CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION
Reinforcing human resources quality has always been the great challenge of all educational system. In this process, school administrators have an important role to play:
leading the school institutions they are in charge, providing a serene climate within which the young generations of workforce can safely evolve and blossom. Although noble, this role does not always prove to be easy doing. School principals are facing a daily struggle to improve their school reputation. Because they are the guides and actors in designing the school values, goals and vision, well knowing their school is a prior to do so. What gives them the necessary will to lead their school despite the function’s difficulties? What do they value most in their job? Determining these values can contribute in minimizing turnover, absenteeism and low productivity rates, enhance teachers and students performance and strengthen principals’ commitment to their job as long as possible.
Background of the Study
Organizational Commitment Is Linked to Identification and Involvement
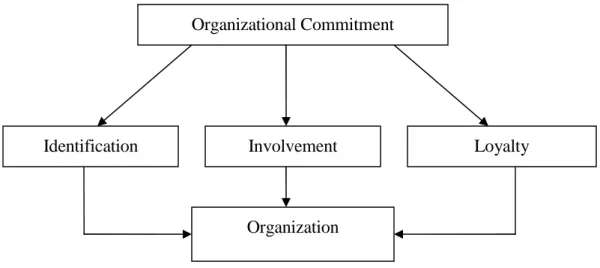
Porter et al. (1974) as well as Allen and Meyer (1990) underpinned organizational commitment as the strength of an individual’s identification with, and involvement in a particular organization. Organizational Commitment is characterized by three main components: (1) identification: a strong belief in and acceptance of the organization’s goals and values; (2) involvement: a willingness to exert considerable effort on behalf
of the organization; (3) loyalty: a distinct and strong desire to stay with the organization.
These components are schematized in Figure 1.1.
Figure 1.1. The Components of organizational commitment
Source: Hawkins, 1998.
Organizational Commitment Is Important in Workplace Development
Creating a harmonious work environment is a great challenge facing school leaders.
Accepting such a challenge involves continuous and sustained efforts from Administrators, partners and employees. The most important problems encountered in the work place, especially those of schools, include disciplinary and decision-making problems, that’s means the organizational culture. Kono and Clegg (1998) defined the organizational culture as “the expression of collective staff attitudes and shared values this enables them to believe in the organization’s values and goals and to want to keep working for that organization”. Thus, the better organization cultural values fit employees’ beliefs and values, the greater the organizational achievement (Boxx &
Odom, 1991). In the contrary, if employees are dissatisfied with their work conditions, their commitment level is low and they look for other opportunities to quit (Lok &
Crawford, 2004).
Organizational Commitment
Organization
Identification Involvement Loyalty
Such difficulties can lead sometimes to negative outcomes from students, employees, teachers, and school leaders. Cheng, Jiang and Riley (2003) reported in their study that in Chinese context, organizational commitment is significantly related to supervisory commitment. Principally, it is strongly correlated with good personal relations with colleagues. For example, poor work conditions make teaching difficult and are likely to accelerate the attrition of new teachers (Metropolitan Life, 1987). Also, supportive school leadership and teacher autonomy play an important role in shaping teachers attitudes toward teaching. The more a teacher is involved in important decision making, the more he is likely to perceive positively the school leadership and culture and to have higher morale and a higher intention to work a long time in the school.
Then identifying the predictors of affective organizational commitment seemed to be of an important role in producing commitment as a means of tying it to desirable organizational outcomes such as improved performance (Mottaz, 1988).
To Explore Affective Organizational Commitment of School Principals Is Necessary School principals are the critical line for all educational administration to reach a successful promotion of an instructional vision. They are required to lead, plan, participate in and act as a resource for teachers and students (Petersen, 1999). Exploring affective organizational commitment of school principals is essential in so far as their stability at work is an important element in diagnosing and preventing schools’ real problems. It is also important in establishing policies that fit the real work environment and the needs of the educational system to adapt to the changing international environment. Examining school principals’ organizational commitment is also necessary in so far as, for diverse reasons, employees’commitment to their organization is decreasing in both public and private sectors and knowing the reasons that may lead an employee to stay with his organization helps supervisors direct their actions in a
desirable way for both employers and employees. Knowing what category of employees are more committed to their organization helps in the selection, training, development, and leading process within an organization.
“As the broad context of organizational commitment was reviewed, studies indicated that some writers raised a concern as to whether or not commitment was a reasonable expectation for employers to hold for their employees in today’s work environment where changes in leadership and organizational focus may occur rapidly”
(Hawkins, 1998). Previous studies stated that, the job itself, the school administration, and the profession compete for principals’loyalty. Principals may develop commitment to a boss or to professional association membership (Hawkins, 1998; Morrow &
McElroy, 1993; Randall & Cote, 1991; Tyree, 1996). Principals may also experience different degrees of commitment to various school district aspects such as organizational philosophy (Meyer & Allen, 1997).
However, Morrow and McElroy (1993) reported that the notions of lack of commitment to organizations today have served as a catalyst for further studies of organizational commitment. The maintenance of employee organizational commitment remains as a viable organizational goal. Whatever the current organizational status of a school, she still needs a core of employees, especially leaders, who are committed to the values and goals of the organization (Caudron, 1996; Meyer & Allen, 1997). As regards to today’s rapidly changing work environment and the continuous desire to make it safe, harmonious and secure, a study related to affective organizational commitment remains a suitable topic for study (Hawkins, 1998), mainly in the educational area where the first advantage is not necessarily money.
Statement of the Problem
Most of the studies conducted in the area of organizational commitment focused mainly on organizational commitment in the western countries. Few of them set great store by Asian countries where national and social culture may influence differently the results of the studies related to organizational commitment.
The current research sought to determine the extent to which hypothesized independent variables could predict affective organizational commitment of vocational high school principals in Taiwan. The relationships between those different variables, schematized in the research framework in chapter 3, were examined to determine the extent to which they explain affective organizational commitment, the dependent variable, and the intended outcomes. Affective commitment is expected to produce some organizational outcomes such as improved teachers, students’, employees’, and principals’performance.
Definition of Terms
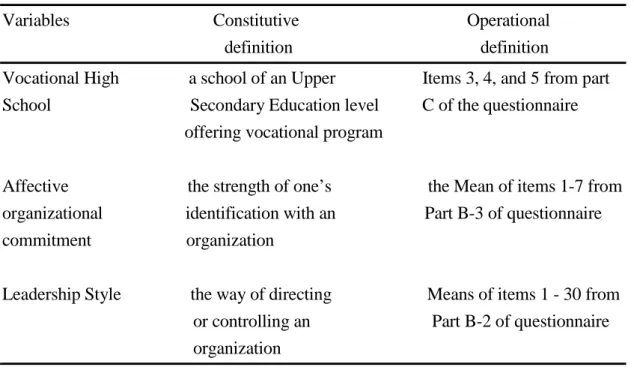
The main terms used in this study can be defined as follow. The constitutive and operational definitions are summarized in Table 1.1.
Vocational high school:
A Vocational high school is defined as a specialized upper-secondary school that offers a full-time program of study in both academic and vocational subjects and in which all or a majority of the students is enrolled in vocational education programs. In Taiwan, vocational high schools enroll students of fifteen ages old for at least three years.
Affective organizational commitment:
Affective organizational commitment is the strength of one’s identification with, involvement in, and loyalty to a particular organization. It is the willingness of social actors to spend their energy and affirm their loyalty to social relations which are seen as self-expressive (Kanter, 1968).
Leadership Style:
The leadership style of a principal is on the interaction between principal and his or her staff members. It is about what principals do rather than what they are (Farahbakhsh, 2004). Following the way the principal leads his school and his school staff, three main leadership styles can be listed: authoritarian, participative and delegative (Clark, 2004).
Authoritarian leader is the one who manages his or her school with autocracy.
Participative leader is a democratic leader. This type of leader is recognized to be one who mostly wants his or her employees to grow in their job. Delegative leader is the one who promotes the laisser-faire or free reign. Most of the time delegative leaders act in that way because he or she may have his or her employees who know more than he or she. He or she may also be a new leader and is trying to feel out the correct leading style (Clark, 2004).
Purpose of the Study
The purposes of this study aimed to assess the predictors of vocational high schools in Taiwan. The different purposes are listed as follows.
1. Determine the abilities of personal background characteristics to predict affective organizational commitment of vocational high school principals.
2. Determine to what extent and in what manner organizational management and leadership style can predict affective organizational commitment of vocational high school principals.
3. Determine to what extent and in what manner school setting characteristics can predict affective organizational commitment of vocational high school principals.
It is assumed that this study is of interest to superintendents, human resource professionals, administrators, partners and other persons who work directly with school principals. The intended results might be useful in reorganizing or strengthen the work relations between administrators, educational and social partners, teachers and students.
Table 1.1. Constitutive and operational definitions of variables
Variables Constitutive Operational
definition definition
Vocational High a school of an Upper Items 3, 4, and 5 from part School Secondary Education level C of the questionnaire
offering vocational program
Affective the strength of one’s the Mean of items 1-7 from organizational identification with an Part B-3 of questionnaire
commitment organization
Leadership Style the way of directing Means of items 1 - 30 from or controlling an Part B-2 of questionnaire organization
Source: Hawkins, 1998.
Research Questions
Research questions are addressed to determine the extent to which the different independent variables influence affective organizational commitment of vocational high school principals in Taiwan. Three main questions are addressed to reach this issue.
1. What are the abilities of personal background characteristics (gender, age, education, and organizational tenure) to predict affective organizational commitment of vocational high school principals?
2. To what extent and in what manner organizational management (pay satisfaction, organizational support, fairness, and autonomy) and leadership style can predict affective organizational commitment of vocational high school principals?
3. To what extent and in what manner school setting characteristics (school location and status) can predict affective organizational commitment of vocational high school principals?
Research hypotheses are listed in chapter three. The result of this study will provide information needed in assessing the factors that predict affective organizational commitment of vocational high school principals in Taiwan.
Delimitations and Limitations
This study is delimited to assess the importance of personal background characteristics (gender, age, education, and organizational tenure), organizational management (pay satisfaction, perceived organizational support, perceived fairness, and perceived autonomy) and leadership style, and school setting characteristics (school status, school location, type and size) in predicting affective organizational commitment
of vocational high school principals in Taiwan. This study did not examine the outcomes following from the relationships between the independent variables cited above and the dependent variable (affective organizational commitment). The findings are expected to give a clear understanding of what principals’ value most in their job and to what extent these values can impact on their commitment to their organization.
The population concerns only the vocational high school principals in Taiwan and may have a limitation in generalizing to the principals in the other educational levels.
The research questionnaire had been mailed to the participants and for lack of time, remembering letters had not been mailed to them, limiting the opportunity to encourage the cooperation of the respondents or to provide assistance in answering the questions by clarifying it for them. Nevertheless, the cover letter mailed with the questionnaire highly resolved this difficulty. As a result, a response rate of 72% of the total sample had been registered one month after mailing the questionnaire.