行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫 成果報告
子計畫四:動態 VR 運動復健輔助系統之人機溝通界面及使
用者情緒瞭解(II)
計畫類別: 整合型計畫 計畫編號: NSC91-2213-E-009-108- 執行期間: 91 年 08 月 01 日至 92 年 07 月 31 日 執行單位: 國立交通大學電機與控制工程學系 計畫主持人: 張志永 報告類型: 精簡報告 處理方式: 本計畫可公開查詢中 華 民 國 92 年 11 月 10 日
行政院國家科學委員會補助專題研究計畫成果報告
※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※
※ ※
※ 子計劃四: ※
※ 動態 VR 運動復健輔助系統之人機溝通介面及 ※
※ 使用者情緒瞭解(II) ※
※ ※
※ ※
※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※※
計畫類別:
□
個別型計畫
■
整合型計畫
計畫編號:NSC-91-2213-E-009-108
執行期間: 91 年 8 月 1 日至 92 年 7 月 31 日
計畫主持人:張志永
共同主持人:
本成果報告包括以下應繳交之附件:
□赴國外出差或研習心得報告一份
□赴大陸地區出差或研習心得報告一份
□出席國際學術會議心得報告及發表之論文各一份
□國際合作研究計畫國外研究報告書一份
執行單位:國立交通大學電機與控制工程學系
中 華 民 國 92 年 10 月 31 日
行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫第二年期末報告
總計畫: 泛用型動態虛擬實境操控與運動復健輔助系統研發
子計畫四: 動態 VR 運動復健輔助系統之人機溝通介面
及使用者情緒瞭解(
II)
(Subproject IV) A Study of Real-Time Human Emotional Understanding
and its Mechanism for Intelligent Human-Computer Interface (II)
計畫編號 : NSC-91-2213-E-009-108
執行期限:91/08/01-92/07/31
主持人:張志永 交通大學電機與控制工程學系
一、 中文摘要
本子計畫藉電子攝影機隨時紀錄操控 者臉部,藉影像處理技術,偵測出操控 者之情緒狀態,並建立操控者與模擬器 間的人性化溝通管道,以將操控者的使 用感受忠實的告知子計畫一與二進行 模擬器的控制變數轉換及後續階層式 控制法則之設計,本子計畫已發展出一 套即時之人情緒狀態判定系統藉線上 拍攝操控者臉部影像序列,由影像處理 技術偵測出操控者之臉部變化,進而推 敲操控者快樂、生氣、與中性情緒狀 態,它的效果經過驗證可達 92﹪辨識 率。在人機系統溝通與與對映方面,我 們設計出一套感覺概念交流所須之對 映 對 映 網 路 的 裝 置 來 進 行 , 我 們 以 Kosko 之 模 糊 關 聯 網 路 Fuzzy Associate Memory 設計之,我們以適應 性 的 局 部 訓 練 法 則 及 口 袋 演 算 法 觀 念 , 所 設 計 的 二 階 聯 想 記 憶 (Second-Order Associative Memory),具 有最大吸引範圍。關鍵詞:虛擬實境, 人臉表情情識, 序
列人臉影像處理, 人性化溝通管 道,抽象式觀念表示法,聯想記憶
英文摘要
The purpose of this project is to construct a human-machine commu- nication interface between the users and the simulators, which can transfer user’s feeling sense of to project 1, to transform the control variables for the project 2 control loop design of the simulator of Steward platform. In this way, the performance of the whole control loop and the method of adjusting parameters can be interacted with the user and the reality of the dynamics can be enhanced. Therefore, the project can be viewed as a higher-level feedback unit of the whole simulator system.
VR system can be more genuine if
the truly sense of users can be communicated to the dynamic systems. This can be achieved by on-line monitoring the user’s facial emotion and transferring the user‘s feeling to the machine and updating the appropriate control parameters. The feeling of human being is an abstract concept and there is no corresponding physical quantity, i.e., universe of discourse, for the membership function to define with. Research on how to extract the user facial emotion, represent the abstract concept and devise a method that can communicate with machine simulator constitutes the major concerns to be investigated in this project.
Keywords: Virtual Reality, Facial
Emotion Recognition, Facial Image Sequence Processing, Abstract Concept Representation, Associative Memory
二、 緣由與目的
動態模擬系統之動態感覺,決定了 虛擬實境之逼真程度,但如何表示動態 模擬系統使用者之感覺概念,並傳遞給 行為轉換與控制模組(子計畫一)及六軸 運動平台、力回饋模組(子計畫二、三) 做適當的參數調整與控制,是本計畫之 重點。為了表示使用者的感覺概念,道, 以將操控者的使用感受忠實的告知子計 畫一與二進行模擬器的控制變數轉換及 後續階層式控制法則之設計,並藉此以 改善整個控制迴路及調整參數的方法, 而提高了模擬器的真實性,本計畫可視 為整個模擬器系統的高階回授單元。本 計畫之兩個主要子題: 計畫將發展出一 套即時之人情緒與注意力狀態判定系 統,及能與機器系統做抽象式觀念感覺 溝通與對映之方法,下面是我們在這一 年的計畫中,對以上兩方面所法提出來 實現方法的描述。三、 研究方法與成果
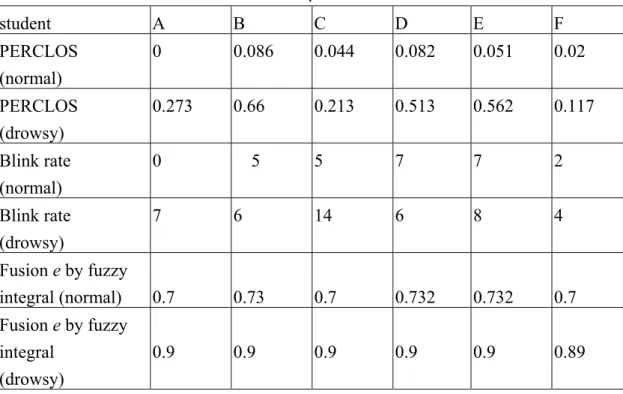
(1a) 人類表情與情緒的辨識 人類表情與情緒的辨識此子系統 第一部份為臉部特徵的選取。臉部特徵 的選取對於辨識人臉和臉部表情是很 重要的。人類臉部有些明顯的特徵如眼 睛、嘴巴、眉毛、臉部輪廓等等。在本 計畫中,我們擷取眉毛、眼睛及嘴巴作 為主要的特徵。我們以前的研究顯示, 我 們 首 先 使 用 粗 略 輪 廓 預 測 程 序 法 (rough contour estimation routine)以及 我 們 所 提 出 的 點 輪 廓 偵 測 法(point contour detection method)這兩種影像處 理的技術,來擷取眉毛、 眼睛和嘴巴 這三個特徵器官的正確輪廓。由於使用 粗略輪廓預測程序法所得到的眉毛輪 廓已經相當精準,足夠做為辨識之用, 故不用再加強其輪廓。而使用粗略輪廓 預測程序法所得到的眼睛和嘴巴的輪 廓不夠精準,所以我們再使用點輪廓偵 測法現正進行臉部表情運動單元的分 析 。我們定義 30 個臉部特徵點;來描 述這三個臉部特徵的位置和形狀。臉部 快樂、生氣、與中性情緒狀態表情我們 藉由一放射狀函數基礎之神經網路辨 識,它的效果經過驗證可達 92﹪辨識 率,此部份已在第一年完成與報告。 (1b) 人類注意力的辨識 在人機系統溝通與與對映方面,我4 們正在進行以觀察臉部影像序列,偵測 使用者之感覺與精神狀態,精神不濟或 昏昏欲睡時,機器會提出暫停機台操作 之警告,以策安全。我們以眼睛縮小閉 合 時 間 比 例 (PERCLOS) 及 眨 眼 頻 率 (Blink Duration) 兩種特徵參數,偵測精 神不濟或昏昏欲睡之程度,我們對幾位 受測者拍攝大約 30 分鐘的影片,包含 受測者精神較佳狀態或打瞌睡狀態,所 計算分析 PERCLOS 及 Blink Duration 量測已經分別完成,準確率蠻高;我們 再 利 用 模 糊 積 分(fuzzy integral) 的 概 念,發展出上述兩種證據跡象資訊整合 的技術,以增加偵測的可靠度。模糊積 分法組合推斷使用者之感覺精神狀態 之定義,如表一所示,我們再利用模糊 積分法提供之證據跡象資訊整合組合 推論,使用者之感覺與精神狀態,如表 二所示,模糊積分融合推論技術,可增 加正確率 12%。 (2) 人機系統溝通與與對映法 人 機 系 統 溝 通 與 與 對 映 之 法 Takagi 等人係利用關聯網路 (Associate Memory; 簡 稱 AM ) 設 計 之 赫 比 式 (Hebbian)學習方法來建構之對映傳遞 之關係,但 AM 之兩對映是由(0,1)之串 列對映至(0,1)之串列,與上述之感覺 對應,為 0〜1 間的任意實數對映,我 們初步的研究其對映精確度很差。本計 畫主要是擴展並衍生觀念模糊集的概 念,以某一層的觀念節點的節點活性度 值組表示一個感覺概念,以機電整合受 控體之物理量為輸入層,感覺概念的溝 通與學習可由函數大約化之對映方法 來執行感覺概念之交流,以使電腦有感 覺概念意識與溝通的能力,而對於觀念 節點溝通所需之函數大約化,我們擬設 計出一套對映網路的裝置來進行,亦即 在受控機器中建立並學習某一感覺概 念交流所須之對映網路。第一年我們以 Kosko 之模糊關聯網路 Fuzzy Associate Memory 設 計 , 所 設 計 關 聯 網 路 (Associate Memory)可以雙向聯想記憶 (Bidirectional Associative Memory),簡
稱 BAM,實現。近來雙向聯想記憶已
經在聯想記憶研究當中扮演一個很重 要 的 角 色 。 非 對 稱 式 雙 向 聯 想 記 憶 (Asymmetric Bidirectional Associative Memory)為雙向聯想記憶放寬鍵結權重 必須要對稱的限制之結果,且相較於常 見的雙向聯想記憶結構有較好的記憶 與回想效能。高階非對稱式雙向聯想記 憶(High-Order Asymmetric Bidirectional Associative Memory)的記憶容量比一階 的好很多,二階非對稱式雙向聯想記憶 設計,已在第一年完成。
延伸此一設計理念,今年設計具有 最大吸引範圍的二階單一向聯想記憶 (Second-Order Associative Memory)即 傳 統 Hopfield 聯 想 記 憶 (Hopfield Associative Memory)是有可能而且很簡 單的。我們首先推導出對於二階聯想記 憶的鍵結權重矩陣能夠保證將所有標 準圖樣組回憶出來之充分條件。為了要 遵守完全回憶定理,接著闡述學習步伐 大小也是適應性的局部訓練法則,它將 導致一個較快的設計時間。最後我們推 導出下列定理:在設計 SOAM 時,增 大符合完全回憶定理的數值,將會增加 一個有雜訊的圖樣能夠正確地收斂到 它的聯想圖樣之能力;以這個定理當作 基礎,我們的演算法也予以修改,能夠 保證每一個訓練圖樣能儲存在具有越 大 的 吸 引 範 圍 。 針 對 color graphics adapter (CGA)字型的電腦模擬,已經證
明出我們所提出的局部訓練法則效果 優於其他主要的 AM 的設計,其結果 如表三與圖一所示。
四、 結論與討論
一理想的虛擬實境系統,應能隨時 掌握操控者的情況與感受,並能讓操控 者與系統模擬器做直覺性的溝通,而讓 使用者有完全沈浸其中的感受,因此研 究發展任何虛擬實境技術時,使用者與 機器系統之間的互動與溝通為相當重要 的一環。本子計畫藉電子攝影機隨時紀 錄操控者臉部,藉影像處理技偵測出操 控者之情緒狀態,並建立操控者與模擬 器間的人性化溝通管道,以將操控者的 使用感受忠實的告知子計畫一與二進行 模擬器的控制變數轉換及後續階層式控 制法則之設計,並藉此以改善整個控制 迴路及調整參數的方法,而提高了模擬 器的真實性,本計畫可視為整個模擬器 系統的高階回授單元。本子計畫已發展 出一套即時之人情緒狀態判定系統藉線 上拍攝操控者臉部影像序列,由影像處 理技術偵測出操控者之臉部變化,進而 推敲操控者快樂、生氣、與中性情緒狀 態,它的效果經過驗證可達 92﹪辨識 率。另外,我們以眼睛縮小閉合時間及 眨眼頻率兩種特徵參數,偵測精神不濟 或昏昏欲睡之程度,本偵測系統提出非 接觸式之使用者是否昏睡及精神不濟的 判定技術,可增加單一特徵參數正確率 12%,整合正確率達 95%。在人機系統溝 通與與對映方面,我們以模糊SOAM 設 計,實現感覺概念交流所須之對映網 路,模擬證明我們所提出的局部訓練法 則效果優於其他主要的AM 設計。五、 參考文獻
[1] H. Ushida, and T. Yamaguchi, and T. Takagi, “ Fuzzy associate memory based knowledge construction with a application to a human machine interface, ” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 46, pp. 851-860, 1999.
[2] T. Takagi, A. Imura, H. Ushida, and T. Yamaguchi, “Conceptual fuzzy sets as a meaning representation and their inductive construction, ” International
Journal of Intelligent Systems, vol. 10,
pp. 929-945, 1995.
[3] Cootes, T. F., C. J. Taylor, D. H. Cooper, and J. Graham, “Active shape models - their training and application,” Computer Vision and Image Understanding,, Vol. 61, No. 1, pp. 38-59. 1995.
[4] P. Ekman, and W. V. Friesen, The
Facial Action Coding System,
Consulting Psychologist Press, San Francisco, CA,1978.
[5] H. Kobayashi, and F. Hara, “Analysis of the neural network recognition characteristics of six basic facial expressions,” in
Proceedings of 3rd IEEE Int. Workshop on Robot and Human Communication, Nagoya, Japan, pp.
222-227, 1994.
[6] A. Lanitis, C. J. Taylor, and T. F. Cootes, “Automatic interpretation and coding of face images using flexible models," IEEE
6
Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. 19,
No. 7, pp. 743-756, 1997.
[7] M. A. Turk A. P. Pentland, “Eigenfaces for recognition,"
Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience,
Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 71-86, 1991. [8] A. L. Yuille, P. W. Hallinan, and D.
S. Cohen, “Feature extraction from faces using deformable templates,”
International Journal of Computer Vision, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 99-111,
1992.
[9] T. Wang, X. Zhuang, and X. Xing, “Designing bidirectional associative memories with optimal stability,”IEEE
Trans. on Syst. Man, Cybern., vol. 24,
pp. 778-790, May. 1994.
[10] H. Oh and S. C. Kothari, “Adaptation of the relaxation method for learning in bidirectional associative memory, ”
IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, vol. 5,
pp. 576-583, July. 1994.
[11] C.-S. Leung, L.-W. Chan, and E. Lai, “Stability and statistical properties of second order bidirectional associative memory, ” IEEE Trans. on Neural
Networks, vol. 8, pp. 267-277, Mar.
1997.
[12] H. Shi, Y. Zhao, and X. Zhuang,“A general model for bidirectional associative memories,” IEEE Trans.
on Syst. Man, Cybern. B, vol. 28, pp.
511-519, Aug. 1998.
[13] F. L. Chung and T. Lee,“On Fuzzy Associative Memory with Multiple
Rule Storage Capacity, ” IEEE
Trans. Fuzzy Syst., vol. 4, no. 3, pp.
375-384, 1996.
[14] S. B. Cho and J. H. Kim, “ Combining multiple neural networks by fuzzy integral for robust classification, ” IEEE Trans. Syst.,
Man, Cybern. B, vol. 25, no. 1, pp
113-120, 1995.
[15] K. Ogawa and M. Shimotani, “Drowsiness detection system,”
Technical Report of Mitshbish Electric, Mar. 1997.
[16] H. Sako and A. V. W. Smith, “Real-time facial expression recognition based on features’ positions and dimensions,” in Proc.
IEEE Int. Pattern Recognition Conf., 1996.
[17] C. D. Wylie et al., “Commercial motor vehicle driver fatigue and alertness study,” Project Report (Report No. FHWAMC-97-002), Washington, D. C: Federal Highway Administration Office of Motor Carriers, Oct. 1996.
[18] H. Tahani and J. M. Keller, “Information fusion in computer vision using the fuzzy integral,”
IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.,
vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 733-741, May 1990.
TABLE 1. Alertness level defined by fuzzy integral.
alertness level fuzzy integral (e)
conscious e < 0.8
moderate drowsy 0.8< e <0.9
severely drowsy e > 0.9
TABLE 2. Results compared by the three detection algorithms . student A B C D E F PERCLOS (normal) 0 0.086 0.044 0.082 0.051 0.02 PERCLOS (drowsy) 0.273 0.66 0.213 0.513 0.562 0.117 Blink rate (normal) 0 5 5 7 7 2 Blink rate (drowsy) 7 6 14 6 8 4 Fusion e by fuzzy integral (normal) 0.7 0.73 0.7 0.732 0.732 0.7 Fusion e by fuzzy integral (drowsy) 0.9 0.9 0.9 0.9 0.9 0.89
TABLE 3.
Recall rates p(r) versus Hamming distance r of auto-AM design (iterative retrieval) schemes over CGA characters
r = 0 r = 1 r = 2 r = 3 r = 4 r = 5 r = 6 r = 7 r = 8 PSOAAM 1.000 1.000 0.994 0.994 0.991 0.970 0.968 0.944 0.548 GBAM 1.000 0.942 0.826 0.697 0.578 0.461 0.365 0.332 0.278 OPSOAAM 0.385 0.348 0.315 0.285 0.262 0.260 0.214 0.187 0.176 OPFOAAM 0.077 0.062 0.046 0.042 0.037 0.035 0.035 0.036 0.034 圖一:使用有 r 個雜訊 CGA 圖樣之各式聯想記憶辨識結果 8