1
行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫成果報告
不同藥物對粒線體功能異常時鼠大腦病變的影響: 磁共振影像,質譜與組
織變化的相關
The cer ebr al lesions induced by mitochondr ial dysfunction in r ats: the
nuclear magnetic r esonance and immunohistochemical studies
計畫編號:NSC 88-2314-B-002-180
執行期限:87 年 8 月 1 日至 88 年 7 月 31 日
主持人:李旺祚 台大醫學院小兒科
E-mail: wtlee@tpts5.seed.net.tw
一、中文摘要 粒線體功能異常會引起許多不同年齡層的神 經病變。最近的研究顯示,抑制興奮性氨基酸的釋 放和施予 NMDA 受體的拮抗物,都會減輕粒線體毒 物引起的腦病變。在本計畫中,我們以粒線體呼吸 鏈複合體 II 的抑制劑(3-Nitropropionic acid, 3-NP,15mg/kg)為實驗藥物,連續注射於八週大的 Sprague-Dawley 株鼠(n=10)五天,並於第六天以磁 共振影像(MRI)和質譜(1H NMR spectroscopy)來評 估其系列的變化。結果發現 Sprague-Dawley 株鼠注 射 3-NP 後,會產生紋狀體和海馬迴的病變,並出 現特別的行為變化,這種變化與組織學上的變化一 致 。 若 接 受 MK-801(2mg/kg) 和 Lamotrigine (10mg/kg 和 20mg/kg)的注射,腦病變則明顯改 善,並且行為的變化也消失;磁共振質譜上的變化 則可看到治療後原先 NAA 的降低也減輕,並且 Lactate 的昇高也消失。整體而言,在治療的藥物 中 lamotrigine(20mg/kg)較 lamotrigine(10mg/kg) 和 MK-801 能 提 供 更 好 的 保 護 作 用 。 由 於 lamotrigine 的副作用較少,因此更有臨床運用的 價值,值得未來更進一步的研究。 關鍵詞:NMDA 受體,磁共振影像,磁共振質譜 Abstr actMagnetic resonance imaging and in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy were used to evaluate the therapeutic effect of lamotrigine and MK-801 on rat brain lesions induced by 3-nitropropionic acid. Systemic administration of 3-nitropropionic acid (15mg/kg/day) to two-month-old Sprague-Dawley rats (n=10 for each group) for five consecutive days induced selective striatal and hippocampal lesions and specific behavioral change. Pretreatment with lamotrigine (10mg/kg or 20mg/kg/day) or MK-801 (2mg/kg/day) attenuated the lesions and behavioral change. There were no significant differences in T2 values of the striatum and hippocampus among rats pretreated with MK-801, lamotrigine (20mg/kg) and sham controls. Significant elevations of succinate/creatine and lactate/creatine ratios and decreases of N-acetylaspartate/creatine and choline/creatine ratios were observed after 3-nitropropionic acid injections (P<0.001). The changes
were nearly prevented after pretreatment with lamotrigine (20mg/kg). However, the N-acetylaspartate/creatine in rats pretreated with lamotrigine (10mg/kg) (P<0.01) and MK-801 (P<0.05) still showed significant reduction as compared with sham controls. We conclude that both lamotrigine and MK-801 are effective in attenuation of brain lesions induced by 3-nitropropionic acid. A higher dose of lamotrigine provides better neuroprotective effect than MK-801. With better therapeutic effect and fewer side effects, lamotrigine is more promising for the potential clinical application.
Key Wor ds: 3-nitropropionic acid, T2 maps,
magnetic
resonance spectroscopy, N-acetylaspartate (NAA)
二、緣由與目的
Neurodegenerative diseases are generally thought to be associated with deficits in energy metabolism (Beal, 1993).56However, the pathogenesis of neuronal death remains unknown. Recently, (3-NP), an irreversible inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) (the complex II in mitochondrial respiratory chain), was found to effectively induce selective striatal lesions in rats and non-human primates (Beal, 1993; Borlongan, 1997). The lesions closely mimic the histologic and neurochemical characteristics of Huntington’s disease (Beal, 1993; Borlongan, 1997).
The mechanism involved in neuronal death in 3-NP-induced brain lesions remains controversial. The possibility that impairment of mitochondrial metabolism might lead to secondary excitotoxic lesions via activation of NMDA receptors was first suggested by Novelli et al (1988). They found that energy-compromised neurons were more vulnerable to excitotoxicity of glutamate. Several drugs have been shown to have a neuroprotective effect in 3-NP-treated rats, including antagonists of NMDA receptors, such as MK-801 (Beal, 1993). However, the adverse effects of NMDA receptor antagonists may limit their clinical application (Fix, 1994). An alternative approach may be the inhibition of glutamate release. Lamotrigine may act at voltage-dependent sodium channels to decrease the presynaptic release of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate (Leach, 1991). However, the neuroprotective effect of lamotrigine and its correlation with cerebral metabolite alteration in the
2 striatum have never been evaluated non-invasively.
Over the past several years, more and more evidence was accumulated to indicate that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) can be used to non-invasively evaluate cerebral lesions and measure the change of regional cerebral metabolites in vivo (Bownell, 1998;Jenkis, 1996). Many intracranial biochemicals can be identified by 1H-MRS, including N-acetylaspartate (NAA), choline-containing compounds (Cho), creatine (Cr), lactate (Lac), myo-inositol, succinate (Suc), glutamine, and glutamate, etc. Being mainly present in neurons, NAA serves as a useful marker for follow-up of lesion progression over time, and is useful in evaluating the severity of neuronal damage (Guimaraes, 1995; Jenkins, 1996). Therefore, 1H-MRS provides a good tool to non-invasively evaluate the potential usefulness of neuroprotective agents in animal models and in patients with neurological diseases.
In the present study, we employed both spin-spin (T2) relaxation time mapping and in vivo 1H-MRS to evaluate the therapeutic and neurochemical effects of lamotrigine and MK-801 on the striatal and hippocampal lesions induced by 5-day 3NP injections.
三、研究方法、結果與討論
Animal pr epar ation and dr ug tr eatment
Two-month-old male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into five groups (10 rats for each group). Group I received daily injection of normal saline as sham control. Group II to V received daily 3-NP injection at a dose of 15mg/kg/day for 5 consecutive days. Groups III to V were pretreated with lamotrigine (10mg/kg/day for Group III and 20mg/kg/day for Group IV), and MK-801 (2mg/kg/day for Group V) before daily 3-NP injection.
Behavior al changes of the animals
3-NP-induced behavioral changes in the animals were recorded daily, and immediately before sacrifice, graded according to the neurological scale described by Guyot et al. (1997).
Magnetic r esonance (MR) measur ements
The MR experiments were performed on the 6th day. The animals were prepared as previously described.18 MR measurements were performed on a Biospec 4.7 T spectrometer with an active shielding gradient at 6.9 G/cm in 500 µsec. Field of view = 5cm, 4 slices (2 mm thick with 1 mm gap), matrix = 256 x 128, TR = 4000msec, and initial TE = 20msec with an echo spacing of 20msec for 6 echoes. The PRESS sequence preceded by three consecutive chemical shift selective saturation (CHESS) pulses for water suppression was used to acquire the localized proton spectra over the striatum.
Statistics
The data were expressed as means ± S.D.. One-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey test was used. P<0.05 was considered to be significant.
RESULTS
Behavior al obser vation
Group II rats began to develop characteristic gait disturbance or hindlimb paralysis 2-3 days after systemic administration of 3-NP (15mg/kg/day). Immediately before the MR experiments were performed, nine of the ten 3-NP-treated rats developed Grade 4-5 behavioral changes. However, except for two rats in Group III (lamotrigine 10mg/kg/day), who developed mild neurological deficits in movement, other rats pretreated with lamotrigine and MK-801 showed only mild decrease of daily activity without prominent limb paralysis.
T2 mapping
Bilateral hippocampal and striatal lesions were observed after subacute 3-NP injections for 5 days. The calculated T2 values of bilateral hippocampus and striatum in 3-NP-treated rats were significantly higher than those in normal controls (P<0.001) (Table1). In rats pretreated with lamotrigine 20mg/kg and MK-801,
Table 1. T2 Values in Rat Brains Obtained from T2 Maps. Values Are Expressed as Mean (ms) ± S.E.M.
No Cerebral cortex Hippocamp us Striatum Thalamus Normal saline 10 62.35 ± 1.27 64.40 ± 1.47 61.79 ± 0.50 57.79 ± 0.74 3NP 10 61.88 ± 0.85 97.88 ± 19.20 107.28 ± 28.12 58.84 ± 2.68 Lamotrigin e (10mg/kg) 10 61.00 ± 1.02 72.36 ± 19.30* 66.28 ± 11.09* 57.55 ± 1.33 Lamotrigin e (20mg/kg) 10 62.13 ± 1.37 63.41 ± 2.30* 62.21 ± 2.36* 57.38 ± 0.63 MK-801 10 63.20 ± 1.91 66.39 ± 2.27* 63.19 ± 1.91* 58.01 ± 1.09 Note: * P <0.001 as compared to 3NP-treated group.
Table 2. In Vivo Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Rat
Brains. Values Are Expressed as Mean (ms) ± S.E.M.
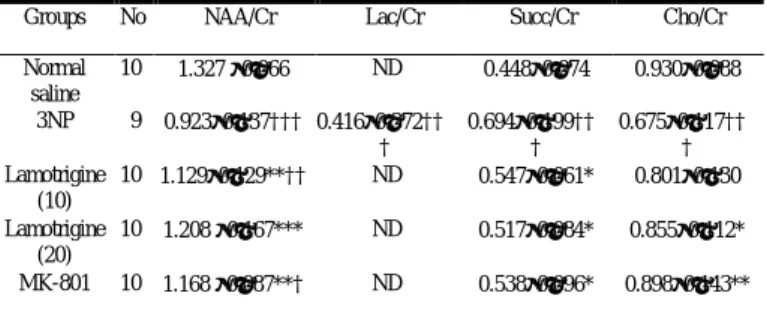
Groups No NAA/Cr Lac/Cr Succ/Cr Cho/Cr
Normal saline 10 1.327 ±0.066 ND 0.448±0.074 0.930±0.088 3NP 9 0.923±0.137††† 0.416±0.372†† † 0.694±0.199†† † 0.675±0.117†† † Lamotrigine (10) 10 1.129±0.129**†† ND 0.547±0.061* 0.801±0.130 Lamotrigine (20) 10 1.208 ±0.167*** ND 0.517±0.084* 0.855±0.112* MK-801 10 1.168 ±0.087**† ND 0.538±0.096* 0.898±0.143** Note: ***P <0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05 as compared to 3-NP-treated group; ††† P<0.001, †† P<0.01, † P<0.05 as compared to normal saline group; ND, not detectable.
the lesions were completely prevented, except for two MK-801-treated rats which had mild hippocampal lesions (data not shown).
3
Neur ochemical changes in in vivo pr oton magnetic r esonance spectr oscopy
The neurochemical change of the striatum after subacute NP injection is shown in Table 2. One 3-NP-treated rat was excluded from analysis due to markedly generalized decrease of Cr, Cho, and NAA. Compared with sham controls, significant elevations of Suc/Cr and Lac/Cr ratios and decreases of NAA/Cr and Cho/Cr ratios were observed after subacute 3NP injections for 5 days (P<0.001).
DISCUSSION
Secondary excitotoxic brain injury has been suggested to be the pathogenetic mechanism of brain lesions in 3-NP-treated rats (Beal, 1993; Brouillet, 1995). Therefore, antagonists of NMDA glutamate receptors, including MK-801, can be used to alleviate excitotoxic brain injuries. However, the severe side effects and neurotoxicity of MK-801 limit its clinical use. Lamotrigine, a new anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy, has fewer side effects than the antagonists of NMDA receptors (Leach, 1991), and may be more promising for clinical application. According to our findings, although lamotrigine (10mg/kg) is not totally effective in alleviating the decrease of NAA/Cr, lamotrigine in a dose of 20mg/kg may be as effective or provide even greater protection than MK-801. This may be partly explained by lamotrigine's ability to act at both presynaptic and postsynaptic levels. As shown previously, 3-NP-induced toxicity may be mediated by both NMDA and non-NMDA receptors. Increasing duration and severity of energy compromise may also activate NMDA receptors. A combination of NMDA and non-NMDA receptor antagonists produces a greater protection than when either antagonist is used alone. MK-801 may even potentiate 3-NP-induced neuronal loss in striatal and cortical neuronal cultures, reflecting the neurotoxicity of MK-801. Therefore, MK-801 may not be as effective as lamotrigine in preventing neuronal death under the conditions of severe energy compromise.
In addition to less effective alleviation of 3-NP-induced lesions, two of the MK-801-treated rats in the present study showed persistently mild hippocampal lesions while their striatal lesions disappeared. The hippocampus is one of the regions with the highest concentration of mitochondrial enzymes and glutamate receptors (both NMDA and non-NMDA) in the brain (Greenamyre, 1985). Neuronal loss and cytoskeletal disruption after intrahippocampal injection of malonate are not protected by MK-801 (Pang, 1996), indicating the possible involvement of other mechanisms that account for the difference of hippocampal and striatal malonate toxicity. Because severe 3-NP intoxication activates both NMDA and non-NMDA receptors, once glutamate receptors in hippocampus are activated by ambient glutamate in prolonged energy
compromise, the hippocampal lesions may not be attenuated only by MK-801 due to plentiful other glutamate receptors in the hippocampus. On the contrary, although hippocampal lesions were seen in rats pretreated with low-dose lamotrigine, the lesions disappeared completely, indicating a good protective effect in both the hippocampus and striatum from treatment with lamotrigine (20mg/kg).
CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, both lamotrigine and MK-801 are effective in attenuation of 3-NP-induced striatal and hippocampal changes in T2 maps and 1H-MRS. Concurrent increase of Lac/Cr and Suc/Cr ratios and decrease of NAA/Cr and Cho/Cr ratios indicate an impairment of energy metabolism as the possible mechanism of brain injuries after 3-NP treatment. With fewer side effects, high-dose lamotrigine, acting at both the presynaptic and postsynaptic levels, has better neuroprotective effect than the NMDA antagonist MK-801, and is more promising for potential clinical applications. The present results may provide useful insights and new therapeutic strategies in the treatment and evaluation of neurodegenerative diseases. 四、計畫成果自評 結果已發表於 “Neuroscience 1999, in press”。具有 臨床與研究運用價值。 五、參考文獻
1. Beal M.F., Brouillet E., Jenkins B.G., Henshaw R., Rosen B. and Hyman B.T. (1993) Neurochemical and histologic characterization of Striatal excitotoxic lesions produced by the mitochondrial toxin 3-nitropropionic acid. J Neurosci 13,4181-4192.
2. Borlongan C.V., Koutouzis T.K. and Sanberg P.R. (1997) 3-Nitropropionic acid animal model and Huntington’s disease. Neurosci Biobehvio Rev 21,289-93.
3. Brouillet E., Hantraye P., Ferrante R.J., Dolan R., Leroy-Willig A., Kowall N.W. and Beal M.F. (1995) Chronic mitochondrial energy impairment produces selective striatal degeneration and abnormal choreiform movements in primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92:7105-7109.
4. Brownell A.L., Jenkins B.G., Elmaleh D.R., Deacon T.W., Spealman R.D. and Isacson O. (1998) Combined PET/MRS brain studies show dynamic and long-term physiological changes in a primate model of Parkinson disease. Nature Medicine 4,1308-1312.
5. Fix A.S., Horn J.W., Wightman K.A., Johnson C.A., Long G.G., Storts R.W., Farber N., Wozniak D.F. and Olney J.W. (1994) Neuronal vacuolization and necrosis induced by the
4 noncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist MK(+)801 (dizocilpine maleate): A light and electron microscopic evaluation of the rat retrosplenial cortex. Exp Neurol 123:204-215.
6. Greenamyre J.T., Olsen J.M.M., Penney J.B. and Young A.B. (1985) Autoradiographic characterization of N-methyl-D-aspartate-, quisqualate- and kainate-sensitive glutamate binding sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 233,254-263.
7. Guimaraes A.R., Schwartz P., Prakash M.R., Carr C.A., Berger U.V., Jenkins B.G., Coyle J.T. and Gonzalez R.G. (1995) Quantitative in vivo 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of neuronal loss in rat brain. Neuroscience 69,1095-1101.
8. Guyot M.C., Hantraye P., Dolan R., Palfi S., Maziere N. and Brouillet E. (1997) Quantifiable bradykinesia, gait abnormalities and Huntington's disease-like striatal lesions in rats chronically treated with 3-nitropropionic acid. Neuroscience 79,45-56.
9. Jenkins B.G., Brouillet E., Chen Y.C.I., Storey E., Schulz J.B., Kirschner P., Beal M.F. and Rosen B.R. (1996) Non-invasive neurochemical analysis of focal excitotoxic lesions in models of neurodegenerative illness using spectroscopic imaging. J Cereb blood Flow Metab 16,450-461. 10. Leach M.J., Baxter M.G. and Critchley M.A. (1991) Neurochemical and behavioral aspects of lamotrigine. Epilepsia 32(suppl), S4-8.
11. Novelli A., Reilly A.J., Lysko P.G. and Henneberry R.C. (1988) Glutamate becomes neurotoxic via N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor when intracellular enregy levels are reduced. Brain Res 451,205-212.
12. Pang Z., Umberger G.H. and Geddes J.W. (1996) Neuronal loss and cytoskeletal disruption following intrahippocampal administration of the metabolic inhibitor malonate: lack of protectiion by MK-801. J Neurochem 66, 474-484.