行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫 成果報告
多重基因即時定量 PCR 法應用於接受 Glivec 治療的慢性骨
髓性白血病患者療效與預後評估之前瞻性研究
計畫類別: 個別型計畫 計畫編號: NSC92-2314-B-002-177- 執行期間: 92 年 08 月 01 日至 93 年 07 月 31 日 執行單位: 國立臺灣大學醫學院內科 計畫主持人: 唐季祿 共同主持人: 姚明 報告類型: 精簡報告 處理方式: 本計畫可公開查詢中 華 民 國 94 年 6 月 1 日
行政院國家科學委員會補助專題研究計畫 ■成果報告
多重基因即時定量PCR法應用於接受Glivec治療的慢性骨
髓性白血病患者療效與預後評估之前瞻性研究
Multiplex quantitative PCR for the assessment of treatment
response and outcome prediction in chronic myelogenous leukemia
patients receiving Glivec treatment: a prospective study
計畫類別:
■ 個別型計畫
□ 整合型計畫
計畫編號:
NSC-92-2314-B-002-177-執行期間:
92年8月1日至93年7月31日
計畫主持人:唐季祿
共同主持人:姚明
計畫參與人員:
成果報告類型(依經費核定清單規定繳交):
■精簡報告
本成果報告包括以下應繳交之附件:
□赴國外出差或研習心得報告一份
□赴大陸地區出差或研習心得報告一份
□出席國際學術會議心得報告及發表之論文各一份
□國際合作研究計畫國外研究報告書一份
處理方式:除產學合作研究計畫、提升產業技術及人才培育研究計畫、列管
計畫及下列情形者外,得立即公開查詢
□涉及專利或其他智慧財產權,□一年□二年後可公開查詢
II 計畫中文摘要。(五百字以內) 關鍵詞:慢性骨髓性白血病,殘存微量白血病,多重基因即時定量PCR。 慢性骨髓性白血病(CML)為造血幹細胞疾病,帶有染色體9和22移位異常,造成bcr和abl 前致癌基因接合,產生之雜合蛋白帶有異常tyrosine kinase活性,使用特殊的kinase抑 制劑(STI571,Glivec)治療新診斷CML有極高療效 : 96﹪血液緩解率及68﹪染色體緩解 率,少部分病人更得到分子緩解,即時定量RT-PCR可以靈敏地定量白血病細胞,作為療效 評估和偵測微量殘存疾病。本實驗室過去已發展出單一步驟即時定量RT-PCR法,在同一試 管內進行RT及PCR反應,靈敏度達到10-5 與文獻報告使用二階段法相當。然而內在對照基因 GAPDH仍需另外進行定量反應,可能成為定量誤差的一個潛在原因,使用多重基因定量 PCR,應可減少實驗操作及測量誤差,但文獻上尚未有運用於CML報告。 本前瞻性研究收集102位在2001年6月至2004年10月間接受Glivec治療的CML病人,包 括49名慢性期、30名加速期及23名急性期病人。Glivec治療時間平均為19.4月(1~45月), 診斷至Glivec治療時間平均為16月(0~120月)。2004年7月起大部分病人以Glivec做為第一 線治療選擇。 新診斷時之骨髓和血液檢體分別作染色體和RT-PCR分析,開始Glivec治療前後每3個 月收集檢體做MRD分析定量。我們設計多重基因即時定量(multiplex RQ-PCR)法,可在單一 試管中同時放大BCR-ABL和GAPD基因(內在對照基因,以控制RNA品質及總量)。利用不 同螢光探針,同時偵測定量PCR產物,評估發現其靈敏度與準確度均不亞於分開作RQ-PCR 結果。單一步驟即時定量PCR:使用ABI Prism 7700儀器及Taqman EZ RT-PCR Kit,Taqman 螢光性探針以Primer Express軟體設計合成,每次反應均使用K562細胞株作為陽性對照基 因以建立標準曲線,每個檢體至少做2次反應。 研究結果發現血液學完全緩解率分別為慢性期98%、加速期70%、急性期35%,染色體 完全加部分緩解率分別為慢性期70%、加速期58%、急性期75%,基因緩解率(MRD小於-3.0log) 分別為慢性期19%、加速期11%、急性期17%。三年白血病無惡化存活率分別為慢性期93%、 加速期51%、急性期4%,白血病無惡化存活率與染色體及基因緩解率均成相關。慢性期或 加速期病人治療後達到MRD小於-2.0log者,追蹤三年尚無人出現白血病惡化者。急性期病 人即使達到染色體或基因緩解,仍然無法有效避免復發惡化,研究發現其中多人出現 BCR-ABL基因突變。以上結果與最近國外研究報告類似。 本研究成果證實Glivec(Imatinib)對於治療慢性期效果顯著,但是加速期或急性期則 需要合併其他藥物或改用新藥,以提升治療效果。多重基因即時定量PCR分析法可以準確 定量殘存微量白血病,有效評估治療療效,為協助臨床決策判斷之最佳工具。(以上結果 已在2005年台灣血液病學會年會發表,論文撰寫投稿中)
2 計畫英文摘要。(五百字以內)
Keywords:acute myeloid leukemia, minimal residual leukemia, real-time RT-PCR, WT-1 gene.
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a clonal disorder of hematopoietic stem cell characterized by t(9;22), which results in fusion of bcr and abl proto-oncogenes and expression of BCR-ABL chimeric protein with abnormal tyrosine-kinase activity. Inhibition of this kinase activity by STI571 (Glivec) resulted in 96% of hematological remission and 68% cytogenetic remission in newly diagnosed CML. Molecular remission is possible in a few patients. Quantification of t(9;22) carrying cells can be achieved by real-time quantitative RT-PCR (RQ-PCR) assay that is highly sensitive for evaluating treatment response and minimal residual disease (MRD). We had successfully developed one-step RQ-RT-PCR method that integrated RT and PCR reaction in single tube. The assay can detect one abnormal CML cells among 105 normal cells (5-log sensitivity). Amplification of GAPDH control gene was done in separate reaction. Since each PCR reaction has its own kinetics, separate PCR assay for target and control genes can potentially result in inaccurate quantification. Multiplex PCR can further minimize the laboratory procedure and increase the assay accuracy. Whether multiplex RQ-RT-PCR can be applied in detecting MRD in CML has not yet been reported in the literature.
Between June 2001 and October 2004, a total of 102 CML patients had been treated with Imatinib in NTUH, including 49 patients in chronic phase (CP), 30 patients in accelerated phase (AP), and 23 patients in blastic phase (BC). Fifty-two were male and 50 female and the median age was 40 years old (ranges 3-80). The median interval from diagnosis to Imatinib treatment was 16 months (0-120) and median Imatinib duration 19.4 months (1-45). Since July 2004, most patients received Imatinib as first-line drug in early chronic phase.
Results: the complete hematological rate (CHR) was 98% in CP, 70% in AP and 35% in BC patients (p < 0.001). Major cytogenetic remission (MCyR) was achieved in 70% of CP, 58% in AP and 75% in BC patients (p=0.08). However, only a few patients could achieved molecular remission as defined as MRD < -3.0log reduction: 19% in CP, 11% in AP and 17% in BC. (p=0.341). The probability of leukemic progression-free survival (PFS) at 3 years was 93% for CP, 51% for AP and 4% for BC (p<0.001). PFS was also correlated with cytogenetic response and molecular response. For patients treated in CP or AP stagesand had achieved MRD < -2.0log reduction, none had leukemic progression. Cytogenetic or molecular remission in BC stage didn’t prevent disease relapse and progression. Sequencing analysis showed that most of them had acquired mutation at BCR-ABL kinase domain.
In conclusion, Imatinib was highly effective in CML-CP. For advanced stages, higher doses of imatinib or combination with other drugs are needed to improve response and prevent leukemic progression to improve survival. Sequential monitoring of cytogenetic and molecular
1
1. Introduction
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a clonal disorder of hematopoietic stem cell characterized by t(9;22), which results in fusion of bcr and abl proto-oncogenes and expression of BCR-ABL chimeric protein with abnormal tyrosine-kinase activity. Inhibition of this kinase activity by STI571 (Glivec) resulted in 96% of hematological remission and 68% cytogenetic remission in newly diagnosed CML. Molecular remission is possible in a few patients. Quantification of t(9;22) carrying cells can be achieved by real-time quantitative RT-PCR (RQ-PCR) assay that is highly sensitive for evaluating treatment response and minimal residual disease (MRD). We had successfully developed one-step RQ-RT-PCR method that integrated RT and PCR reaction in single tube. The assay can detect one abnormal CML cells among 105 normal cells (5-log sensitivity). Amplification of GAPDH control gene was done in separate reaction. Since each PCR reaction has its own kinetics, separate PCR assay for target and control genes can potentially result in inaccurate quantification. Multiplex PCR can further minimize the laboratory procedure and increase the assay accuracy. Whether multiplex RQ-RT-PCR can be applied in detecting MRD in CML has not yet been reported in the literature.
2. Objectives
The goal of this project is to develop a novel multiplex real-time RT-PCR method to co-amplify the BCR-ABL fusion mRNA and a housekeeping gene (as internal control) as therapeutic monitoring of molecular response to Glivec treatment in CML patients.
The specific aims include:
1) Establishment of optimal condition for multiplex RQ-RT-PCR that can be used for sensitive and accurate quantification of rare targets (such as BCR-ABL in CML) when co-amplification is performed for a relative abundant control gene (such as GAPDH or cyclophilin).
2) Sequential monitoring of molecular response and quantification of MRD by this multiplex RQ-PCR in CML patients after Glivec treatment.
3. Patients and Methods:
Between June 2001 and October 2004, a total of 102 CML patients had been treated with Imatinib in NTUH, including 49 patients in chronic phase (CP), 30 in accelerated phase (AP), and 23 in blastic phase (BC). Fifty-two were male and 50 female and the median age was 40 years old (ranges 3-80). The median interval from diagnosis to Imatinib treatment was 16 months (0-120) and median Imatinib duration 19.4 months (1-45). Since July 2004, most patients received Imatinib as first-line drug in early chronic phase. PB or BM samples were collected every 3-4 months to monitor the molecular responses after Glivec treatment. Chromosomal or FISH analysis was performed whenever indicated to assess cytogenetics responses. Bone marrow or PBSC mononuclear cells was isolated by Ficoll-Hypaque and lyzed with Trizol-B and stored at -70℃ until used for RNA extraction by standard procedure as described previously.
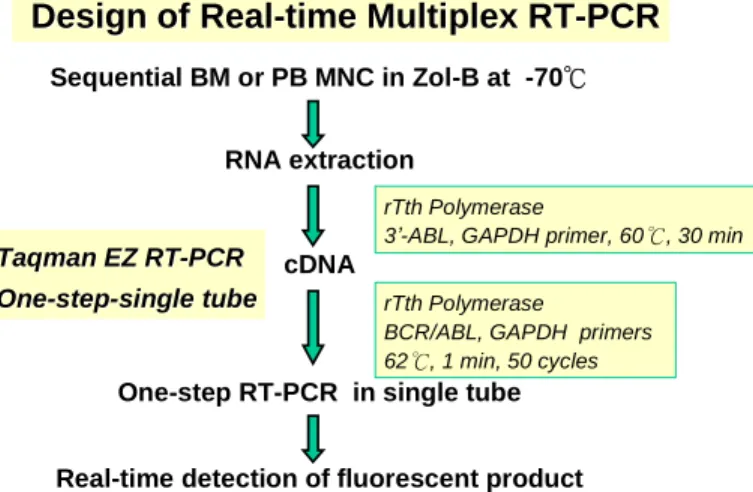
Design of Real
Design of Real--time Multiplex RTtime Multiplex RT--PCRPCR
Sequential BM or PB MNC in Zol-B at -70℃ RNA extraction
cDNA
One-step RT-PCR in single tube Real-time detection of fluorescent product
Taqman EZ RT
Taqman EZ RT--PCRPCR One
One--stepstep--single tubesingle tube
rTth Polymerase
3’-ABL, GAPDH primer, 60℃, 30 min rTth Polymerase
BCR/ABL, GAPDH primers 62℃, 1 min, 50 cycles
K-562 leukemia cell line was used as BCR-ABL expression standard for establishment of standard curve for each experiment of MRQ-PCR. GAPDH housekeeping gene was used as internal control of RNA integrity and normalization of loading RNA amount. Although GAPDH has 56 pseudogenes in human genome, it does not interfere with the measurement of loaded total cellular RNA (1,000ng for each sample).
The PCR primers are listed at below for amplification of BCR-ABL and GAPDH. Table 1 Nucleotide sequences of PCR primers and probes
Gene Primer Sequences
BCR-ABL Sense CATTCCGCTGACCATCAATA
Anti-sense TCCAGCGAGAAGGTTTTCCT
Probe FAM-TCAGCGGCCAGTAGCATCTGACTT-TAMRA
GAPDH Forward GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGT
Reverse GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC
Probe JOE-CAAGCTTCCCGTTCTCAGCC-TAMRA
One step multiplex quantitative RT-PCR reaction was used to detect the expression of BCR-ABL and GAPDH in the same reaction tube on the ABI Prism 7700 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems,CA).Oneμg oftotalRNA wasapplied in a finalvolumeof50λ with TaqMan EZ RT-PCR reaction mixture which contained 1x TaqMan buffer, 3mM Mn(OAc)2,
0.3μM ofeach d(A,T,C)TP,0.6μM dUTP,0.01 unitsofAmpEraseUNG,0.1unitsofrTth,0.2μM each primer, and 0.1μM each probe.RT-PCR program started with 2 min incubation at 50℃ for UNG activation followed by 30 min at 60℃ for reverse transcription synthesis of cDNA. The temperature was elevated to 95℃ for 5 minutes to inactivate UNG, then proceed for 40 cycles of PCR reaction consisting of 94℃ denaturing for 15s and 60℃ annealing/extension for 1 min.
3
Definition and Interpretation of MRQ-PCR Results
1. Sensitivity:
Since the variation of CT value increase dramatically after PCR cycle 36-37 that correspond
to input K562 RNA of 0.1-0.01ng, the sensitivity for BCR-ABL MRD in k562 = 0.001/1000 = 10-5. For practical purpose of MRD monitoring in AML patients, a sensitivity of > 10-3 should be fulfilled. So, we will define WT1 overexpression as WT1 expression at diagnosis > 10-2level of K562 after normalization of GAPDH housekeeping gene.
2. MRD estimation by standard curve method:2
For each sample, the amount of WT1 and GAPDH level is determined from the standard curve generated from k562 cell at each experiment. Assuming there was 100% leukemic cells at diagnosis bone marrow, the MRD value was calculated as:
MRD = ( BCR-ABLX/ GAPDHX) / ( BCR-ABLDX/ GAPDHDX)
4. Results and Discussions:
1) Sensitivity and accuracy of BCR-ABL mRNA measurement by multiplex RQ-PCR in K562 cell line:
First, we establish the standard curve by serial 10-fold dilution of K562 total RNA from 1,000ng to 0.1ng and co-amplify BCR-ABL and GAPDH at the same reaction. As shown in Fig. 1, the CT.value was inversely correlated with log (input K562 RNA amount) and the
sensitivity of accurate quantitation was at the level of 0.01ng (10-5). There was good intra-assay between duplicate sample results and inter-assay reproducibility between separate experiments. (a) (b) Quantitative Real-time RT-PCR: CTvs. Concentration (BCR -ABL) y = 4.3894x + 21.141 r=0.99 20 25 30 35 40 45 0 1 2 3 4 5 -Log [Ct]/[C0] CT Quantitative Real-time RT-PCR: CTvs. Concentration (GAPDH) y = 2.7522x + 18.699 r = 0.99 15 20 25 30 0 1 -Log [Ct]/[C0]2 3 CT
Fig.1 Standard curve of BCR-ABL (a) and internal control GAPDH (b) by MRQ-PCR in K562
leukemia cell line (10 experiments)
2) Imatinib treatment response as evaluated by hematological, cytogenetic and molecular assays.
The treatment response to Imatinib was associated with disease status. (Table 2) Complete hematological remission (CHR) was achieved in 48/49 (98%) patients in chronic phase (CP), but in 70% of accelerated phase (AP) and 35% of blastic crisis (BC). Cytogenetic response
was evaluable in 56 patients and major response (complete + partial) was achieved in 70% of CP, 58% of AP and 75% of BC. However, progression of CML occurred in 38 (37%) patients and currently 27 have died of leukemia. This result could be related to long-standing disease before use of Glivec.
3) Molecular response after Imatinib treatment:
As of Dec. 31, 2004, 88 patients had been treated with Imatinib for longer than 6 months and were eligible for molecular response (Table 2). Using MRQ-PCR, the best molecular response was categorized between 3 groups: 0-2 (poor response indicating drug resistance), 2-3 (equal to cytogenetic remission) and <3 (molecular remission) log reduction of MRD. The kinetic changes of MRD for these 88 patients were plotted in Fig.2.
-6 -4 -2 0 (6) 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 Molecular remission Cytogenetic remission Acquired resistance months LOG-MRD level (normalized BCR-ABL/GAPDH ratio)
compared to k562 cells
Fig. 2 Kinetic of minimal residual disease (MRD) measured by MRQ-PCR in 88 CML
patients after Imatinib treatment.
4) Correlation of molecular response with leukemic progression and survival:
With a median follow-up of 24 months, the leukemic progression-free survival (PFS) was 695% at 1 year, 616% at 2 years, and 537% at 3 years. The PFS was correlated with leukemia status, hematological response, cytogenetic response, and molecular response. The probability of PFS at 3 years was 935% for CP patients, 5110% for AP patients, and only 44% for BC patients (p<0.001 by log rank method). The PFS was 727% for CHR, 1110% for PHR and 0% for regractory patients (p<0.001). For CP and AP patients, the PFS was 935% if CCyR achieved as contrasted with 5312% PFS if no cytogenetic remission (p=0.008).
For 33 patients treated at CP/AP stages and could achieved MRD < -2.0log reductionas measured by MRQ-PCR, none of them had leukemia progressed (Fig.3a). By contrast, 14 of 39 patients with MRD >-2.0log had progressed (p=0.001). Molecular response was not correlated with PFS for patients treated at blastic stage (Fig. 3b). Sequencing analysis showed that many of
5
patients (p<0.001 by log rank method). The OS was 846% for CHR, 1916% for PHR and 8
8%for regractory patients (p<0.001). For all patients, the OS was 856% if CCyR achieved as contrasted with 6211% PFS if no cytogenetic remission (p=0.076). The probability of OS was
8911% for patients had MRD <-3.0log, 87 7% for MRD between -2-3log reduction and 55
10% for MRD >-2.0log (p=0.027). (a) (b) CP + AP P= 0.001 CP+AP Log <-3 , Log>-2, 14/39 (49±11 % at 3 years) Log -2~-3 33 pts ABC Lo g 0~2 Log <-3,3/18 Log -2~-3, 4/18 Log>-2, 11/18 ABC P= 0.004
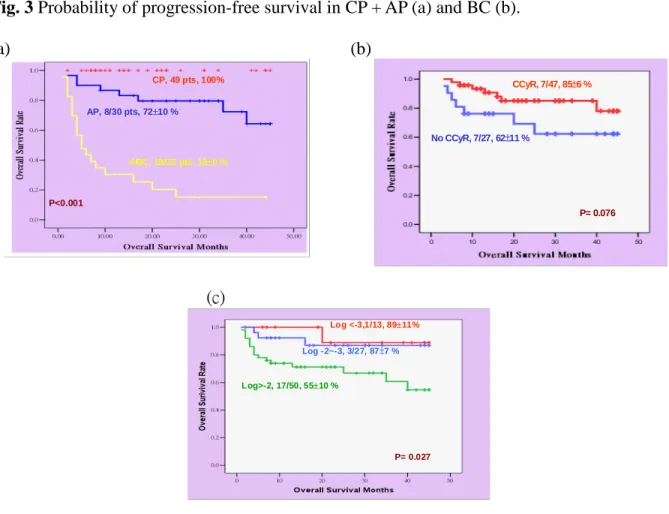
Fig. 3 Probability of progression-free survival in CP + AP (a) and BC (b).
(a) (b) CP, 49 pts, 100% AP, 8/30 pts, 7210 % ABC, 19/23 pts, 158 % P<0.001 No CCyR, 7/27, 62±11 % P= 0.076 CCyR, 7/47, 85±6 % (c) Log <-3,1/13, 8911% Log -2~-3, 3/27, 87±7 % Log>-2, 17/50, 5510 % P= 0.027
Fig. 4 Probability of overall survival as correlated with leukemia status (a), cytogenetic response
5) Conclusion
Imatinib was highly effective in CML-CP. For advanced stages, higher doses of imatinib or combination with other drugs are needed to improve response and prevent leukemic progression to improve survival. Sequential monitoring of cytogenetic and molecular analysis is helpful in clinical decision-making. (The result was presented at the annual meeting of the Taiwan Society of Hematology, March 26, 2005 and manuscript in preparation for submission)