Department of Business Administration
I-Shou University
Master Thesis
Evaluating the Impact of Cross Cultural Training
on Job Performance
of Vietnamese Government Official
Advisor: Dr. Wan Ching Chang
Advisor: Dr. Le KhacDoa
Graduate Student: Nguyen Manh Tuan
(August/ 2015)
Department of Business Administration
·
1-Sho
.u Unive.rs
.itv
Sign!lture
Page
This
is to cc
i
1ify that
the the5isprepared.by
N
G-U
YflY
H/I N/t
Tl/AN
entitled "
Eva.la±in1
Me
Irnpod
Sf
fuss
-
Cd!WtaJ
T;i ata'1
F1t .?l.M1 an Job ll"rfo
'"!?1411C&
°i
Vi. t
!lM'JfM, hovW1m1nf'?/.pc,aA .
"
has been approved by h'is/her committee aE satisfuctory completion of thethesis requirement for the degree of !v1aster of BusinessAdministration.
Supervising Committee:
Dcpa rtm•••
chatr:
Y«
1'.-
('QW
Acknowledgements
First of all, I want to send many thanks to my advisors, Wan - Ching Chang, Ph.D, LeKhacDoa, Ph.D, for inspiring me with constructive comments and motivating me to complete this research paper. Their guidance and assistance were undeniably precious to my work.
Secondly, I want to give a special thanks to participants of the research. They gave me priceless feedbacks and ideas to improve the accuracy of my research results. Without them, the research is impossible to be done
Thirdly, this research paper is unable to be completed without the great help of teachers and lecturers at Hanoi University of Business and Technology (HUBT) and I-Shou University. They professionally organized an academic environment where we can improve valuable knowledge and skills. I want to express my deepest thank to them and hope we could have other opportunities to work together in the future.
Lastly, I would like to give thanks to my farmilys, my wife for supporting me, encouraging me, staying by my side, and giving me valuable advices.
Abstract
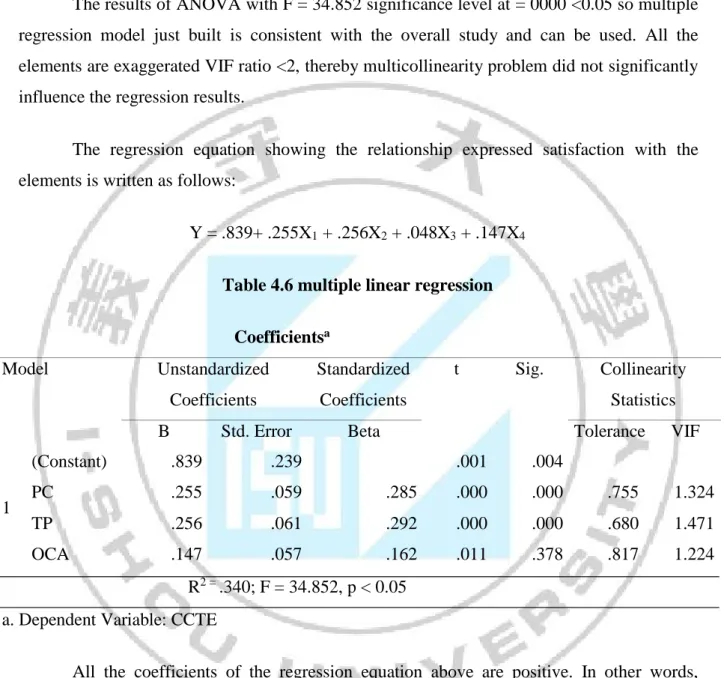
The purpose of this study is to evaluate of the effectiveness of cross-culture training on job performance of the officials in Vietnam. The data were collected from 207 students who ever participated in cross-culture training program, namely Project 165. Results of this study showed that all the coefficients of the regression equation above are positive. In particular, Cross-cultural training effectiveness most affected by personal training program (ß2 = .256), followed by the characteristic factor (ß1 = .255) the third factor is Off – Class activities (ß3 = .147). The hypothesis 4 is supported that Cross-cultural training effectiveness has a significant impact on Job performance (ß3 =.588). From the t-test and ANOVA, we can conclude that there is not different average job performance mean score between male and female (reject H5), There is different average job performance mean score between Leader and Staff (accept H6), people of different age shows the different level of job performance (accept H7), people of different study from different country shows the different level of job performance (accept H8) and people study different program have the different of job performance mean score (accept H9). Based on the findings, the implications, and limitations of this study and directions for the future researches were discussed.
Table of Contents
Acknowledgements ... I
Abstract ... II
Table of contents ... III
List of tables ... VI
List of figures ... VII
Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION ... 1
1.1 Research background ... 1
1.2 Government official oversea training situation in Vietnam ... 3
1.3 The purpose of research ... 7
1.4 Research question ... 7
1.5 Research contribution ... 8
Chapter II LITERATURE REVIEW... 10
2.1 Introduction ... 10
2.2 Human resource concepts and officers ... 10
2.2.1 Human resource concepts ... 10
2.2.2 Definition of officer ... 11
2.3 The theory of training and cross- culture training ... 14
2.3.2 Cross- culture training ... 16
2.4 Job performance ... 18
2.5 The relationship between cross culture training and job performance ... 19
Chapter 3 METHODOLOGY ... 22
3.1 Introduction ... 22
3.2 Sampling design ... 22
3.3 Data collection ... 23
3.4 Variable structure... 24
3.5 Data analysis ... 25
3.5.1 Reliability Analysis ... 25 3.5.2 Factor analysis ... 253.5.3 Develop regression and correlation analysis ... 28
Chapter IV RESULT ANALYSIS ... 31
4.1 Rate of response ... 31
4.2 Sample characteristics ... 31
4.3 Reliability ... 33
4.4 Factor analysis ... 33
4.5 Hypothesis testing ... 35
4.5.2 Assess the relevance of the model multiple linear regression ... 36
4.6 T-Test and Anova ... 39
Chapter V CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION ... 45
5.1 Conclusion ... 45
5.2 Findings conclusion ... 45
5.3 Recommendation for oversea training management ... 46
5.4 Limitation and future research ... 47
References ... 49
List of Tables
Table 3.1 Variable structure ... 24
Table 4.1: Respondent profife ... 31
Table 4.2 Summary of the Measurement Reliability (Cronbach’s Alpha) ... 33
Table 4.3 Factor analysis for independent variables ... 34
Table 4.4: Factor analyses for dependent variable ... 35
Table 4.5: Variable correlation ... 36
Table 4.6 multiple linear regression ... 37
Table 4.7 the relationship of Cross-cultural training effectiveness and Job performance ... 38
Table 4.8 T-Test of job performance levels between male and female ... 40
Table 4.9 T-Test of job performance levels between working position ... 40
Table 4.10ANOVA test of job performance level among age group. ... 41
Table 4.11 Homogeneous subsets for Age group ... 41
Table 4.9 ANOVA test of job performance level among country group ... 42
Table 4.13. Homogeneous subsets of country group ... 42
Table 4.14 ANOVA test of job performance level among training program group. ... 43
List of Figures
Figure. 2.3 "Model of Training System", Mathis and Jackson, p. 278 ... 16 Figure 2.5: Research framework ... 21 Figure 4.5 Regression standardized value ... 39
Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION
1.1 Research background
Increased internationalization in the economic, political, and social arenas has led to greater interpersonal cross-cultural contact. Because much of this contact has not been successful, cross-cultural training study has been proposed by many scholars as a means of facilitating more effective interaction (Black and Mendenhall, 1990; Farooq et al., 2015; Caligiuri, and Lundby, 2015).
In recent years, along with the general trends of education development in the world, Vietnam has made significant achievements in education renovation and education system modernization. These achievements play an important role in Vietnam’s industrialization- modernization strategy and international economic integration as well as meeting the learning needs of government officials. They create favorable conditions for government officials to approach other education in the world including some advanced education systems.
Government managers play a vital role in government agencies. Holding important positions in management system, senior and middle managers run the whole government’s operation to get the planned targets (Durazo et al., 2015). They define objectives and directions clearly so that government agencies can be organized effectively. It is necessary to train and improve the capacity of managers in government agencies. Many policies which encourage government officials to study master abroad are issued to enhance the quality of management staffs. It is the requirement in the age of industrialization and modernization and also the first step in personnel planning for a long term. To evaluate the effectiveness of cross- cultural training, many government agencies do the survey on the officials who are selected to study abroad by the government such as:
Article: Project 165: Results of Phase I and orientation for the next stage1, author Nguyen Van Quynh. In this article, the author evaluated the obtained results of the State budget-funded overseas training of managerial officials Project that added young, educated, professional and foreign language competent officials to locals and units in the contry. Many officials promoted their knowledge, were highly evaluated by units, locals and appointed to
budget-funded overseas training of managerial officials under Project 165 regarding training, training quality, management of employees sent for training.
Article: Project 165 Steering Committee summarizing the work in 2014, deploying tasks in 2015. 1 by Hong Phuc that summarized achievements, inadequacies and limitations in the implementation of Project 165 in 2014 and the deployment of mission in 2015. The article pointed out that in 2014, 67 students completed training programs in the country, the number of students of distinction and credit occupied 85%.
Article: Improving the overseas training quality of leaders, managers1 by Nguyen Van Du gave results and limitations after project 165. Besides, the author gave solutions to improve the overseas training quality of leaders, managers like perfecting mechanisms, policies and guidelines; Innovating training content, method in effective and quality direction; Strictly performing management overseas trained Vietnamese cadres and civil servants especially their quality, ethics; Coordinating with agencies and units in management, arrangement, effective use of personnel after training ; Solutions for: Improving the provisions on forms of organization, deployment, management of collaborative training forms; Focusing on some necessary specialties, in accordance with the actual conditions and training requirement of Vietnam. Only selecting employees with real demand for foreign language for professional service.
Article: Issues of training, strengthening of leaders, managers abroad, by Bui Van Tieng pointed out the achieved results since the date of the Politburo approved implementation of the State budget-funded overseas training of managerial officials Project (referred to as Project 165) as proposed by Central Organizing Committee. The author argued that Project 165 has brought significant results, contributing to improving the operational proficiency of most officials, leaders, managers selected to take part in the scheme. But according to the author, this important scheme remains some issues to be resolved ultimately, which areas such leaders, managers should be trained abroad? Which areas Party cadres should be trained abroad? Which country, training establishments should be chosen as partners of the scheme? Which form the organization of training should be - Should train both master’s and doctorate, both foreign language and short-term major? Management should focus on the Central Organizing Committee or be dispersed to localities, ministries, committees? ...
However, the results haven’t showed factors that affect the satisfaction of officials as well as the quality of cross-cultural training. So I choose this topic Evaluating the Impact of
Cross Cultural Training on Job Performance of Vietnamese Government Official” to give
the government in general and my organization in particular a scientific basic which can improve the quality of cross-cultural training.
1.2 Government official oversea training situation in
Vietnam
In the process of leading the revolution, the Communist Party of Vietnam always paid attention on the training of staff and considered this as a key step in the staff work of the government. On September 10, 2008, Secretary of the Central Committee of Communist Party of Vietnam issued Decision No. 187-QD/TW, establishing the Steering Committee for implementation of the scheme on State budget-funded training of leaders, managers studying abroad (referred to as Project 165).
Project objective:
- Following the process of training and retraining of personnel in the country to enhance the capability of leaders, managers of the political system according to the requirements of each job position; linked closely with planning officers short and long term.
- Training and retraining of expertise, foreign languages for staff in planning, talented young staff, ensuring that many leaders, creatives of the future are experienced professionals, with views wide, able to work independently in international communication relations.
- Facilitating the leaders, incumbent Quam participation of courses, the study tour to survey, explore the experience of countries at the request of professionals and expanding international cooperation.
Subject of training and retraining:
- Leaders, managers and staff in office planning area in the immediate and long-term deputy director level or equivalent and above in departments, ministries, unions at the
- The new young university graduates have worked a few years with the prospect of leading cadres and management.
The training programs fostering:
- Training and retraining of management science, such as: Administration, Economic Management, Environmental Management, Urban, Social Management, HR Management, International law, Justice, utilities, information technology ...
- Training and retraining for language.
- Fostering leadership skills, managing on the field. The form of training, retraining
- Long-term training in the training institutions abroad from 1- 4 year (interns, graduate students, high school).
- Fostering enhanced professional qualifications, foreign language from 3 months - less than 1 year.
- Fostering overseas short term from 2 weeks - 2 months (thematic classes)
- Training at the local facility in the form of collaboration with training institutions abroad.
Place the training and retraining:
In the years ahead, priority sends leaders, school management in several areas:
- East Europe, West Europe, North America: Learn about the administrative management, economic management, social management and public administration reform, urban management, environmental management, foreign languages ...
- Northeast Asia, India: Learning foreign languages, information technology, international law, e-government, public services ...
- The countries of Southeast Asia, Australia, NewZland: Study of corporate governance, economic management, public services, environmental management, foreign languages ...
- Period 2009 - 2010: Expected to go every year 30 fellows; 300 high school students; 200 trainees, 400 people learn foreign languages, fostering short 20 unions, 20 people / group = 400.
- From 2010 - 2015: Expected to increase the number of students the kind of 10%. Enhanced training classes, training in the country; invite foreign experts in training and retraining of staff in domestic institutions. Every year about 1,500 people will send and invite 20-30 faculty, foreign professionals into teaching in Vietnam.
Finance:
Financial resources for the training and retraining of leaders, managers abroad under the Project165 mainly state budget; and mobilize more international funding and contributions from agencies, local elected trainee.
State budget spent on staff training and retraining are summarized below:
- Portuguese language support and testing in the country before going abroad to study. - Tuition fee, enrollment fee, registration.
- Health Insurance. - Airfare travel. - Living fee
Organization and management staff to study abroad
The organization and management of staff to study abroad to follow the current regulations of the Party, State and regulation by the Steering Committee for implementation of the Project 165 issued.
The State budget-funded overseas training of Vietnamese officers has been implemented since the beginning of 2009. So far it has achieved important results. The project has organized various training program: Master, PhD; Short-term training; fostering language proficiency for 11,690 officers. Among 941 people attending master, doctoral programs, 158 doctorates and 444 masters are trained abroad, 339 masters are trained in the form of collaboration; To date, 621 officers have completed the curriculum, in which 282 officers are trained abroad (grade of distinction, excellence: 34%; credit) 339 officials are trained master
courses in 22 countries, 31 officers are Members of the Party Central Committee, 336 deputy ministers and equivalent; 40 general managers, deputy general managers and equivalent of the state economic corporations; 4,329 officers of departmental level and equivalent; 460 planning officers of departmental level, grassroots level and equivalent. With the objective of improving foreign language competence of officers in their work, trade, international relations, meeting the requirements of integration, among 4,275 officers involved in fostering foreign proficiency in domestic and foreign countries, 1,746 officers being sent for training abroad with English, Chinese, Laos, Cambodian, French, German, Russian, Japan, South Korean languages. After training, foreign language proficiency of officers is improved markedly; Most officers can use language well in external relations, meetings, negotiations with foreign partners.
Training results of the project has added young, highly qualified, foreign language knowledgeable officers for units in the country. Many officials have promoted their knowledge, been highly appreciated by units and localities and appointed to higher positions. Training specialties have been focused on necessary areas, in accordance with the strategic development of national human resources, such as public administration, public management, public policy, law, international relations, economic management, business administration, social management, investment management, urban management, education management, traffic management, human resource management, sociology, international economics, etc. For short-term training courses, content focuses on sector management, such as the organization, construction of the Party, testing, prevention of corruption, public relations, office, propaganda, foreign affairs, security and defense, etc.; fostering leading capacity, leading skill, management and experience of public administration reform, management of advanced countries. Most officers of the project trained in foreign institutions are appreciated for learning spirit, exemplariness in living; many officers are pivotal in gathering Vietnamese students abroad.
Training programs meet the requirement for practical overseas research, especially in developing countries. The result is not only limited to the training content, but also help expand vision and be a source of encouragement to officers, especially those who in remote areas. The party, mass, armed force who have fewer opportunities for overseas studies. After the training course, many practical contents are applied at different levels and many
cooperation programs for officer training have been connected between local and foreign partners.
Through Project 165, we organized a significant number of level cadres training studying abroad with many programs in many different countries, hope to help expand their vision, raise their awareness; strengthen their leading skill, management, communication and external relations; and accumulate experience in the implementation of overseas training towards higher and higher professionalism.
Besides these achievements, the overseas training of leaders, managers under Project 165 also has some limitations and shortcomings, such as the main target group for M.S. and Ph.D degree. overseas training programs was at departmental level or departmental planning level, In fact, those with the need for master, doctoral training accounted for low rate. Besides, leaders in some units, for immediate job requirements of the agency, were not active in selecting and sending staff to study. Therefore, the subjects of departmental level or equivalent attending postgraduate education programs occupied a low rate, only 5.6%. Officers attending short term courses were unfamiliar with the environment and learning methods abroad, learning time was short, learning must be through interpreter, participants in training courses worked in many different areas... so the efficiency was limited. The quality of short-term training programs depends on group organization and translation; delegation members’ awareness of purpose of the business trip was also different, some were not exemplary to abide by the common rules.
1.3 The purpose of research
This research objective is as following:
- To study the factors that affect cross-cultural training of government officials who are selected to study abroad by state-level training plan (Project 165)
- To test how the cross-cultural training factors affect job performance
- To Test the different effects of gender, field of training, type of training, countries on officials’ job performance
For achieving the research objective, this study will set out to respond to the succeeding research questions: Determine the factors of cross-cultural training and how they influences job performances of officials in Vietnam.
1.5 Research contribution
The findings of this study provide further evidence of the importance of factors of cross-cultural training for job performances of officials in Vietnam. The findings also demonstrate the effectiveness of cross-cultural training and its important role in developing cultural competence of officials in Vietnam, in consultation with 165 project managers, has a significant role to play in the further development and sustainability of the state’s budget for oversea study.
1.6 Thesis structure
Besides the introduction, conclusion, references and appendices; the thesis is structured by 5 main chapters, namely:
- Chapter 1. Introduction. The issues related to the background, objective, and contribution of this study.
- Chapter 2. Literature review. Firstly going to overview of Human resource concepts and leadership officers, the theory of training and cross- culture training, job performance and the relationship between effectiveness of cross- culture training and job performance. From the literature review the research model and hypotheses were developed.
- Chapter 3. Methodology. Include the research design, data collection and variable to assess effectiveness of cross- culture training on job performance of Vietnamese officers, civil servants through the State budget-funded overseas training of managerial officials Project.
- Chapter 4. Data Analysis includes: Respondent characteristics, reliability analysis, EFA and regression result. Also the t-test and ANOVA is given to find out the different in job performance from the Respondent characteristics.
Chapter 5. Conclusion: Forecasting and giving solutions to improve effectiveness of the State budget-funded overseas training of Vietnamese officers, civil servants.
Chapter II Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
There are many evidences and aware that training and education are the strategic investments key to the prosperity of the nation. The overwhelming success of Japan, Korea, and Singapore ... is positive proof for their victory when investing in education. Today's competition between nations or between enterprises is in fact competing on the quality of human resources. But the quality of human resources is close contact with the process of education, training and development. From awareness of the important objectives of the training and retraining of personnel during the period of industrialization and modernization of the country, international integration, dated 27-6-2008 Politburo Notice No. 165 affairs, / TW on the project "Training and retraining of leaders, managers abroad by the state budget" (hereinafter referred to as "Project 165").
Project 165 was launched in early 2009, though far less time performing much but has achieved important results. The scheme was essentially based on the requirements, objectives, audience, content and organization of this type of training, retraining achieved initial results; draw practical lessons useful for the training and retraining of personnel abroad. The scheme has also received the attention and positive evaluation of the local unit, related organizations at home and abroad. Recently, the Politburo also evaluates the results of operations of the scheme and set the direction for the next phase.
This chapter firstly going to overview of Human resource concepts and leadership officers , The theory of training and cross- culture training, job performance and the
relationship between effectiveness of cross- culture training and job performance. From the literature review the research model and hypotheses were developed.
2.2 Human resource concepts and officers
2.2.1 Human resource concepts
Human resources and development of human resources is one of the core issues of economic development - society in each country. Especially for developing countries, solving
this problem is the requirement posed an extremely urgent, because it has topical, strategic fit through the process socio - economic development of each country (Snell, 2015; Najam, 2015)
As defined by the UN: "Human resources are the skilled level, the knowledge and capabilities of the entire human life is reality or attitude has the potential for economic development - society in a community ". The management and human resource utilization tough attitude has been much more complex than other resources by human attitude has a biological entity - socially, very sensitive to the interaction of all natural relations, economic and social environment happening in their lives.
According to Begg (1999): "Human capital is the whole process of human expertise accumulated, it is appreciated for bringing potential future income. Like physical capital, human resources is the result of investment in the past with the aim of bringing income in the future "[25, tr.282].
According to Prof. Pham Minh Hac: "Human resources is overall the labor potential of a country or a locality, that workforce is prepared (at different levels) are ready to take a job certain workers, ie skilled workers (or ability in general), by way of response mechanisms are required by the labor restructuring, economic restructuring towards industrialization and modernization “. (Pham, 2001, 269).
2.2.2 Definition of officer
Officer is a concept adopted from China and is widely used during the war against France. In China, the word officers are for general employees, staff only to distinguish the odd employees, soldiers, workers and leaders of the unions. Gradually, the word officers refer to all those engaging in escapism Resistance, as sole distinction with people.
In Vietnamese - Japanese dictionary, the word officers are also used to refer to leadership of the unions. Currently in Japan, officers are those working in the army holding frame role, civil servants or public employees are called with the word bureaucracy, common sense is the people who work in the State apparatus. The meaning of the word officer in Japan is more loyal to the original that is translated into (Cadre). In English and French, this means that the core, the military commander, forming a core in an organization
In Vietnamese dictionary, officers are defined as:
- Those having professional expertise in agencies, the State, the Party, and the unions; - Those with positions in an agency or an organization, as opposed to people who do not have positions.
In the Party and mass organizations, officers mean:
- Those who are elected to the leadership and command from the grassroots to central facility (leaders) to distinguish them from party members, trade unionists, members (not holding position in the organization);
- Those who work full-time and are paid in the Party and mass organizations. In the military, officers mean:
- Commanders from squads above; - Officers from the lieutenant or higher.
are:
In the state system, officers are understood primarily as identical with office-holders,
- Those working in state institutions under administrative, judicial, economic, cultural and social sector;
- Those with command, leading position
Thus, from above, we can draw out a more comprehensive conception. Officer is a concept that means those with key positions, roles and titles in an organization, has impacts on the operation of the organization and relationships of leadership, command and management, administration, contributing to shaping the development of the organization.
Definition of civil servant
The first time the term "civil servant" was recorded in Vietnam civil servant regulation issued under Ordinance No. 76/SL dated 20-5-1950 of Ho Chi Minh President. Under this
Regulation, the civil servant scope was very narrow, only including those working regularly in government agencies, ie those working in state administrative system. However, as the country had to focus on the struggle for national independence, this civil servant Regulation was not fully implemented.
In the years 1960-1980, activities of civil servants were regulated by the provisions of labor law in general. Along with the country's comprehensive innovation, civil servant terminology was used in the documents of the Party and the laws of the State. On May 1991, the President of the Council of Ministers has issued Decree 169/HDBT defining the concept of civil servants: "Citizens of Vietnam recruited and appointed to a permanent civil service in the State central or local, domestic or international offices who have been arranged in a salaried rank provided by the State budget are called civil servants". This concept included basic signs of civil servants in modern administration.
In 2008, the 7th National Assembly enacted legislation of officers, civil servants, legalizing at the highest level officer, civil servant institutions in our country. Article 4 of the Law on civil servants defines:
Civil servants are citizens of Vietnam, who are recruited, promoted to the rank, position in agencies of Communist Party of Vietnam, the State, political organizations, socio - central, provincial, district level; in agencies and units of the People's Army, that are not officers, professional soldiers, defense workers; in agencies and units of the People's Police that are not officers, professional soldiers and in the leadership and management of public service units of the Communist Party of Vietnam, the State, political – social organizations (hereinafter referred to as public service units), in the payroll and be paid from the state budget; for public employees in the leadership and management of public business units, salary is guaranteed from the salary fund of public service units in accordance with the law. Civil servants have three basic characteristics: recruitment and appointment, keeping a regular civil service (stability and continuity) in a state office; Be put in a category, demonstrating the stability of public servants; Be paid from the state budget.
Thus, the “ civil servants are those recruited by the State, appointed to a permanent civil service with continuous work in state agencies (or agencies or units of the People's Army
or the People's Police ), are classified according to qualification and specialization, are classified in a category of administration, business, payroll and paid from the state budget"
2.3 The theory of training and cross- culture training
2.3.1 Concept of training
As defined byNilsson, and Nyberg, (2003, p.229). "Training is the process of providing specific skills for specific objectives". and “Education is the organization's efforts are taken to change the behavior and attitudes of staff to meet the requirements of the job effectively"
Discussing about development Nilsson, and Nyberg (2003, 230) show that "Development is the process of preparing and providing the necessary capacity for the organization in the future." "Development is included activities to prepare for staff to keep up with the organizational structure as it changes and development".
Training, by definition, the most common is the impact on people, making them comprehend and master the knowledge, skills, techniques, etc. in a systematic way so that they can adapt and have ability to receive a certain division of labor, contributing their efforts to the development of society in general. That process makes people become qualified under certain criteria, requirements, the process armed with knowledge and new skills.
Fostering is the process that impact human and “add more capacity or quality", is the process of improving professional skill, knowledge and professional skill on a regular basis, strengthening general capacity on the basis of obtained knowledge and skills (Gliessman et al, 1979, Aguiar et al, 2014). Fostering undertake tasks of renovation, addition of knowledge, skills and attitudes to civil servants so that they can perform their work better, more efficiently
Thus, training is seen as a process that makes people "become qualified under certain criteria", and fostering is determined to be a process that makes people "increase capacity or quality". The separation of the concept of training and fostering is only for convenience in analyzing the similarities and differences between training (Aguiar et al, 2014).
A general definition for training of civil servants can be understood as process that change human behavior in a systematic way through the study which is the result of education, guidance, development, and acquisition of experience in a methodical, planned manner. Thus, training is the organization of opportunities for officers and civil servants to study and to help organizations achieve their goals by enhancing the capacity and increase the value of the most important and basic resources of people, civil servants working in organizations (Androniceanu, 2012).
Training of officers, civil servants is the process of organizing learning opportunities for them to equip, update and improve knowledge, skills and attitudes to their work and complete their assignments more efficiently (Silverstone et al.,2013).
With such notions, training aimed to the following main objectives: Equip, update and improve the knowledge, skills, attitudes toward actual works for each job position, employment of civil servants and employees, to meet the requirements for increasing current capacity of individuals and organization. Equip knowledge, skill and ways of working to meet the future requirements of job positions, rank standards of civil servants and employees at the request of the organization (Androniceanu, 2012). Equip, provide necessary knowledge, skills, attitudes and working manner to help civil servants, officers familiar with, renovation the new jobs by rotation, transfer, promotion.
The success of any training can be gauged by the amount of learning that occurs and is transferred to the job. In organizational environments, training and learning will take place anyway - especially through informal groups - whether an organization has a coordinated training and development effort or not. But without a well-designed systematic approach to training, what is actually learned may not be what is best for the organization
Figure 2.1 shows the relevant components of the three major phases in a training system7: [1] the needs assessment phase; [2] the implementation phase; and [3] the evaluation phase.
Figure. 2.3 "Model of Training System", Mathis and Jackson, p. 278
2.3.2 Cross- culture training
Cross-cultural training has long been proposed as an anticipatory mechanism to increase adjustment to foreign cultures (Torelli, 2011). “In cross-cultural training programs, a wide variety of training methods are typically used, including lectures, video films, experiential exercises, culture assimilators, and behavior modification” (Bochner, S. (Ed.). (2013). Bhagat and Prien (1996) discussed “the main differences between traditional training
and cross-cultural training”. As they described, traditional training is characterized by a focus on the “acquisition of information, rather than on change in attitudes” (Bhagat&Prien, 1996, p. 223). By way of comparison, Bhagat and Prien observed that cross-cultural training addresses the acceptance of differences between cultures (Fischer, 2011).
The process of globalization is taking place on a powerful, fast and become the mainstream of the world. Globalization creates information revolution throughout the world, increasing migration flows between nations and civilizations, formed the economic center, the world's financial and global financial flows ... Process This brings new opportunities for mankind, towards a humane society and prosperity of every nation with civilization on the basis of effective use of intellectual achievements(Rehg et al., 2012). Globalization also creates the maximum exposure characteristics and cultural identity, thereby sharing and towards the common cultural values based on the cultural diversity of different areas. The development of science and technology also contributed to changing the face of the world, create more favorable opportunities for communication between communities on earth. However, globalization also contains latent contradictions and challenges to humanity such as the world model links are now obsolete, incapable of solving global problems; the gap between rich and poor ethnic widening; Environmental pollution; climate change, ethnic conflicts, religious, regional conflicts between cultures and civilizations more complicated (Koo, 2012). The problem is the human need for dialogue to select relevant model to meet the new world reality of twenty-first century, in order to develop a global civilization.
Moreover, while cultural awareness training is “the study of the trainee’s home culture and its effect on his/her behavior to enable the trainee to understand the nature of cultural differences” (Eschbach et al., 2001), sensitivity training leads the trainees to understand their own values and culture and to be aware of cultural differences by demonstrating a behavior that may be completely different from that of their own culture. The strength of cultural awareness training comes from the fact that the trainees learn to appreciate cultural differences and to apply whatever they learn to enhance the effectiveness of cross-cultural interactions ( Brandl&Neyer, 2009). On the other hand, cultural awareness training “does not necessarily help the trainees learn anything specific about the host culture in which they will be interacting” (Bhawuk&Brislin, 2000, p. 170).
2.3.3 The factors affecting Cross- culture training
According to many writers, there are four key factors that contribute towards success of an international assignment that are selection, preparation, Management Support and repatriation (Mendenhall, 1998).
Research of Deresky (2003) shows that most Multinational Corporations do not properly estimate the importance of the function of human resource planning in perspective of selection and training of managers detailed for abroad assignments. Cross Cultural Training has taken very important contributory role for apprising the expatriates about the cultural differences and adopting oneself in new environment and culture.
Black and Mendenhall (1990) reviewed 29 empirical studies that evaluated the effectiveness of various cross-cultural training programs. Their comprehensive literature review showed that cross-cultural training had a strong positive impact on participants’ self-confidence, on their interpersonal relationships with host nationals, and on their perceptions of the host culture
Caligiuri, (2000)s measured a Big Five factor, subscale scores were averaged to obtain a score on the Big Five factor . “Learn by doing” (Littrell& Salas, 2005, p. 312) best spells out the nature of experiential learning. Look-see visits, role-playing, intercultural workshops, and simulations are major techniques used in experiential learning. The main advantages of experiential training come from the fact that it helps trainees develop the skills necessary for effective performance, for positive interaction with the locals, and for cognitive skills to make correct attributions ( Littrell& Salas, 2005; Morris &Robie, 2001). However, it has not yet been backed up by empirical research (Bhawuk&Brislin, 2000).
2.4 Job performance
To assess the effectiveness of employee in working is a measure widely used since the 1980s when the issue of competition in the market is fierce, forcing firms to focus and encourage employees to perform better the objectives and requirements of the job (Williams and Anderson, 1991).
Assessing the effectiveness of staff work shall be understood as the review process to evaluate a systematic work efficiency and capacity of the staff, including the results of work, working methods, the product qualities and skills do the job.
Assessing the effectiveness of staff work is used for many different purposes such as: Provide feedback to staff about the level of their job performance than the standard model and compared with other employees; Help employees adjust and fix the mistakes in the course of work; Stimulate, motivate employees through the provision of assessment, recognition and support; Provide the information as the basis for the issue of training, salary, reward, transfer of employees, improved organizational structure ...; Develop an understanding of the company through conversation about the opportunities and career planning;To enhance good relations between superiors and subordinates (Gibbs et al., 2004).
The evaluation system is effective job Vietnam Productivity Center developed based on the basic theory of human resource management, management approach by objectives (MBO), the KPIs (index significant effect), and in some cases the application method 360. However, WeiBo Z, Kaur S, Jun W (2010) find that the use of subjectivity introduces conflict including complaints of favoritism and bias. Ultimately, the firm in the) study replaced its contracting system with a one-measure, formulaic system
2.5 The relationship between cross culture training and job
performance
Caligiuri, Lazarova, and Tarique (2005) point out that “cross-cultural training aims at helping employees feel comfortable living and working in a host country, thus enhancing their cross-cultural adjustment and strengthening their ability to understand and appreciate multiple cultural perspectives”. However cross-cultural training has long been regarded as a vital means with which to facilitate the development and to refine the competencies that expatriate managers need to successfully work when come back country (Linehan, M., & Scullion, H. (2008). Its effectiveness has been corroborated by the pertinent literature while a great number of studies assert that cross-cultural training is critical to cross- cultural interaction, they bring the culture from other countries to their countries however, the evidence of its effectiveness upon employee ( officer) assignment is still inconclusive
(Black & Mendenhall, 1990; Litlrell& Salas, 2005) because it lacks adequate empirical support.
Furthermore, research devoted to investigating cross-cultural training effectiveness has been primarily conducted through the quantitative research approach and from the experiences of Vietnam officer. Therefore, there is a need to engage in a qualitative research approach that looks into the insights and the knowledge of its effectiveness as provided by Robert Bean (2008), This work has been produced by the National Centre for Vocational Education Research (NCVER) under the National Vocational Education and Training Research and Evaluation (NVETRE) Program, which is coordinated and managed by NCVER on behalf of the Australian Government and state and territory governments. is study by Robert Bean investigated the contribution to workplace performance of cross-cultural training, a term used to describe training that develops a person’s ability to interact effectively with individuals from different cultures and in different cultural settings. The study is based on a survey of 134 vocational education and training (VET) graduates. The practices and views of 38 training providers and 31 employers on the current and future provision of cross- cultural training are also described. The report highlights the positive experiences of VET graduates with cross-cultural training, as well as employers’ support for it. It lists the challenges for cross-cultural training as perceived by trainers, a specific challenge being to ensure that there is sufficient and appropriate cross-cultural training embedded in training packages, particularly those covering sales and service industries, industries with high customer contact.
2.6 Research model and hypothesis
As objective of this research is evaluation of the effectiveness of CCT and its impact on job performance. Since the impact of effectiveness of CCT on job performance is predict by the factor affect on CCT. The donor organization would prepare an exhaustive feasibility study of the Cross Cultural training program. The program could be either general one or enhanced one depending upon the learner characteristic and knowledge requirements needs to the receiver organization (Qi & Lange, 2005, p. 10). Based on the literature review, the research frame work is designed in the figure 2.1
Off- class activities
Figure 2.5: Research framework
Hypothesis based on the research framework this thesis propos the hypothesis as flowing H1: Personal characteristics have a positive impact on Cross-cultural training effectiveness H2: Training program have a positive impact on Cross-cultural training effectiveness
H3: Off- class activities have a positive impact on Cross-cultural training effectiveness H4: Cross-cultural training effectiveness has a positive impact on Job performance
H5: Student of different gender might have different effectiveness received level towards the Job performance
H6: Student of different age might have different effectiveness received level towards the Job performance
H7: Student study in different country might have different effectiveness received level towards the Job performance
H8: Student study in different program might have different effectiveness received level Personal characteristics Training Program Cross-cultural training effectiveness Job performance
Chapter 3 Methodology
3.1 Introduction
Quantitative research was conducted to test the scale of the research model. This is a detailed analysis of the data collected through questionnaires sent to the client to determine the logical correlation of these factors together and then give specific results of this research.
This study used the questionnaire (in the level of Likert from 1- strongly disagree to 5 - strongly agree) to collect data to test hypotheses quantitative approach is applied to the test the hypothesis of this study.
3.2 Sampling Design
The target population are leaders who have been finished or studying oversea that funded by project 165. According to Bulmberg et al. (2011), the important reasons that researchers use methods of non-probability sampling is the savings in cost and time. In addition, the author also reminds that the probability sampling is not always ensuring the accuracy and in some cases the probability sampling is not possible. However, the authors also state the biggest weakness of non-probability sampling method is a subjective in the sampling process could lead to distort research findings.
Since the fact of difficulties to identify respondents, in this research to reach the above research objective sampling design was conducted in the form of non-probability sampling with snowball sampling. Snowball Sampling is a method used to obtain research and knowledge, from extended associations, through previous acquaintances, “Snowball sampling uses recommendations to find people with the specific range of skills that has been determined as being useful” (David, Morgan, 2008, p.816-817). An individual or a group receives information from different places through a mutual intermediary.
This sampling is considered favorable and reasonable because respondents will easily welcome and answer the questionnaire that does not take much time and costs. Snowball sampling is a useful tool for building networks and increasing the number of participants. However, the success of this technique depends greatly on the initial contacts and connections
made. Thus it is important to correlate with those that are popular and honorable to create more opportunities to grow, but also to create a credible and dependable reputation.
Sample size
The sample size depends on the research problem. Research problems are diverse and complex requires the larger number of sample. A general rule is the number of sample bigger will lead to accuracy of the research results higher (Kumar, 2005). But in fact, the sample size depends on one another important factor is the financial capacity and time researchers able to. In this research, due to financial limitations and time, the sample size will be determined at the level of the minimum standard.
The determination how much of the sample size is appropriate remains controversial and many different standpoint. Myers, Ahn, and Jin (2013) have summarized the views of the previous studies on minimum standards of sample size for factor analysis subject. They cite studies of Gorsuch, he suggested that the sample size should at least five times the number of variables.
3.3 Data collection
Primary data has a very important role in this research. According to Hussey (1997), he said that primary data as the new material obtained from collecting data. Collecting data can include asking question, making observations and conducting experiments. This research will be used quantitative research via a survey questionnaire. In Gronhaug’s research (2005), he indicated that a questionnaire is the best tool for obtaining opinions, attitudes and descriptions.
In order to distribute and collect questionnaires, this research used mail survey approach. The questionnaires will be sent by email to respondents and ask their help to send to their other friends. To ensure the number of responses as much as possible and the minimum is 150 responses valid the researcher also conducted directly survey approach. The questionnaires will be distributed directly to the employees of organizations. Then ask them self-administered questionnaires they got.
3.4 Variable structure
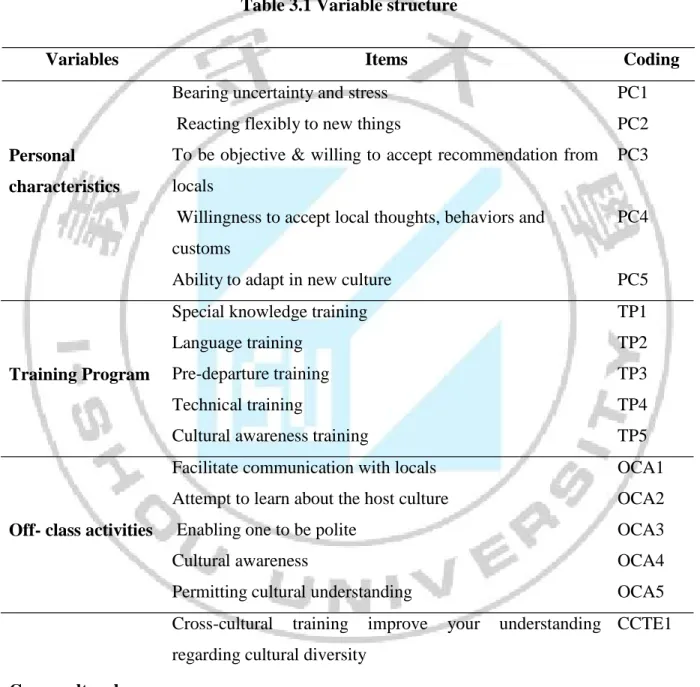
Base on the literature review and interview with the student and expert in study design the variable structure as table 3.1
Table 3.1 Variable structure
Variables Items Coding
Bearing uncertainty and stress PC1 Reacting flexibly to new things PC2
Personal characteristics
To be objective & willing to accept recommendation from locals
Willingness to accept local thoughts, behaviors and customs
PC3
PC4
Training Program
Off- class activities
Ability to adapt in new culture PC5
Special knowledge training TP1
Language training TP2
Pre-departure training TP3
Technical training TP4
Cultural awareness training TP5
Facilitate communication with locals OCA1 Attempt to learn about the host culture OCA2
Enabling one to be polite OCA3
Cultural awareness OCA4
Permitting cultural understanding OCA5
Cross-cultural training effectiveness
Cross-cultural training improve your understanding regarding cultural diversity
Cross-cultural training increase your awareness and knowledge of the ways in which your own culture influences your thoughts and feelings
CCTE1
CCTE2
Job performance
understanding of cross-cultural communication skills Cross-cultural training increase your knowledge and understanding of the customs, values and beliefs of other cultures
Cross-cultural training increase your confidence in dealing with people from different cultures
Demonstrates knowledge to accomplish job duties effectively and uses work time and resources efficiently Treats all others with respect and understands the impact of culture/background on the behavior of others
Shares information and resources and seeks clarification to ensure understanding CCTE4 CCTE5 JB1 JP2 JP3
3.5 Data analysis
3.5.1 Reliability Analysis
Nunnally (1978) defined reliability as “the extent to which [measurements] are repeatable and that any random influence which tends to make measurements different from occasion to occasion is a source of measurement error” (p.206). “Cronbach’s coefficient is a reasonable indicator of the internal consistency of instruments that do not have right-wrong (binary) marking schemes, and can thus be used for both essay.
3.5.2 Factor analysis
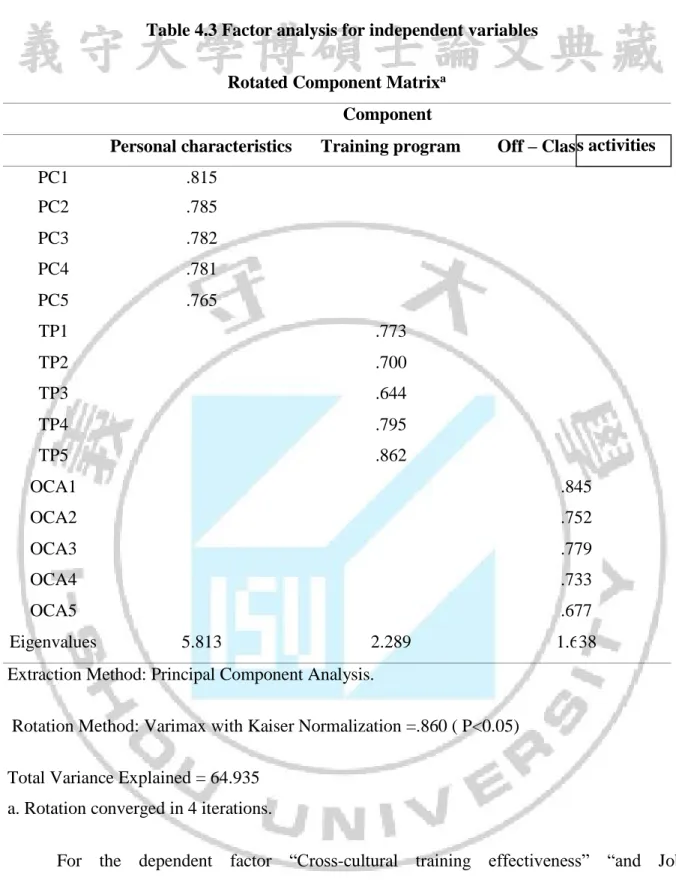
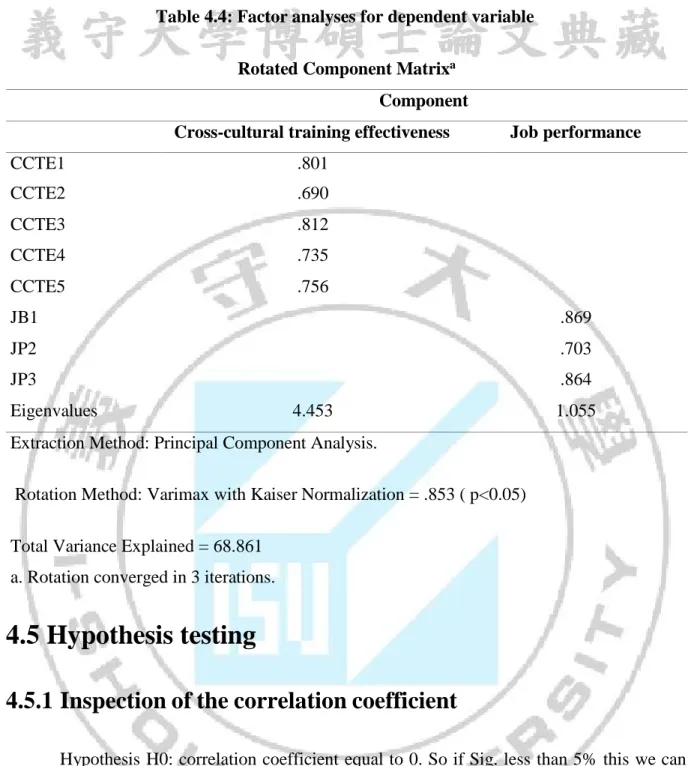
After assessing the reliability of the scale with Cronbach alpha coefficients and eliminate the variables are not reliable enough, factor analysis techniques to discover that are used to shrink and summarized data (all groups the variables into a number of factors). Factor analysis method to discover (EFA) was used to test the value of the scale concept. The weighted variable low (<0.3) will be disqualified and will only be accepted when measuring the total variance extracted> 0.5.
Methods of factor analysis to discover EFA (Exploratory Factor Analysis, called the method EFA) help us assess the value of two types of scale are important values and values converge distinction. Analysis method of heading EFA factor multivariate analysis of interdependence (interdependence TECHNIQUES), meaning no dependent variable and independent variables that rely on correlations between variables together (interrelationships). EFA is used to set k shortened observed variables into a set F (F <k) the more significant factor. The basis of this reduction is based on a linear relationship of the factors with the original variables (observed variables).
According Hair & et al., (2013), Factor loading (load factor weighting factor or factor) is the target to ensure that the practical implications of EFA:
• Factor loading> 0.3 is considered the minimum level reached • Factor loading> 0.4 is considered important
• Factor loading> 0.5 are considered to have practical significance
Conditions to explore factor analysis is required to satisfy these requirements: System load factor (Factor loading)> 0.5
≤ 1 ≤ 0.5 KMO coefficient KMO (Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin) is an index used to examine the appropriateness of factor analysis. KMO value significantly larger factor analysis is appropriate.
Accreditation Bartlett statistical significance (Sig. <0.05): This is a quantity used to examine statistical hypothesis no correlation variations in general. If testing has a statistically significant (Sig. <0.05), the observed variables are correlated with each other in general.
Total variances > 50%: Shown percentage variation of the observed variables. Ie 100% variable see this value factor analysis that explains how much%.
The scale meets the requirements of reliability to be used factor analysis to a set of much shortened observed variables into a variable (called factors) less; shortened factors will be more meaningful but still contains most of the information content of the original collective observed variables (Hair, Anderson, Tatham and Black, 1998). Methods of factor
analysis was used to explore accreditation EFA value concept of scale (according to Le Ngoc Duc guide, 2008).
overall
- Verification Bartlett: the observed variables are correlated with each other in the
- Considering the value KMO: 0,5≤KMO≤1 the factor analysis is appropriate to the data; 0.5 is backwards KMO≤ analyze factors potentially incompatible with the data (Hoang Trong& Chu Ngoc Nguyen Mong, 2005)
- To analyze EFA has practical value: conducting observations kinds of variables factor load factor <0.5
- Review the eigenvalues parameters (representing the fraction of variation explained by each factor) value> 1
Considering the value of the total variance extracted (≥ 50% is required): to know the factors that are extracted unexplained% variation of the observed variables
Implementing and evaluation criteria of factor analysis to discover EFA:
- Use the extraction method is Principal components factor with Varimax rotations and stops when criticized elements eigenvalues = 1. With the scale, the use unidirectional element extraction method Princial components. Proceed type variables weighted factors (also known as load factor coefficient) of less than 0.4 and a total variance extracted is equal to or greater than 50% (the scale is accepted) (Gerbing& Anderson, 1988; Nguyen DinhTho tutorial Nguyen Thi Mai Trang& 2009).
- Standard for factor load factor is greater than or equal to 0.5 to ensure that the practical implications of EFA. The level of load factor value factors: greater than 0.3 is to achieve a minimum; greater than 0.4 is important; is greater than 0.5 have practical significance. Select the value standard load factor factor: sample size of at least 350, you can choose factor load factor greater than 0.3; if selected sample size of 100, the load factor greater factor of 0.55; if the sample size, the load factor of about 50 factors that must be greater than 0.75 (Hair, Anderson, Tatham and Black, 2008).
3.5.3 Develop regression and correlation analysis
After extracting the element from factor analysis EFA discovery, correlation analysis and regression to see the relationship between factors affecting employee satisfaction and level of impact of these factors. Testing the theoretical model: theoretical model for the study hypothesis was tested by means of multivariate regression significance level of 5%.
Hypothesis H0: correlation coefficient equal to 0. So if Sig. less than 5% this we can conclude that the two variables are correlated with each other. The correlation coefficient greater correlation tighter. if Sig. larger than 5%, the two variables are not correlated with each other.
- As one of the conditions necessary for the regression analysis is the independent variable must be correlated with the dependent variable, so if at this step correlation analysis independent variable is correlated with the dependent variable, we kind of turn This independence from the regression analysis.
- Results of Pearson correlation analysis showed that a number of independent variables are correlated with each other. Hence the regression analysis should pay attention to the problem of multicollinearity. The independent variables are correlated with the dependent variable and therefore will be included in the model to explain the dependent variable.
Theoretical model after analyzing factors that all seven components as indicated. Research continues to conduct regression analysis to determine the specific weight of each component affects the satisfaction of SV regression analysis was performed by multiple regression method with SPSS Statistics 20.0 software
Model of a multiple linear regression was assessed through the suitability determination coefficient R2 (R square) and R2 adjusted (Adjusted R square). In which R2 adjusted to reflect more closely the relevance of the model. Inspection F in the analysis of variance is a test of the relevance of the linear regression model overall. It considered the dependent variable is associated with the entire linear set of independent variables or not. H0 hypothesis is this: all the regression coefficient is 0 (Hoang Ngoc Trong foundation, 2008).
The variables in the model is rated important by considering partial correlation coefficient (correlation coefficient Part) and partial correlation coefficients (Partial correlation
coefficient). Partial correlation coefficient is a correlation between the dependent variable Y and independent variable export the linear influence of independent variables on the dependent variable XK removed. If all the independent variables are not correlated with each other, the degree of change of R2 as an independent variables included in the equation is the square of the correlation coefficient between independent variables and the dependent variable. If the level of R2 change as independent variables included in this larger change of R2 level when put on other independent variables, the independent variable predesigned more important role. The correlation coefficient is separately correlated k independent variables and the dependent variable Y when the linear influence of independent variables for both the Y and XK removed. (Hoang Trong - Mong Ngoc, 2008)
Next, the researchers will have to examine and detect violations of the assumption of a linear regression model because if the assumptions are violated, the regression results are not reliable anymore. These assumptions include assumptions about linear association, assuming the variance of the error, the assumption of the normal distribution of residuals, the assumption of independence of errors and assumptions about the relationship between independent variables (Most collinear measurement) (Hoang Ngoc Trong foundation, 2008)
The extracted factors in factor analysis were used for multivariate regression analysis to test the research model and the accompanying theory. The statistical hypothesis testing are applied significance level of 5%.
Research conducted multivariate regression method Enter: all the variables are taken into consideration once and the related statistical results.
Testing hypotheses using SPSS software:
Assess the suitability of multivariate regression models Hypothesis Testing of the relevance of the model
Check the assumption of multicollinearity phenomenon (correlation between the independent variable) through the value of tolerance (tolerance) or exaggerated coefficient variance VIF (Variance Inflation Factor): VIF> 10 may commented multicollinearity phenomenon (Hoang Trong& Chu Ngoc Nguyen Mong, 2008)
Determining the extent of the influence of: factor beta greater the possible remarks that elements that have a higher degree of influence of other factors in the model study.
Hey. Analysis of variance factor (oneway-ANOVA)
After the model has been processed, the performance analysis of variance factor set out to test whether or not the difference in satisfaction levels of employees in individual characteristics. Inspection of differences in the level of staff satisfaction commune Women's Union under the variable course with ANOVA analysis with significance level of 5%. Some assumptions when analyzing ANOVA:
- The comparison group must be independent and are selected at random.
- The comparison group to have a normal distribution or sample size should be large enough to be seen as asymptotic normal distribution.
- Variance of the comparison group must be consistent. ANOVA analysis
Levene test
Ho: "The variance equal" Sig <0.05: reject Ho
Sig> = 0:05: accepting Ho -> eligible for further analysis anova ANOVA test
Ho: "Average equal"
Sig> 0.05: reject Ho -> unqualified to confirm no difference... Sig <= 0.05: accepting Ho -> confirmed eligible to differ...
Chapter IV Result analysis
This chapter presents the major findings of this study. The results are summarized in three sections: rate of response, sample characteristics, and hypotheses testing results.
4.1 Rate of Response
A total of 300 subjects were invited to participate in this study. 234 participants agreed to complete the online survey, making the participation rate in this survey 78 percent. A total of 220 participants completed the on-line survey, making the response rate in this survey 73 percent. The total usable surveys yielded a response rate of 83.5 percent for the e-mail sampling (207 out of 220 cases were usable).
4.2 Sample Characteristics
The demographic characteristics of samples project 165, 207 students in this study were measured by gender, age, country study, program study, working position. Respondents were asked to provide their answers to questions that were designed by nominal scales. The summary of demographic characteristics of respondents is reported in Table 4.1.
Table 4.1: Respondent profife
Gender Frequency Percent
Male 103 49.8
Female 104 50.2
Total 207 100.0
Age Frequency Percent
Less than 25 40 19.3
26 to 35 97 46.9
36 to 45 40 19.3
Over 45 30 14.5
Total 207 100.0
Staff 166 80.2
Total 207 100.0
Country study Frequency Percent
Asia 47 22.7
EU 68 32.9
USA 92 44.4
Total 207 100.0
Program study Frequency Percent
PhD 12 5.8 Master 31 15.0 Bachelor 62 30.0 Language 80 38.6 Short course 22 10.6 Total 207 100.0
The respondents were comprised of male (49.8%) and female (50.2%), after recoding respondents’ age, the result showed respondent who is less than 25 year old count for 19.3% . the majority of respondent ware ranged from 26 to 35 year old (46.9%) followed by 36 to 45 year old (19.3% %) while respondent who is over 45 year old count for 14.5% .
Working position of student revealed that 19.8% of respondents is leader before study oversea and 80.2% is staff. This result implies that most of the respondents were staffs in this study. In terms of country study, the majority of respondents selected USA for oversea study (44.4%) there are 68 respondents (32.9%) selected EU country and 22.7% who studied in Asia country.
Regarding to the Program study oversea of respondents, there are only 5.8% go oversea for PhD program in this study, master program count for 15.5%. There are 30% of respondents who study bachelor degree while respondents (38.6 %) go oversea for language learning; beside respondent study short course is just 10.6%.