Utilization of National Health Insurance Database
Utilization of National Health Insurance Database
to Analyze Medication Risk in Taiwan
to Analyze Medication Risk in Taiwan
~ Aspects of IPR and Drug Pricing Policy ~ Aspects of IPR and Drug Pricing Policy ~~
HUI
HUI--PO WANG, Ph.D.
PO WANG, Ph.D.
Professor and the Dean of College of pharmacy Professor and the Dean of College of pharmacy
Taipei Medical University Taipei Medical University
1
2007-10-26-Hui-po Wang-AASP 2007-Manila
e
e--mail: mail: hpw@tmu.edu.twhpw@tmu.edu.tw
website: http://pharm.tmu.edu.tw/principle.htm website: http://pharm.tmu.edu.tw/principle.htm
1. Irrational medication is part of the culture.
2. Campaign for pharmacovigilance planning (PvP) is like
Background and Objective of the Study
p g p g p g ( )
canoeing upstream.
3. Risk from drug overuse starts to call for public attention. 4. PE study is important for identifying risk (ICH E2E).
5. National Health Insurance Research Database-Taiwan (NHIRD) is powerful for PE studies.
6 M l ti f h ti l IPR i ht b k f t
2
6. Malpractice of pharmaceutical IPR might be a key factor causing irrational medication.
7. The impact of IPR and drug pricing policy on drug consumption and expenditure was investigated.
Education on Safe Medication for the silver
Education on Safe Medication for the silver--hair
hair
1.
1. >500 pharmacists/year were >500 pharmacists/year were involved as lecturers. involved as lecturers. 2.
2. >100 pharmacy students >100 pharmacy students served as teaching assistants. served as teaching assistants.
3
via 50 community colleges via 50 community colleges
“Drug Free Teenagers”
“Drug Free Teenagers”
Program
Program
>200 pharmacy college kids meet pre>200 pharmacy college kids meet pre--teenagers.teenagers.
via 370 elementary schools via 370 elementary schools
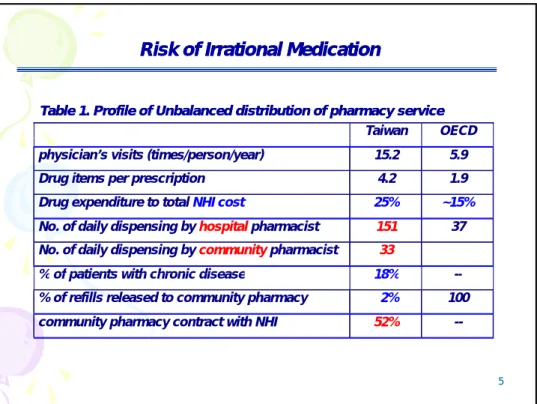
Table 1. Profile of Unbalanced distribution of pharmacy service Table 1. Profile of Unbalanced distribution of pharmacy service
Risk of Irrational Medication
Risk of Irrational Medication
Taiwan OECD
physician’s visits (times/person/year) 15.2 5.9 Drug items per prescription 4.2 1.9 Drug expenditure to total NHI cost 25% ~15% No. of daily dispensing by hospital pharmacist 151 37
No. of daily dispensing by community pharmacist 33 % of patients with chronic disease 18%
5
% of patients with chronic disease 18% -- % of refills released to community pharmacy 2% 100 community pharmacy contract with NHI 52% --
Undetermined Risk: Risk Factor goes to Individual or System? Undetermined Risk: Risk Factor goes to Individual or System?
year ESRD prevalence
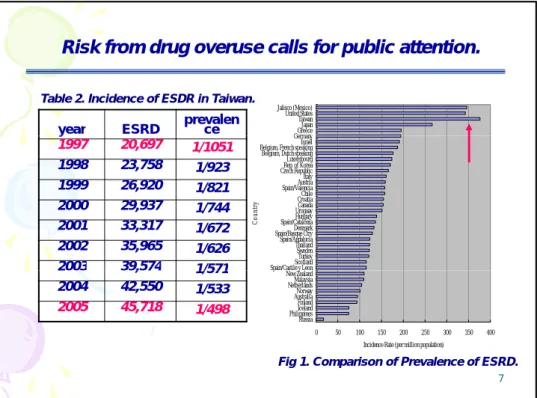
Risk from drug overuse calls for public attention.
GermanyGreece Japan Taiwan United States Jalisco (Mexico)
Table 2. Incidence of ESDR in Taiwan.
y 1997 20,697 1/1051 1998 23,758 1/923 1999 26,920 1/821 2000 29,937 1/744 2001 33,317 1/672 2002 35,965 1/626
2003 39,574 1/571 Spain/Castile y LeonScotland Turkey Sweden Thailand Spain/Andalucia Spain/Basque CtryDenmark Spain/CataloniaHungary UruguayCanada CroatiaChile Spain/ValenciaAustria Italy Czech RepublicRep. of Korea Luxembourg Belgium, Dutch speaking Belgium, French speakingIsrael Germany C oun tr y 7 2003 39,574 1/571 2004 42,550 1/533 2005 45,718 1/498 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 Russia PhilippinesIceland Finland AustraliaNorway NetherlandsMalaysia New Zealand p y
Incidence Rate (per million population)
Fig 1. Comparison of Prevalence of ESRD.
From GPP to GP
From GPP to GP
D
D
P
P
Risk exists where pharmacists’ effort can not reach.
G
G
ood
ood
Pharmacy
Pharmacy
&
&
Delivery
Delivery
P
P
ractice
ractice
Pharmacists Pharmacists
medicine medicine
Definition and Pricing
Definition and Pricing of NHI payable Medicineof NHI payable Medicine 1. Patented proprietary medicine (PM) 2 Off-patent proprietary medicine (OPM)
NHI Pricing Policy
NHI Pricing Policy not Based on Drug
not Based on Drug IPR
IPR
2. Off patent proprietary medicine (OPM)
3. BE generic medicine (BEGM): 80% or less to OPM 4. Generic medicine (GM): 80% or less to OPM
*
Hatch-Waxman Act-USA: drug pricing& patentrestoration act * BE is required for generic approval since 1988 in Taiwan.Consequences: Consequences:
9
Consequences: Consequences:
1. Everlasting better pay on OPMended with unfair competition and complicated pharmacoeconomic profile in medical circle. 2. Granted protection to OPMled to unnecessary NHI expenditure. 3. Patient risk due to drug overuse is under-estimated.
OPM
OPMgets everlasting better paygets everlasting better pay
Pricing Policy Stimulates Clinical Trials
Pricing Policy Stimulates Clinical Trials
OPM
OPM gets everlasting better pay.gets everlasting better pay.
⇒
⇒ Desire to beDesire to be thethefirst runnerfirst runnerstimulates stimulates CTCT.. ⇒
⇒ Is quality being sacrificed?Is quality being sacrificed?
⇒
⇒ risk might be underestimated.risk might be underestimated.
⇒
⇒ Ethical andEthical andhuman righthuman rightissue.issue.
10
www.habsgirls.org.uk/ images
⇒
⇒
Method for Risk Analysis Studies
Method for Risk Analysis Studies
♦
♦ Database of National Health Insurance for Database of National Health Insurance for Research Research ((NHIRDNHIRD): ): 1. Systematic Sampling Database
1. Systematic Sampling Database (SSD)(SSD) 2. Longitudinal Health Insurance Database 2. Longitudinal Health Insurance Database (LHID) (LHID) 3 Speicial Disease Sampling Database
3 Speicial Disease Sampling Database (SDSD)(SDSD) 3. Speicial Disease Sampling Database
3. Speicial Disease Sampling Database (SDSD) (SDSD)
4. All sampling databases have ambulatory and inpatient subsets 4. All sampling databases have ambulatory and inpatient subsets
♦
♦ Data retrieved: NHI payable priceData retrieved: NHI payable price and amount usedand amount used of year 2002 to 2004 of year 2002 to 2004
♦
♦ ReferencesReferences
1. Global statistics of NHI
1. Global statistics of NHI --Taiwan, http://www.nhi.gov.tw Taiwan, http://www.nhi.gov.tw 2 Pricing
2 Pricinghttp://www nhi gov tw/inquire/query1 asp?menu=1 & menu id=8
11
2. Pricing
2. Pricinghttp://www.nhi.gov.tw/inquire/query1.asp?menu=1 & menu id=8
3. Expenditure
3. Expenditure http://www.nhi.gov.tw/webdata/webdata.asp?menu=3
4. OECD reform of health care systems
4. OECD reform of health care systems--A review of 17 OECD countries. A review of 17 OECD countries. 5. Merck Index
5. Merck Index
6. Taiwanese Physicians’ Desk Reference, CA Chen ed., 2006, Taiwan 6. Taiwanese Physicians’ Desk Reference, CA Chen ed., 2006, Taiwan 7. Physicians’ Desk Reference. Medical Economics Company, Montvale, NJ. 7. Physicians’ Desk Reference. Medical Economics Company, Montvale, NJ.
Table 3: Number of drugs classified by IPR and unit price status. Table 3: Number of drugs classified by IPR and unit price status.
IPR status of the top 200 NHI payable drugs
IPR status of the top 200 NHI payable drugs
unit price Years
off patent
No. of
medicine OPM>GM OPM<GM OPM=GM
Information unclear 0 19 5 0 0 14 1-5 34 19 1 0 14 6-10 30 20 1 1 8 11-15 16 11 1 0 4
Market Price of Highest
P i
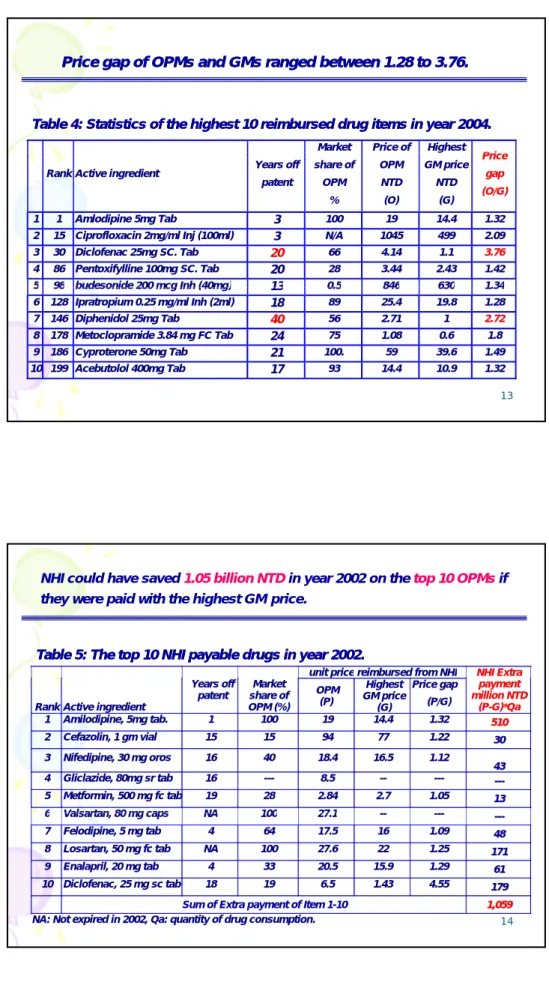
Table 4: Statistics of the highest 10 reimbursed
Table 4: Statistics of the highest 10 reimbursed drug itemsdrug items in year 2004. in year 2004.
Price gap of OPMs and GMs ranged between 1.28 to 3.76. Price gap of OPMs and GMs ranged between 1.28 to 3.76.
Rank Active ingredient Years off patent share of OPM % OPM NTD (O) g GM price NTD (G) Price gap (O/G) 1 1 Amlodipine 5mg Tab 3 100 19 14.4 1.32 2 15 Ciprofloxacin 2mg/ml Inj (100ml) 3 N/A 1045 499 2.09 3 30 Diclofenac 25mg SC. Tab 20 66 4.14 1.1 3.76 4 86 Pentoxifylline 100mg SC. Tab 20 28 3.44 2.43 1.42 5 98 budesonide 200 mcg Inh (40mg) 13 0 5 846 630 1 34 13 5 98 budesonide 200 mcg Inh (40mg) 13 0.5 846 630 1.34 6 128 Ipratropium 0.25 mg/ml Inh (2ml) 18 89 25.4 19.8 1.28 7 146 Diphenidol 25mg Tab 40 56 2.71 1 2.72 8 178 Metoclopramide 3.84 mg FC Tab 24 75 1.08 0.6 1.8 9 186 Cyproterone 50mg Tab 21 100. 59 39.6 1.49 10 199 Acebutolol 400mg Tab 17 93 14.4 10.9 1.32
unit price reimbursed from NHI NHI Extra
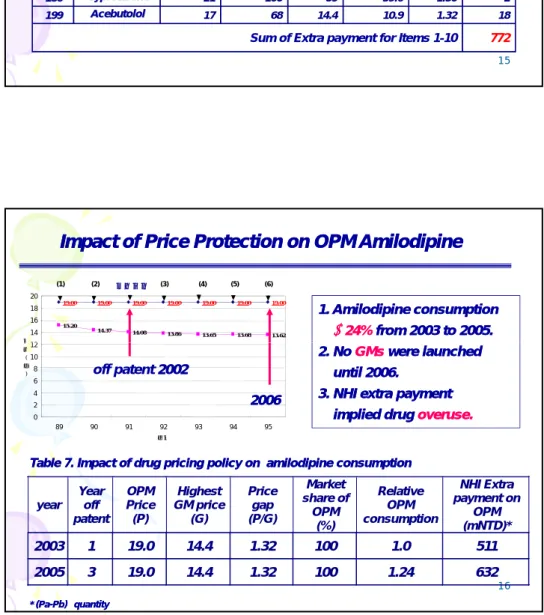
Table 5: The top 10 NHI payable drugs in year 2002. Table 5: The top 10 NHI payable drugs in year 2002.
NHI could have saved 1.05 billion NTDin year 2002 on the top 10 OPMsif they were paid with the highest GM price.
Rank Active ingredient
Years off patent Market share of OPM (%) OPM (P) Highest GM price (G) Price gap (P/G) payment million NTD (P-G)*Qa 1 Amilodipine, 5mg tab. 1 100 19 14.4 1.32 551100 2 Cefazolin, 1 gm vial 15 15 94 77 1.22 3300 3 Nifedipine, 30 mg oros 16 40 18.4 16.5 1.12 4 433 4 Gliclazide, 80mg sr tab 16 --- 8.5 -- --- ----- -5 Metformin, 500 mg fc tab 19 28 2.84 2.7 1.05 1133 6 Valsartan 80 mg caps NA 100 27 1 14 6 Valsartan, 80 mg caps NA 100 27.1 -- --- ----- -7 Felodipine, 5 mg tab 4 64 17.5 16 1.09 4488 8 Losartan, 50 mg fc tab NA 100 27.6 22 1.25 117711 9 Enalapril, 20 mg tab 4 33 20.5 15.9 1.29 6611 10 Diclofenac, 25 mg sc tab 18 19 6.5 1.43 4.55 117799
Sum of Extra payment of Item 1-10 11,,005599
NHI could have saved 772 million NTD on OPM in year 2004 for the top 10 drugs with largest price gap.
unit price reimbursed from NHI Years off Market share P i
Extra payment
Table 6.
Table 6. The top 10 drug items with largest price gap between between OPM and GM in year 2002. and GM in year 2002.
Rank
Active ingredient
Years off
patent Market share of OPM (%) OPM (P) Highest GM price (G) Price gap (P/G) payment (P-G)×Qa million NTD 1 1 AAmmllooddiippiinnee B l 3 100 19 14.4 1.32 632 1 155 CCiipprrooffllooxxaacciinn 2 /100 l 3 87 1045 499 2.09 24 3 300 DDiiccllooffeennaacc2255mmgg 20 19 4.14 1.1 3.76 5 8 866 PPeennttooxxiiffyylllliinnee 100 20 49 3.44 2.43 1.42 7 9 988 BBuuddeessoonniiddee220000 /40 13 69 846 630 1.34 26 1 12288 IIpprraattrrooppiiuumm00..2255 18 89 25.4 19.8 1.29 32 15 /2 l 1 14466 DDiipphheenniiddooll2255mmgg 40 7.50 2.72 1 2.72 1 1 17788 MMeettoocclloopprraammiiddee 3 84 24 92 1.08 0.6 1.80 25 1 18866 CCyypprrootteerroonnee 0 21 100 59 39.6 1.50 2 1 19999 AAcceebbuuttoollooll 400 17 68 14.4 10.9 1.32 18
Sum of Extra payment for Items 1-10 772
Impact of
Impact of Price Protection on OPM Amilodipine
Price Protection on OPM Amilodipine
1. Amilodipine consumption 1. Amilodipine consumption ↑↑24%24%from 2003 to 2005.from 2003 to 2005. 19.00 19.00 19.00 19.00 19.00 19.00 19.00 15.20 14.37 14.08 13.86 13.65 13.68 13.62 12 14 16 18 20 金 (1) (2) 專利到期 (3) (4) (5) (6) 2. No
2. No GMsGMswere launchedwere launched until 2006.
until 2006. 3.
3. NHI extra payment NHI extra payment implied drug
implied drug overuse.overuse.
off patent 20022002 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 年度 金 額 ( 元 ) 2006 2006
Change of price gap: 4.14 to 3.76 Change of price gap: 4.14 to 3.76
Change of market share: 19% to 9% Change of market share: 19% to 9%
6.9 6.7 6.5 5.32 5 6 7 8 金 ( 1) ( 2) ( 3) ( 4 ( 5) ( 6)
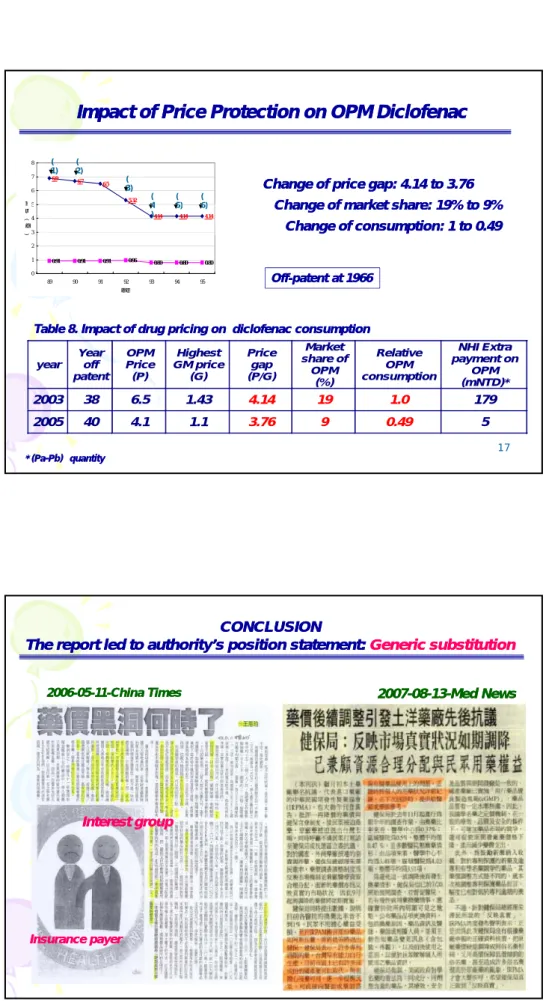
Impact of
Impact of Price Protection on OPM Diclofenac
Price Protection on OPM Diclofenac
Off
Off--patent at 1966patent at 1966
Change of market share: 19% to 9% Change of market share: 19% to 9% Change of consumption: 1 to 0.49 Change of consumption: 1 to 0.49 4.14 4.14 4.14 0.91 0.91 0.91 0.96 0.80 0.80 0.80 0 1 2 3 4 5 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 年份 金 額 ( 元 ) 原廠藥藥價 學名藥藥價 4 ) 5) 6)
Table 8. Impact of drug pricing on diclofenac consumption Table 8. Impact of drug pricing on diclofenac consumption
17
* (Pa
* (Pa--Pb) Pb) ××quantityquantity
year Year off patent OPM Price (P) Highest GM price (G) Price gap (P/G) Market share of OPM (%) Relative OPM consumption NHI Extra payment on OPM (mNTD)* 2003 38 6.5 1.43 4.14 19 1.0 179 2005 40 4.1 1.1 3.76 9 0.49 5 CONCLUSION CONCLUSION The report led to authority’s position statement:
The report led to authority’s position statement: Generic substitutionGeneric substitution
2007
2007--0808--1313--Med NewsMed News 2006
2006--0505--1111--China TimesChina Times
Interest group Interest group
18
Insurance payer Insurance payer
System building for Safe Medication
System building for Safe Medication
~ The voice from Taiwanese Pharmacists ~
~ The voice from Taiwanese Pharmacists ~
19 ~Shel Silverstein~
THANK YOU
THANK YOU
Conclusion
Conclusion
1. System Building for risk minimization1. System Building for risk minimization is important in societies like is important in societies like Taiwan where irrational medication is prevalent
Taiwan where irrational medication is prevalent Taiwan where irrational medication is prevalent. Taiwan where irrational medication is prevalent.
2. PE studies for risk analysis led important input to public policy. 2. PE studies for risk analysis led important input to public policy. 3. PvP
3. PvP challenged the culture, the medical profession, the challenged the culture, the medical profession, the pharmaceutical industry and the political environment. pharmaceutical industry and the political environment. 3.