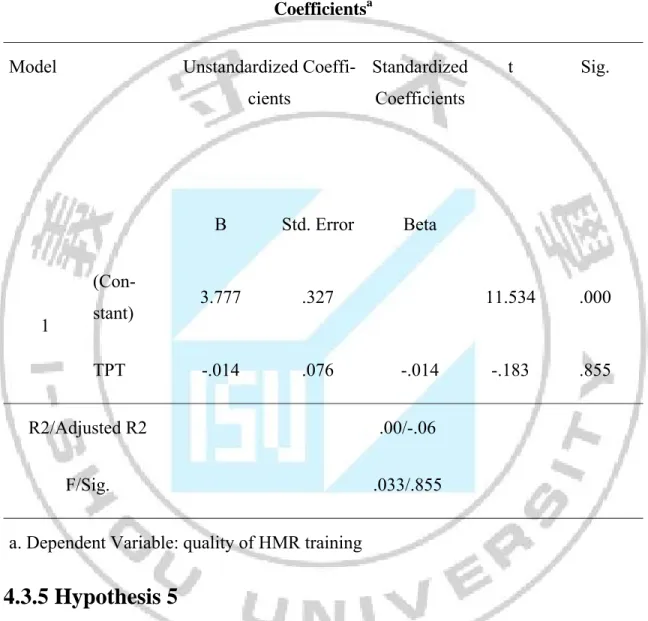
4.3.4 Hypothesis 4
Hypothesis postulates that Training program instructor has significant effect on Quality of HMR training
H4: Training program instructor and quality of HMR training are positively re-lated to each other.
The quality of HMR training is explained by Training program instructor, which is evident by the value; F = 0.033 at P = 0.855 explains the model instructor, which is fit. The standardized coefficient beta (β) for organization commitment factor is -.014 (p >0.05) is the evident of not significant positive relationship between
inde-pendent and deinde-pendent variable (negative relationship). Therefore, on the basis of these results it can be inferred with confidence that H3 is not accepted.
Table 4.8 The relationship of Training program instructor and quality of HMR training
Coefficientsa
Model Unstandardized
Coeffi-cients Standardized Coefficients t Sig. B Std. Error Beta 1 (Con-stant) 3.777 .327 11.534 .000 TPT -.014 .076 -.014 -.183 .855 R2/Adjusted R2 .00/-.06 F/Sig. .033/.855
a. Dependent Variable: quality of HMR training
4.3.5 Hypothesis 5
Hypothesis postulates that Assessment of training has significant effect on qual-ity of HMR training
H5: Assessment of training and quality of HMR training are positively related to each other.
35.4% variance in quality of HMR training is explained by Assessment of ing, which is evident by the value; F = 93.542at P = 0.00 explains the model HR
train-ing is explained by Assessment of traintrain-ing, which is evident by the value; F = eta (β) .598 (p <0.01) is the evident of significant positive relationship between inde-pendent and deinde-pendent variable. Therefore, on the basis of these results it can be inferred with confidence that H5 is accepted.
Table 4.9 The relationship of Assessment of training and Quality of HMR training Coefficientsa
Model Unstandardized
Coeffi-cients Standardized Coefficients T Sig. B Std. Error Beta 1 (Con-stant) 1.484 .234 6.330 .000 AT .581 .060 .598 9.672 .000 R2/Adjusted R2 .047/.041 F/Sig. 8.297/.000 a. Dependent Variable: QHT
4.4. Discussion
Hypothesis result show that among 5 hypotheses, there is one not accepted as proposal in chapter 2. It mean that the Training program instructor is not the predictor factor of Quality of HMR training in XTIC. Other factors, such as needs and objective of training, type of training, method of training, assessment are found as the significant effect factors on quality of HMR training.
In recent years, due to the important role of human resources to the business performance, company leaders have paid great attention on training activities and tried
to create favorable conditions for employees to improve their ability through training. Thus, the training of human resources of the company has achieved the following ac-complishments:
Training scale of annual increased over the years. On average, during the period 2010-2012, the company has trained 252 employees each year with the appropriate training content with the business areas within the company, to meet production and business plans of the companies.
The quality of human resources of company is constantly improving, the num-ber of people with university degrees and above are increasing, the numnum-ber of skilled workers growing proportion of the total workforce of the company.
Funding for training is constantly increasing, in 2012, funding for training of the company reached over 01 billion VND. Thus, the number of people trained has in-creased and workers are participating in training courses of good quality.
The training courses are not only equipped with the knowledge, new skills, im-prove and enhance the professional qualifications for workers, but also to help ployees better understand the tasks, duties and responsibilities of them, to help em-ployees feel more love your job, more confident in performing work and collaborate better with colleagues, thereby improving performance of their work.
In the last 3 years, the company has received many valuable ideas from employ-ees to improve management and operation effectiveness. Thereby, helping the company to gain substantial benefits and saving tens of billions VND. The company has built a systematic training program which is managed by an experienced council to ensure the training quality. The Company has applied the methods of training in work and training methods outside of work matching the requirements of training and trainees.
Along with these achievements, the training of human resources in companies still revealed many shortcomings: Teaching staff includes highly qualified instructor have much teaching experience are invited from well-known universities in the fields of economy, technology ... the same leadership team has qualified skilled, highly expe-rienced work undertaken but it still did not contribute to the results of the training in this study. This issue may be raise from following; Officers in charge of training for
units is usually leaders of those units at work. However, not all of these officers are well-trained and experienced in human resource training. Thus, the training activity may be conducted solely on an officer’ experience and opinion instead of more effec-tive ways. The need for training is mainly based on business plans and business objec-tives instead of the analysis of employee’s performance. Thus, the company is slow to react to the need of training from employees. Besides, the assessment system of the company is nit standardized and systematic. This reason makes it difficult for the company to address which personnel should be put in training.
The content of training program of the company is only focusing on the profes-sional knowledge while employees also need training on other aspects such as com-munication skills, negotiation skills, foreign languages or computer as well.
The quality of trainers for training program is unstable. Trainers are usually care about the quality of trainers for professional in training field. For trainers from outside, they may not understand clearly the characteristics of the company; therefore, their lectures only focus on theoretical part without practical part for employees. Thus, many em-ployees find the training unnecessary and waste of efforts.
Chapter 5 CONCLUSION AND
RECOMMENDATION
5.1 Summary
This study aims to investigate the relationship among Needs and objective of training, Type of training, Method of training, Training program and Instructor and Assessing and Quality of HMR training. Also, from the research result, some solutions to improve the quality of human resources in XTIC is provided. The result indicates that Training program instructor did not have effect on quality of HMR training. On the other hand, four of five factors are predicted factors of quality of HMR training. This result has meaning in the situation that XTIC is now focused on human resource quality as discussed in chapter 4. In this issue, training is used as a success planning technique within the organization. Gupta (2006) identified a number of reasons for training as: job requirements, technological change, organization viability, internal mobility and globalization.
5.2 Recommendation for Xuan Thanh Insurance
Corpo-ration
Xuan Thanh Insurance Corporation should have the solution in order to im-prove recruitment. Recruiting is the most important task in the implementation of re-cruitment goals. Whether or not the company can find good employees depend on the effectiveness of its recruitment. Thus, the company should put more effort on improv-ing its recruitment system. Below are some proposed ideas of the author to help the company to improve its recruitment quality.
1. Completing the training program content that matches training objects.
The training content directly influences the outcome and quality of training courses. Thus, the company should enrich its training content so that trainees can ac-quire knowledge and skills necessary for their works.
2. Diversification of types of training and training methods.
Currently, most of company are still using the traditional training methods. How-ever, with the rapidly changing business environment, it is important for companies to apply more advanced training methods. The company may consider providing electronic and online training lectures to its employees. It can also consider holding workshops and conferences to boost the exchange of knowledge within the organization.
Application of teaching methods to attract the participation of employees in lec-tures as methods discussion group: instructors make a topic related to course content and all to study and exchange of draft Comments on the issue, from which to draw useful knowledge.
Methodology Situational: Instructors make specific situations occurring in prac-tice, instructors and employees together to analyze the situation and make the way to resolve the situation. These methods help to promote the creative independence of em-ployees, help employees to actively participate in lectures, grasp quickly the training content can be applied in practice. This method is suitable for the application of train-ing for management staff and production workers. For example, traintrain-ing for managers in how to resolve a situation is an employee inquires about a colleague was promoted, but not him. As for the workers, it gives a side crash situation while operating machin-ery happened in reality and how to solve, troubleshoot.
In addition, the company may apply other training methods as provided docu-ments, videotapes for employee self-study, professional practice skills, then the organ-ization will conduct the examination. With this method will encourage self-learning workers while saving costs.
Training by means of a transfer job rotation to help the training of knowledge accumulated experience in many fields, many positions. Especially for those employ-ees to be more vocational training, so that they have the opportunity to apply the knowledge and skills learned.
The company should increase staff enabling employees to participate in long term courses such as Master’s and Doctoral studies in order to improve the qualifica-tions of workers. Increase training in the form to send people to study, exchange prac-tical experience abroad. Training in this way will help learners to acquire the
knowledge and experience of advanced enterprise management, modern and efficient. On that basis, consider applying to the actual situation of the company. For this meth-od should appoint those who are highly qualified, have extensive experience in school, then go back to teaching other employees in the company.
Improving the quality of instructors: Instructors are the direct transmission of professional expertise in the program of courses for employees, so the level and quality of instructor staff have tremendous impact on learning outcomes of trainees. Currently instructors are part-time officers of the company have not been trained in the pedagogi-cal knowledge and skills, thereby imparting knowledge still shaky, fragmented, making it difficult for the acceptance of school member. As for instructors, also outsource heavy on teaching general theory, less fit the actual situation of the company. So to improve the quality of instructors in service training of human resources, the company should:
Conduct training of knowledge, pedagogical skills for instructors as a part-time to raise the issue, how to communicate knowledge and methods of attracting employ-ees to the lecture. Before teaching, the department in charge of the training needed to conduct exchanges with trainers on training objectives, training participants, providing them with the documents on the company to better understand about their work, there-by creating conditions for them to prepare and teach better.
For instructors are invited from universities, colleges, centers .... before teach-ing need to create conditions for them to access company, learn about the characteris-tics of the manufacturing business company, contact with workers in the company, namely the future employees. On this basis so that they can compile the program con-tent, the choice of teaching methods appropriate to the actual situation of the company, in accordance with different learners to achieve the best results. In addition to signing contracts with outsourced instructors should have the provision of quality training and their responsibilities in training the company should also create conditions for part-time teaching staff of the company to visit the learning experience at home and abroad. The company should also consider inviting foreign experts to teach. In addition com-panies should have policies in order to encourage and motivate them to serve better teaching mode as wages, bonuses, allowances ...
3. Mobilization and effective use of financial resources for the training of human re-sources.
Funding for the training of human resources have a decisive role to the training plan has been implemented or not. We can have a detailed training plan, specific train-ing programs, but without fundtrain-ing it will not be done, or if there are insufficient funds for the training program will be postponed. Currently with huge training demand, the company needs to have solutions to increase funding for training:
4. Re-evaluate the effectiveness of the training of human resources.
Evaluate the effectiveness of training is a very important part of the training process in human resources. Through the evaluation results would help people organ-ize the training learned have achieved the target set or not, achieve some degree. The purpose of evaluating the effectiveness of training is not just the view of training achieved anywhere, but more importantly is to find the cause of this result so that there are solutions for improvement in the training later.
Currently working in the company to assess the effectiveness of training have not been interested, training effect has only been assessed learning outcomes of employees. Therefore not accurately reflect the effectiveness of the training of human resources.
To accurately assess the training of human resources, in addition to assessment methods through the learning outcomes of employees, companies should apply the following methods: Review via reflection of learner, Review job performance of em-ployees after training, In the long term, insurance Training Center aims to coordinate with partners are the universities and training institutions and foreign insurance to ex-tend the training program to the next level, as Long-term programs on insurance busi-ness management, accounting management and insurance ...
5.3 Recommendation improve the quality of human
re-sources in insurance industry
First, the need to expand and improve the training quality of the training base of insurance. Accordingly, the insurance training organization focused on providing training courses on insurance operations, both knowledge and practical skills. In