行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫 成果報告
管理一及管理二學門國際學術期刊分級及排序專案計畫
計畫類別: 個別型計畫 計畫編號: NSC92-2416-H-110-005- 執行期間: 92 年 06 月 01 日至 93 年 03 月 31 日 執行單位: 國立中山大學資訊管理學系(所) 計畫主持人: 梁定澎 共同主持人: 戚樹誠,陳世哲,洪世章,邱志聖,林丙輝,陳振明,李賢得, 盧瑞芬,王泰昌 計畫參與人員: 顧宜錚 報告類型: 完整報告 處理方式: 本計畫可公開查詢中 華 民 國 93 年 7 月 7 日
行政院國家科學委員會推動規劃補助計畫成果報告
管理學門國際期刊分級之研究
計畫編號:NSC 92-2416-H-110-005
執行期限:92 年 6 月 1 日至 93 年 3 月 31 日
主持人: 梁定澎 國立中山大學資管系
共同主持人:
王泰昌 國立台灣大學會計學系
李賢得 國立成功大學工業與資訊管理學系
林丙輝 國立台灣科技大學財務金融研究所
邱志聖 國立政治大學國際貿易學系
洪世章 國立清學大學科技管理研究所
戚樹誠 國立台灣大學工商管理學系
陳世哲 國立中山大學人力資源管理研究所
陳振明 國立中央大學工業管理研究系
盧瑞芬 長庚大學醫務管理學系
研究助理: 顧宜錚
2004 年 3 月 31 日
目 錄
一、研究背景與目的 ... 2
二、期刊品質判定方法 ... 3
1. 期刊排名調查... 3
2. 影響係數... 5
3. 彙總研究... 7
三、研究方法與流程 ... 10
四、執行過程 ... 13
(一)期刊篩選... 13
(二)專家調查... 14
(三)加權彙總... 15
五、研究結果 ... 16
1. 資訊管理次領域... 16
2. 生產作業管理與計量方法次領域... 20
3. 會計次領域... 22
4. 行銷管理次領域... 24
5. 一般管理次領域... 27
6. 財務管理次領域... 30
7. 醫務管理次領域... 31
六、結論與研究限制 ... 35
參考文獻
... 37
附錄一 期刊分級研究相關文獻彙整資料 ... A-1 附錄二 問卷–資訊管理次領域為例 ... A-51 附錄三 國外學者評分結果 ... A-54 附錄四 文獻排名彙總資料 ... A-74 附錄五 影響係數排名彙總資料 ... A-91一、研究背景與目的
隨著管理學門學術研究風氣之提昇及研究成果之迅速成長,愈來愈多的國內管理學 者在國際期刊上發表論文。由於國際期刊數量繁多,品質良莠不齊,不論在計畫評審、 研究績效評估等各方面,都往往造成困難,加上社會上近來經常批評,國內學者的研究 績效重量不重質,使得學者辛苦研究的努力遭到誤解,而優秀學者高品質的研究則未能 充分獲得應有的肯定。 期刊品質的排名或分級是個非常困難的工作,但是對於學術研究人員又具有重要的 參考價值,因為在有影響力的期刊中發表的論文,不但可以做為其它研究的基礎,而且 對知識的傳播和學術聲望的建立,都極為重要。因此,在管理的各領域中,不論是財務 管理、資訊管理、生產管理、企業管理與會計等各功能領域,過去均有國外的學者進行 期刊評比的工作。 國外學術機構對專業領域期刊經常有就品質及影響力兩個方面的評比,常被國內使 用的是 SCI 及 SSCI 中的 Impact factor。然而,由於 Impact factor 乃根據論文的引用資 料計算而得,對新期刊或高度自行引用的期刊,都容易造成偏差,而基礎領域或較專精 的狹窄領域也會有比較高的值,並不完全公平。另一種國外常見的方法則是專業領域學 者的調查評比,由領域內學者對不同期刊作品質的評分,然後依分數高低排序。在管理 領域中,不論財務管理、資訊管理、生產管理、會計等領域均有不少期刊評比報告在期 刊中發表。然而,同領域中不同的評比報告,有時亦會有不同的排名而造成評斷上的困 難,因此有需要作彙總整理,再配合國內學者的特性及需求,作出適合國內管理學術界 使用的分級,供未來在評定學術績效及鼓勵學者投稿之參考。 基於以上的認知,本研究之目的在透過廣泛的資料整理及調查,建立一套適合國內 管理學界的期刊分級,提供在 SCI 或 SSCI 資料庫中的期刊名單外,管理領域內專家們 的專業看法,讓更多人瞭解優良期刊的資訊,一方面鼓勵學者向高品質的期刊發表,另 一方面亦可彌補國外 SCI 及 SSCI 期刊資料庫中完全以機械式計算來決定期刊品質的缺 失。 本研究經過八過月的資料蒐集,國內外專家諮詢及多次會議討論後,獲得初步結 論。在本報告中,第二節對相關文獻作一個整理,第三節說明研究的方法及步驟,第四節則報告研究的結果,最後是結論與限制。
二、期刊品質判定方法
目前和期刊分級相關的研究主要包括三種方法,第一是各領域的學者針對特定領域 所做的排名調查;第二是 ISI 出版的 Journal Citation Reports(簡稱 JCR)中提供的論文引 用資料;第三則是各大學院系所彙總,作為內部參考的分級資料。分別說明如下: 1. 期刊排名調查 瞭解各領域期刊排名最常見的方法之一是對同領域的學者作調查,通常列出該領域 相關之期刊,再以問卷方式尋求同領域學者之意見,並以平均值或加權方式計算出不同 期刊之品質排名。在管理的不同功能領域中,期刊排名調查均相當普遍,在表一中列出 各管理功能領域相關的排名文獻,包括會計、財務、一般管理、行銷、資訊、生產與數 量方法等七個次領域1 ,及管理在醫務的應用領域中最近發表的排名文獻。 表 一 各領域相關排名文獻 管理次領域 相關排名文獻 會計
1. Brown, L.D. “Ranking Journals Using Social Science Research
Network Downloads,” Review of Quantitative Finance and Accounting (20:3), 2003, pp. 291-307.
2. Brown, L.D. and Huefner, R.J. “The Familiarity with and Perceived Quality of Accounting Journals: Views of senior accounting faculty in leading U.S. MBA programs,” Contemporary Accounting Research
(11:1), 1994, pp. 223-250.
3. Hasselback, J.R. and Reinstein, A. “A Proposal for Measuring Scholarly Productivity of Accounting Faculty,” Issues in Accounting
Education (10:2), 1995, pp. 269-306. 4. Hull, R.P. and Wright, G.B. “Faculty Perceptions of Journal Quality:
An Update,” Accounting Horizon (4:1), 1990, pp. 77-98.
財務管理
1. Oltheten, E., Theoharakis, V., and Travlos, N.G. “Faculty Perceptions and Readership Patterns of Finance Journals: a Global View,” Working Paper, 2003.
2. Chan, K.C., Fok, R. C.W., and Pan M.S., “Citation-Based Finance Journal Rankings: An Update,” Financial Practice and Education (10:1), 2000, pp.132-141.
一般管理 1. Tahai, A. and Meyer, M.J. “A Revealed Preference study of
1
Management Journals' Direct Influences,” Strategic Management
Journal (20), 1999, pp. 279-296.
2. Johnson, J.L. and Podsakoff, P.M. “Journal Influence in the field of Management: An Analysis using Salancik's Index in A Dependency Network,” Academy of Management Journal (37:5), 1994, pp. 1392-1407.
行銷管理
1. Baumgartner, H. and Pieters, R. “The Structural Influence of Marketing Journals: A Citation Analysis of the Discipline and Its Subareas Over Time,” Journal of Marketing (67), 2003, pp. 123-139. 2. Hult, G. Tomas M., Neese, W.T. and Bashaw, R.E. “Faculty Perceptions
of Marketing Journals,” Journal of Marketing Education 19(1), 1997, pp. 37-52.
3. Theoharakis, V. and Hirst, A. “Perceptual Differences of Marketing Journals: A Worldwide Perspective,” Marketing Letters (13:4), 2002, pp. 389-402.
資訊管理
1. Gillenson M. and Stutz, J. “Academic Issues in MIS: Journals and Books,” MIS Quarterly (15:4), 1991, pp. 447-452.
2. Hardgrave, B. and Walstrom, K. “Forums for MIS Scholars,”
Communications of the ACM (40:11), 1997, pp. 119-124.
3. Holsapple, C., Johnson, L., Manakyan, H., and Tanner, J. “Business Computing Research Journals: A Normalized Citation Analysis,”
Journal of Management Information Systems, (11:1), 1994, pp.
131-140.
4. Mylonopoulos, N.A. and Theoharakis, V. “On-Site: Global Perceptions of IS Journals,” Communications of the ACM (44:9), 2001, pp. 29-33. 5. Peffers, K. and Tang, Y. “Identifying and Evaluating the Universe of
Outlets for Information Systems Research: Ranking the Journals,” The
Journal of Information Technology Theory and Application (5:1), 2003,
pp. 63-84.
6. Walstrom, K., Hardgrave, B., and Wilson, R. “Forums for Management Information Systems Scholars,” Communications of the ACM (38:3), 1995, pp. 93-102.
7. Walstrom, K.A., and Hardgrave, B.C. “Forums for Information Systems Scholars: Ⅲ,” Information & Management (39:2), 2001, pp.117-124.
8. Whitman, M., Hendrickson A. and Townsend A. “Research
Commentary. Academic Rewards for Teaching, Research and service: Data and Discourse,” Information Systems Research (10:2), 1999, pp. 99-109.
生產管理
1. Soteriou, AC, Hadjinicola, GC, and Patsia, K. “Assessing Production and Operations Management related Journals: the European
Perspective,” Journal of Operations Management (17), 1999, pp. 225-238.
and Classifying POM Journals,” Journal of Operations Management (15), 1997, pp. 123-138.
3. Barman, S., Hanna, M.D. and LaForge, R.L. “Perceived Relevance and Quality of POM Journals: A Decade Later,” Journal of Operations
Management (19:3), 2001, pp. 367-385.
4. Vokurka, R.J. “The Relative Importance of Journals Used in
Operations Management Research: A Citation Analysis,” Journal of
Operations Management (14:4), 1996, pp. 345-355.
5. Vastag, G., and Montabon F. “Journal Characteristics, Rankings and Social Acculturation in Operations Management,” Omega (30), 2002, pp. 109-126.
數量方法與 作業研究
1. NL94, Survey by VSNU (Vereniging Samenwerkende Nederlandse Universiteiten) in year 1994.
2. Olson, J.E. “Top Journals in Operations Management and Operations Research,” Working Paper, 2002.
3. WU Wien Journal Rating (http://hal.boku.ac.at/fao/journal_ranking), 2001.
醫務管理
1. Brooks, C. H., Walker, L. R., and Szorady, R. “Rating Journals in Health Care Administration: The Perceptions of Program
Chairpersons,” Medical Care (29:8), August 1991, pp.755-763. 2. Dame, M. A. and Wolinsky, F. D. “Rating Journals in Health Care
Administration: The Use of Bibliometric Measures,” Medical Care (31:6), 1993, pp. 520-524.
3. Larson, J. S. and Kershaw, R. “Rating Journals in Health Care Administration by the Textbook: Citation Method,” Medical Care (31:11), 1993, pp. 1057-1061.
4. McCracken, M.J., Coffey, B.S. “An Empirical Assessment of Health Care Management Journals: A Business Perspective,” Medical Care
Research and Review (53:1), March 1996, pp. 48-70.
5. Williams, E. S., Steward, R. T., O'Connor, S., Savage, G. T., and Shewchuk. R. “Rating Outlets for Health Care Management Research: Update and Extension,” Medical Care Research and Review (59:3), 2002, pp. 337-352.
2. 影響係數
評估期刊品質的另一種方法是使用影響係數(Impact Factors)或引用半衰期(Half Life)的計量方法,這種方法主要源自於 1963 年創立的 ISI 公司所出版的 Citation Index (引 用文獻索引資料庫)收錄論文引用的資料,供圖書館員及研究人員參考。目前 ISI 收錄大 量的自然科學、社會科學及人文類別的期刊論文資料於 Web of Science 中,主要分為三 大索引資料:
年),收集自然科學領域的期刊引用文獻資料庫,共收錄超過 5700 種期刊,每 週更新超過 17,000 筆資料。
! Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI, 1956 年),收錄社會科學期刊中的引用文獻 資料庫,共收錄超過 1700 種期刊,每週更新約 2,700 筆資料。
! Arts and Humanities Citation Index (AHCI, 1975 年),收集藝術及人文類期刊論 文的引用文獻資料庫,共收錄超過 1,100 種期刊,每週更新約 2,200 筆資料。 由於 ISI 在收錄論文時,已對期刊是否定期出刊及引用狀況作過篩選,因此列入上 述資料庫中的期刊大多具備有相當的水準,加上 ISI 每年會依期刊的影響作新增及淘 汰,因此列入資料庫的期刊雖然並不一定保證品質優良,但是至少達到一定水準,這些 量化的指標,也被教育部及許多學術機構採用,作為研究成果品質的指標之一。
提供期刊論文被引用狀況的 JCR Web (Journal Citation Reports on the Web),主要是 將 SCI, SSCI 及 AHCI 中所收錄論文之引用資料,依期刊別加以彙總之後計算影響因素。 JCR 分為 Science Citation Index Expanded 及 Social Sciences Citation Index 兩個版本, 共包括了 60 餘個國家,3,300 家出版商出版之 6,000 餘種學術期刊之分析,這些期刊主 題涵蓋約 200 餘個不同學術領域。ISI 在每年夏季時更新前一年度的期刊引用資料。為 了比較不同期刊之影響力,ISI 使用影響係數 (Impact Factor)、時間性 (Immediacy Index)、被引用半衰期 (Cited Half-Life) 及引用半衰期 (Citing Half-Life) 等不同指標, 以協助使用者瞭解不同期刊表現。 在上述各項指標中,被使用最多的是「影響係數」,該指標計算該期刊前 2 年所出 版的論文,在某一特定年份中被其它論文所引用的平均次數(見公式 1)。因此,影響係 數愈高表示該期刊所發表的論文被引用的平均次數愈高;若影響係數愈低,表示該期刊 中所發表的論文被後續論文引用的次數較少。這個指標的價值是基於一個假設,就是被 引用愈多的論文就愈有影響力。 該期前 2 年被收錄於 ISI 資料庫的論文被引用次數的和 影響係數 = 該期刊前 2 年所有出版論文總數 (1)
然而,由於 ISI 在計算引用資料時,只根據它所收錄的期刊來計算,於是就會造成 有些領域,若大部份期刊不在其中,則即使被引用次數很多,也不會被注意,而產生下 列偏差: (1). 對歷史較久的領域有利,對新領域不利。 (2). 對基礎科學有利,對應用科學不利。 (3). 未排除自我引用,因而對自我引用多的封閉領域有利,對較廣的開放領域不 利。 3. 彙總研究 (Meta-research) 由於期刊論文發表不僅代表研究人員的成果,也是大學教師升等及敘薪的重要參 考,因此,國外有些著名的大學系所或學院,會建立認可的重要期刊列表,以作為研究 績效評估之參考。由於這些分級為學者依據本身的專業再參考各種排名所建立的,所以 也極具參考價值。 對外公布的彙總研究中涵蓋最廣泛的是 Anne-Wil Harzing 針對不同的期刊評比加 以彙總,製作的報告,目前最新的版本為 2003 年。該研究主要針對經濟、財務與會計、 一般管理、創新、行銷、組織行為與人力資源管理、生產與作業研究、政府資助、數量 方法與資管及社會學等領域相關的期刊做評等,彙整的文獻資料來源如表二所示。 表 二 Anne-Wil Harzing 的期刊品質列表採用的資料 彙整文獻來源 說明 SOCIAL SCIENCE CITATIONS INDEX
包括 1992, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001,欄位代號分別為 CI92, CI97, CI98, CI99, CI00, CI01
LAN94 —
LANCASTER 1994
Based on a polling exercise of selected academics to ascertain their opinion of selected journals. The journals to be evaluated were nominated by the Lancaster Management School not by the assessor.
I = enhancing international reputation N = enhancing national reputation
NL94 — NL 1994 List constructed by VSNU (Vereniging Samenwerkende Nederlandse Universiteiten) and based on a survey of Dutch academics in economics and business. Has a bias towards Economics, Finance and Quantitative Methods, but covers all subject areas mentioned above.
A = Top publications in heavily refereed journals
B = Excellent publications in - mostly - English and heavily refereed journals C = Very good publications in refereed journals
D = Good publications in moderately refereed journals E = Publications in other journals
NL99 — NL 1999 List based on a large survey of opinions of academics in Business Administration in the Netherlands (Professors, Directors of Research Schools & Editorial Board
members of Maandblad voor Accountancy & Bedrijfseconomie, Bedrijfskunde,
International Journal of Research in Marketing and Journal of Empirical Finance).
Please note that this list has a narrower focus than the 1994 list and covers only F&A, General & Strategy, Marketing, OS, QM & MIS.
A = Top academic journals A (P) = Top professional journals B = Very good academic journals B (P) = Very good professional journals C = Good academic journals
C (P) = Good professional journals NOT95 —
NOTTINGHAM 1995
List based on a survey of opinions of 397 UK academics from 27 institutions (all institutions rated 5 or 4 in the 1992 RAE and a random selection of 3-rated
institutions). Academics were asked to rate a predefined list of journals “using a 1-5 scale, where 1 represents the lowest and 5 the highest quality assessment bearing in mind the forthcoming Research Assessment Exercise”. Journals with less than 10 responses were not included in the list.
BFD97 — BRADFORD APPENDIX 1997
This appendix was produced in an attempt to improve upon the grading of journals in the VSNU (NL 1994) listing. This listing was circulated to all members of staff, who were asked to suggest modifications, upon the assumption that A - C grades
represented journals of international standing. The list should be read in conjunction with other lists (especially the VSNU 1994 list) and should not be used as a list on its own.
A = Top publications in heavily refereed journals
B = Excellent publications in - mostly - English and heavily refereed journals C = Very good publications in refereed journals
D = Good publications in moderately refereed journals E = Publications in other journals
Q = New journals for which judgments on their standing would be premature US98 — US 1998 List used for determining doctoral-level graduate faculty status in the US, uses author
affiliation indices (AAI). The AAI is the ratio of articles authored by faculty at 60 US universities and colleges
with highly rated business programs to total articles authored by faculty at US universities and colleges. As such it is an objective, peer-based measure of the extent to which one competes against faculty at highly rated U.S. universities in order to publish in the journal. Ratings from 0.01 to 1.0 (only those above .20 are included), higher ratings indicate higher level journals. Journals with a 0.00 score are journals that are seen as important, but for which data are not yet available.
AST99 — ASTON 1999
List based on a large survey of opinions of academics of the Midlands universities. 5 = Top international journals (top ten for the discipline)
4 = International standing but not in the top tier 3 = Well regarded national standing journals 2 = Other nationally rated journals
1 = Lower level national journals SMJ99 —
STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT JOURNAL 1999
Published as Tahai & Meyer (1999), Strategic Management Journal, vol. 20, pp. 279-296. The list attempts to determine which management journals have the greatest influence on the field of management. Uses a dataset of 1275 articles published in 17 source journals (the top 17 management journals in the SSCI) over a 2-year period. Journals that are cited most frequently are those that have had the most influence on the current literature (revealed preference). Journals are ranked by citation proportion (1= most cited, 65 = least cited).
HKB00 — HONG KONG BAPTIS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF BUSINESS 2000
List approved by the Executive Committee of HKBU, June 2000. Ratings on a A , B+, B and Bscale, where A represents the highest and B- the lowest rating. Journals that were only mentioned on the HKBU list were not included in the Journal Quality List.
WIE01 — WU WIEN JOURNAL RATING 2001:
List developed by the Wirtschaftsuniversität Wien (Vienna University of Economics and Business Administration). For more information and the complete list see: http://www.wuwien.
entries in the research areas covered by the current JQL have been included. The list has five categories:
A+ Top journals with world-wide distribution and readership; covering the entire scope of a discipline; contributions are scientifically and methodologically most fastidious and innovative; very frequently pioneer work and milestones of the respective discipline; incomprehensible for non-scientists or readers without in-depth method knowledge; toughest competition of authors from all over the world (very high refusal rate of manuscripts); refereed in a double blind procedure (at least two referees); highest impact scores.
A World-wide distributed journals; emphasis in just one linguistic area as the exception; covering an entire discipline or an established subdiscipline;
contributions are scientifically and methodologically most fastidious and innovative; frequently pioneer work and milestones of the respective discipline; understandable for graduates of relevant studies; strong competition of authors from an international realm; refereed in a double blind procedure (at least two referees); high impact scores.
B Journals with at least supraregional distribution in any language; covering at least an established subdiscipline; contributions are scientifically or methodologically innovative; understandable for practitioners without any degree in relevant studies; manuscript submissions from a supraregional realm; refereed in a double blind procedure (at least two referees); impact score not relevant.
C At least national distribution; covering at least established subdiscipline; the editors pay attention to legibility for non-scientist, although research results have editorial priority; practitioners rank among the core target group; at least national
contributions; not necessarily anonymously refereed; however one external referee at least; impact factor not relevant.
D At least national distribution; specialized on any level; contributions contain results in simplified form; practitioners appear frequently as authors; contributions are aimed at teaching or vocational training of practitioners; at least national contributions; no formal reviewing procedures; impact factor not relevant.
資料來源:Harzing (2003), pp. 2-4
調查期刊排序的方法不論是文獻引用、調查法以及資料彙總等,均有其優點及限 制。文獻引用率(Citation-based research)係衡量特定領域的期刊之間相互引用的比率來決 定期刊的排序(Holsapple et al., 1993; Hollsapple et al., 1995; Kleijnen and Groenendaal, 2000)。調查法(Survey-based research)則是針對學者或業界主管進行知覺調查,由受訪人 員針對期刊進行排序(Tsai et al., 1991; Gillenson and Stutz ,1991; Koong and Weistroffer, 1989; Doke and Luke, 1987; Forgionne and Kohli, 2001)。至於彙總研究(Meta Research)則 是針對特定期間內,將特定領域的期刊排序研究加以彙整分析,以獲得廣泛的研究結果 (Nord, 1995; Harzing, 2003) 。在表三中,我們列出不同方法的優缺點比較。
綜合以上說明,可以知道期刊品質評比並非一件簡單的工作,而且有許多不同的角 度可以進行,分別可能造成不同的偏差。
表 三 不同分級方法的優缺點比較 期刊分級 方法 優缺點 學者調查 影響因素 綜合彙總 優點 專家學者 對該領 域 有 深 入 的 瞭 解,較能作更專業 的判斷。 客 觀 計 算 的 數 據,較不會受到個 人好惡的影響。 可以結 合 不同角 度而有 綜 合的判 斷。 缺點 學者可能 主觀的 對自己熟習或有 論文發表的期刊 作較高的評等。 只有引用 數字而 未能對 論文的真 正品質有瞭解,而 且易受 自 我引用 等人為操弄(如作 者傾向 於 多引用 欲發表期刊之論 文) 不同資料 可能因 取得方式不同,是 否能合併考量,或 不同資料的權重 該如何 賦 予等均 不易掌握。
三、研究方法與流程
雖然在管理各領域中都已有許多國外的排名,但是目前國內並沒有為大家所共同接 受的準則,為了在眾多排名資料中建立一個可供國內學者參考的指標,本研究綜合整理 各領域中近年已發表的排名資料,再結合焦點座談與國外學者意見諮詢,以便建立可供 國內學者參考之資料。 研究的步驟包括四個階段。首先,針對國外既有的期刊排名資料作廣泛的搜集,並 作彙總整理,再配合國外大學(如香港)管理學院的既有分級資料,作出初步的清單。其 次,針對初步清單,邀請學門複審委員及優秀研究學者,召開焦點團體討論,對研究範 圍及作法進行深入的意見徵詢。第三,根據焦點座談的結果,建立期刊分級的問卷,並 以網路及郵寄兩種方式,分別針對國內及國外的管理學者進行調查。最後,經主持小組 開會,針對排名文獻、期刊影響係數及問卷回收結果等構面進行分析與討論,再根據各 構面進行加權平均以完成分級排序,並作成報告。整體研究流程如圖一所示。資料彙整分析 決定各管理次 領域期刊名單 依問卷調查結 果進行排名 加權平均排名 依影響係數資料 (00-02)進行排名 撰寫報告 討論與修正 國外學者問卷調查 依重要排序文 獻資料排名 徵詢國內 學者建議 搜集國外著名大 學的相關資料 搜集 2000-2002 年 的期刊影響係數 搜集各領域相關 的期刊排序文獻 決定管理次領域 圖 一 研究流程 各步驟工作內容說明如下: 1.決定研究涵蓋的次領域 管理學門目前在國科會分成管理一與管理二兩個學門,主要依企業功能來區分,下 面又包括幾個次領域。管理一包括會計、財務及一般管理(包括策略、組織與人管),管 理二則以生產與作業管理、資訊管理及行銷管理為主。這種分法也是目前企業內部的部 門區分和管理學院中系所或是課程編排設計時最常用的次領域區分方法。然而,除了企 業功能外,因為管理可以被應用到各種不同的行業,因此也有部分學校著眼於不同產業 的應用實務,依產業別來區分,如餐飲管理、休閒管理、傳播管理、非營利機構管理、 醫務管理等。
由於依照企業功能別的劃分是管理學領域普遍的慣例,也和企業的實務功能充分結 合,研究結果更可以普遍應用到各不同產業(如,投資的研究發現便可以應用幾乎任何 行業),因此,本研究主要也依企業的功能進行分組。在應用領域除醫務管理因特殊原 因外,其餘並未加以探討。 因考量某些學科之間相關性高、期刊重疊性很高的情況下,先將相關領域作整合。 策略管理、組織行為與人力資源管理整合為「一般管理」,而生產管理、數量方法與作 業研究亦合併為「生產作業管理與計量方法」。因此,將管理領域共分為會計、財務、 一般管理、行銷、資訊、生產與數量方法等六個次領域,加上醫務管理的應用領域,共 七個次領域來進行。有些學術人口少,獨立性低的次領域(如運輸、科管等)均整合到 相關的主要領域中一起考量。 2.資料搜集 為了對既有的的排名資料作充分的瞭解,本研究廣泛蒐集次級資料加以整理。資料 蒐集主要分成三大部份,包括各次領域的期刊排序文獻、2000-2002 年的期刊影響係數, 及香港中文大學管理學院的期刊分級資料。 3.資料彙整分析 依據次級資料,再由各次領域的主持人及共同主持人(表四)分別邀請各領域的國內 學者進行討論,並根據討論結果舉辦焦點座談,以確定期刊篩選原則及排名準則。 表 四 次領域負責人及單位 (依姓名筆劃排序) 領域 姓名 單位 會計 王泰昌 國立台灣大學會計系 生產及作業管理 李賢得 國立成功大學工管系 財務管理 林丙輝 國立台灣科技大學財務金融所 行銷管理 邱志聖 國立政治大學國貿系 策略管理 洪世章 國立清學大學科管所 組織行為 戚樹誠 國立台灣大學工管系 資訊管理 梁定澎 國立中山大學資管系 人力資源管理 陳世哲 國立中山大學人資所 作業研究/數量方法 陳振明 國立中央大學工管系 醫務管理 盧瑞芬 長庚大學醫管系
4.決定各管理次領域期刊名單 各次領域依據排名文獻、影響係數與國外著名大學的排名資料等構面,以及期刊 篩選原則,整理出前四十名的期刊,並依期刊品質分成 A+, A, B+三個等級,編製成問 卷後寄給國外於該次領域中有卓越研究成果的學者進行確認。 5.各構面排名 完成問卷調查後,本研究分別依據文獻排名資料、2000-2002 年的期刊影響係數與 問卷調查結果進行排名。 6.加權平均 上述的排名結果,將依排名順序進行正規化,使得各構面排名第一的期刊得分為 1 分,最後一名(或未納入排名)的期刊得 0 分,其它依排名順序等距分佈於 0-1 之間。各 構面完成正規化分數後,再依文獻資料-40%,影響係數 20%,問卷調查結果 40%的權重 進行加權平均,以完成期刊排名。 7.討論與修正 初步排名順序完成後,將再舉行一次焦點座談,針對排名結果進行最後確認,並舉 辦座談會,以廣納國內學者的意見。 8.撰寫報告 依據上述七個步驟的研究過程,各次領域分別對領域內期刊進行分析,並將結果撰 寫成報告。
四、執行過程
(一)期刊篩選 各次領域的期刊篩選,主要是根據既有的排名資料,由該領域的專家決定。各次 領域分別搜集近年發表的期刊排名 2-5 份(見表一),計算出各次領域的期刊平均排名, 同時也收集 2000-2002 年的期刊影響係數及 Harzing(2003)所做的期刊品質分析(見表三) 等資料進行彙整,結果如附錄一所示。根據彙整後的次級資料,各次領域主持人(見表 四)亦分別安排領域內的焦點座談,邀請該領域中的學者提供意見,以決定該領域中列入排名的專業期刊名單。 各領域的專業期刊名單篩選原則除領域另有特殊考量外,經數次會議所決定的共 同篩選原則如下: 1. 以該領域內的期刊為主,參考領域或參考學門的相關期刊,以不列入為原則。例如: 財務可以不列入經濟的相關期刊,資管可以不列入資訊工程的相關期刊。若需要一 併列入,所顯示的亦以該相關期刊對該領域的影響力,而不是該期刊在原屬領域的 影響力。例如:Management Science 屬於生產作業管理與計量方法領域,資訊管理 領域即可不列入該項期刊進行排名。 2. 下列類別的期刊不列入分級名單 (1). 由書局出版的研討會系列論文集
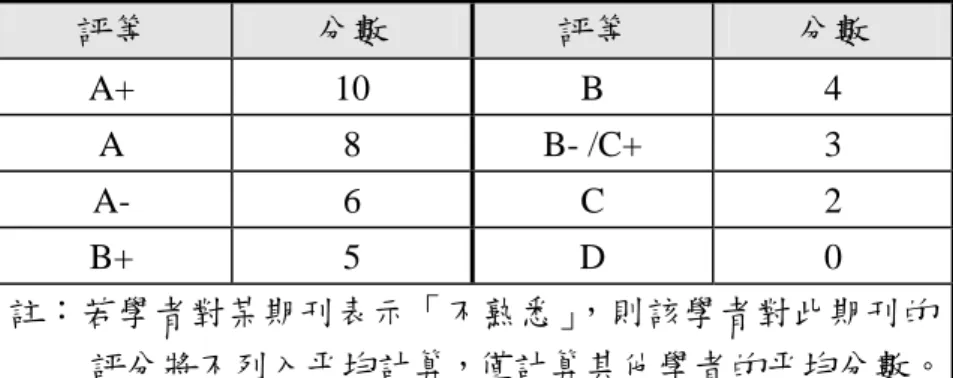
(2). 非學術性的期刊,如 Harvard Business Review (3). 非管理學門相關的期刊 (4). 管理應用或產業應用領域2 的期刊,如休閒管理 (二)專家調查 完成期刊名單的篩選後,再依下列原則進行各次領域期刊的初步分級,再依據分 級結果製作問卷,請各領域的專家學者進行複核。初步分級原則如下: 1. 將各領域的期刊分成三級: # A+和 A 級期刊總數至多為 15 本,而 A+頂級期刊以不超過 5 本為原則。 # 所有列入分級的期刊總數不超過 40 本為原則 2. 各領域的負責人參考附錄一的結果與該領域的學者討論後,擬定初步分級名單。 各領域再依上述原則將初步分級結果做成問卷(見附錄二),並郵寄給國外專家學 者進行複核,結果詳見附錄三。根據調查結果發現,多數的國外學者建議期刊分級除了 原有問卷 A+, A 和 B 三個等級外,應有 A-,B+或 C 等級別,經所有各主持人的共同討論 後,依國外專家的修正評等結果進行分數轉換(見表五),再以學者的平均評等分數做為 該期刊在專家學者調查構面的分數。 2 除醫務管理外,其它應用領域將另外排名。
表 五 評等轉換分數原則 評等 分數 評等 分數 A+ 10 B 4 A 8 B- /C+ 3 A- 6 C 2 B+ 5 D 0 註:若學者對某期刊表示「不熟悉」,則該學者對此期刊的 評分將不列入平均計算,僅計算其他學者的平均分數。 (三)加權彙總 由於本研究採用排名文獻、影響係數與專家評論等三構面進行評估,因此,必須 先針對各構面進行正規化後,再做加權平均排名。各構面單獨的排名計算方式如下: 1. 文獻排名方面,各領域依研究方法嚴謹和近五年出版等客觀原則,挑選最具代表性 的排名文獻資料,再將各排名文獻中不列入排名的期刊名單刪除後,依原有排名往 前遞補的方式調整排名,最後依據各文獻的調整排名進行正規化分數轉換,將排名 轉換為 0 至 1 的正規化分數,再取平均分數來計算排名結果(見附錄四)。 2. 影響係數方面,各領域自 JCR 資料庫中查詢各期刊 2000 年至 2002 年的影響係數 值後,取平均分數進行排名並計算成 0 至 1 的正規化分數。平均分數的計算以有影 響係數值的年度為範圍,例如若某期刊於 JCR 2000 資料庫無影響係數值,而 JCR 2001 與 JCR 2002 年有,則取 2001 與 2002 二年的平均值。若某期刊不在 SSCI、SCIE 名單中,或者屬於 SSCI 或 SCI 名單的新期刊,但因發行年限短而無影響係數值時, 仍以 0 分計算以維持計算基礎一致(結果見附錄五)。 3. 在國外學者評分統計分面,以有評分的問卷進行平均,若受訪學者表示對於某期刊 並不熟悉或無法評論,則該項分數不予計算;若未對問卷上的排名表示意見,則以 問卷上的原排名計算。最後再依各期刊的平均分數進行排名並計算出 0 至 1 的正規 化分數(見附錄三)。 各構面的權重經各主持人討論後定為:文獻排名 40%,影響係數 20%,專家評論 40%。採取這樣權數分配主要是因為文獻排名具有廣泛的代表性,而專家評分顯示該領 域內專業的看法,應該較機械式的影響係數更有準確性,實際上三者亦有高度相關。
各構面分別排名後的結果換算成正規化分數(附錄三-五)後,再依權重進行加權平 均,即獲得排名的結果。
五、研究結果
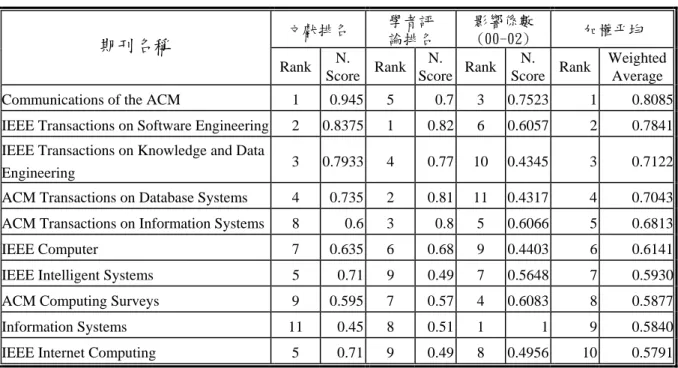
本節說明根據以上程序所完成的各次領域期刊排名結果。 1. 資訊管理次領域 資訊管理領域的研究與資訊科技的發展有相當高的關係,加上電子化企業的發展 趨勢使得電子商務成為資管理域中一項非常重要的研究範疇,因此,除了對資訊管理期 刊進行排名外,亦將資訊科技和近年成長的電子商務期刊進行排名。資訊管理領域的期 刊,經過收集過去排名資料後,再經幾位教授討論,篩選了 40 本較具歷史與水準的學 術期刊送給國際上的知名學者審查(包括 5 位美國學者,3 位亞洲學者、1 位歐洲學者, 及 1 位紐澳學者,其中部分為對國內情況瞭解之華人學者),並找出影響係數後,根據 排序原則,將結果加以計算。 資管領域的期刊排名結果,前 30 名期刊見表六所示。由於部份期刊可能因為歷史 較短或是主編知名度等因素,並非 SCI/SSCI 期刊,因此,沒有影響係數資料而會造成 排名下滑。但此結果亦合理,因為不在 SCI/SSCI 中的期刊論文被引用的機會相對會較 小些。整體而言,除少數期刊排名變動受影響較大之外,大部份並不影響結果。表六中 三個構面排名的關係很大,相關係數分別為文獻排名與專家評分 0.539(p<0.01),專家評 分與影響係數 0.813(p<0.001),而文獻排名與影響係數則無顯著相關。 由表六中可以看出,總排名前 10 名的期刊,在三個構面幾乎都名列前茅,在資管 領域一般也都認為前五名的期刊,大致上為 A 級期刊,其中前三名則常被視為 A+的期 刊,而前 15 名的期刊亦有 B+的水準。 和資管相關的也有部份屬於資工的期刊,亦常有作技術性研究的資管學者投稿, 並且在許多資管期刊排名中會被涵蓋。在表七中我們也對資訊科技的期刊作了排序,其 中 Communication of the ACM 因為刊登許多管理或應用性論文,因此在表六中亦有列 入。由表中可見許多科技性期刊亦對資管有相當影響力,且其加權分數一般而言均相當 不錯,大致上均可排在資管期刊的前 20 名。在表八中,我們將資管和相關的資工期刊做了個合併排名,供大家參考。
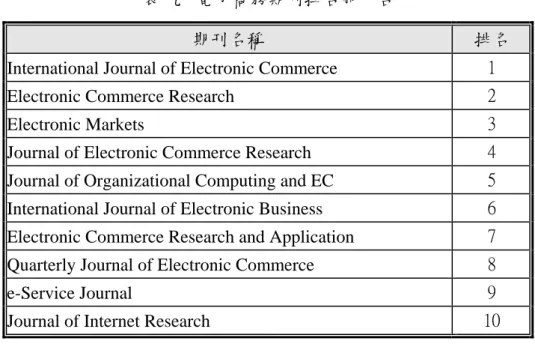
另外,近年來電子商務的盛行亦帶動了許多電子商務的相關期刊受到大家的注 意,因為電子商務涉及跨領域的特性,因此有些並未和資管期刊一起排名。在表九中我 們根據現有的兩份電子商務期刊的排名,加以彙整供大家參考。由於電子商務領域目前 仍在起步,相關期刊歷史尚短,要立即斷定期刊品質仍有困難,表中資料可能隨時間仍 會變化。不過因為 International Journal of Electronic Commerce (IJEC) 已被 SSCI 收錄, 因此,可視為目前為電子商務領域之最佳期刊,在整個資管領域亦排名第八名。 表 六 資訊管理期刊排名 文獻排名 學者評 論排名 影響係數 (00-02) 加權平均 期刊名稱 Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank Weighted Average MIS Quarterly 1 1 2 0.98 1 0.9451 1 0.981
Information Systems Research 2 0.95 1 1 4 0.5044 2 0.8809 Communications of the ACM 3 0.945 4 0.7 2 0.7523 3 0.8085 Journal of Management Information
Systems 4 0.898 3 0.86 9 0.2872 4 0.7606
Decision Support Systems 5 0.752 5 0.68 11 0.2576 5 0.6243
Information and Management 8 0.69 9 0.54 6 0.4434 6 0.5807
European Journal of Information Systems 6 0.7467 9 0.54 13 0.2401 7 0.5627 International Journal of Electronic
Commerce 10 0.535 7 0.57 5 0.4455 8 0.5311
Journal of the Association for Information
Systems 11 0.53 8 0.56 23 0 9 0.436
Information Systems Journal 9 0.5933 16 0.41 20 0.1195 10 0.4252 INFORMS Journal on Computing 23 0.28 6 0.58 7 0.3597 11 0.4159 Journal of Strategic Information Systems 14 0.446 12 0.445 10 0.2811 12 0.4126 DATA BASE for Advances in Information
Systems 12 0.506 15 0.425 19 0.1249 13 0.3974
International Journal of Human-Computer
Studies 20 0.34 13 0.44 12 0.2418 14 0.3604
Journal of Organization Computing and
Electronic Commerce 19 0.3433 14 0.435 17 0.1668 15 0.3447
Information Processing and Management 30 0.08 17 0.4 3 0.5759 16 0.3072 Journal of Computer Information Systems 17 0.358 22 0.39 22 0.0253 17 0.3043 Journal of Information Technology 29 0.1 11 0.49 8 0.3082 18 0.2976
Communications of the AIS 7 0.705 23 0 23 0 19 0.282
Expert Systems with Applications 27 0.19 17 0.4 15 0.2123 20 0.2785 Journal of Systems and Software 25 0.195 17 0.4 16 0.187 21 0.2754 International Journal of Information
Knowledge-Based Systems 25 0.195 17 0.4 18 0.1452 23 0.267 Information Systems Frontiers 13 0.48 23 0 23 0 24 0.192 Journal of Database Management 15 0.4325 23 0 23 0 25 0.173 Journal of Global Information Technology
Management 16 0.38 23 0 23 0 26 0.152
Information and Organization 18 0.345 23 0 23 0 27 0.138 Journal of Information Technology Theory
and Application 20 0.34 23 0 23 0 28 0.136
Information Systems Management 22 0.288 23 0 21 0.0382 29 0.1228 Information Resources Management Journal 24 0.268 23 0 23 0 30 0.1072
表 七 資訊科技期刊排名前十名 文獻排名 學者評 論排名 影響係數 (00-02) 加權平均 期刊名稱 Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank Weighted Average Communications of the ACM 1 0.945 5 0.7 3 0.7523 1 0.8085 IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering 2 0.8375 1 0.82 6 0.6057 2 0.7841 IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data
Engineering 3 0.7933 4 0.77 10 0.4345 3 0.7122
ACM Transactions on Database Systems 4 0.735 2 0.81 11 0.4317 4 0.7043 ACM Transactions on Information Systems 8 0.6 3 0.8 5 0.6066 5 0.6813
IEEE Computer 7 0.635 6 0.68 9 0.4403 6 0.6141
IEEE Intelligent Systems 5 0.71 9 0.49 7 0.5648 7 0.5930
ACM Computing Surveys 9 0.595 7 0.57 4 0.6083 8 0.5877
Information Systems 11 0.45 8 0.51 1 1 9 0.5840
IEEE Internet Computing 5 0.71 9 0.49 8 0.4956 10 0.5791
表 八 資訊管理期刊與資訊科技期刊混合排名 文獻排名 學者評 論排名 影響係數 (00-02) 加權平均 期刊名稱 Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank Weighted Average MIS Quarterly 1 1 2 0.98 2 0.9451 1 0.9810
Information Systems Research 2 0.95 1 1 10 0.5044 2 0.8809 Communications of the ACM 3 0.945 8 0.7 4 0.7523 3 0.8085 IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering 5 0.8375 4 0.82 7 0.6057 4 0.7841 Journal of Management Information
Systems 4 0.898 3 0.86 19 0.2872 5 0.7606
IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data
Engineering 6 0.7933 7 0.77 15 0.4345 6 0.7122
ACM Transactions on Database Systems 9 0.735 5 0.81 16 0.4317 7 0.7043 ACM Transactions on Information Systems 15 0.6 6 0.8 6 0.6066 8 0.6813
Decision Support Systems 7 0.752 9 0.68 21 0.2576 9 0.6243
IEEE Computer 14 0.635 9 0.68 14 0.4403 10 0.6141
IEEE Intelligent Systems 10 0.71 18 0.49 9 0.5648 11 0.5930
ACM Computing Surveys 16 0.595 12 0.57 5 0.6083 12 0.5877
Information Systems 23 0.45 17 0.51 1 1 13 0.5840
Information and Management 13 0.69 15 0.54 13 0.4434 14 0.5807 IEEE Internet Computing 10 0.71 18 0.49 11 0.4956 15 0.5791 European Journal of Information Systems 8 0.7467 15 0.54 23 0.2401 16 0.5627 International Journal of Electronic
Commerce 18 0.535 12 0.57 12 0.4455 17 0.5311
Human-Computer Interaction 22 0.47 26 0.4 3 0.7946 18 0.5069 Journal of the Association for Information
Systems 19 0.53 14 0.56 33 0 19 0.4360
Information Systems Journal 17 0.5933 25 0.41 30 0.1195 20 0.4252 INFORMS Journal on Computing 33 0.28 11 0.58 17 0.3597 21 0.4159 Journal of Strategic Information Systems 24 0.446 21 0.445 20 0.2811 22 0.4126 DATA BASE for Advances in Information
Systems 20 0.506 24 0.425 29 0.1249 23 0.3974
International Journal of Human-Computer
Studies 30 0.34 22 0.44 22 0.2418 24 0.3604
Journal of Organization Computing and
Electronic Commerce 29 0.3433 23 0.435 27 0.1668 25 0.3447
Information Processing and Management 40 0.08 26 0.4 8 0.5759 26 0.3072 Journal of Computer Information Systems 27 0.358 32 0.39 32 0.0253 27 0.3043 Journal of Information Technology 39 0.1 18 0.49 18 0.3082 28 0.2976
Communications of the AIS 12 0.705 33 0 33 0 29 0.282
Expert Systems with Applications 37 0.19 26 0.4 25 0.2123 30 0.2785 Journal of Systems and Software 35 0.195 26 0.4 26 0.187 31 0.2754 International Journal of Information
Management 38 0.17 26 0.4 24 0.2284 32 0.2737
Knowledge-Based Systems 35 0.195 26 0.4 28 0.1452 33 0.267 Information Systems Frontiers 21 0.48 33 0 33 0 34 0.192 Journal of Database Management 25 0.4325 33 0 33 0 35 0.173 Journal of Global Information Technology
Management 26 0.38 33 0 33 0 36 0.152
Information and Organization 28 0.345 33 0 33 0 37 0.138 Journal of Information Technology Theory
and Application 30 0.34 33 0 33 0 38 0.136
Information Systems Management 32 0.288 33 0 31 0.0382 39 0.1228 Information Resources Management Journal 34 0.268 33 0 33 0 40 0.1072
表 九 電子商務期刊排名前十名
期刊名稱 排名
International Journal of Electronic Commerce 1
Electronic Commerce Research 2
Electronic Markets 3
Journal of Electronic Commerce Research 4
Journal of Organizational Computing and EC 5 International Journal of Electronic Business 6 Electronic Commerce Research and Application 7
Quarterly Journal of Electronic Commerce 8
e-Service Journal 9
Journal of Internet Research 10
註:本排名取 Bharati and Tarasewich (2002) and Peffers and Tang (2003)二篇文獻 中,電子商務期刊的排名資料。
2.生產作業管理與計量方法次領域
生 產 作 業 管 理 (POM-Production and Operations Management) 與 計 量 方 法 (QM- Quantitative Method)兩個次領域的期刊由於高度重疊,因此將計量方法的原始 57 本期刊 與生產作業管理相關的 106 本期刊合併,再依現有文獻排名與影響係數(Impact Factor) 高低做綜合排序,同時考量期刊性質與本領域相關性,以及一些具備相當學術品質與潛 力卻未列入 SCI/SSCI 之期刊,最後篩選出 40 本期刊作為學者調查評比的初步樣本。 此樣本經由領域內多位學者專家的意見徵詢與討論之後,經過小幅度的調整(在 原樣本中加入品質工程與管理及運輸管理的專業優良期刊,屬於較廣義之作業管理與計 量方法),才定案作為國外學者評比的樣本。參與評比的國外學者包含 5 位北美教授、3 位亞洲籍(香港、新加坡)教授及 2 位歐洲籍教授。 在本領域期刊排名的研究文獻當中,由於 POM 類別的前四份文獻(見表一)均發表 於 Journal of Operations Management,其結果重複程度太高,因此只採用最新的一份文 獻(2001 年發表),第五篇文獻(Omega 2002)則僅包含五個期刊之排名,樣本個數太低, 亦無法列入:再加上原有 QM 類別的三份文獻的排名結果共四份,作為本領域的文獻排 名的依據。
MSOM)並非 SCI/SSCI 收錄之期刊,因此,沒有影響係數的資料而會造成排名下滑,其 中排名較後之期刊(共 15 本)也因為沒有文獻排名的資料而不利其排名。表十中三個 構面排名的關係很大,相關係數分別為文獻排名與專家調查評分 0.783(p<0.001),專家 調查評分與影響係數 0.527(p<0.01),文獻排名與影響係數 0.337(p<0.05)。 由表十中可以看出,總排名前 15 名的期刊,在三個構面幾乎都名列前茅;在本領 域中,一般學者也大多認為前 10 名的期刊大致上為 A 級期刊,其中前 4 名則常被視為 傑出類的 A+期刊,而前 20 名的期刊亦有相當於 B+的水準。本研究的敏感度分析顯示, 因考慮因素與不同權重之組合,會影響少數期刊有較大的排名變動外;整體而言,不同 權重組合對於大部份排名前 15 名期刊的總排序結果影響並不大。 表 十 生產作業管理與計量方法綜合期刊排名 文獻排名 學者評 論排名 影響係數 (00-02) 加權平均 期刊名稱 Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank Weighted Average Management Science 1 1 1 1 3 0.6314 1 0.9263 Mathematical Programming 4 0.8826 1 1 4 0.5685 2 0.8667
Mathematics of Operations Research 2 0.9985 4 0.92 7 0.4504 3 0.8575
Operations Research 3 0.8917 1 1 8 0.4433 4 0.8453
SIAM Review 12 0.6052 16 0.62 1 1 5 0.6901
Journal of Operations Management 7 0.701 9 0.68 2 0.6463 6 0.6817
Transportation Science 9 0.6909 6 0.8 11 0.344 7 0.6652
Manufacturing And Service Operations
Management 5 0.8624 6 0.8 38 0 8 0.665
IIE Transactions 6 0.7133 5 0.82 27 0.1993 9 0.6532
Operations Research Letters 10 0.6606 13 0.65 20 0.2485 10 0.5739
Decision Sciences 11 0.6281 14 0.64 13 0.29 11 0.5652
Naval Research Logistics: An International
Journal 16 0.5406 8 0.76 28 0.1931 12 0.5589
Production and Operations Management 8 0.6936 16 0.62 33 0.1638 13 0.5582
Interfaces 13 0.5667 9 0.68 17 0.251 14 0.5489
European Journal of Operational Research 14 0.5593 14 0.64 16 0.2513 15 0.53
Networks 15 0.5446 21 0.52 24 0.2148 16 0.4688
Annals of Operations Research 18 0.5145 19 0.55 35 0.1434 17 0.4545 Journal of The Operational Research Society 20 0.3894 23 0.515 14 0.2582 18 0.4134 International Journal of Computer Integrated
Manufacturing 17 0.522 37 0.38 23 0.2248 19 0.4058
International Journal of Production Research 19 0.4695 27 0.4 15 0.2521 20 0.3982
Computers and Operations Research 22 0.3503 26 0.43 29 0.1893 22 0.35 International Journal of Production
Economics 21 0.3862 27 0.4 32 0.1679 23 0.3481
Transportation Research Part B-Methodology 25 0 9 0.68 10 0.3464 24 0.3413
Journal of Quality Technology 25 0 21 0.52 5 0.5033 25 0.3087
Omega - International Journal of Management
Science 23 0.2505 27 0.4 22 0.2369 26 0.3076
Journal of Optimization Theory &
Applications 25 0 18 0.56 19 0.2498 27 0.274
Journal of Global Optimization 25 0 20 0.54 18 0.2505 28 0.2661 Computers & Industrial Engineering 24 0.213 37 0.38 37 0.129 29 0.263
Queueing Systems 25 0 24 0.48 12 0.2996 30 0.2519
Computational Optimization and Applications 25 0 27 0.4 9 0.3787 31 0.2357 Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and
Transportation Review 25 0 25 0.45 31 0.1682 32 0.2136
International Journal of Operations And
Production Management 25 0 27 0.4 21 0.2477 33 0.2095
Applied Mathematical Modeling 25 0 27 0.4 26 0.2088 34 0.2018 International Journal of Flexible
Manufacturing Systems 25 0 37 0.38 25 0.2122 35 0.1944
Journal of Manufacturing Systems 25 0 34 0.39 30 0.1772 36 0.1914 Production Planning & Control 25 0 27 0.4 34 0.1462 37 0.1892 International Journal of Systems Science 25 0 34 0.39 36 0.1411 38 0.1842 International Transactions in Operations
Research 25 0 34 0.39 38 0 39 0.156 3.會計次領域 在會計方面,由於一般在國外期刊發表之會計相關期刊評比文章均將稅務方面的 期刊納入,本次評比亦採用同樣的作法,由於稅務方面的研究,許多實務性相當高,我 們未將一些較偏實務的期刊納入,也未納入少數較偏法學的稅務期刊。由於最後列示排 名的期刊僅三十種,因此影響應該不大,有可能在三十名之內的期刊而未列入排名的可 能只有 Tax Law Review。另外,一些還不錯的歐洲會計期刊(如 British Accounting Review 及 European Accounting Review)此次研究並未納入,原因在於,我們找到的期刊排名 文獻中許多均未將這些期刊納入評比。美國會計學會的 International Accounting Section 最近出版的新期刊 Journal International Accounting Research 也頗受到國外學者的重視, 由於期刊排名文獻中沒有此期刊,故亦未納入評比,以免結果失真。最後,有些看物有 變更名稱,相關資料也加以合併。例如,International Journal of Accounting 原來的刊名 是 International Journal of Accounting, Education & Research。
Review、Contemporary Accounting Research、Journal of Accounting & Economics、Journal of Accounting Research、Review of Accounting Studies。由於 Contemporary Accounting Research 及 Review of Accounting Studies 進入 SSCI 名單的時間尚短,在 2002 年尚未有 影響係數的資料,因此影響係數都只是零。
會計領域的期刊排名結果,前 30 名期刊見表十一所示。由於大部分的會計期刊並 非 SSCI 期刊,沒有影響係數資料的期刊排名也難較高。除前述之 Contemporary
Accounting Research 及 Review of Accounting Studies 外,基本上都是 SSCI 期刊排名在前 面,在未來有這些期刊的影響係數後,結果可能會有更動。 表 十一 會計期刊排名 文獻排名 學者評 論排名 影響係數 (00-02) 加權平均 期刊名稱 Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank N.
Score Rank N. Score
Journal of Accounting Research 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Journal of Accounting & Economics 2 0.9746 1 1 3 0.8703 2 0.9639
Accounting Review 3 0.957 1 1 2 0.8991 3 0.9626
Accounting, Organizations & Society 4 0.8961 6 0.7386 5 0.3628 4 0.7264
National Tax Journal 5 0.7766 7 0.6477 4 0.5736 5 0.6844
Review of Accounting Studies 7 0.7333 4 0.8182 8 0 6 0.6206 Contemporary Accounting Research 6 0.7392 5 0.7955 8 0 7 0.6139 Auditing: A Journal of Practice & Theory 16 0.5916 9 0.6136 6 0.3042 8 0.5429 Journal of Accounting, Auditing & Finance 9 0.715 8 0.6364 8 0 9 0.5406 Journal of Accounting & Public Policy 11 0.6629 9 0.6136 8 0 10 0.5106 Journal of the American Taxation Association 13 0.6528 9 0.6136 8 0 11 0.5066 Journal of Management Accounting Research 15 0.6071 12 0.5909 8 0 12 0.4792 Behavioral Research in Accounting 10 0.6761 13 0.5114 8 0 13 0.475 Journal of Business Finance & Accounting 8 0.7157 14 0.4318 8 0 14 0.459
Journal of Taxation 12 0.6568 21 0.375 7 0.1384 15 0.4404
Journal of Accounting Literature 14 0.6131 14 0.4318 8 0 16 0.418
Abacus 17 0.5213 18 0.3864 8 0 17 0.3631
Accounting Horizons 19 0.4815 16 0.4205 8 0 18 0.3608
Accounting & Business Research 18 0.4831 21 0.375 8 0 19 0.3432 Research in Governmental & Non-profit
Accounting 21 0.4057 18 0.3864 8 0 20 0.3168
Advances in Accounting Information Systems 20 0.4106 29 0.3409 8 0 21 0.3006 Review of Quantitative Finance and Accounting 22 0.2933 18 0.3864 8 0 22 0.2719 International Journal of Accounting 24 0.241 17 0.4091 8 0 23 0.26
Issues in Accounting Education 23 0.2474 21 0.375 8 0 24 0.249 Research in Accounting Regulation 25 0.2341 26 0.3636 8 0 25 0.2391 Advances in Accounting 26 0.2333 29 0.3409 8 0 26 0.2297 Journal of Accounting Education 27 0.1977 26 0.3636 8 0 27 0.2245 Journal of Information Systems 28 0.1395 21 0.375 8 0 28 0.2058 Journal of Systems Management 29 0.0951 26 0.3636 8 0 29 0.1835 Journal of Cost Management 30 0.068 21 0.375 8 0 30 0.1772
就加權平均排名前七名的期刊來看皆是頗負盛名的會計期刊。前三種期刊應是公 認最佳的期刊,就三種指標來看皆然,其次,第四、五名及第六、七名的排名則稍有不 一致,學者的排名相對於文獻及影響係數排名剛好相反。其餘的結果應不至於突兀。表 11 中三個構面排名的關係很大,若以原始的排名來看,相關係數分別為文獻排名與專 家評分 0.877(p<0.001),專家評分與影響係數 0.633(p<0.001),文獻排名與影響係數 0.638(p<0.001)。若以標準化以後的數字來看,相關係數分別為文獻排名與專家評分 0.834(p<0.001) , 專 家 評 分 與 影 響 係 數 0.782(p<0.001) , 文 獻 排 名 與 影 響 係 數 0.657(p<0.001)。 在會計領域一般也都認為前七名的期刊,大致上為 A 級期刊,其中前三名則常被 視為 A+的期刊。 4. 行銷管理次領域 行銷管理領域的研究在過去三十年中蓬勃發展,除了以傳統行銷管理為主題(如消 費者行為、通路管理、零售管理、廣告管理、品牌管理等)的文章與期刊之外,近幾年 有關服務業管理、網路行銷、與國際行銷的文章與期刊更是蓬勃發展,根據荷蘭 Tilburg 大學網站的統計,英語系行銷相關的期刊到目前為止已經有將近一百本,而且數目是不 斷的在增加,這還不包含一些非英語系的行銷期刊。 行銷管理領域的期刊排名結果,前 30 名期刊見表十二所示。由於部份期刊並非 SCI/SSCI 期刊,因此,沒有影響係數的資料而會造成排名下滑。但整體而言,除少數 期刊排名變動影響較大之外,大部份並不影響結果。表十二中三個構面排名的關係很 大 , 相 關 係 數 分 別 為 文 獻 排 名 與 專 家 評 分 0.759(p<0.001) , 專 家 評 分 與 影 響 係 數 0.740(p<0.001),而文獻排名與影響係數 0.726 (p<0.001)。 由表十二中可以看出,行銷界歷史較悠久,同時也是大家比較推崇的三大期刊
(Journal of Marketing, Journal of Consumer Research, Journal of Marketing Research)如預 期的排名前三名,以發表行銷數理與數量模型文章為主的 Marketing Science 緊接在後, 第五名的 Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 近幾年則不斷的竄升,在 ISI 的影 響指數可以看到此現象。
排名六至十名的期刊也是行銷傳統上幾個主要期刊,比較特殊的是歐洲行銷學會 所出刊的 International Journal of Research in Marketing 在這次排名的成績相當優異(排 名第七),行銷的主流期刊過去皆是以美國本土期刊為主。排名十一至二十的期刊中除 了 Journal of Consumer Psychology 為比較新的期刊外,其餘皆是在行銷學界各專門領域 中享有甚名。 表 十二 行銷管理期刊排名 文獻排名 學者評 論排名 影響係數 (00-02) 加權平均 期刊名稱 Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank Weighted Average Journal of Marketing 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Journal of Consumer Research 3 0.9416 1 1 2 0.978 2 0.9722 Journal of Marketing Research 2 0.9895 1 1 3 0.768 3 0.9494
Marketing Science 4 0.882 4 0.9661 4 0.7619 4 0.8916
Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 6 0.8457 5 0.7458 5 0.7061 5 0.7778
Journal of Retailing 5 0.8594 7 0.6864 8 0.3728 6 0.6929
International Journal of Research in Marketing 11 0.5943 6 0.7211 6 0.4403 7 0.6142 Journal of Advertising 9 0.6802 10 0.527 13 0.2481 8 0.5325 Journal of Business Research 7 0.7405 12 0.4407 19 0.1569 9 0.5039 Journal of Product Innovation Management 16 0.4639 9 0.5593 7 0.4339 10 0.4961 Journal of Advertising Research 8 0.7148 15 0.3983 12 0.25 11 0.4952 Journal of Consumer Psychology 18 0.4249 8 0.6441 17 0.1652 12 0.4606 Journal of Public Policy and Marketing 12 0.5271 14 0.4068 9 0.3377 13 0.4411 Industrial Marketing Management 10 0.6275 23 0.3513 14 0.2191 14 0.4353
Marketing Letters 17 0.4622 11 0.4831 21 0 15 0.3781
Psychology and Marketing 15 0.484 18 0.3729 18 0.1611 16 0.375 Journal of Personal Selling and Sales
Management
13
0.5233 170.3898 21 0 17 0.3652 European Journal of Marketing 14 0.5141 22 0.3644 21 0 18 0.3514 Journal of Consumer Affairs 19 0.3919 25 0.3236 15 0.1905 19 0.3243 Journal of International Marketing 22 0.3002 20 0.3698 11 0.2782 20 0.3236 Journal of Business Ethics 23 0.2812 24 0.339 10 0.3082 21 0.3097 International Journal of Market Research 26 0.2081 16 0.3966 16 0.1864 22 0.2792
(Formerly Journal of the Market Research Society)
Journal of Service Research 25 0.225 12 0.4407 21 0 23 0.2663 Journal of Interactive Marketing 24 0.2613 18 0.3729 21 0 24 0.2537 Journal of Consumer Marketing 20 0.3287 28 0.2681 21 0 25 0.2387 Journal of Services Marketing 21 0.3019 27 0.2712 21 0 26 0.2292 Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice 27 0.1791 28 0.2681 21 0 27 0.1789 Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing 28 0.1703 28 0.2681 21 0 28 0.1754 Journal of Business Logistics 29 0.0671 21 0.3686 21 0 29 0.1743 International Marketing Review 30 0.0375 26 0.3051 20 0.1214 30 0.1613
排名二十至三十名的期刊中除了歷史比較悠久的期刊(如 Journal of Business Ethics, Journal of the Market Research Society(更名為 International Journal of Market Research), Journal of Business Logistics, International Marketing Review)外,新近的期刊(如 Journal of Service Research, Journal of Service Marketing, Journal of Consumer Marketing) 也嶄露 頭角。
整體而言,這次的排名統計除了幾本比較新的期刊有明顯的排名竄升之外,大部 分的期刊排名在三方面的評比皆是非常一致的,不過以國際行銷為主攻領域之學者或許 會感到以國際議題為主的行銷期刊在歐美主導的行銷學術領域中要得到好的聲望確實 不容易,這次只有三本以國際行銷議題為主的行銷期刊(European Journal of Marketing, Journal of International Marketing, International Marketing Review)排名前三十名,Journal of Global Marketing 與 International Journal of Advertising 分別列名第三十一與三十二 名。針對以國際行銷議題為主的行銷期刊的排名列於表十三。 如同本研究報告前言所述,領域的大小影響排名甚巨,行銷管理的學術領域近年 來有愈來愈趨多元化的現象,相信有非常多學者的主攻領域頂級期刊在整合的排名報表 中並不一定會有好的成績,此點由國外專家的問卷回覆中,也可以感覺出來,不同領域 的專家對於其他領域期刊的的評價也不盡相同,所以說能在這麼多的行銷期刊中排名前 三十名,其實已經相當不簡單。因此,排名順序的使用必須考慮個別學者主攻領域的差 異作適當的調整。 表 十三 國際行銷議題為主的行銷期刊的排名
文獻排名 學者評 論排名 影響係數 (00-02) 加權平均 期刊名稱 Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank Weighted Average European Journal of Marketing 1 0.5141 2 0.3644 3 0 1 0.3514 Journal of International Marketing 2 0.3002 1 0.3698 1 0.2782 2 0.3236 International Marketing Review 5 0.0375 3 0.3051 2 0.1214 3 0.1613 Journal of Global Marketing 3 0.0869 5 0.2589 3 0 4 0.1383 International Journal of Advertising 4 0.075 4 0.2681 3 0 5 0.1372
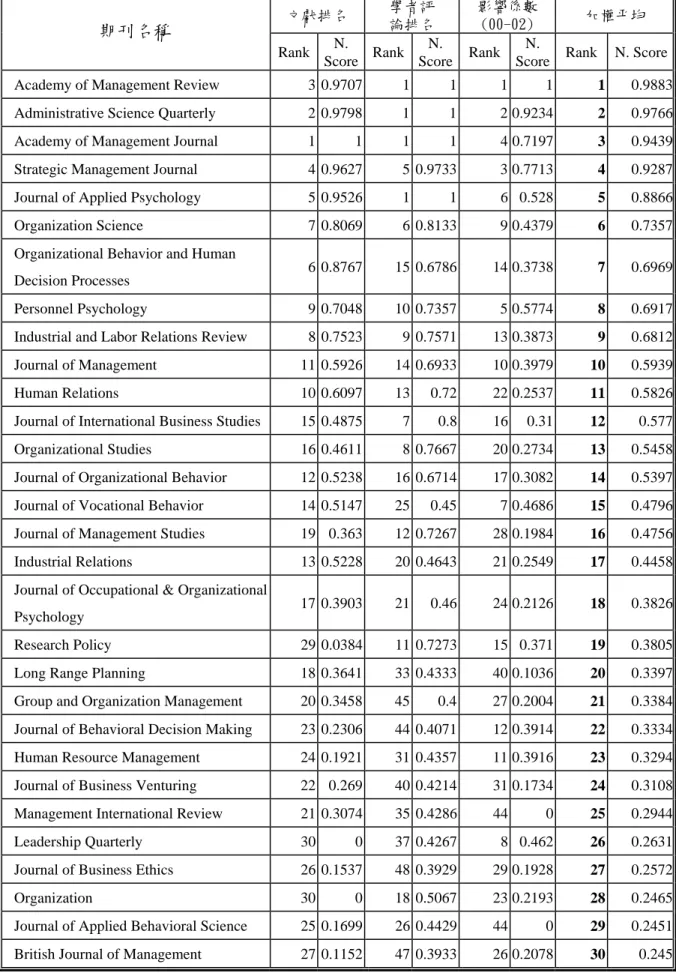
5. 一般管理次領域(含組織行為、人力資源管理、組織理論、策略管理、國際企業) 一般管理領域的期刊排名結果,整理於表十四。針對此份排名,有人或許會提出質 疑,如有些知名期刊(如:Industry and Corporate Change)不在這裡面,有點奇怪,我 們也同意。惟根據目前之評估標準,不在 SSCI 名單本就吃虧。至於 Management Science 不列名在此之原因,則之前已有解釋。另外,好的新期刊(如:Strategic Organization) 因為沒有文獻支持與 SSCI impact factor 也排不上去。而國際企業之另一個知名期刊 Journal of Word Business 也 吃 虧 在 文 獻 排 名 不 高 ( 落 後 Management International Review )。 事 實 上 , Advances in International Management 與 Advances in Strategic Management 也(可能)因為 SSCI impact factor 未列名或分數不高之原因,很遺憾的, 未能列入。
另外有一點值得補充的是,本研究並沒有為科技管理(Technology and Innovation
Management)做特別考量,也或許因為在一般管理之學術主軸思考下,Research Policy 之
排名並不特別高,而 R&D Management、IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management、 Journal of High Technology Management 以及 Journal of Engineering and Technology Management 也根本排不上去。惟對科管領域之排名,Cheng, C-H et al. (1999)3最近的期刊
排 名 研 究 則 有 得 出 , 科 管 領 域 之 前 三 大 期 刊 為 IEEE Transactions on Engineering
Management、Research Policy、Journal of Product Innovation Management,而此或可作
為補充本研究之不足與相關領域學者之參考。
3 Cheng, C. H., Kumar, A., Motwani, J. G., Reisman, A., and Madan, M. (1999) ‘A citation analysis of
表 十四 一般管理期刊排名 文獻排名 學者評 論排名 影響係數 (00-02) 加權平均 期刊名稱 Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank N.
Score Rank N. Score
Academy of Management Review 3 0.9707 1 1 1 1 1 0.9883
Administrative Science Quarterly 2 0.9798 1 1 2 0.9234 2 0.9766
Academy of Management Journal 1 1 1 1 4 0.7197 3 0.9439
Strategic Management Journal 4 0.9627 5 0.9733 3 0.7713 4 0.9287 Journal of Applied Psychology 5 0.9526 1 1 6 0.528 5 0.8866
Organization Science 7 0.8069 6 0.8133 9 0.4379 6 0.7357
Organizational Behavior and Human
Decision Processes 6 0.8767 15 0.6786 14 0.3738 7 0.6969
Personnel Psychology 9 0.7048 10 0.7357 5 0.5774 8 0.6917 Industrial and Labor Relations Review 0.7523 9 0.7571 13 0.3873 9 0.6812 Journal of Management 11 0.5926 14 0.6933 10 0.3979 10 0.5939
Human Relations 10 0.6097 13 0.72 22 0.2537 11 0.5826
Journal of International Business Studies 15 0.4875 7 0.8 16 0.31 12 0.577 Organizational Studies 16 0.4611 8 0.7667 20 0.2734 13 0.5458 Journal of Organizational Behavior 12 0.5238 16 0.6714 17 0.3082 14 0.5397 Journal of Vocational Behavior 14 0.5147 25 0.45 7 0.4686 15 0.4796 Journal of Management Studies 19 0.363 12 0.7267 28 0.1984 16 0.4756 Industrial Relations 13 0.5228 20 0.4643 21 0.2549 17 0.4458 Journal of Occupational & Organizational
Psychology 17 0.3903 21 0.46 24 0.2126 18 0.3826
Research Policy 29 0.0384 11 0.7273 15 0.371 19 0.3805
Long Range Planning 18 0.3641 33 0.4333 40 0.1036 20 0.3397 Group and Organization Management 20 0.3458 45 0.4 27 0.2004 21 0.3384 Journal of Behavioral Decision Making 23 0.2306 44 0.4071 12 0.3914 22 0.3334 Human Resource Management 24 0.1921 31 0.4357 11 0.3916 23 0.3294 Journal of Business Venturing 22 0.269 40 0.4214 31 0.1734 24 0.3108 Management International Review 21 0.3074 35 0.4286 44 0 25 0.2944
Leadership Quarterly 30 0 37 0.4267 8 0.462 26 0.2631
Journal of Business Ethics 26 0.1537 48 0.3929 29 0.1928 27 0.2572
Organization 30 0 18 0.5067 23 0.2193 28 0.2465
Journal of Applied Behavioral Science 25 0.1699 26 0.4429 44 0 29 0.2451 British Journal of Management 27 0.1152 47 0.3933 26 0.2078 30 0.245
8
有整合之排名(欄一),與因為領域之分歧性而分別列舉之組織行為/人力資源管理/組織 理論(欄二)與策略管理、國際企業、組織理論之個別排名(欄三)。 表 十五 一般管理領域及次領域期刊整合排名 一般管理領域期刊綜合排名 組織行為、人力資 源管理、組織理論 領域期刊排名 策略管理、國際 企業、組織理論 領域期刊排名
1. Academy of Management Review 1 1
2. Administrative Science Quarterly 2 2
3. Academy of Management Journal 3 3
4. Strategic Management Journal 4
5. Journal of Applied Psychology 4
6. Organization Science 5
7. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes
5
8. Personnel Psychology 6
9. Industrial and Labor Relations Review 7
10. Journal of Management 8 6
11. Human Relations 9 7
12. Journal of International Business Studies 10 8
13. Organization Studies 11 9
14. Journal of Organizational Behavior 12
15. Journal of Vocational Behavior 13
16. Journal of Management Studies 14 10
17. Industrial Relations 15
18. Journal of Occupational & Organizational Psychology
16
19. Research Policy 11
20. Long Range Planning 12
21. Group and Organization Management 17 22. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making 18
23. Human Resource Management 19
24. Journal of Business Venturing 13
25. Management International Review 14
26. Leadership Quarterly 20
27. Journal of Business Ethics 21
28. Organization 22 15
29. Journal of Applied Behavioral Science 23
6. 財務管理次領域
財務管理領域的研究有一些刊登於經濟、會計、計量、與統計的期刊。此次期刊 的選擇係根據 FLI(Financial Literature Index)所列的期刊,再配合參照 Chan, Fok, and Pan (2000)與 Oltheten, Theoharakis, and Travlos (2003)所選擇的期刊,排除經濟(如 Journal of Credit, Money, and Banking,與 Journal of Risk and Uncertainty 等)、會計(Accounting Review,與 Journal of Accounting Research 等)領域導向的期刊後,所得的期刊種類共 有 48 種,名單與排名結果如表十六所示。 由於部份期刊並非屬於 SSCI 期刊,因此,沒有影響係數的資料而會造成排名下滑, 但整體而言,除少數期刊排名變動影響較大之外,大部份並不影響結果。表十六中三個 構面排名的關係很大,相關係數分別為文獻排名與專家評分 0.7736(p<0.01),文獻排名 與影響係數 0.7093(p<0.01),專家評分與影響係數 0.8193(p<0.001),表示排名相當一致, 可靠程度也相當大。 表 十六 財務管理期刊排名 文獻排名 學者評 論排名 影響係數 (00-02) 加權平均 期刊名稱 Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank N. Score Rank Weighted Average Journal of Finance 2 0.9984 1 1 1 1 1 0.9994
Journal of Financial Economics 1 1 1 1 2 0.8397 2 0.9679 Review of Financial Studies 3 0.9556 1 1 3 0.5285 3 0.8879 Journal of Business 6 0.8821 4 0.8636 4 0.4632 4 0.7909
Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis 4 0.9112 4 0.8636 7 0.2997 5 0.7699
Journal of Financial Intermediation 7 0.7983 10 0.7386 6 0.3242 6 0.6796 Financial Management 5 0.8855 14 0.6818 8 0.2373 7 0.6744 Journal of Banking and Finance 10 0.761 8 0.75 9 0.2159 8 0.6476 Mathematical Finance 11 0.6717 6 0.7727 5 0.3441 9 0.6466 Journal of Empirical Finance 8 0.7692 12 0.7045 17 0 10 0.5895 Journal of International Money and Finance 12 0.6426 10 0.7386 12 0.179 11 0.5883 Journal of Derivatives 16 0.5401 7 0.7614 17 0 12 0.5206 Financial Analysts Journal 9 0.7642 16 0.5 17 0 13 0.5057 Journal of Real Estate Finance and Economics 22 0.3516 13 0.6932 10 0.1893 14 0.4558 Journal of Portfolio Management 13 0.6344 19 0.4432 15 0.087 15 0.4484 Journal of Financial Markets 24 0.3168 8 0.75 17 0 16 0.4267