【臺灣臨床藥學雜誌】投稿封面
中文
英文
標題
Colistin 之臨床使用評估 Clinical Medication Use Evaluation of Colistin簡題
Colistin 之靜脈注射及霧化吸入給藥途徑之臨床有效性和安 全性
The clinical efficacy and safety of Colistin administered by intravenous and aerosolized inhalation routes
作者
姓名
林旭志1,張秀芳1,鄭清連1,
劉彥吟1,陳子殷1,吳錦生1, 2,* Hsu-Chih Lin
1, Hsiu-Fang Chang1,
Cing-Lian Jheng1, Yen-Yin Liu1, Tzu-Yin
Chen1, Chin-Sheng Wu1, 2,*
作者
單位
1 李綜合醫療社團法人大甲李綜 合醫院藥劑科 2 中國醫藥大學藥用化妝品學系1 Department of Pharmacy, Dajia Lee’s
General Hospital, Lee’s Medical Corporation
2 Department of Cosmeceutics, China
Medical University
通訊作者
稿件聯絡人
姓名
吳錦生 吳錦生服務
單位
中國醫藥大學藥用化妝品學系 中國醫藥大學藥用化妝品學系地址
台中市 40402 北區學士路 91 號中 國醫藥大學藥用化妝品學系 台中市 40402 北區學士路 91 號中國醫藥大學藥用化妝品學系電話
04-22053366 轉 5305 04-22053366 轉 5305傳真
04-22078083 04-22078083行動
0921-336388 0921-336388林旭志1,張秀芳1,鄭清連1,劉彥吟1,陳子殷1,吳錦生1, 2,* 1 李綜合醫療社團法人大甲李綜合醫院 藥劑科 2 中國醫藥大學 藥用化妝品學系
摘
要
本研究以回溯性分析某區域教學醫院自2011 年 1 月至 5 月間接受 Colistin 治療的住 院病患。評估病患接受治療後30 天的存活率、臨床適應症、用法/用量、療效及副作用。共 收案33 名患者(男性 22 名,女性 11 名),平均年齡 78.5±12.4 歲。其中 13 名(39.4%)達成 30 天存活率,19 名(57.6%)病危出院或死亡,1 名(3%)因轉院而無法評估。患者疾病之 嚴重度及年齡也會影響30 天存活率的評估。患者感染症為肺炎(28 名,84.8%)、敗血症 (4 名,12.1%)、泌尿道感染(1 名,3.0%);細菌報告有 28 名(81.8%)為多重抗藥性鮑氏 不 動 桿 菌 (multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, MDRAB) ; 平 均 用 藥 天 數 11.7(±5.7)天。13 名(39.4%)使用霧化吸入(劑量皆為 66.8 mg q12h);靜脈注射有 20 名(60.6%),其中 5 名腎功能正常者用 66.8 mg q8h、10 名腎功能正常者用 66.8 mg q12h、3
名腎功能異常者用66.8 mg qd、2 位腎功能異常者用 33.4 mg q12h。患者中有 7 名之 Crea
值呈上升(21.2%),其中靜脈注射 5 名(25%)、霧化吸入 2 名(13.2%),兩者副作用發生 率並無顯著性差異(P>0.05)。患者中有 21 名(63.6%)達到治療效果或改善。研究顯示 colistin 是 治 療 碳 青 黴 烯 抗 藥 性 鮑 氏 不 動 桿 菌 (carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, CRAB)和其他高度抗藥性細菌的重要抗生素,雖已被設定為後線的管制性抗 生素,但唯有在有效的管理下使用,才能遏止抗藥性菌株的出現。
關鍵詞:Colistin、多重抗藥性鮑氏不動桿菌(multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, MDRAB)、碳青黴烯抗藥性鮑氏不動桿菌(carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, CRAB)
引
言
Colistin又名polymyxin E,屬於多黏菌素類抗生素(polymyxin antibiotics),是一沉寂 已久,且價格便宜的老藥,因多重抗藥性菌的出現,賦予colistin重新進入臨床使用的 必要性。
回顧相關文獻發現,國內、外因為鮑氏不動桿菌(Acinetobacter baumanni, 簡稱AB 菌)導致院內感染的案例顯著增加[1-2]。在美國,AB菌是加護病房患者院內感染菌血症 常見致病菌種的第10名,也是導致死亡的第3名[3]。在台灣,AB菌的感染,從1999年每 一萬人有25人增加到2003年的每一萬人有55人[1]。多重抗藥性菌感染通常會造成嚴重的 不良結果,研究顯示:會延長13.4天的住院天數、增加3,758美元的住院費用,且30天的
死亡率達49%[4]。 Colistin在1960年到1980年初最常被使用,但因具有毒性副作用(主要是腎毒性、神 經肌肉阻斷和神經毒性),導致被臨床使用者所遺棄。近年來研究發現colistin會作用在 革蘭氏陰性桿菌細胞膜上的磷脂質(phospholipids)和脂多醣(lipopolysaccharides),經由 改變細胞膜的通透性,使細胞質內容物流出而達到殺菌效果。研究顯示:colistin對AB 菌具有極佳的感受性,可用來治療假單胞菌屬(Pseudomonas)及其他革蘭氏陰性菌引起 的慢性肺部感染,是治療AB菌和其他高度抗藥性細菌的重要藥物[5]。 以研究醫院為例,Colistin對於多重抗藥性菌分離出的綠膿桿菌(P. aeruginosa)和 AB菌株具有感受性。然而,使用colistin來治療多重抗藥性鮑氏不動桿菌(multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, MDRAB)/碳青黴烯抗藥性鮑氏不動桿菌(carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, CRAB)會受限於其腎毒性和神經毒性,故臨床上使用 霧化吸入做為替代給藥途徑。本研究目的在評估使用colistin來治療多重抗藥性菌所引起 的感染,評估其有效性和安全性。
材料與方法
背景
本研究以中部某區域教學醫院為例。評估的方法為採用回溯性的藥物使用評估方法 取樣期間為2011 年 1 月 1 日至 5 月 31 日止。取樣對象為研究醫院的住院患者。收案對象
收案對象為接受colistin 治療感染症,且治療期間必須大於 48 小時的嚴重感染症患 者 。 以 colistin 治 療 嚴 重 感 染 症 必 須 被 診 斷 具 有 全 身 性 發 炎 反 應 症 候 群 (systemic inflammatory response syndromes, SIRS),並有做細菌培養,且對 colistin 具有感受性的
感染症。SIRS 的定義為存在有以下兩種以上的臨床徵兆:體溫大於 38℃或小於 36℃; 心跳速率大於每分鐘90 下;呼吸頻率大於每分鐘 20 次或 PaCO2小於32mmHg;白血球 數目大於12,000cells/L 或小於 4,000cells/L。收案對象必須排除無充份資訊可評估其感染 症狀或是治療結果者。
資料收集
資料收集主要來自於病歷上的記載,查閱,並收錄病歷上記載與colistin 使用相關 的病患資訊及治療結果,包括:年齡,性別,病患現存的疾病,感染的來源或器官, 感染的診斷,免疫功能缺損的狀況,住院治療的天數,呼吸器的使用,抗生素的合併 使用,使用的劑量、途徑、頻率與天數,與感染症相關的臨床檢驗數據和治療結果。治療結果的評估
治療結果主要評估病患接受colistin 治療後 30 天的死亡率和推論 colistin 治療成功 與否(患者的感染症狀被治癒)。治癒可分為臨床症狀的治癒或是微生物學的治癒。臨床 症狀的治癒指的是感染的症狀或徵候最終被抗生素所治療。微生物學的治癒指的是經由 再次的細菌培養追蹤證實感染的菌株被消滅。另外,評估colistin 治療所造成的副作用,統計分析
數值資料的呈現依其特性採用平均值、平均值和標準差(mean ± SD)的表示方法。單 變量分析,使用學生T 檢定(Student’s t-test)或曼-惠特尼 U 考驗法(Mann-Whitney U test)
來比較每一個群體的平均數值是否有顯著差異。當p-value<0.05 時在統計上具有顯著的 意義。
結
果
病患特性分析
收集2011 年 1 月 1 日到 5 月 31 日期間研究醫院符合使用 colistin 治療感染症患者 共33 名個案。33 名接受 colistin 治療感染症的患者,主要感染症為肺炎(28 名,84.8%)、 敗血症(4 名,12.1%)、泌尿道感染 (1 名,3.0%);細菌學分析,有 28 名(81.8%)為CRAB、2 名(6.1%)為克雷伯氏肺炎菌(Klebsiella pneumoniae)及 3 名(9.1%)為綠膿桿菌; 平均用藥天數11.7(±5.7)天;平均年齡為 78.5(±12.4)歲,其中男性約占 66.7%(Table 1)。 依用法/用量分析:33 名接受 colistin 治療感染症的患者,有 13 名(39.4%)使用霧化吸入 (劑量皆為 66.8mg q12h);靜脈注射有 20 名(60.6%),其中 5 名腎功能正常者用 66.8mg q8h、10 名腎功能正常患者使用 66.8mg q12h、有 3 位腎功能異常者使用 66.8mg qd、2 位 腎功能異常患者使用33.4mg q12h (Table 2)。
臨床結果評估
整體死亡率評估,33 名患者中有 13 名(39.4%)患者達成 30 天存活率,19 名患者(57.6%)病危出院或死亡,另 1 名患者(3%)因轉院無法評估治療結果(Table 1)。使用 colistin 者多為病況嚴重或有多重感染的病患,其疾病嚴重度、合併症及年齡亦會影響 30 天存活率的評估。 治療效果評估,33 名患者中有 21 名(63.6%)達到治療效果或改善;19 名(57.6%)患 者達到臨床治癒,21 名(63.6%)患者達到微生物治癒(菌種消除) (Table 1)。 副作用評估,33 名患者中有 7 名(21.2%)之 Crea 值呈上升,其中靜脈注射有 5 名 (25%)平均上升 0.3±0.6mg/dL、吸入有 2 名(13.2%)平均上升 0.1±0.3mg/dL,兩者副作用 發生比率並無顯著性差異(p>0.05) (Table 2)。 若針對使用colistin 來治療 CRAB 菌做討論,33 名收案的患者中共有 28 名感染 CRAB 菌,9 名(32.1%)患者死亡未完成治療,19 名(67.9%)患者治癒。使用 colistin 治癒 的平均給藥日數為13.8±5.2 天 (Table 3)。
結
論
院內感染AB 菌,特別是 CRAB 菌,具有很高的致死率。Hello 等人的研究顯示: 感染CRAB 菌比起其他多重抗藥性菌種具有高比率的 30 天死亡率[6]。研究顯示: CRAB 菌 感 染 的 死 亡 率 約 32-34%[7] , 這 個 論 述 與 本 研 究 的 結 果 似 乎 是 相 呼 應 的 (32.1%)。研究顯示:選擇適當的抗生素來治療 AB 菌的感染可以有效的降低感染 CRAB 菌的死亡率[8]。經由本研究調查顯示,使用 colistin 可以有效治療 CRAB 菌和其他高度 抗藥性細菌達63.6%。 Colistin 主要由腎臟代謝,故在腎臟功能不良之病患需做劑量調整量。主要的副作用為腎毒性及神經毒性,神經毒性是可以恢復的。為了避免這些副作用,其他替代的給 藥方式,如吸入給藥及腦室內給藥已為臨床上所使用。其中吸入型colistin 已經被報告, 用來減少多重抗藥性革蘭氏陰性菌在囊胞性纖維症(Cystic fibrosis, CF)的病患上[9]。經 由本研究顯示:對於腎功能異常的患者只要適當的調整用藥劑量,不論是經由注射給 藥或是吸入給藥對腎功能並無明顯的傷害,且兩者之間並無顯著性的差異。重回臨床的 colistin 是治療 MDRAB/CRAB 和其他高度抗藥性細菌的重要抗生素。目前雖已經被設 定為後線的管制性抗生素,但唯有在有效的管理下使用,才能遏止抗藥性菌株的出現。
參考文獻
1. Hsueh PR, Chen WH, Luh KT. Relationships between antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative bacteria causing nosocomial infections from 1991-2003 at a university hospital in Taiwan. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2005; 26: 463-72.
2. Wadl M, Heckenbach K, Noll I, Ziesing S, Pfister W, Beer J, et al. Increasing occurrence of multidrug-resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from four German University Hospitals, 2002-2006. Infection 2010; 38: 47-51.
3. Wisplinghoff H, Bischoff T, Tallent SM, Seifert H, Wenzel RP, Edmond MB. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 309-17.
4. Kuo LC, Lai CC, Liao CH, Hsu CK, Chang YL, Chang CY, et al. Multidrug-resistant
outcome. Clin Microbiol Infect 2007; 13: 196-8.
5. Charra B, Hachimi A, Nejmi H, Benslama A, Elmdaghri N, Belabbes H, et al. "Colistin and rifampicin in the treatment of nosocomial infections from multiresistant Acinetobacter
baumannii". J Infect 2006; 53 (4): 274-278.
6. Le Hello S, Falcot V, Lacassin F, Mikulski M, Baumann F. Risk factors for carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections at a tertiary care hospital in New Caledonia, South Pacific Scand J Infect Dis 2010; 42: 821-6.
7. Livermore DM, Hill RL, Thomson H, Charlett A, Turton JF, Pike R, et al. Antimicrobial treatment and clinical outcome for infections with carbapenem and multiply-resistant
Acinetobacter baumannii around London. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2010; 35:19-24.
8. Falagas ME, Kasiakou SK, Rafailidis PI, Zouglakis G, Morfou P. Comparison of mortality of patients with Acinetobacter baumannii bacteraemia receiving appropriate and inappropriate empirical therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother 2006; 57: 1251-4.
9. Katz SL, Ho SL, Coates AL. Nebulizer choice for treatment of cystic fibrosis patients with inhaled colistin. Chest 2001; 119, 250-255.
Clinical Medication Use Evaluation of Colistin
Hsu-Chih Lin1, Hsiu-Fang Chang1, Cing-Lian Jheng1, Yen-Yin Liu1, Tzu-Yin Chen1,
Chin-Sheng Wu1, 2,*
1 Department of Pharmacy, Dajia Lee’s General Hospital, Lee’s Medical Corporation 2 Department of Cosmeceutics, China Medical University
ABSTRACT
The aims of this retrospective study were to assess the clinical medication use of colistin in a regional teaching hospital. A total 33 hospitalized patients with infections was included, 28 patients with pneumonia (84.8%), 4 with sepsis (12.1%), and 1 with urinary tract infection (3.0%). The 30-day survival rate was 39.4% (13), 19 patients (57.6%) were discharged in critical condition or death, and 1 (3%) could not be assessed due to transfer. The disease severity and age of patients also affect the 30-day survival rate. The bacterial cultures showed 28 patients (81.8%) were infected from multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (MDRAB). The average medication was 11.7±5.7 days. Thirteen patients (39.4%) were given by aerosolized inhalation (dose: 66.8 mg q12h); 20 (60.6%) were given intravenously wherein 5 of normal renal function at the dose 66.8 mg q8h, 10 of normal renal function at 66.8 mg q12h, 3 of renal dysfunction at 66.8 mg qd, and 2 of renal dysfunction at 33.4 mg q12h. The Crea values of 7 patients (21.2%) were elevated, intravenous injection of 5 (25%) and aerosolized inhalation of 2 (13.2%). Side effects had no significant differences between two routes (p> 0.05). Twenty one patients (63.6%) were cured or improved. Carbapenem-resistant
susceptibility to colistin in this study, Though it has been currently set to as a final-line controlled antibiotic, it should be used under the effective management in order to prevent the emergence of resistant strains.
Key words: Colistin, multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (MDRAB), carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB)
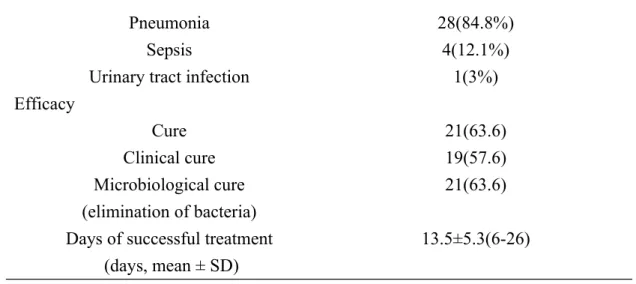
Table 1. Patient characteristics and the treatment outcome of colistin (N=33)
Item Evaluation data, N (%)
Age (years, mean ± SD) 78.5±12.4
Gender
Male 22(66.7)
Female 11(33.3)
Average length of stay (days, mean ± SD)
39.2±23.7(13-133) Colistin treated days (days, mean ± SD) 12.3±5.3(6-26)
Diabetes mellitus 11(33.3)
Cancers 5(15.2)
Ventilator patients 22(66.7)
Patients with clotting abnormalities 7(21.2) Patients with renal dysfunction 19(57.6) Patients with hepatic dysfunction 11(33.3) Source of infection
Lower respiratory tract 27(81.8)
Blood 3(9.1)
Urine 2(6.1)
Other sources 1(3.0)
Infected bacteria
Acinetobacter baumannii, CRAB 28(81.8%)
Klebsiella pneumoniae 2(6.1%)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa 3(9.1%)
Pneumonia 28(84.8%)
Sepsis 4(12.1%)
Urinary tract infection 1(3%)
Efficacy Cure 21(63.6) Clinical cure 19(57.6) Microbiological cure (elimination of bacteria) 21(63.6) Days of successful treatment
(days, mean ± SD)
13.5±5.3(6-26)
Table 2. Comparison the treatment outcome of colistin between intravenous injection and aerosolized inhalation (N=33)
Item Intravenous injection Aerosolized inhalation p-vale
Patient number 20(60.6%) 13(39.4%)
Cured number 11(11/20) 10(10/13) 0.10
Average daily dose 133.6mg (66.8-200.4) 133.6mg(133.6-133.6) 0.5 Average treated days
(days, mean ± SD)
12.5±4.8(6-22) 14.6±5.6(6-22) 0.19
Serum creatinine (Crea) elevated
0.3±0.6 0.1±0.3 0.09
Table 3. Treatment outcome of CRAB infections treated by colistin (N=28)
Item Evaluation data, N (%)
CRAB infections 28
Treatment outcome
Death 9(32.1%)
Average medication days (days, mean ± SD)