行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫 成果報告
空氣負離子對生物氣膠殺菌及去除效率之研究
計畫類別: 個別型計畫 計畫編號: NSC93-2211-E-002-028- 執行期間: 93 年 08 月 01 日至 94 年 07 月 31 日 執行單位: 國立臺灣大學環境工程學研究所 計畫主持人: 李慧梅 共同主持人: 李芝珊 計畫參與人員: 吳致呈 報告類型: 精簡報告 處理方式: 本計畫可公開查詢中 華 民 國 94 年 11 月 4 日
行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫成果報告
空氣負離子對生物氣膠殺菌及去除效率之研究
Germicidal and Removal Efficiencies of Bioaerosols using Negative Air Ions計畫編號:NSC 93-2211-E-002-028
執行期限:93 年 8 月 1 日至 94 年 7 月 31 日
主持人:李慧梅 國立台灣大學環境工程學研究所
共同主持人:李芝珊 國立台灣大學環境衛生研究所
計畫參與人員:吳致呈 國立台灣大學環境工程學研究所
一、中英文摘要 本研究探討空氣負離子(NAIs)對生物氣 膠之移除與殺菌效能。生物氣膠分別以兩種 細菌(Escherichia coli (E. coli), Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis) endospores)與兩種真菌(spores ofPenicillium citrinum (P. citrinum), yeast cells of Candida famata (C. famata) var. flareri)作為實
驗之標的。實驗之NAIs 利用負極高壓放電產
生(5×105 ions cm-3),放電電壓為 10.0 kV。反 應器中的放電裝置以dark discharge 設計,用
以防止 O3 與 NOx副產物之產生。本研究分
別利用APS (aerodynamic particle sizer)與高速 衝擊器(AGI-30)探討空氣負離子對生物氣膠 之移除效能與殺菌效能。實驗結果顯示 NAIs 對四種生物氣膠之移除效率隨生物氣膠在空 氣負離子反應器中的停留時間增加而增加, 例如E. coli 在停留時間為 3.1, 6.2, 7.8, 10.4 與 15.5 分鐘之移除效率分別為 12.5, 33.8, 42.1, 68.2 與 80.1%。空氣負離子對四種生物氣膠之 移除效能顯示。B. subtilis endospores > E. coli
> spores of P. citrinum ≈ yeast cells of C.
famata 。 本 研 究 以 survival factor (SF),
[(Csurvial/Cunremoval)NAIs/(Csurvial/Cunremoval)without_NAIs] 評估空氣負離子對生物氣膠之殺菌效能。SF 小於1 或趨近於 1,分別代表殺菌效能顯著或 不具殺菌效能。實驗結果顯示整體實驗之 SF 為0.96 ± 0.19,表示空氣負離子對生物氣膠不 具有有效的殺菌效能。此外,實驗結果顯示 相對溼度(30 至 70%)對於空氣負離子對生物 氣膠的移除以及殺菌效能並沒有顯著的影 響。本研究結果顯示空氣負離子對生物氣膠 的控制機制,主要為空負離子使生物氣膠帶 電而加以移除。 關鍵詞:空氣負離子、負極針尖放電、生物 氣膠、殺菌率、移除率 Abstract
Although negative air ionizers have been used in indoor air cleaning, little study have been done on the elimination of bioaerosols by negative air ions (NAIs). This study investigated the removal and germicidal effects of NAIs on bioaerosols. Bioaerosols,
Escherichia coli (E. coli), Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis) endospores, spores of Penicillium citrinum (P. citrinum), and yeast cells of Candida famata (C. famata) var. flareri, were
produced at a concentration of approximately 400 number cm-3 by six-jet Collison nebulizer, which aerosolized the suspension of microorganisms in DI water and PBS (phosphate buffer solution). NAIs were generated at a concentration of 5×105 ions cm-3 in an experimental chamber (9.32×10-2 m3) by negative electric discharge at 10 kV. The removal and germicidal efficiencies of bioaerosols were measured by aerodynamic particle sizer (APS) and high velocity impinger (AGI-30), respectively. Bioaerosols collected by AGI-30 was cultured for colony forming unit (CFU) counting. The results indicated that the removal efficiency of bioaerosols was enhanced by NAIs and increased with the retention time of bioaerosol in the experimental chamber. The influence of relative humidity on the removal efficiency of bioaerosol was unobvious at relative humidity between 30 and 70% at 25ºC. The germicidal efficiency of bioaerosols was evaluated by the survival factor (SF),
[(Csurvival/Cunremoval)NAIs/(Csurvival/Cunremoval)without_NAIs]. The SF less than 1 and approach of 1, respectively, showed that the NAIs with and without germicidal efficiency of bioaerosols. The results indicated that the SF was 0.96 ± 0.19 at different retention time and relative humidity, therefore, the germicidal function of NAIs on bioaerosols was invalid. However, the removal effect of NAIs on bioaerosols was the major mechanism for eliminating the bioaerosols using negative air ionizers.
Keywords: Negative air ions; Bioaerosol;
Removal effect; Germicidal effect
二、緣由與目的 近來警戒日益升高的禽流感、嚴重急性 呼吸道症候群(SARS)、流行性感冒,以及我 國日益上升的兒童氣喘比率等,都與公共場 所、室內環境、大眾運輸工具等空氣中的生 物性氣膠息息相關。Daniels(2002)之研究指出 空氣負離子的應用包含消除室內粒狀物、微 生物、臭味,以及揮發性有機污染物。有關 空氣負離子對生物氣膠的作用,主要來自空 氣 負 離 子 中 的 氧 陰 離 子 自 由 基(superoxide, O2⋅-),與空氣中的生物氣膠進行反應或使其帶
電,而產生移除或殺菌的機制。Wu and Lee (2003)指出空氣負離子能有效的去除室內空 氣中的次微米微粒。Shargawi et al. (1999)的研 究顯示空氣負離子能對一些非氣膠狀態的微 生物具有殺菌的效能。然而目前對於空氣負 離子對生物氣膠的控制,仍然沒有明確的研 究指出其確實的控制效能。因此本研究以空 氣負離子反應器探討空氣負離子與生物氣膠 之反應,釐清空氣負離子對生物氣膠之移除 與殺菌效能。 三、結果與討論 本實驗系統之示意圖如圖 1 所示,整個 實驗系統包含:乾淨空氣及溼度控制系統、 空氣負離子反應器,以及生物氣膠產生系統 (包含:Collison nebulizer、Kr-85 particle charge neutralizer 、 diffusion dryer 與 mass flow controller)。生物氣膠之採樣與量測系統,包
含:aerodynamic particle sizer (APS, model 3310A, TSI, MN, USA)與生物氣膠衝擊器 AGI-30。AGI-30 所採樣的生物氣膠,再經適 當的培養基與培養條件進行培養,並計算可 培養生物氣膠之濃度。
圖1. Illustration of experimental system
實驗結果顯示,一般以 PBS (phosphate buffer solution)緩衝劑,產生生物氣膠之方 法,無法利用 APS 量測生物氣膠之濃度。如 圖2 所示,使用 PBS 當作微生物之懸浮溶液, 會產生大量 PBS 乾燥所形成的氣膠,因而無 法區分出生物氣膠與 PBS 氣膠。本研究以去 離子水懸浮微生物,來產生生物氣膠,可以 解決PBS 氣膠之干擾,因而能有效運用 APS 直接偵測生物氣膠之濃度。 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 0 1 2 3 4 5 particle size (µm) par tic le conc net ra tion ( num ber cm -3 ) . . phosphate buffer solution (PBS) PBS with E. coli bioaerosol
圖2. Particle size distribution of PBS and PBS with bioaerosol E. coli
此外,以去離子水懸浮微生物產生生物 氣膠之方法,於本實驗中對產生生物氣膠之 活性,並無明顯之影響。然而有關空氣負離
子對生物氣膠之殺菌實驗,則分別使用 PBS 與去離子水做為微生物之懸浮溶液以作為實 驗結果之比對。 (1) E. coli 空氣負離子與生物氣膠之反應,在連續 式空氣負離子反應器中進行。空氣負離子對 生物氣膠移除效能之探討,利用 APS 量測生 物氣膠在空氣負離子作用下,生物氣膠濃度 之變化。下圖3 顯示,生物氣膠 E. coli 在與 空氣負離子作用前,以及與空氣負離子作用 後粒徑分布的變化。實驗結果顯示,在空氣 負離子之作用下,生物氣膠之濃度隨空氣負 離子作用之時間逐漸下降,約於空氣負離子 操作5 分鐘之後,生物氣膠 E. coli 之粒徑分 布變化在連續式反應器中逐漸達到穩定。 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 0.4 0.9 1.4 1.9 2.4 particle size (µm) pa rt ic le c onc en tr at ion ( num be r c m -3 ) . .
DI water with E. coli bioaerosol NAIs emission 1 min NAIs emission 2 min NAIs emission 3 min NAIs emission 5 min NAIs emission 10 min NAIs emission 20 min
圖3. Particle size distribution of bioaerosol E.
coli with and without NAIs emission
空氣負離子對生物氣膠總濃度之移除效 能評估,依據如下圖 4 之單次實驗結果進行 分析與計算。如下圖 4 所示,釋放空氣負離 子之前,總生物氣膠濃度約為 348 number cm-3。經釋放空氣負離子1 分鐘之後,總生物 氣膠濃度降為238 number cm-3,去除效率為 31.6%;釋放空氣負離子達 2 分鐘之後,總生 物氣膠濃度降低至170 number cm-3;去除效 率為51.1%。當操作空氣負離子產生器 5 分鐘 之後,總生物氣膠濃度趨於穩定,約為 72.0 number cm-3,去除效率約達到79.3%。此一單 次實驗,進行至22 分鐘之後關閉空氣負離子 產生器,實驗結果顯示總生物氣膠濃度逐漸 上升。此一現象並非生物氣膠之再揚起,而 是由於本實驗之空氣負離子反應器為連續性 反應裝置,在關閉空氣負離子產生器之後, 生物氣膠繼續穩定持續流入反應器。 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
reaction time (minute)
bi oa er os ol c onc en tr at io n (num be r c m -3 ) .
. DI water with bioaerosol E. coli under NAIs emission NAIs genertator turned off
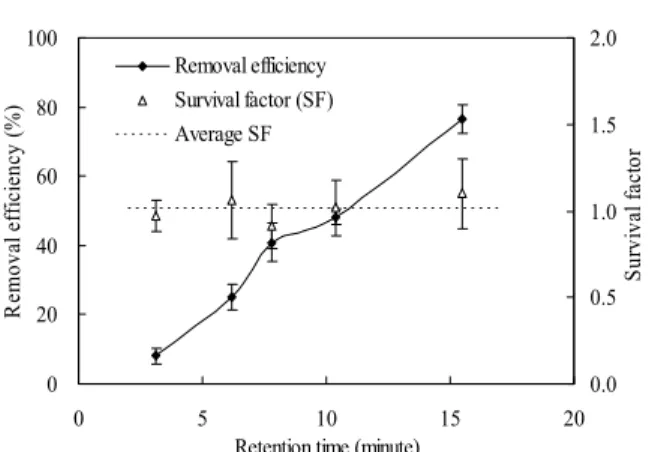
圖4. Bioaerosol E. coli concentration versus reaction time 空氣負離子對生物氣膠之殺菌效能,以 Survival Factor (SF)進行評估。SF 之定義如下 式Eq. (1)所示: s withoutNAI unremoval survival NAIs unremoval survival C C C C SF ) / ( ) / ( = (1) SF 為 0~1 之無因次因子,SF 越小表示殺菌效 能越高,SF 趨近於 1 則表示無殺菌效能。 (Csurvival/Cunremoval)NAIs 表示在空氣負離子反應 下經由 AGI-30 所得到的”可培養生物氣膠濃 度” Csurvival 除以空氣負離子反應下經由 APS 所 得 到 的” 未 移 除 之 生 物 氣 膠 濃 度 ” Cunremoval。(Csurvival/Cunremoval)withoutNAIs表示在空 氣負離子未作用下經由 AGI-30 所得到的”可 培養生物氣膠濃度” Csurvival 除以空氣負離子 未作用下經由 APS 所得到的”未移除之生物 氣膠濃度” Cunremoval。本研究以SF 來評估,未 被空氣負離子移除的生物氣膠,其被NAIs 殺 菌的程度。 空氣負離子對生物氣膠 E. coli 之移除效 能與殺菌效能,如下圖 5 所示。圖 5 顯示空 負離子濃度5×105 ions cm-3,溼度30%,在不 同停留時間下生物氣膠 E. coli 之移除效率與 SF 值。實驗結果顯示,生物氣膠 E. coli 在空 氣負離子反應器中的停留時間越長,其移除 效率隨之增加。當停留時間為 15.5 分鐘時,
其移除效率達到 80.1%。另外,SF 的平均值 為 0.93。SF 值並無隨著停留時間之增加而明 顯下降,如此顯示生物氣膠 E. coli 在經過空 氣負離子 15.5 分鐘的反應之後,仍然沒有明 顯的殺菌效能。 0 20 40 60 80 100 0 5 10 15 20
Retention time (minute)
R em oval ef fi ci ency ( % ) . 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 S ur vi val f act or . Removal efficiency Survival factor (SF) Average SF
圖5. Removal efficiency and SF of Bioaerosol E.
coli at different retention time in NAIs
reaction chamber (2) B. subtilis endospores 空 氣 負 離 子 對 生 物 氣 膠 B. subtilis endospores 之移除效能與殺菌效能,如下圖 6 所示。圖 6 顯示空負離子濃度 5×105 ions cm-3,溼度30%,在不同停留時間下生物氣膠 B. subtilis endospores 之移除效率與 SF 值。實 驗結果顯示,生物氣膠B. subtilis endospores 在空氣負離子反應器中的停留時間越長,其 移除效率隨之增加。停留時間為3.1、6.2、7.8、 10.4 與 15.5 分鐘時,其移除效率分別為 21.6、 43.7、55.0、72.2 與 88.9%。另外,SF 值的平 均值為 0.97。SF 值並無隨著停留時間之增加 而明顯下降,如此顯示生物氣膠 B. subtilis endospores 經過空氣負離子 15.5 分鐘的反 應,仍然沒有明顯的殺菌效能。實驗結果顯 示空氣負離子對B. subtilis endospores 的移除
效能比E. coli 高。B. subtilis endospores 的 SF
值略高於E. coli 之 SF 值。 (3) spores of P. citrinum 空 氣 負 離 子 對 生 物 氣 膠 spores of P. citrinum 之移除效能與殺菌效能,如下圖 7 所 示。圖7 顯示 NAIs 濃度 5×105 ions cm-3, 0 20 40 60 80 100 0 5 10 15 20
Retention time (minute)
R em oval ef fi ci ency (% ) . 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 S ur vi val f act or . Removal efficiency Survival factor (SF) Average SF
圖6. Removal efficiency and SF of Bioaerosol B.
subtilis endospores at various reten- tion
time in NAIs reaction chamber
溼度30%,在不同停留時間下生物氣膠 spores of P. citrinum 之移除效率與 SF 值。實驗結果 顯示,生物氣膠spores of P. citrinum 在空氣負 離子反應器中的停留時間越長,其移除效率 隨之增加。停留時間為 3.1、6.2、7.8、10.4 與15.5 分鐘時,其移除效率分別為 7.6、25.9、 36.3、50.7 與 73.0%。另外,SF 值的平均值為 0.94。SF 值並無隨著停留時間之增加而明顯 下降,如此顯示生物氣膠spores of P. citrinum 經過空氣負離子 15.5 分鐘的反應,仍然沒有 明顯的殺菌效能。實驗結果顯示空氣負離子 對spores of P. citrinum 的移除效能比 E. coli 低。spores of P. citrinum 的 SF 與 E. coli 之 SF 值相近。 0 20 40 60 80 100 0 5 10 15 20
Retention time (minute)
R emo val ef fi ci en cy ( % ) . 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 S ur vi val f act or . Removal efficiency Survival factor (SF) Average SF
圖7. Removal efficiency and SF of Bioaerosol, spores of P. citrinum, at various retention time in NAIs reaction chamber
(4) yeast cells of C. famata
空氣負離子對生物氣膠 yeast cells of C.
示。圖8 顯示空負離子濃度 5×105 ions cm-3,
溼度30%,在不同停留時間下生物氣膠 yeast
cells of C. famata 之移除效率與 SF 值。實驗結 果顯示,生物氣膠yeast cells of C. famata 在空 氣負離子反應器中的停留時間越長,其移除 效率隨之增加。停留時間為 3.1、6.2、7.8、 10.4 與 15.5 分鐘時,其移除效率分別為 8.1、 25.1、40.9、48.2 與 76.6%。另外,SF 值的平 均值為 1.01。SF 值並無隨著停留時間之增加 而明顯下降,如此顯示生物氣膠yeast cells of C. famata 經過空氣負離子 15.5 分鐘的反應, 仍然沒有明顯的殺菌效能。實驗結果顯示空 氣負離子對yeast cells of C. famata 的移除效 能與spores of P. citrinum 相近。yeast cells of C.
famata 的 SF 值為 4 種生物氣膠中最高,SF 值1.01 是由於實驗偏差所致,理論上 SF 值 ≤ 1。 0 20 40 60 80 100 0 5 10 15 20
Retention time (minute)
R emo va l ef fi ci en cy ( % ) . 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 S urv iv al fa ct or . Removal efficiency Survival factor (SF) Average SF
圖8. Removal efficiency and SF of Bioaerosol, yeast cells of C. famata, at various reten- tion time in NAIs reaction chamber
(5) Reaction of NAIs and bioaerosols
本研究之研究結果顯示空氣負離子對生 物氣膠之作用機制,主要為空氣負離子致使 生物氣膠帶電,進而使得帶有大量負電荷之
生物氣膠自氣相中移除,且對 4 種生物氣膠
的移除效能為B. subtilis endospores > E. coli >
spores of P. citrinum ≈ yeast cells of C.
famata。Wu and Lee (2003) 的研究指出,空
氣負離子對室內懸浮微粒具有良好的去除效 能。因此生物氣膠與非生物氣膠一樣,在空 氣負離子的作用下具有移除的效能。在空氣 負離子對生物氣膠之殺菌效能方面,研究結 果顯示,空氣負離子對生物氣膠的殺菌效能 不明顯(反應時間 15.5 分鐘以內)。雖然空氣負 離子的主要組成為具有反應性之氧陰離子自 由基(superoxide, O2⋅-),且具有氧化揮發性有 機污染物的能力(Wu and Lee, 2004)。然而空
氣負離子面對粒徑約為 1 µm 左右的生物氣 膠,其氧化能力並無法在實驗的反應時間之 內破壞生物氣膠的繁殖能力。另一方面如果 生物氣膠與NAIs 的反應時間增加,也許具有 殺菌效能,然而生物氣膠在長時間下原本就 會失去活性,因此長時間的反應實驗則失去 意義。 雖然空氣負離子對於生物氣膠不具有有 效的殺菌效能,然而空氣負離子對生物氣膠 的移除機制,已經足以使空氣負離子控制生 物氣膠之技術,具有生物氣膠感染控制的效 能。生物氣膠只要能經由空氣負離子之作用 而自氣相中移除,便能避免生物氣膠對人體 健康的衝擊,並且防治在防疫上不易控制的 飛沫傳染。 四、計畫成果自評 本計畫針對空氣負離子與四種生物氣膠 之移除作用與殺菌效能,進行深入的研究。 研究成果能作為相關控制技術之應用基礎。 此研究之成果目前已投稿於A&WMA 國際研
討會(Wu, C.C. et al., Removal and germicidal effcts of negative air ions on bioaerosol.),並準
備投稿於相關的SCI 期刊。
五、參考文獻
[1] Daniels, S.L., 2002. On the ionization of air for removal of noxious effluvia. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 30, 1471-1481.
[2] Shargawi, J.M., Theaker, E.D., Drucker, D.B., MacFarlane, T., Duxbury, A.J., 1999. Sensitivity of Candida albicans to negative air ion streams. Journal of Applied Microbiology 87, 889-897. [3] Wu, C.C., Lee, G.W.M., 2003. The temporal
aerosol size distribution in indoor environment with negative electric discharge. Journal of Aerosol Science 34 (Suppl. 2), S999-S1000. [4] Wu, C.C., Lee, W.M.G., 2004. Oxidation of
volatile organic compounds by negative air ions. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 6287-6295.