4G LTE在台灣成功推動的關鍵因素:研究消費者之期望 - 政大學術集成
全文
(2) 4G LTE在台灣成功推動的關鍵因素:研究消費者之期望 Critical Success Factors for 4G LTE Launching in Taiwan: A Study on Customers’ Expectations 研究生:宋天瑞. Student: Teerasit Songtis. 指導教授:朱時龍. Advisor: Andrew C. Chu. 學. ‧ 國. 立. 政 治 大 國立政治大學. ‧. 商學院國際經營管理英語碩士學位學程. er. io. A Thesis. sit. y. Nat. 碩士論文. n. a l to International MBA Program Submitted iv n U i National Chengchi e n g c hUniversity. Ch. in partial fulfillment of the Requirements for the degree of Master in Business Administration. 中華民國一○一年十二月 December 2012.
(3) Acknowledgements To my thesis advisor, Professor Andrew C. Chu, I would like to express my great gratitude for your generous advice, inspiring guideline and encouragement throughout my thesis project. To all the IMBA professors, thank you for providing me with business management knowledge and hand-on experiences. To Lichi Ho and all IMBA staffs who always assists me during my study at NCCU.. 政 治 大. To NCCU students, my friends and colleagues who completed the survey questionnaire giving me with a very meaningful input data for this thesis project.. 立. Special Thanks to Frank Lee (Nokia Siemens Networks) and. ‧ 國. 學. Jacob Huang (IMBA NCCU Class 2009) for helping me with Chinese translation for this thesis questionnaire.. ‧. To my dear classmates at IMBA NCCU,. Nat. sit. y. Thank you for unforgettable experiences during the classes and your friendships.. er. io. To my supervisors at Nokia Siemens Networks, Soo Siow Ping,. al. v i n CThank all my colleagues and customers, providing me this great opportunity to come U h e nyougfor i h c n. Tan Hansiang, Edmond Chen, Graham Xu, Jerry Song, Brian Lan, David Liao,. to Taiwan, supporting me at work and giving me a chance to study at IMBA NCCU.. Finally, I would like to express the most wholehearted gratitude to my dad, mom, sister, and my best friend, Prin Mokapun for their support and encouragement.. i.
(4) Abstract Critical Success Factors for 4G LTE Launching in Taiwan: A Study on Customers’ Expectations By Teerasit Songtis LTE- Long Term Evolution, marketed as 4G LTE, is a new generation of mobile-phone network which enable the mobile operator to provide significantly faster mobile broadband data rates. With the new redesign and simplification of the network architecture, 4G LTE can provide five time faster data rates than the current 3G networks. It will help the mobile. 政 治 大. operators to cope with ever growing mobile data traffic demands in a cost-effective manner.. 立. In Taiwan, the licenses for 4G LTE will be issued by the end of 2013, opening another. ‧ 國. 學. business opportunities for the mobile industry. It’s expected that all the big mobile operators will acquire for the licenses. Telecom equipment vendor such as Nokia Siemens Networks. ‧. and Ericsson are preparing for 4G LTE network trial and deployment as well.. y. Nat. In light of the upcoming 4G LTE deployment in Taiwan, this thesis project was conduct to. sit. gain a better understanding of the current mobile users in Taiwan. The goal is to identify and. er. io. understand customers’ attitudes, preferences, and satisfactions towards the current mobile. al. v i n C hcollected by on-line input of this thesis are survey data e n g c h i U questionnaire from the students at n. carriers as well as customers’ expectations of the next generation carrier – 4G LTE. The data. National ChengChi University, and people living in Taiwan. The sample size was 872.. The collected data was analyzed by SPSS, a computerized statistical program. The analysis report includes description of the sample, customers’ attitudes, and preferences of the current mobile carriers in general, satisfactions towards their current using carriers, expectations of 4G LTE carriers as well as their preferable carriers. The report also discusses the carrier switching pattern, and the factors influencing the switching behavior. After analyzing the findings of the study, the thesis report proposes that the mobile operators should deploy 4G LTE network coverage as soon as possible, concentrate on increasing mobile data service speed, maintain voice call service quality, offer a wide variety of handsets at some attractive prices and setting tariff rate competitively.. ii.
(5) TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.. Executive Summary ............................................................................................................ 1. 2.. Introduction ......................................................................................................................... 4. 3.. Revolution of Mobile Telecommunication ......................................................................... 5 2G – Digital Cellular Networks .................................................................................. 5. 3.2.. 3G – Mobile Broadband Data ..................................................................................... 5. 3.3.. 4G LTE – Long Term Evolution ................................................................................ 6. 4.2.. 治 政 Key Players in the Mobile Telecommunication大 Industry in Taiwan .......................... 8 立 Evolution of the Mobile Telecommunication Industry in Taiwan ............................. 8. 4.3.. Revenue Trend Analysis ........................................................................................... 10. 4.4.. Challenges in the Mobile Telecommunication Industry........................................... 11. Exploration of the Current Mobile Telecommunication Industry in Taiwan...................... 8 4.1.. 學. ‧. ‧ 國. 4.. 3.1.. Statement of the Problem .................................................................................................. 12. 6.. Methodology ..................................................................................................................... 12. sit. io. Questionnaire ............................................................................................................ 13. n. al. er. 6.1.. y. Nat. 5.. 7.. i n U. v. Survey Data Analysis ........................................................................................................ 17. Ch. engchi. 7.1.. Data Collection ......................................................................................................... 17. 7.2.. Description of the Sample ........................................................................................ 17. Demographic Information of Survey Respondents ........................................................... 17 Current Mobile Handsets .................................................................................................. 19 7.3.. Mobile Carriers in General ....................................................................................... 20. Spending on Mobile Phone Bills ....................................................................................... 20 Importance of Basic Services ............................................................................................ 22 Importance of Mobile Carrier Features and Willingness to Pay More ............................. 22 7.4.. Current Using Mobile Carriers ................................................................................. 24. iii.
(6) Current Mobile Carriers Distribution ................................................................................ 24 Years of Subscription ........................................................................................................ 25 Motivations for Choosing the Carriers .............................................................................. 26 Spending on Mobile Phone Bills ....................................................................................... 27 Internet Usages .................................................................................................................. 28 Satisfactions towards the Current Carriers ........................................................................ 28 7.5.. Future Mobile Carrier – 4G LTE .............................................................................. 30. 治 政 大 32 Importance of Mobile Carrier Features in 4G LTE........................................................... 立 Feelings about Subscribing to 4G LTE ............................................................................. 33 Evaluation of Price Acceptance and Intention to Subscribe ............................................. 30. ‧ 國. 學. Favorable Features for People Intend to Subscribe and Not Intend to Subscribe ............. 33. 7.6.. ‧. Preferable 4G LTE Carriers .............................................................................................. 34 Intension of Subscribing to 4G LTE versus Current Internet Usage ........................ 35. y. Nat. sit. Current Internet Usage ...................................................................................................... 35. n. al. er. io. Spending on Mobile-phone Bills versus Mobile Internet User Group.............................. 36. i n U. v. Intention to Subscribe for 4G LTE versus Mobile Internet User Group ........................... 37. Ch. engchi. Willingness to Pay More versus Mobile Internet User Group .......................................... 38 Prices Acceptance versus Mobile Internet User Group .................................................... 38 7.7.. Carrier Switching Analysis ....................................................................................... 40. Carrier Switching in 4G LTE ............................................................................................ 40 Satisfactions towards Current Carriers versus Carrier Switching ..................................... 41 Reasons for Subscribing to the Current Carriers versus Carrier Switching ...................... 42 8.. Conclusions ....................................................................................................................... 44 8.1.. Spending on Mobile Phone Bills: Lower than ARPU in 2011 ................................. 44. iv.
(7) 8.2.. Motivations for Choosing the Carrier: Cheaper to Call Boyfriend, Girlfriend,. Husband, Wife is the Most Appealing Feature ..................................................................... 44 8.3.. Important Carrier Features: Network Coverage, Monthly Rate Plan, Voice Call. Quality, and Internet Speed are the Most Important Features but People are just willing to Pay More for Better Coverage, and Internet Speed .............................................................. 45 8.4.. Satisfaction towards the Current Carriers: Chunghua Telecom is the Most Satisfying. Carrier 45 8.5.. Expectations towards 4G LTE Carriers: High Speed Data Rates, Mobility, and. 政 治 大. Voice Call Quality are the Most Favorite Features; Chunghua Telecom is Most Preferable Carrier 45. 立. Subscribing to 4G LTE: Wait and Listen to Other Comments, Wait for Favorite. 學. ‧ 國. 8.6.. Phones and Promotions, Subscribe after 1 Year ................................................................... 46 Carrier Switching: Many Subscribers Plan to Switch to Chunghua Telecom in 4G. LTE. 46. 8.8.. 4G LTE Price: 888 TWD Monthly Plan is Appealing to Heavy Internet Users Spend. y. sit. io. Factors Influencing Carrier Switching: Bad Network Coverage, Poor Voice Call. n. al. er. 8.9.. Nat. More 47. ‧. 8.7.. i n U. v. Quality, and Slow Data Rates Could Influence Subscribers to Switch to Other Networks . 47 8.10.. Ch. engchi. Factors Influencing Customers to Use the Same Carriers: Network Quality and. Cheap Rate to Call Family are the Most Important Factors to Retain the Subscribers in the Networks ............................................................................................................................... 48 9. 10.. Recommendations ............................................................................................................. 49 References .................................................................................................................... 50. Appendix A – SPSS Data Analysis Output .............................................................................. 51 Appendix B – Questionnaire .................................................................................................. 114. v.
(8) Table of Figures and Tables Figure 1: Current Mobile Carrier Market Share in 2011 ............................................................ 8 Figure 2: Evolution of Mobile Market in Taiwan ...................................................................... 9 Figure 3: Expansion of Mobile Internet Subscribers in Taiwan ................................................. 9 Figure 4: Mobile Data Service Revenue as Proportion of Total Mobile Revenue ................... 10 Figure 5: Average Revenue per User (ARPU) of Mobile Services .......................................... 10 Figure 6: Operator Challenges – The Widening Gap between Traffic and Revenue [7] ......... 11 Figure 7: Demographic Information of the Survey Respondents ............................................. 18 Figure 8: Profession Distributions of the Survey Respondents ................................................ 18. 政 治 大 Figure 10: Distribution of the Current Mobile Handsets Types ............................................... 19 立 Figure 9: Income Ranges of the Survey Respondents .............................................................. 19. Figure 11: Distribution of the Current Mobile Handsets Brands ............................................. 20. ‧ 國. 學. Figure 12: Total Spending on Monthly Mobile Phone Bills .................................................... 21 Figure 13: Spending on Mobile Phone Bills ............................................................................ 21. ‧. Figure 14: Importance of Basic Services .................................................................................. 22. y. Nat. Figure 15: Importance of Mobile Carrier Features ................................................................... 23. sit. Figure 16: Willingness to Pay More for Better Mobile Carrier Features ................................. 23. er. io. Figure 17: Distribution of Current Mobile Carriers of Respondents........................................ 24. al. n. v i n C h ............................................................................... Figure 19: Average Years of Subscription 26 engchi U Figure 20: Motivation for Choosing the Current Carriers ........................................................ 27 Figure 18: Year of Subscription to Current Mobile Carrier ..................................................... 25. Figure 21: Spending on Mobile Phone Bills in Each Carrier ................................................... 28 Figure 22: Hours of Internet Usages of the Users in Each Carrier ........................................... 28 Figure 23: Satisfactions towards Carrier Features .................................................................... 29 Figure 24: Intention to Subscribe, Intention to Recommend, Value for Money ...................... 31 Figure 25: Time to Subscribe for 4G LTE ............................................................................... 32 Figure 26: Importance of Mobile Carrier Features in 4G LTE ................................................ 32 Figure 27 Feeling about Subscribing to 4G LTE ..................................................................... 33 Figure 28: Favorable Features for People Intend to Subscribe ................................................ 34 Figure 29: Favorable Features for People Who Don’t Intend to Subscribe ............................. 34 Figure 30: Preferable 4G LTE Carriers .................................................................................... 35. vi.
(9) Figure 31: Distribution of Heavy and Light Mobile Internet Users ......................................... 35 Figure 32: Total Spending on Mobile-phone Bill per Month................................................... 36 Figure 33: Voice Call Spending on Mobile-phone Bill per Month .......................................... 37 Figure 34: Mobile Internet Bill per Month ............................................................................... 37 Figure 35: Intention to Subscribe for 4G LTE Mean Score of Heavy and Light Mobile Internet Users ......................................................................................................................................... 37 Figure 36: Willing to Pay More for Better Carrier Features of Heavy and Light Mobile Internet Users ............................................................................................................................ 38 Figure 37: Prices Acceptance of Heavy and Light Mobile Internet Users ............................... 39. 治 政 Figure 39: Satisfaction Levels of Switch and Non-switch大 Carrier Users ................................. 42 立 Figure 40: Reasons for Subscribing to the Current Carriers of Switch and Non-switch Carrier Figure 38: Current Carrier and Preferable 4G LTE Carrier Distributions ............................... 40. ‧ 國. 學. Users ......................................................................................................................................... 43 Figure 41: Years of Subscriptions of Switch and Non-switch Carrier Users ........................... 43. ‧. Table 1: Satisfaction Score / Adjusted Satisfaction Score of Each Carrier .............................. 30 Table 2: Current Carrier and Preferable 4G LTE Carrier Distribution .................................... 41. n. er. io. sit. y. Nat. al. Ch. engchi. vii. i n U. v.
(10) 1. Executive Summary LTE – Long Term Evolution, marketed as 4G LTE, is a new generation of mobile-phone network which will enable the mobile operator to provide significantly faster data rates for mobile broadband. With the new redesign and simplification of the network architecture, 4G LTE technology will be able to provide download peak rates of 300 Mbit/s, uplink peak rates of 75 Mbit/s, which is five time faster than the current 3G networks. It will allow the mobile operators to cope with ever growing mobile data traffic demands and provide a faster mobile broadband service in a cost-efficient manner. [4]. 政 治 大 mobile broadband service. In Taiwan, the government has been supporting the WiMAX 4G 立 WiMAX is another 4G technology that allows the wireless operators to provide a superfast. technology aiming to boost the local Taiwanese wireless device producer industry. The. ‧ 國. 學. WiMAX licenses have been issued to the six operators in 2007. Apparently, the launch of WiMAX 4G was not successful. The operators could attract only about hundred thousand. ‧. subscribers after 5 years of operation. [5]. Nat. sit. y. 4G LTE will be the future mobile broadband technology globally as more mobile carriers worldwide have committed to it. The licenses for 4G LTE in Taiwan will be issued by the end. io. n. al. er. of 2013. It’s expected that all the big operators will acquire for the licenses. To ensure. i n U. v. successfully deployment of 4G LTE, it’s important for the mobile operators to understand the customers’ wishes and needs.. Ch. engchi. This thesis project is conducted to gain a better understanding of the current mobile users in Taiwan. The goal is to identify and understand customers’ attitudes, preferences, and satisfactions towards the current mobile carriers.. Besides, it also studies customers’. expectations of the next generation mobile carriers – 4G LTE. The data input of this thesis project was a survey data collected from National ChengChi University students, and people living in Taiwan by on-line questionnaire. The sample size was 872.. 1.
(11) Key findings from the analysis are listed below. . 61% of the respondents spend less than 599 TWD a month on their total mobile phone bills. 58% spend less than 199 TWD a month for mobile internet while about 10% spend more than 800 TWD a month for mobile internet service.. . Voice call is the most important service among all the services provided in mobile network, followed by short message service (SMS), and mobile internet service. Multimedia message service (MMS) and video call are not important mobile services.. . ChungHua Telecom is the most popular carrier in Taiwan. Of all the respondents, 57%. 政 治 大. use ChungHua Telecom, 28% use Taiwan Mobile, and 13% use FarEasTone.. 立. Subscribers tend to stay with ChungHua Telecom than other carriers.. ‧ 國. 學. . The most common reason for choosing the mobile carrier is cheaper rate to call their family and close friends. The second most common reason is the network quality. The respondents rated network coverage, monthly rate plan, voice call quality, and. sit. y. Nat. . ‧. reputation.. io. more for the better coverage and the internet speed.. al. v i n The most satisfying current is ChungHua Telecom, followed by Taiwan C mobile U h e ncarrier i h c g Mobile and FarEasTone. ChungHua Telecom was rated as the best in network n. . er. internet speed as the most important features. However, they are just willing to pay. coverage and voice call quality satisfactions while it was rated as the lowest satisfactions in customer loyalty program, choice of handsets, and discounted price handsets. FarEasTone was rated as the best discounted price handsets. . With regard to expectations of 4G LTE; the respondents rated network coverage, rate plan, internet service speed, and voice call quality as the top most important features. 50% of the respondents plan to subscribe for 4G LTE after one year. Regarding the feeling to subscribe for 4G LTE; 42% stated that they will wait and listen to other comments, 29% stated they will wait for promotion, 21% stated they will wait for. 2.
(12) favorite mobile phone, and 4% tend to be one of the first to use 4G LTE. ChungHua Telecom is the most preferable carrier for 4G LTE. . Regarding the price acceptance testing of 4G LTE service, 888 TWD a month package is the most preferable by heavy mobile internet user group, who spend more than 6 hours a week using internet on their mobile devices. Most of them currently pay more than 800 TWD a month on total bill and more than 400 TWD a month for internet service. Apparently, this heavy mobile internet user group is willing to pay more for better service, especially for faster data service.. 政 治 大 subscribers prefer to subscribe for the same carriers. Only 65% of current Taiwan 立 Mobile and 52% of current FarEasTone subscribers prefer to subscribe for the same Concerning the preferable 4G LTE carrier, 95% of current ChungHua Telecom. 學. ‧ 國. . carriers in 4G LTE. 32% of current Taiwan Mobile subscribers and 42% of FarEasTone subscribers plan to switch to ChungHua Telecom when they subscribe for. Regarding mobile carrier switching, top reasons for the mobile users discontinuing. sit. y. Nat. . ‧. 4G LTE.. subscriptions and switching to other carriers are poor network coverage, voice call. io. er. quality, slow internet speed, unsatisfying customer service and support. The most. al. n. v i n C network quality call family and close friends,hand e n g c h i U reputation.. common motivations for the mobile users to stay with the carriers are cheaper rate to. The analysis result reveals that network coverage, monthly rate plan, and voice call quality are very important to the mobile users in 4G LTE. While 4G LTE allow the operators to provide superfast mobile broadband, the mobile operators should concentrate on not only increasing mobile data service speed but also expanding the network coverage as soon as possible, maintain voice call service quality, offer a wide variety of handsets at some attractive prices, and setting tariff rate competitively.. 3.
(13) 2. Introduction Recently, the ways people use mobiles phone have changed tremendously. People used to use mobile phones just to make phone calls to their friends. Now, people spend more time using their phones for surfing the webs, chatting with friends, taking photos, and sharing with friends, connecting with friends through social networks, e.g. Facebook, watching streaming video contents, etc. Smartphones and social networks have been key factors influence these changes. Mobile broadband or data service on mobile devices has become more important than the traditional voice calls. Data traffic in mobile broadband network has increased. 政 治 大. dramatically. In Taiwan, according to the latest statistics data from the National Communications Commission, the number of mobile internet subscribers has increased to. 立. 20.7 million, accounted for 71.3% of mobile phone subscribers in 2011.. ‧ 國. 學. To cope with this drastic demand increase in data service of mobile network, LTE – Long Term Evolution network is designed and being introduced. It will help operators to provide. ‧. high speed data service for mobile phone users in a cost efficiency way. In Taiwan, National. y. Nat. Communication Commission has been working on 4G LTE licenses, and planning to have an. sit. auction for the licenses by the end of 2013. Taiwan mobile operators, device producers as. al. n. LTE networks.. er. io. well as telecom equipment vendors are currently working on preparation and testing for 4G. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. In light of the upcoming 4G LTE deployment in Taiwan, this thesis project was conducted to gain a better understanding of mobile phone users in Taiwan. The main goal was to identify and understand customers’ attitudes, preferences and satisfactions towards current mobile carriers, and their expectations of 4G LTE services. The survey data were collected by on-line questionnaire from National ChengChi University students, and people living in Taiwan. The report is organized as follow. First, a brief overview of revolution of mobile telecommunication and exploration of the industry in Taiwan are provided. Then, the research methodology is discussed and described. Data collection is discussed, and the sample is described, and analyses are provided. The report concludes with recommendations for mobile operators in Taiwan to ensure successful deployment of their 4G LTE networks.. 4.
(14) 3. Revolution of Mobile Telecommunication 3.1.. 2G – Digital Cellular Networks. In 1990s, the second generation mobile phone system (GSM) was introduced. It provided mobility and allowed people to use mobile phone mainly for voice conversation. The second generation also introduced a new variant of communication called SMS or text messaging, which became popular amongst the young. 2G also introduced the capability to access media content on mobile phones. It became widespread and people began to utilize mobile phone in their daily lives. Demand for data service or internet access on mobile devices was growing. [1]. 立. 3G – Mobile Broadband Data. 學. ‧ 國. 3.2.. 政 治 大. In 2000s, 3G introduced the use of package switching for data transmission rather than circuit switching, which allowed higher speed for internet access on mobile phones. 3G was. ‧. introduced to the markets in order to provide a base for even more demanding multimedia. It. sit. y. Nat. provided additional capacity for voice calls as the 2G systems started to saturate. With its multiple generations and releases, the mobile telecom operators and vendors started to realize. io. n. al. er. the challenges in the field as new services typically require support from both networks and. i n U. v. terminals. On the other hand, the terminals' lifecycle is shorter because users consider them to. Ch. engchi. be everyday consumer objects, and more attractive models constantly appear on the market. There is a positive balance between users, operators and equipment vendors as enhanced services typically require updates to terminals and networks. The deployment of the packet data service as an add-on for GSM, and then its adaptation from the first phase of UMTS, were the important triggers for the use of Internet services via mobile terminals. The rapidly evolving Internet environment itself had a great impact on mobile communications, resulting in the development of multi-usage equipment for services, combining voice connections, messaging, and multimedia. With the deployment of the third-generation networks, data rates increased in order to provide a smoother user experience. The new business environment started to strengthen. In contrast. 5.
(15) to the initial model of only few voice service providers in controlled markets, there were now increasing numbers of operators, equipment vendors, service providers, measurement equipment producers, and many other entities contributing to mobile communications. The increasing speed of standardization made development seem unlimited. Along with the increased data rates associated with the Internet, fixed and mobile communications have also evolved steadily. Open standards, competing operators and multivendor equipment offerings have ensured that the markets developed favorably from the end user's point of view.. 治 政 大 efficient platform to provide the generation networks. It is easier to create a new, more 立 required data rate and capacity than to develop existing ones. Statistics from recent years. Evolution of 2G and 3G is gradually becoming saturated, as happened with the first-. ‧ 國. 學. indicate that there has been a huge growth in multimedia data transfer. The exponential growth in the use of data sets higher performance targets for the networks than ever before. [1]. ‧. 3.3.. 4G LTE – Long Term Evolution. y. Nat. sit. LTE – Long Term Evolution, marketed as 4G LTE, is a new standard for wireless. al. er. io. communication of high-speed data for mobile phones and data terminal. As its name indicates,. n. LTE has been planned to meet the ever growing demands of mobile communication network. Ch. i n U. v. customers in the forthcoming years. It has been developed based on the GSM/EDGE and. engchi. UMTS/HSPA network technology to increase the capacity and speed of mobile phone internet service using a different radio interface together with core network improvements. It allows the service providers to utilize their network resources more efficiently. The goal of LTE was to increase the capacity and speed of wireless data network using new DSP (digital signal processing) techniques and modulations. A further goal was the redesign and simplification of the network architecture to an IP-based system with significantly reduced transfer latency compared to the 3G architecture. However, the LTE wireless interface is incompatible with 2G and 3G networks, so that it must be operated on a separate wireless spectrum. [4]. 6.
(16) The LTE specification provides downlink peak rates of 300 Mbit/s, uplink peak rates of 75 Mbit/s, and QoS provision permitting a transfer latency of less than 5ms in the radio access network. With 4G LTE, the end-users will be able to access superfast mobile internet at speed FIVE times faster than the current 3G speeds today. The customers will be able to access the web on the go without waiting, connect with their friends on social network quicker and easier, download high-definition movies in minutes, watch live TV on the move without buffering, play live multiplayer games on the go, download large email attachments quicker than ever, make crystal clear audio quality phone through Voice over LTE (Available in the near future), make high quality video calls on the move, and enjoy superfast service on. 政 治 大. computers, or other peripheral by connecting through the 4G LTE handset.. 立. ‧. ‧ 國. 學. n. er. io. sit. y. Nat. al. Ch. engchi. 7. i n U. v.
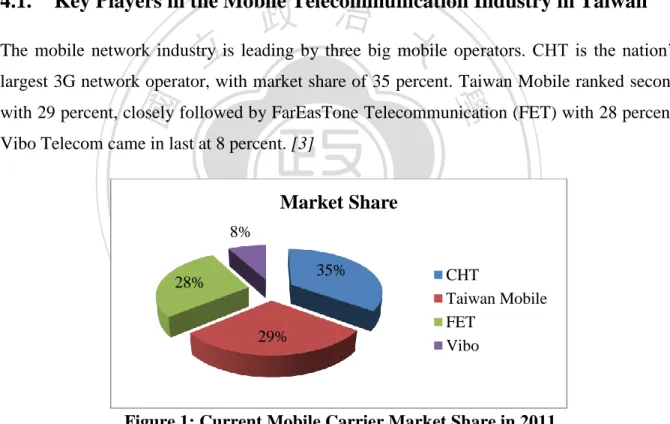
(17) 4. Exploration. of. the. Current. Mobile Telecommunication. Industry in Taiwan Taiwan has one of the most advanced telecom networks in Asia. It was one of the first countries deploying 3G mobile network services and 4G WiMax. This section discusses the current mobile-phone network industry in Taiwan, including key players in the industry, evolution of the mobile telecommunication industry, revenue trend analysis, and challenges confronting the mobile operators.. 政 治 大 The mobile network industry is leading by three big mobile operators. CHT is the nation’s 立 4.1.. Key Players in the Mobile Telecommunication Industry in Taiwan. largest 3G network operator, with market share of 35 percent. Taiwan Mobile ranked second. ‧ 國. 學. with 29 percent, closely followed by FarEasTone Telecommunication (FET) with 28 percent. Vibo Telecom came in last at 8 percent. [3]. ‧. Nat. y. Market Share. n. al. 35%. C h29% engchi. CHT Taiwan Mobile FET Vibo. er. io. 28%. sit. 8%. i n U. v. Figure 1: Current Mobile Carrier Market Share in 2011. 4.2.. Evolution of the Mobile Telecommunication Industry in Taiwan. According to the data from National Communication Commission, the first 3G network was launched in Taiwan in July 2003. At that time the overall mobile-phone services penetration rates have already been over 100%, dominated by 25.1 million of 2G subscribers. There was no much room for growing in the mobile market in Taiwan as it was becoming very saturated. Nevertheless, 3G subscribers are still growing, which is contributed by users who switch from. 8.
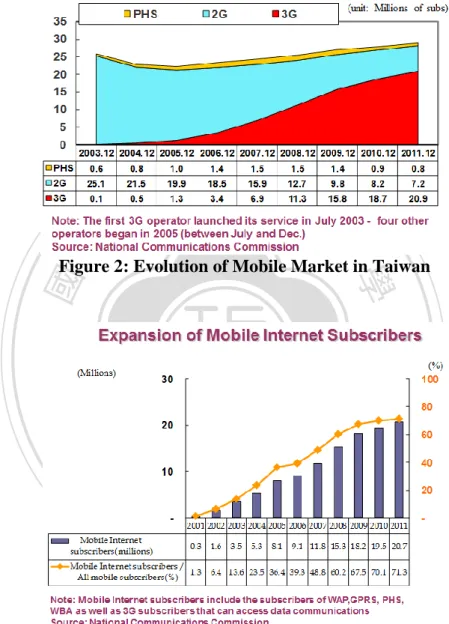
(18) 2G mobile networks to 3G mobile networks. In 2011, mobile penetration rates have reached 120%, accounted for 28 million total subscribers, with 20.9 million 3G subscribers. [2]. 立. 政 治 大. ‧. ‧ 國. 學. Figure 2: Evolution of Mobile Market in Taiwan. n. er. io. sit. y. Nat. al. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. Figure 3: Expansion of Mobile Internet Subscribers in Taiwan. Mobile internet subscribers have expanded since 3G was introduced in 2003, with annual growth rate about 3-5% until 2008. The growth rate became slower after 2009 as the market became almost mature. In 2011, about 71.3% of total mobile-phone users or 20.7 million users have already subscribed for mobile internet services. [2]. 9.
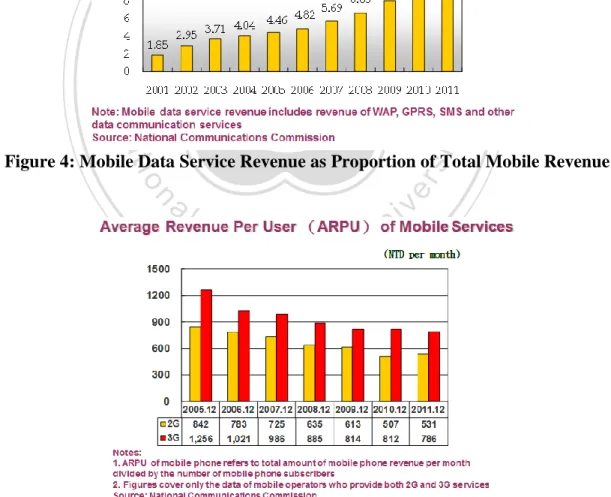
(19) 4.3.. Revenue Trend Analysis. As for revenue point of view, the service revenue from mobile data service has been growing continuously. In 2011, the mobile data service revenue is 13.87% of total mobile revenue. It’s inevitable that mobile data service is becoming very important for mobile operators. While the revenue from the mobile data service is growing, average revenue per user – ARPU of the mobile services have been declining. In 2011, APRU of 3G subscribers declined to 786 NTD per month, while 2G subscribers declined to 531 NTD per month.. 立. 政 治 大. ‧. ‧ 國. 學 sit. y. Nat. n. al. er. io. Figure 4: Mobile Data Service Revenue as Proportion of Total Mobile Revenue. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. Figure 5: Average Revenue per User (ARPU) of Mobile Services. 10.
(20) 4.4.. Challenges in the Mobile Telecommunication Industry. The dramatically increase in the mobile data service demands has brought numerous challenges to the mobile operators. First, the market is highly competitive. In order to attract new subscribers, the operators have been offering cheaper rate plan packages such as a flat rate for unlimited data usages. There has been also a drastic change in the mobile users’ behavior. People spend more time using the mobile internet services than before. An increase in the mobile internet traffic has triggered congestions in the networks. The internet services have become more latency and slower. The mobile operators have to allocate abundant. 政 治 大. investment on expanding the network capacity to bridge the gap, adding higher costs in network operations. ARPU – Average Revenue per User has been retracting while investment. 立. and operation cost has been increasing.. ‧ 國. 學. To cope with this drastic change, LTE – Long Term Evolution network is designed meet the ever growing demands of the mobile communication network customers. It will help operator. ‧. to offer higher speed data services for mobile phone users in a cost efficiency way.. n. er. io. sit. y. Nat. al. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. Figure 6: Operator Challenges – The Widening Gap between Traffic and Revenue [7]. In Taiwan, National Communication Commission has been working on 4G LTE license, and planning to have an auction by the end of 2013. Taiwan mobile operators as well as telecom vendors are currently working on preparation and testing for 4G LTE networks.. 11.
(21) 5. Statement of the Problem The main goal of this thesis project is to gain a better understanding of mobile users in Taiwan, to identify the customers’ preferences, their satisfactions toward the current carriers, and their willingness to pay more for better services. The project also analyzes the customers’ expectation of their future carriers – 4G LTE, their purchase intension, and their preferable carriers. Apart from that, the project also analyzes mobile users’ carrier switching patterns, and attempts to identify important factors that make the mobile users decide to stay with their current carriers or switch to other carriers. In addition, the project also discusses users’. 政 治 大. behavior, attitudes and expectations of 4G LTE by comparing between heavy mobile internet user group and light mobile internet user group. It is crucial for mobile operators to monitor. 立. the preference and behavior of their customers especially because the market is becoming. ‧ 國. 學. saturated so that they can effectively respond and identify new opportunities in the marketplace, 4G LTE.. ‧. 6. Methodology. y. Nat. sit. The approach of the thesis project included two phases. In the first phase, the author studied. er. io. the current mobile phone carrier industry in Taiwan, and conducted a focus group by. al. v i n well as their knowledge on 4G LTE. survey was developed based C hAfter that, the questionnaire U i e h n gc on the collected data. n. discussing with few Taiwanese friends about their attitudes towards their current carriers, as. In order to study satisfactions of mobile users and other related issues, 11 important features of mobile carriers were defined. The mobile carriers features used in this thesis project are listed below: . Network coverage. . Voice call quality. . Data/Internet service quality and speed. . Video call quality. 12.
(22) . Reliability of SMS & MMS. . Helpful customer service and support. . Value-added services (e.g. Voicemail service, Selective ring back tone service, etc.). . Customer loyalty program (e.g. 1hr free parking in department store, Birthday gift, Personal assistant hotline for VIP customers, etc.). . Choices of available handsets. . Discounted price handsets with contract. . Rate plan / Monthly subscription fee. 立. 政 治 大. ‧ 國. 學. To perform service price testing of 4G LTE, the survey participants were randomly separated to two groups to answer different survey questionnaire form. The questions in the two forms. ‧. are identical. Only the price shown in the product descriptions are different. Details can be. sit. y. Nat. found in the following section.. -. al. n. 6.1.. io. Appendix B.. er. The survey questionnaire was comprised of three parts. Full questionnaire can be found in. Questionnaire. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. Part 1 (Form A) The questions in this part of the questionnaire asked about the carrier that participants are currently using, and their attitudes towards the current carriers. o Currently using mobile network carrier o Yeas of using this carrier o Reasons for selecting this carrier o Spending on current mobile phone bill on each services, including voice call, video call, SMS, and MMS. 13.
(23) o Importance of each basic services, including voice call, video call and SMS o Importance of the 11 defined mobile carrier features o Satisfaction with the current carrier on the 11 defined mobile carrier features o Willingness to pay more on the 11 defined mobile carrier features o Hours of using mobile internet in typical week o Activities on internet-enable mobile phone -. 治 政 into two cells – Cell I and Cell II. They are asked 大 to answer to the two separated questionnaire forms 立 – Form B and Form C. The questions in both forms were identical. Part 2 (Form B and Form C) In this part, the participants were randomly separated. ‧ 國. 學. At the beginning of both forms, the participants were given the product descriptions of 4G LTE network and its main features as well as the monthly subscription plan. The. ‧. difference of these two forms was the monthly subscription plan shown on the product descriptions. This was done for price acceptance testing purpose. The following are. Nat. sit. y. the product descriptions of 4G LTE shown in the questionnaire forms.. er. io. 4G LTE is the next generation of telecom technology, which can deliver significantly. n. al. i n C speeds typically FIVE times faster than 3G speeds today. he ngchi U. v. faster, more consistent mobile broadband speeds. It can offer superfast mobile internet at. -. With superfast 4G LTE mobile, customers will be able to:. -. Access the web on the go without waiting. -. Connect with your friends on social network quicker and easier. -. Download high-definition movies in minutes. -. Watch live TV on the move without buffering. -. Play live multiplayer games on the go. -. Download large email attachments quicker than ever. 14.
(24) -. Make crystal clear audio quality phone through Voice over LTE (Available in the near future). -. Make high quality video calls on the move. -. Enjoy superfast service on your computer, or your other peripheral by connecting through the 4G LTE handset.. Form B (For Cell I participants) Monthly Fee: 888 NT (Low price package). 政 治 大 0.00061 NT/Byte; Upper立 limited charge is 2,000 NT. Data / Internet service: Free for 800 MByte ; If you use over 800 Mbyte, we will charge. ‧. ‧ 國. NT/minutes. 學. Voice Call: Free 100 minutes; If you call over 100 minutes, we will charge 3.5. Text message: Free 100 SMS. Nat. n. al. Ch. er. io. Monthly Fee: 1,888NT (High price package). sit. y. Form C (For Cell II participants). i n U. v. Data / Internet service: Free for 2,000 MByte ; If you use over 2,000 MByte, we will. engchi. charge 0.00041 NT/Byte; Upper limited charge is 2,200 NT) Voice Call : Unlimited for intra-network ; Free 100 minutes for inter-network; if you call over 100 minutes, we will charge 3.5 NT / minutes for inter-network calls. Text message: Free 500 SMS After providing the product descriptions of 4G LTE, the participants were asked to answer the questions about their purchase intension and expectations of their future mobile carriers. o Intension to subscribe 4G LTE o Most favorite and un-favorite feature of 4G LTE. 15.
(25) o Value for money of 4G LTE o Reason for subscribing to 4G LTE o Intension to recommend the 4G LTE service to others o Preferable carrier or top of mind carrier of 4G LTE o Preferable substitute if 4G LTE is not available o When to subscribe. 政 治 大. o Importance of the 11 defined mobile carrier features. 立. Part 3 (Form D) In this part, the participants were asked to provide demographic. 學. information such as nationality, hometown, gender, age, profession, income range,. ‧ 國. current mobile phone, and other gadgets.. ‧. io. sit. y. Nat. n. al. er. -. Ch. engchi. 16. i n U. v.
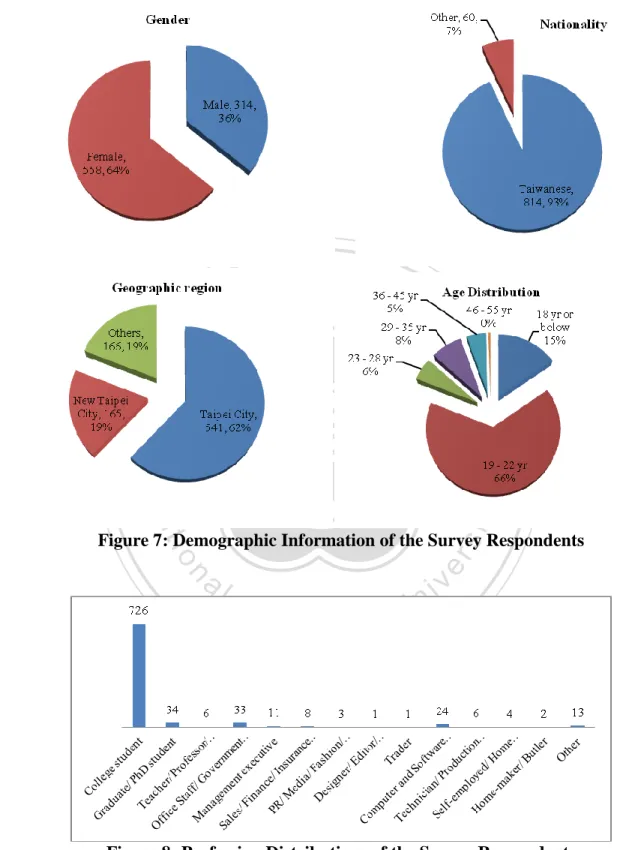
(26) 7. Survey Data Analysis This section includes a discussion of the data collection, the sample, data analysis and results.. 7.1.. Data Collection. Based on the survey questionnaire discussed in the previous section, the questionnaire forms were created on-line by using google document in both Chinese and English languages. The questionnaires were distributed via e-mail to National ChengChi University students by using the university’s mailing list system, IMBA students and alumni, Nokia Siemens Network. 政 治 大 Of all the survey sent out,立 872 were completed online on google document website. The colleagues, and the author’s Facebook friends who live in Taiwan.. ‧ 國. 學. survey data was downloaded and entered into SPSS 14.0, a computerized statistical analysis program, for further analysis.. Description of the Sample. ‧. 7.2.. y. Nat. The survey data were collected from NCCU students, IMBA students and alumni, Nokia. n. al. er. io. demographic information on survey respondents.. sit. Siemens Network colleagues, and the author’s friends on Facebook. The chapter discusses. i Demographic Information ofCSurvey Respondents n hengchi U. v. The following charts illustrate demographic information of the survey respondents. Split by gender, as indicated in Figure 7, the sample was 64% female and 36% male. Most of the respondents are Taiwanese; age group is between 19 – 22 years old; live in Taipei City and Taipei County area. Most of them are college students therefore their income range is mostly less than 15,000 TWD a month.. 17.
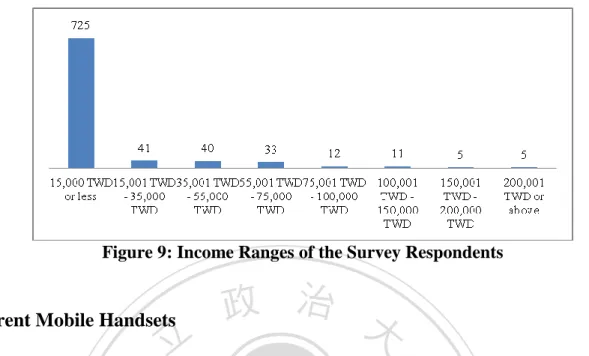
(27) 立. 政 治 大. ‧. ‧ 國. 學 sit. y. Nat. n. al. er. io. Figure 7: Demographic Information of the Survey Respondents. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. Figure 8: Profession Distributions of the Survey Respondents. 18.
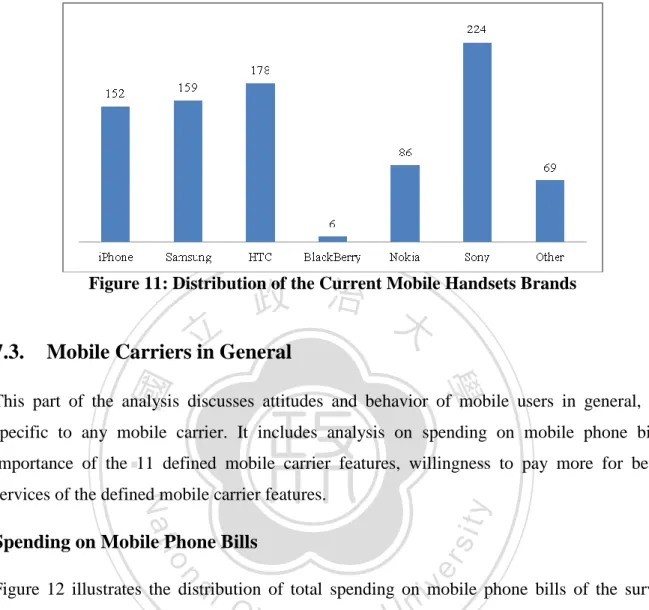
(28) Figure 9: Income Ranges of the Survey Respondents. Current Mobile Handsets. 立. 政 治 大. The following charts illustrate current mobile handset type of the survey respondents. As can. ‧ 國. 學. be seen from Figure 10, 74% of total respondents use smartphone. The rest 26% use other phone types or feature phones. The most popular brand among the respondents is Sony,. ‧. following by HTC, Samsung, iPhone and Nokia. Just few people use Black Berry.. n. er. io. sit. y. Nat. al. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. Figure 10: Distribution of the Current Mobile Handsets Types. 19.
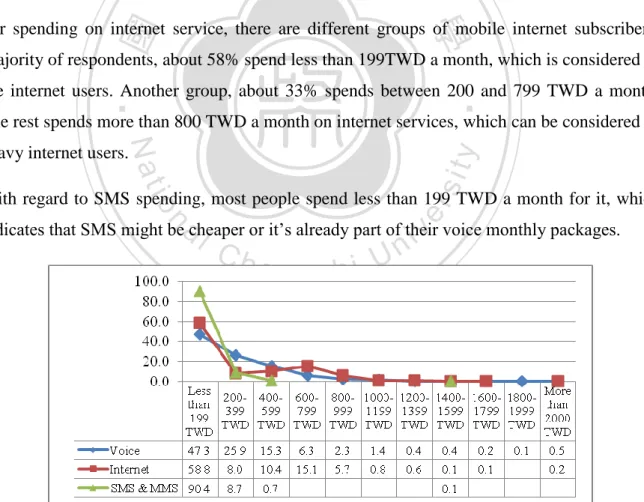
(29) 政 治 大. Figure 11: Distribution of the Current Mobile Handsets Brands. 立. Mobile Carriers in General. 學. ‧ 國. 7.3.. This part of the analysis discusses attitudes and behavior of mobile users in general, not specific to any mobile carrier. It includes analysis on spending on mobile phone bills,. ‧. sit. Nat. services of the defined mobile carrier features.. y. importance of the 11 defined mobile carrier features, willingness to pay more for better. er. io. Spending on Mobile Phone Bills. al. n. v i n C h chart, 61% of the respondents. As can be seen from the e n g c h i U survey respondents spend less than. Figure 12 illustrates the distribution of total spending on mobile phone bills of the survey. 599 TWD a month while 39% spend more than 600 TWD a month. It means more than half of the respondents spend less than 599 TWD a month. Comparing to ARPU of average revenue per user from National Communication Commission, the ARPU from 3G subscribers are 786 TWD in 2011. This probably indicates that people tend to spend less on the total mobile phone bill in 2012, or due to the fact that the survey samples in this project are mostly students, who maybe spend less than average.. 20.
(30) Figure 12: Total Spending on Monthly Mobile Phone Bills. 政 治 大 voice call less than 399 TWD 立a month.. Figure 13 shows the distribution of spending on each basic service. Most people spend on. 學. ‧ 國. For spending on internet service, there are different groups of mobile internet subscribers. Majority of respondents, about 58% spend less than 199TWD a month, which is considered as. ‧. lite internet users. Another group, about 33% spends between 200 and 799 TWD a month. The rest spends more than 800 TWD a month on internet services, which can be considered as. y. Nat. sit. heavy internet users.. n. al. er. io. With regard to SMS spending, most people spend less than 199 TWD a month for it, which. v. indicates that SMS might be cheaper or it’s already part of their voice monthly packages.. Ch. engchi. i n U. Figure 13: Spending on Mobile Phone Bills. 21.
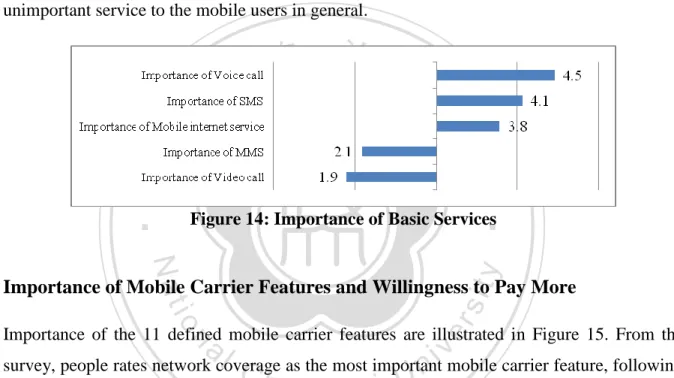
(31) Importance of Basic Services Figure 14 illustrates important levels of mobile network basic services, including voice calls, video calls, short message service (SMS), multimedia message service (MMS) and internet service. According to the survey, voice call is rated for the most important service among all the basic services. It’s also in line with previous analysis that mobile subscribers tend to spend more on the voice call service than other services. The second important basic service is SMS, and following by internet services on the mobile device. MMS and video calls seem to be unimportant service to the mobile users in general.. 學 ‧. ‧ 國. 立. 政 治 大. Figure 14: Importance of Basic Services. y. Nat. al. er. io. sit. Importance of Mobile Carrier Features and Willingness to Pay More. n. Importance of the 11 defined mobile carrier features are illustrated in Figure 15. From the. Ch. i n U. v. survey, people rates network coverage as the most important mobile carrier feature, following. engchi. by monthly rate plan, voice call quality, and mobile internet quality and speed. Discounted price handsets, choices of handsets, reliability of SMS and MMS, and customer service support are also quite important features of the mobile carriers. Customer loyalty program, quality of video calls, and value-added services seem to be unimportant features of the mobile phone carriers.. 22.
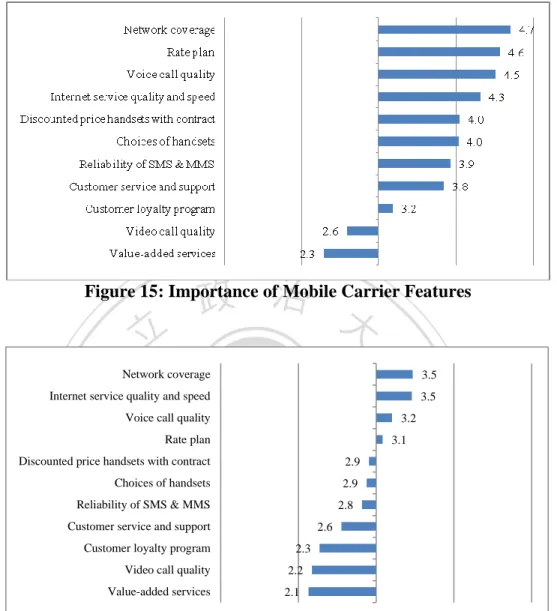
(32) 政 治 大. Figure 15: Importance of Mobile Carrier Features. Network coverage. 學. ‧ 國. 立. Internet service quality and speed Voice call quality. 3.2. Rate plan 2.9. Choices of handsets. Nat. y. 2.9. Reliability of SMS & MMS. 2.3 2.2. Value-added services. 2.1. n. Video call quality. engchi. er. 2.6. Customer loyalty program. io. sit. 2.8. Customer service and support. Ch. ‧. 3.1. Discounted price handsets with contract. al. 3.5. 3.5. i n U. v. Figure 16: Willingness to Pay More for Better Mobile Carrier Features. Figure 16 illustrates willingness to pay more from the collected survey data. It can be seen that mobile users might consider paying more for better network coverage and internet service quality and speed. For the other carrier features, it seems that people don’t want to pay more, especially for customer loyalty program, video call quality, and value-added services. To sum up, it should be highlighted in this analysis that network coverage, suitable rate plans, voice call quality and internet speed are very important features of the mobile carriers. Customers are willing to pay more for better services, especially for better coverage and faster mobile internet speed.. 23.
(33) 7.4.. Current Using Mobile Carriers. This part of the data analysis discusses more details about attitudes and behaviors of customers comparing across three big mobile carriers in Taiwan. It includes distribution of mobile users in each carrier, years of subscription, reasons for choosing the carriers, spending on the current subscriptions, and satisfactions towards the current carriers.. Current Mobile Carriers Distribution Distribution of mobile users in each carrier from the survey data are illustrated in Figure 16.. 政 治 大. As indicated in the chart, the most common mobile carrier is ChungHua Telecom, accounted for 57%. Taiwan Mobile is 28% and FET is 13%. Very few respondents subscribed for other. 立. carriers.. ‧ 國. 學. The data indicates that the mobile industry in Taiwan is dominated by big three operators including ChungHua Telecom, Taiwan Mobile and FET. The amount of people using. ‧. ChungHua Telecom is even more than the market share data of National Communication Commission. It seems that ChungHua Telecom is very popular among the samples; probably. y. Nat. n. er. io. al. sit. it’s more popular to the NCCU students than other carriers.. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. Figure 17: Distribution of Current Mobile Carriers of Respondents. 24.
(34) Years of Subscription Figure 18 illustrates the distributions of years of subscription of survey respondents. In the chart, Y-axis represents percentage of respondents within the carriers. X-axis represents years of subscription.. 立. 政 治 大. ‧. ‧ 國. 學. Figure 18: Year of Subscription to Current Mobile Carrier. sit. y. Nat. It’s noticeable that distributions of subscribers who have been using the carrier less than one. io. n. al. er. year (0 year) are much more in Taiwan Mobile (17%), FET (22%) and other networks (23%). i n U. v. than ChungHua Telecom (8.9%). There are two ways to interpret this finding. Firstly,. Ch. engchi. customers tend to stay with ChungHua Telecom longer than other carriers. The other way is that Taiwan Mobile and FET have just gained more new subscribers due to the fact that the recent marketing strategy of Taiwan Mobile and FET might be more attractive than ChungHua Telecom. However, it seems that the subscribers tend to use ChungHua Telecom longer than the other carriers as can be seen from the chart that the blue line (CHT) is always above all other lines from 4 years or more.. 25.
(35) 6. CHT. TWM. FET. Other. All. 5 4 3 2 1 0 CHT. TWM. FET. Other. All. 政 治 大. Figure 19: Average Years of Subscription. 立. ‧ 國. 學. Figure 19 shows the average years of subscription for each carrier. It’s confirmed that the average years of subscription for ChungHua Telecom is longer than Taiwan Mobile, FET and other carriers.. ‧. Motivations for Choosing the Carriers. y. Nat. io. sit. Figure 20 illustrates percent distributions of motivations for choosing the carriers. It’s obvious. n. al. er. that the most common reason for choosing the carrier is lower cost on making calls to their. i n U. v. boyfriend, girlfriend, husband or wife. It indicates that lower rate for intra-network call is one. Ch. engchi. of the most important factors for people on subscribing to the mobile carriers. For Taiwan Mobile, the second most common reason is that the carrier offered the most suitable rate plan, which also means that customers tend to be quite concerned on usage cost and rate plans of Taiwan Mobile is probably quite appearing to the customers. For FET, the second most common reason for choosing FET as a carrier is cheaper handset prices with packages, which indicates FET probably offer lower cost handsets and more appearing than other carriers. In contrast to Taiwan Mobile and FET, the second most common reason for choosing ChungHua Telecom as a carrier is recommended by friend for best network quality, which indicates that ChungHua Telecom has quite well reputation on the network quality.. 26.
(36) 立. 政 治 大. ‧ 國. 學. Figure 20: Motivation for Choosing the Current Carriers. ‧. It’s interesting to highlight here that while network coverage is rated as the most important feature, mobile phone users still tend to choose their carriers based on the monthly rate plans. sit. n. er. io. Spending on Mobile Phone Bills. al. y. Nat. and mobile phone prices rather than network quality.. i n U. v. Figure 21 illustrates the distribution of total spending on mobile phone bill of each mobile. Ch. engchi. carrier subscribers. Among the survey respondents, most people spend around 200 to 799 TWD a month. It’s noticeable that there are more percent of ChungHua Telecom’s and FET’s subscribers spending less on total monthly phone bill. It seems subscribers in Taiwan Mobile network spend more on total monthly phone bill than other networks.. 27.
(37) Figure 21: Spending on Mobile Phone Bills in Each Carrier. Internet Usages. 立. 政 治 大. Distribution of hours of using the internet on mobile phones illustrates in Figure 22. In this. ‧ 國. 學. analysis, the mobile internet users were categorized into two parts. It seems from the chart that more than 60% of people from all the carriers use internet on their mobile phone less than. ‧. 6 hours in a typical week. It’s also noticeable that percent of people who use internet on mobile phone more than 6 hours in Taiwan Mobile Network are more than other carriers.. Nat. n. al. er. io. sit. y. Light and heavy mobile internet user group will be discussed more details in Chapter 7.7.. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. Figure 22: Hours of Internet Usages of the Users in Each Carrier. Satisfactions towards the Current Carriers Figure 23 illustrates means of customers’ satisfactions scores categorized by mobile carrier features and operators. In general, customers seem to be quite satisfied with their carriers with. 28.
(38) satisfaction score over 3 in several aspects, except for video call quality and customer loyalty program, which were also rated as unimportant features. By comparing the satisfaction mean scores between the carriers, it’s quite obvious that mobile users in ChungHua Telecom network seem to be quite satisfied with the carrier, especially in terms of network coverage and voice call quality. With regard to network coverage, ChungHau Telecom was rated with significantly higher satisfaction scores than the other carriers. However, customer loyalty program was rated with lower satisfaction scores than other carriers.. 立. 政 治 大. ‧. ‧ 國. 學. n. er. io. sit. y. Nat. al. i n U. v. Figure 23: Satisfactions towards Carrier Features. Ch. engchi. To evaluate customers’ satisfactions towards their current carriers precisely, it’s necessary to take important levels of the carriers’ features into consideration. Adjusted satisfactions scores of each carrier features were estimated by multiplying the important rates (important level score divided by 5) with satisfaction scores, as shown in Table 1. It’s confirmed that ChungHua Telecom was rated as the most satisfying carriers, following by Taiwan Mobile and Far EasTone.. 29.
(39) Table 1: Satisfaction Score / Adjusted Satisfaction Score of Each Carrier Carrier Features. Important Rates. Adjusted Satisfactions Score CHT TWM FET. CHT. TWM. FET. Network coverage. 3.96. 3.68. 3.43. 4.71 / 5. 3.73. 3.46. 3.23. Voice call quality. 3.84. 3.74. 3.59. 4.51 / 5. 3.46. 3.37. 3.24. Internet service quality and speed. 3.20. 3.26. 3.26. 4.32 / 5. 2.76. 2.81. 2.81. Video call quality. 3.02. 3.01. 2.98. 2.59 / 5. 1.56. 1.56. 1.54. Reliability of SMS & MMS. 3.60. 3.69. 3.56. 3.93 / 5. 2.83. 2.90. 2.79. Customer service and support. 3.35. 3.30. 3.31. 3.84 / 5. 2.57. 2.53. 2.54. Value-added services. 3.03. 3.09. 3.04. 2.29 / 5. 1.39. 1.41. 1.39. Customer loyalty program. 2.51. 2.66. 2.63. 3.18 / 5. 1.59. 1.69. 1.67. Choices of handsets Discounted price handsets with contract. 立. 政 治 大 3.19. 3.29. 3.26. 4.03 / 5. 2.57. 2.66. 2.63. 3.10. 3.16. 3.20. 4.04 / 5. 2.51. 2.56. 2.59. 3.50. 3.39. 3.47. 4.57 / 5. 3.20 2.56. 3.10 2.55. 3.17 2.51. Adjusted Satisfaction Score. Future Mobile Carrier – 4G LTE. 學. ‧ 國. Rate plan. 7.5.. Satisfactions Score. ‧. This part of the analysis discusses customers’ attitudes and expectations towards 4G LTE,. y. Nat. including evaluation of price acceptance, intention to subscribe, time to subscribe, importance. er. io. sit. carrier features, feelings for subscribing, and preferable carrier.. Evaluation of Price Acceptance and Intention to Subscribe. al. n. v i n C To evaluate intention to subscribehand e nprice h i U of 4G LTE of mobile users, the g cacceptance. survey participants were randomly divided into two cells by the on-line questionnaire system and asked to answer to the two different questionnaire forms. The questions in the two forms are identical. The difference is only the monthly plans shown in the product descriptions, as described previously in Chapter 6 – Methodology. For Cell I participants, the lower price monthly plan shown in the questionnaire From B is pricing at 888 TWD a month with 800MB data service, 100 minutes free calls, and 100 free SMS.. 30.
(40) For Cell II participants, the higher price monthly plan in the questionnaire From C is pricing at 1,888 TWD a month with 2000MB data service, unlimited intra-network calls, Free 100 minutes inter-network calls, and 500 free SMS. Figure 24 illustrates intention to subscribe, intention to recommend and value for money comparing between low price package and high price package. Low price package seems much more appealing to the customers. Participants in Cell I (Low price package) intend to subscribe for 4G LTE service more than participants in Cell II (High price package). Also, participants in Cell I (Low price package) tend to recommend the service to their others than participants in Cell II (High price package). With regard to value for money, the lower price. 政 治 大. package has much better perceived value for money than the higher price package.. 立. ‧ 國. 學. Cell I (Low price package) Cell II (High price package). 3.23. Intention to subscribe. 2.79. ‧. 3.39. Intention to recommend. 3.18. Value for money. 2.71. n. al. Ch. engchi. er. io. sit. y. Nat. 3.19. i n U. v. Figure 24: Intention to Subscribe, Intention to Recommend, Value for Money. Figure 25 illustrates time to subscribe for 4G LTE, comparing between Cell I (Low price package) participants and Cell II (High price package) participants. The result shows that Cell I participants who saw the lower price package tend to subscribe earlier than Cell II participants who saw the higher price package. This is also in line with the previous analysis that mobile phone users are price sensitive. The lower price package is more appealing than the higher price package to the users in general.. 31.
(41) 60 50. 56. Cell I (Low price package) Cell II (High price package). 47. 40 30. 26 21 17. 20 11. 13. 11. 10 0 Within 3 months. Within 6 months. Within 1 year. After 1 year. 政 治 大. Figure 25: Time to Subscribe for 4G LTE. 立. Importance of Mobile Carrier Features in 4G LTE. ‧ 國. 學. Important levels of the mobile carrier features in 4G LTE is illustrated in Figure 26. Similarly. ‧. to the features of the current carriers, network coverage again is the most important feature to the mobile users for all carrier features. Rate plan, internet service speed, and voice call. Nat. sit. y. quality are also quite important features. Customer loyalty program, video call quality and. io. n. al. er. value-added services are unimportant features.. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. Figure 26: Importance of Mobile Carrier Features in 4G LTE. 32.
(42) Feelings about Subscribing to 4G LTE This section of the analysis discusses the customers’ feeling for subscribing to 4G LTE. Distribution of the respondents’ feelings about 4G LTE is shown in Figure 27. From the chart, the most common one is waiting and listening to other comments before subscribing, following by waiting for promotion, and waiting for favorite mobile phone. There are few people said they want to be the one of the first to use 4G LTE. 4242. 政 治 大 23. 30. 19. 4 3. Only Wait for subscrib Wait for favorite e for promoti Other mobile special on phone occasio n 23 27 1 2. ‧. ‧ 國. 2 3. 學. Wait Tend to and be one listen of the other first comme nts Cell I (Low price package) 4 42 Cell II (High price 3 42 package). 1 2. 30. 2. 3. sit. Nat. 19. y. 立. 27. er. io. Figure 27 Feeling about Subscribing to 4G LTE. al. n. v i n C Intend Favorable Features for People to Subscribe and Not Intend to Subscribe U heng i h c. This part of the analysis discusses the customers’ preferences towards 4G LTE carriers. It’s divided into two groups. The first group is from people who intend to subscribe for 4G LTE point of view. As shown in Figure 28, faster internet speed is the most favorite features, following by mobility and convenience, and high quality voice call. Participants in Cell I who saw lower price package are more likely to like monthly rate plan than participants in Cell II who saw higher price package of 4G LTE. The second group is from people who don’t plan to subscribe for 4G LTE, Figure 29. People in this group still like faster internet speed very much. However, the most undesirable feature is monthly rate plan, especially to the Cell II participants who learnt about high price package.. 33.
(43) This indicates that the operators might need to offer lower price package to attract this group of people.. 4.6 4.7. Faster internet speed 4.2 4.3. Mobility and convenience 3.8. High quality voice call. 4.0. 3.2 3.4. High quality video call. 3.2 3.0. Monthly rate plan. 政 治 大. Cell I (Low price package). 立. Cell II (High price package). Figure 28: Favorable Features for People Intend to Subscribe. 1.7. 2.1. ‧. ‧ 國. 學. Monthly rate plan. 2.8 2.9. High quality video call. 3.3 3.5. sit. y. Nat. High quality voice call. 3.7 3.8. io. al. er. Mobility and convenience. n. Faster internet speed. Ch. n U engchi. Cell I (Low price package). iv. 4.0 4.2. Cell II (High price package). Figure 29: Favorable Features for People Who Don’t Intend to Subscribe. Preferable 4G LTE Carriers This section discusses preferable 4G LTE carriers in Taiwan. As shown in Figure 30, the most preferable carrier of 4G LTE is ChungHua Telecom, following by Taiwan Mobile and Far EasTone. ChungHua Telecom seems to be top of mind brand for mobile carriers among the people in Taiwan.. 34.
(44) Figure 30: Preferable 4G LTE Carriers. 7.6.. 治 政 大 Current Internet Usage Intension of Subscribing to 4G LTE versus 立 ‧ 國. 學. This part of the analysis discusses the intention of subscribe for 4G LTE. In this study, mobile users are categorized into two groups based on hours of internet usage in a typical week from. Light internet users are the respondents who spend time less than 6 hours a week using. ‧. internet on their mobile phone. Heavy internet users are the one who use internet more than 6. sit. y. Nat. hours a week on mobile phones.. n. al. er. io. Current Internet Usage. i n U. v. Figure 31 illustrates users categorized by hour of internet usage. As showed in the chart, 73%. Ch. engchi. of respondents are light internet users and 27% of respondents are heavy internet users.. Figure 31: Distribution of Heavy and Light Mobile Internet Users. 35.
(45) Spending on Mobile-phone Bills versus Mobile Internet User Group The following charts illustrate distributions of spending mobile-phone bills comparing across mobile internet user groups. For total spending on bills, the heavy mobile internet users seem to spend more than the light mobile internet users. 44% of the heavy mobile internet users spend more than 800 TWD a month while only 18% of the light mobile internet users spend more than 800 TWD a month. With regard to voice call bills, the heavy mobile internet users also seem to spend more than. 政 治 大 TWD a month for voice calls while 47% of the light mobile internet users spend more than 立 200 TWD a month. the light mobile internet users. 68% of the heavy mobile internet users spend more than 200. ‧ 國. 學. As for mobile internet bills, obviously the heavy mobile internet users spend more than the light mobile internet users. 71% of the light mobile internet users spend less than 199 TWD a. ‧. month on the internet service. 62% of the heavy mobile internet users spend more than 400. n. al. er. io. sit. y. Nat. TWD a month on the internet service.. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. Figure 32: Total Spending on Mobile-phone Bill per Month. 36.
(46) Figure 33: Voice Call Spending on Mobile-phone Bill per Month. 立. 政 治 大. ‧. ‧ 國. 學 er. io. sit. y. Nat. al. n. Figure 34: Mobile Internet Bill per Month. Ch. engchi. i n U. v. Intention to Subscribe for 4G LTE versus Mobile Internet User Group Figure 35 illustrates intention to subscribe for 4G LTE service for different mobile internet user groups. It’s obvious that the heavy mobile internet user group has significantly higher intention score to subscribe than the light mobile internet user group.. Figure 35: Intention to Subscribe for 4G LTE Mean Score of Heavy and Light Mobile Internet Users. 37.
(47) Willingness to Pay More versus Mobile Internet User Group Figure 36 shows comparisons willingness to pay more for each feature between light mobile internet user group and heavy mobile internet user group. It’s obvious that heavy mobile internet users are willing to pay more for some particular features. Internet service quality and speed seems to be very important to this user group so that they definitely pay more for better service quality. Besides, they tend to be more willing to pay for better network coverage voice call quality, and rate plan than the light mobile internet user group.. 立. 政 治 大. ‧. ‧ 國. 學. n. er. io. sit. y. Nat. al. i n U. v. Figure 36: Willing to Pay More for Better Carrier Features of Heavy and Light Mobile Internet Users. Ch. engchi. Prices Acceptance versus Mobile Internet User Group Figure 37 discusses prices acceptance across mobile internet user groups. As explained earlier in Chapter 7.5, the survey participants are randomly separated into two groups answering to the two different questionnaire forms. Cell I participants saw lower price package of 4G LTE pricing at 888 NT a month. Cell II participants saw higher price package pricing at 1,888 NT a month.. 38.
(48) Lite Internet User. Heavy Internet User 74. 64. 63. 62 38. 37. 36 26. Would not subscribe Would subscribe Would not subscribe Would subscribe Cell I (Low price package). Cell II (High price package). 政 治 大. Figure 37: Prices Acceptance of Heavy and Light Mobile Internet Users. 立. As shown on the left side of the chart for Cell I participants, 64% of the heavy mobile internet. ‧ 國. 學. users would subscribe for 4G LTE but only 36% of the light mobile internet users answered that they would subscribe for 4G LTE.. ‧. On the other hand for Cell II participants in the right side of the chart, only 37% of the heavy. y. Nat. mobile internet users and 26% of the light mobile internet users answered that they would. er. io. sit. subscribe for 4G LTE.. This means that while the heavy mobile internet users are really interested to subscribe for 4G. n. al. Ch. i n U. v. LTE service, price is still an important factor. Too high price might lead to less people. engchi. subscribe for. As discussed earlier, 44% of the heavy mobile internet users spend more than 800 TWD a month. The low price package shown for Cell I participants is 888 TWD a month which a bit higher than their current monthly bills. Many people in this heavy mobile internet user group are willing to pay a bit more but not to that high price of the high price package, 1888 TWD a month. The lower price package is still much more appealing to the heavy mobile internet users. Most probably 1,888 TWD a month package is too expensive for Taiwan mobile market.. 39.
(49) 7.7.. Carrier Switching Analysis. According to the survey data, it’s noticeable that there are more respondents choosing ChungHua Telecom as their preferable 4G LTE carrier and fewer respondents choosing Taiwan Mobile and Far EasTone. This part of the analysis discusses carrier switching patterns and factors influencing the carrier switching behavior by comparing the current carriers with the preferable 4G LTE carriers.. 政 治 大. 立. ‧. ‧ 國. 學. Figure 38: Current Carrier and Preferable 4G LTE Carrier Distributions. sit. y. Nat. n. al. er. io. Carrier Switching in 4G LTE. Ch. i n U. v. Table 2 illustrates amounts of the respondents in each current mobile phone carriers. engchi. comparing with their preferable 4G LTE carriers in percentage. As can be seen from the table, most of the current ChungHua Telecom subscribers accounted for 95% prefer to subscribe for 4G LTE from the same carrier. On the other hand, fewer percent of other carriers’ subscribers prefer to subscribe for the same carrier; 65% of Tawian Mobile, 52% of Far EasTone, and 47% of Vibo current subscribers. It’s obvious that most of the people who plan to change to other carriers in 4G LTE tend to subscriber for ChungHua Telecom rather than other carriers. As can be seen from the table, 32% of Taiwan Mobile, 42% of Far EasTone, and 41% of Vibo current subscribers plan to switch to ChungHua Telecom in 4G LTE. This indicates that ChungHua Telecom probably has better image than other carriers in terms of innovations and network quality.. 40.
(50) Table 2: Current Carrier and Preferable 4G LTE Carrier Distribution Preferable 4G LTE carrier (%) CHT. TWM. FET. Vibo. CHT. 95. 2. 1. 1. TWM. 32. 65. 2. 0. FET. 42. 5. 52. 0. Vibo. 41. 0. 6. 47. Current mobilephone carrier (%). 政 治 大 Satisfactions towards Current 立 Carriers versus Carrier Switching. ‧ 國. 學. To find out major causes users discontinuing the service and switching to the other carriers, satisfactions towards the current carriers were analyzed. This section discusses satisfactions. ‧. towards the current mobile carriers, comparing between mobile users who plan to switch to other carriers and the one who plan to use the same carriers in 4G LTE. Figure 39 shows a. Nat. sit. y. comparison of satisfactions level towards mobile carrier features. It’s obvious that the. er. io. satisfactions levels of those who want to switch to other carriers are significantly lower than the ones who plan to subscribe for the same carriers, especially towards network coverage,. n. al. Ch. i n U. v. voice call quality, data service speed, and customer service and support.. engchi. It’s proved that these features are crucially important for mobile carriers. The poor network quality, voice call quality, slow internet speed, unsatisfying customer service and support can influence mobile users discontinue their subscription and subscribe for other carriers instead.. 41.
(51) 治 政 Non-switch Carrier Users Figure 39: Satisfaction Levels of Switch and大 立 ‧ 國. 學. Reasons for Subscribing to the Current Carriers versus Carrier Switching To understand the reasons for subscribers staying with the same carriers or switch to other. ‧. carriers, attitudes of respondents when subscribing to the current carriers were analyzed.. sit. y. Nat. Figure 40 illustrates a comparison between carrier-switching users and non-switching users in 4G LTE. As can be seen in the chart, the most common reasons for choosing the carriers of. io. er. those who plan to use the same carriers are cheaper to call boyfriend, girlfriend, husband, and. al. n. v i n C h to switch to other common reasons of those who plan e n g c h i U carriers are cheaper rate plan, and wife and recommended by friends for best network quality. On the other hand, the most. cheaper prices of handsets. For those who plan to subscribe for other carriers in 4G LTE, network quality reputation doesn’t seem to be an important influence when subscribing to their current carrier.. 42.
(52) 政 治 大. Figure 40: Reasons for Subscribing to the Current Carriers of Switch and Non-switch Carrier Users. 立. ‧ 國. 學. Figure 41 illustrates years of subscription of the current carriers comparing between carrierswitching users and non-switching users. It’s obvious that non-switching users tend to use the. ‧. current carriers longer than those who plan to switch to other carriers.. y. Nat. These findings indicate that cheaper monthly rate plan and cheaper handset prices could be. sit. very appealing to the customers. It may help to attract more subscribers to the carriers.. al. n. important to retain subscribers in mobile carriers.. Ch. engchi. er. io. However, subscribers may not stay with the carriers. Network quality reputation is more. i n U. v. Figure 41: Years of Subscriptions of Switch and Non-switch Carrier Users. 43.
數據
![Figure 6: Operator Challenges – The Widening Gap between Traffic and Revenue [7]](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/9libinfo/8320626.175016/20.893.128.809.382.932/figure-operator-challenges-widening-gap-traffic-revenue.webp)
相關文件
There is a growing recognition that China will change the world, not only economically, but also politically, intellectually, ideologically and culturally...
Doing-undoing (the capacity not only able to use a process to get to a goal, but also to understand the process well enough to work backward from the answer to the starting
On the contrary, apart from the 18.95% decrease of the price index of Education, reduced charges for mobile phone services and lower rentals for housing drove the price indices
Shih, “On Demand QoS Multicast Routing Protocol for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks”, Special Session on Graph Theory and Applications, The 9th International Conference on Computer Science
Provide all public sector schools with Wi-Fi coverage to enhance learning through the use of mobile computing devices, in preparation for the launch of the fourth IT in
Provide all public sector schools with Wi-Fi coverage to enhance learning through the use of mobile computing devices, in preparation for the launch of the fourth IT in
• A formal usage policy and procedures should be in place, and appropriate security measures should be adopted to protect against the risks of using mobile computing and
However, in the mobile tags identification, tags do not have the frame size of the current read cycle immediately at the time of the tag arrives at the reader