College of Management
I-Shou University
Master Thesis
Determinant Factors and Consequences
of Customer Satisfaction in Vietnamese
Internet Banking Sector
Advisor: Dr. Heidi Chang
Graduate Student: Duong Phuong Linh (Candy)
Acknowledgements
In order to finish this thesis, I was granted a lot of assistance, guidance and supervision from professors, respondents and supporters. Hence, I want to thank to all who support, direct and motivate me throughout the process of completing the research. Especially, I would like to express my special thanks of gratitude to my supervisor Dr. Heidi Chang who initiated the project; guided and suggested me a lot of valuable and constructive comments; and gave me a good opportunity to complete my Master thesis.
Besides, I would like to express my deep gratitude to our research committee members who assisted to improve my thesis paper. They worked hard and corrected my mistakes and errors to help my thesis better. I also want to thank all the respondents who have paid time to get through the entire survey with their enthusiastic and supporting manner.
Moreover, I am particularly grateful for my family, my friends and my classmates. They always trusted and supported me when the study difficulties came. Their deepest love and sacrifice were spiritual inspiration to cheer me up. Lastly, thanks are extended to everyone who encouraged and guided me to finish my research work directly and indirectly.
Abstract
The development of Internet-based technologies in the last two decades significantly changes the way businesses operate. Banking sector is along with the evolution of computer and specialized technologies in order to provide the highest quality to customers. Internet Banking is new service so it pays more and more attention of customers in Vietnam. Internet Banking services and perceived value is basically essential to satisfy and retain customers. They are also the critical elements to achieve customer satisfaction and then leads to customer loyalty and brand reputation. These research findings showed that there is positive relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction, perceived value and customer satisfaction, brand reputation and customer satisfaction, as well as customer loyalty and customer satisfaction.
Key works: Internet Banking, Banking Sector, Customer Satisfaction, Service Quality, and Perceived Value
Table of Contents
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... 2 ABSTRACT ... 3 LIST OF TABLES ... 6 LIST OF FIGURES ... 7 CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 8 1.1. Introduction ... 8 1.2. Research Objectives ... 9 1.3. Research Questions ... 10 1.4. Research Significance ... 10CHAPTER II: LITERATURE REVIEW ... 11
2.1. Internet Banking ... 11
2.2. Customer Satisfaction ... 12
2.2.1. Definition ... 12
2.2.2. Models of Assessing Customer Satisfaction... 13
2.3. Perceived Value ... 14
2.4. Service Quality ... 16
2.5. Brand Reputation ... 17
2.6. Customer Loyalty ... 19
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY ... 21
3.1. Conceptual Framework ... 21 3.2. Research Design ... 22 3.3. Sampling ... 23 3.4. Measures ... 24 3.4.1 Measures ... 24 3.4.2 Key Variables ... 24 3.5. Data Analysis ... 27
CHAPTER 4: RESULT AND DISCUSSION ... 29
4.1 Descriptive Analysis ... 29 4. 2 Mean and Standard Deviation ... 32 4.3 Reliability Cronbach’s Alpha ... 35 4.3.1 Perceived value ... 37 4.3.2 Service quality ... 37 4.3.3 Customer satisfaction... 38 4.3.4 Brand reputation ... 38 4.3.5 Customer loyalty ... 38 4.3 Hypothesis testing ... 38 4.3.1 Correlation test ... 39
4.3.2 Linear regression analysis ... 41 4.4 One way ANOVA analysis ... 43 4.4.1: The differences of perceived value, service quality, brand reputation, customer loyalty and customer satisfaction among respondents’ age ... 43 4.4.2 The differences of perceived value, service quality, brand reputation, customer loyalty and customer satisfaction among respondents’ job ... 44 4.4.3 The differences of perceived value, service quality, brand reputation, customer loyalty and customer satisfaction among respondents’ monthly income ... 46
CHAPTER 5: CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS ... 48
5.1 Research summary ... 48
5.2 Theoretical and Practical implication ... 49
5.3 Research limitations and Future research... 52
5.4 Concluding statement ... 53
REFERENCES ... 55
APPENDIX A ... 61
List of Tables
Table 3.1: The sources of measurement scale……….25 Table 4.1 Demographic characteristics for overall respondents……….30 Table 4.2: Descriptive statistics for variables………...33 Table 4.3: Reliability analysis……….35 Table 4.4: Reliability Cronbach’s alpha of respective factors………...……….37 Table 4.5: Correlation Matrix…………..………...40 Table 4.6: ANOVA summary………...41 Table 4.7: Coefficient summary ………..……….42Table 4.8: One way ANOVA tests of variables among respondent’s age…..……….43
Table 4.9: One way ANOVA tests of variables among respondent’s job…..……….……….44
Table 4.10: One way ANOVA of monthly income……...……….46
List of Figures
Figure 3.1: Frame of the study……….………..21 Figure 4.1: Age distribution of respondents………....30 Figure 4.2: Monthly income distribution………....32CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION
1.1. Introduction
The development of Internet-based technologies in the last two decades significantly changes the way businesses operate. Information and communication are exchanged rapidly and therefore it leads to the development and expansion of service sector. As the inevitable result, electronic commerce holds the prominent position in the global market by delivering an inexpensive, direct and immediate way to sell or buy products and services as well as deliver information (Abor, 2004). Banking sector is along with the evolution of computer and specialized technologies in order to provide the highest quality to customers. Jagdish (2008) stated that the beginning step to attain success derived from how leaders deal with long-term relationship with new and potential customers. It seems more reasonable provided costs to potential customers using Internet Banking in financial services sector. They can connect and use at any place and any time over the world with just a click. Moreover, due to breakthrough in technology in recent decades and easiness to browse into World Wide Web, Internet has brought an easy channel and method to manage customer’s banking account, make necessary enquiries and undertake banking transactions.
In Vietnam, Internet Banking is new service so it has not received much attention of customers. It is on the process of advertising to attract new users and broadening the market. The commercial banks almost offer Internet banking services in their operation nowadays. The Director of Operations and Technology Division of Techcombank, one of the leading banks in the technology sector in Vietnam market, said: "We see technology as a core part of the strategy business strategy and we are committed to focus all resources to develop this area, create a sustainable competitive advantage. In
addition to the average investment of $ 15 million per year for several consecutive years for the technology, banking has also focused human development with a team of experienced professionals from the leading banks in Vietnam and world “(Doan, 2013). Using a smart phone or a computer with a network connection, the consumers’ needs are rapidly performed via a few clicks.
However, there is a real situation of insecurity services using Internet banking in Vietnam. Some customers have lacked money to hackers. The Internet banking system has still some weaknesses in securing customers’ account. Therefore, the need to ensure customers’ rights and enhance their attitudes and awareness to Internet Banking services is basically essential to retain customers. It is explained the importance of customer satisfaction to reach customer loyalty.
1.2. Research Objectives
Internet banking services face a number of challenges in the operation process. Al-Sukkar and Hasan (2004) had indicated some major issues in their study: data and network security, especially privacy problems, lack and limitations of government policies, regulations and legislation to protect users and to make the Internet secure, lack of infrastructure and weak telecommunications, broken and slow Internet connections, lack of Internet awareness, especially in the rural areas. Internet banking there is still unaccepted therefore enhancing customers’ awareness about benefits of Internet banking services could encourage a higher level of acceptance, customers tend to be fear in using Internet Banking services because they think any mistake and error could cause a loss of money, connection costs and costs of building and managing Internet Banking system seems unreasonable.
Therefore, the study tries to measure and find understanding of factors affecting adoption of Internet Banking services and its possible consequences in Vietnam and find out the influence determinants towards customer satisfaction.
1.3. Research Questions
The research aims to examine which factors influence to customer satisfaction by replying the following questions:
1. What is the real situation of Internet Banking service in Vietnam?
2. What is the level of customers’ awareness of using Internet Banking services? 3. Which factors mostly influence customer satisfaction?
4. What benefits banks achieve when its customers satisfy?
5. What solutions should be recommended to enhance customer satisfaction?
1.4. Research Significance
The thesis aims to provide an explanation on the Determinant Factors and Consequences of Customer Satisfaction Using Internet Banking in Vietnam. This research can be applied in Vietnam and other countries because it is an essential need to realize factors being responsible for maintaining customer satisfaction in internet banking services. This topic isn't somehow new, but it is to be one of the meaning basis researches to support for the development of internet banking system in Vietnam.
CHAPTER II: LITERATURE REVIEW
The basic idea of this chapter is to discuss the main concepts of the study and find out the conceptual framework and models in assessing customer satisfaction using Internet banking services.
2.1. Internet Banking
Internet banking is defined as “the usage of Internet and telecommunication networks to deliver banking services to customers” (Nguyen & Singh, 2004). Daniel (1999) describes that customer is able to connect Internet via high technology media as computer, television, cable phone or mobile phone, and PDA to use offer banking products and services. Customer can gather interested information and use most banking services such as checking account balance, making banking transfers, deducting for registered monthly bills and invoices, buying online products and services and using money in advance even without money with Credit card and paying interest later.
Due to differences on user’s requirement (i.e. Strategic objectives for e-banking; Scope, scale, and complexity of equipment, systems, and activities; Technology expertise; and Security and internal control requirements), Internet banking system varies in configuration. The following is a sample of Internet banking architecture (IT examination Handbook InfoBase, 2003). Internet Banking is a substitute channel of distribution of financial services which becomes a competitive advantage of operation process in global basis. Also, it gives advantages to both bankers and customers. It has low cost transactions, saves times and increases employees’ productivity. Tuchilla (2000) listed some other benefits such as an ability to customize users’ accounts, innovation of new products and services, and the lowest cost of communication and advertising.
With over 40% of the population uses the Internet (2013), Vietnam is a potential destination for attracting and retaining customers using Internet Banking services. Since Internet banking is given to Vietnamese market for ten years, Internet banking services are increasingly popular and attract more and more users. According to estimates, until the end of 2013, the number of people using the service has increased by 45% for the last three years. Vietnam Banking Association said 40 banks have announced deployment internet banking system at different levels so far. IB is the most powerful system of several major banks like Vietcombank and Techcombank commercial banks.
2.2. Customer Satisfaction
2.2.1. Definition
Although the term “customer satisfaction” is popularly recognized and valued in business environment, it has been arguing how to define the term. Kotler & Keller (2006) defines satisfaction is “a person’s feelings of pleasure or disappointmnet resluting from comparing a product’s performance (outcome) in relation to his expectation”. According to Oliver (1981), satisfaction is apsychological state resulting from a process of emotional and cognitive evaluation. Since customers have their own attitudes and experience, they value outcome with different level of satisfaction. Customer satisfaction means “a measure of how your organization’s total products’ performs in relation to a set of customer requirements (Hill, Brierley, & MacDougall, 2003). And therein, customer satisfaction of Internet banking services mean that banks fully attain customer’s expectations. Anderson et al. (1994) clearly categorizes banking customer satisfaction into two conceptialization: transaction-specific and overal satisfaction. The first one results from a specific service encounter transaction’ experience while the other is the result of overal transactions. The more expectations are met or exceeded, the more an organization attain comprtitive advantages compared
to other competitors.The gap of expectation and real outcome is as short as possible will get more customers’ loyalty.
2.2.2. Models of Assessing Customer Satisfaction
There are a number of models used to assess customer satisfaction. Firstly, Swedish Customer Satisfaction Barometer (SCSB) was constructed by Fornel and his colleagues under supervision of University of Michigan-National Quality Research Center and the Swedish Center in 1989. The model describes two primary drivers of satisfaction: perceived value and customer expectations. Perceived value is the comparison between the price paid and quality received, while expectation is about customer’s desire products and services. The second connection is customer’s complaints and his loyalty/commitment to bought products and services.
Secondly, American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) is introduced in 1994 by American Quality Association and University of Michigan Business School. The model which is constructed based on the knowledge of SCSB model, is the satisfaction of American consumer about products and services in local market. ACSI explains the link of input factors (perceived quality, perceived value and expectations) and the outcome (customer’s complaints and loyalty). It differs from SCSB by breaking down perceived quality of perceived value.
The European Customer Satisfaction Index (ECSI) is an analytical tool to harmonize customer satisfaction index and support organizations’ marketing strategy under encouragement of European Quality Institute and European Quality Management. ECSI is divided by two sub-models, i.e. structural model and measurement model. Customer satisfaction is the central variable related to drivers: company’s image,
perceived quality, perceived value and expectations. The significant outcome of these links is customer’s loyalty.
Using these above knowledge and through empirical studies, Nguyen and Singh (2004) developed a conceptual model of the relationships between Internet banking system and customer satisfaction and loyalty. The model explains the relationship of customer characteristics (age, income, education, experience, disability and emotion); Internet banking system quality (transaction speed, ease of use, convinience, accessibility, costs vs benefits, security/privacy, and user powerment) ; cusomer system contraints (user’s software, hardware and Internet bandwith); and customer satisfaction. If customers are satisfied with bank attributes like brand reputation, costs, convinience and banking service quality, they will be loyal to the bank’s services.
2.3. Perceived Value
Perceived value can be confirmed like as a difference between total consumers value that a consumer can get from a product or a service. Evaluating, receiving, using and eliminating any product or any service is incurred from total customer cost (Roig et al., 2006). Value is the judgment behavior of preference by customers toward products and services (Gan et al, 2005). Value refers to: function of overall quality and price of the firm’s products and services compared to the competitors” (Mokhtar et al, 2005). The sellers can't confirm perceived value exactly, only customer can perceive this value because they are people who directly use the product or the service. When customer decides to buy any product or any service from any company, they will inspect and evaluate customer value as a method to decision standard to choose their suit product or the best service for them. Therefore, the key success for their organization is focused on supplying value for their customers.
There are two major approaches can be discovered about the level of perceived value. The first approach defines perceived value as a construct what has two parts, one benefit gets and one benefits sacrifices (Dodds et al., 1991; Cronin et al., 2000). Customer benefits are those value derived from quality of product or services and a chain of psychological benefits. The sacrifices component is formed from monetary and non-monetary (Dodds et al, 1991.). The second approach defines perceived value of customers like as a multidimensional construct (De Ruyter et al., 1997 & 1998; Sweeney & Soutar, 2001; Roig et al., 2006). It means that perceived value has five main components which are social value, emotional value, functional value, epistemic value and conditional value (Sheth et al., 1991).
Customer perceived value is the basis of all marketing activity. Higher value leads to users’ higher motivation of purchasing the firm’s products and services. In PERVAL model, Jillian and Geoffrey (2001) broke down elements of perceived value as quality, emotional value, price and social value.
(1) Quality: the value derived from actual quality comparing with a product’s or service’s expected performance.
(2) Emotional value: the value which explains the feelings or affective states from real experience of using products or services.
(3) Price: the value which stated the lower on costs in short-term and long-term period.
(4) Social value: the value which defined and enhanced self- concept of a product or service.
Higher perceived value will achieve more customers awareness and preferences of products and services. And therefore it will have a positive effect on customer satisfaction.
H1: There is a positive relationship between perceived value and customer satisfaction.
2.4. Service Quality
Almost businessman understands the importance of service quality provided to customers but it is continuously arguing how to define the term “service quality”. The term mainly defined under customers’ view as the result of service that achieves their expectations. It influence customer’s experience and volatile the demand volume of products and services sold. Under financial managers’ point of view, service quality must be assessed as a core strategy of business performance because it impacts the company’s profit and financial indicators (Hinson, Mohammed, & & Mensah, 2006) as well as the company’ image. Service quality is considered as a sustainable competitive advantage to competitors (Kotler & Keller, 2006; Gronroos, 2001) and a measurement of products’ and services’ improvement process. Under Internet banking sector, service quality has been identified as the gap between service expectation and service performance or the comparison of what customers expect to receive and what they actually receive (Gefen, 2002). Service quality often depends on the current and past experience of customers (Berry & Leonard, 1995). The higher service quality is provided, the higher customers satisfy.
In order to analyze and deeply understand Internet banking service quality, it is necessary to get knowledge of elements relevant to achieving service quality, i.e. accessibility, convenience, speed, fees and charges, website content and design. Firstly,
accessibility is the capacity to acquire information and services from a bank’s website depending on user’s hardware and software; internet connection; size and format of documents (Goodwin-Jones, 2001). The vital strength is the ability to access information centers at any time with immediate responsiveness. Next, today, Internet banking is configured to help user access online service such as internet banking, telephone banking, mobile banking, ATM & so on at all time and place. Internet banking is easy to access is an advantage better understand of website contents & applications. Plus, the speed & responsiveness will be a main concern of information system & e-commerce. Therefore, the link of downloading speed & user’s satisfaction speed & time fees & changes of Internet banking services is much lower than documented process making. It’s save time of employees & divided by smaller load of work, so that bank can save administrative costs. In respect of customers’ viewpoints, they expect all products and services achieve the highest quality. A positive perception of customers about the quality of Internet banking services will be a contribution on customer satisfaction. The higher quality is provided, the better customers satisfy.
H2: There is a positive relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction.
2.5. Brand Reputation
Brand is a symbol describing an organization’s name, term, symbol, design and products and services compared to other rivals (American Marketing Association, 1995). Na, Marshall, and Keller (1999) argued that "image cannot be measured by attribute measurements alone but must include measurements of consumers' perceptions of the value and benefits attainable from using the brand" (p. 171). This indicates that the effectiveness of test images is very important so it affect to consumer satisfaction clearly. Brand image is considered as a faithful combination between consumers in the
brand –specific. Brand image has influence and motivate buying behavior of consumers if the brand image of quality assurance products for consumer awareness (Kotler and Gertner, 2002). Perceived brand image has an effect on customer satisfaction and a customer's beliefs about brand. They are sourced from personal use experience, word-of-mouth endorsements/criticisms, and/or the marketing efforts of firms (Woodruff et. al., 1983). In banking sector, one of the most essential aspects is a brand awareness what refers to the banks reputation and expiable bank place in the banking industry (Che-Ha & Hashim, 2007; Reynolds, 2007).
The measure about customer experience is how customer fills with the brand image or the services. Some combination of beliefs about the brand’s various performance dimensions determines a perceived overall brand performance (Woodruff et al., 1983; Che-Ha & Hashim, 2007). An important factor is a brand image perception what provides by service because customer satisfaction with brand image can promote service to others around them. According to Park et al (1986), the organization brand image is measured by customers’ perceptions of value and benefits achievable from use of brand. The scholar highly values the importance of brand’s benefits. Benefits are derived from functional needs, experiential needs and symbolic needs. ACSI proved the close link of reputation and customer satisfaction through a number of marketing researches. Internet banking reputation refers to the bank’s well-known and the standing in the banking industry (Che-Ha & Hashim, 2007). Kotler & Gertner (2002) provide evidence that a well known brand will assure quality of products and services provided. Thus, it has a great effect on purchasing behavior and motivation of customers.
Reputation is assessed as an evaluation of the consistency over time of an entity’s operation and performance (Herbig & Milewicz, 1993). So in an organization, there are possibilities of reputations as cost, product quality, global reputations or creative
reputations. Reputation is said to be understood not only in the web. It also depends on the whole organization (Casalo et al., 2008). Moreover, reputation is considered as a consequence what can interactive between business and its environment. The company and customers will have certain interactions as a source of information can help their customers to assess more clearly about offered quality (Yoon, Guffey & Kijewski, 1993). Standifird et al. (1999) also said that reputation depends on assess about company from desirability what is be viewed from a number of people or a group of people from the external. According to researchers, a good brand reputation is a result of customers’ purchasing and assessing process. If a company provides good quality and high value of products and services, customers will be satisfied. Customer satisfaction is the best and fastest marketing tool to retain existing customers and attract new customers; therefore, it leads to customer loyalty and builds up a well-known brand reputation.
H3: There is a positive relationship between brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
2.6. Customer Loyalty
Many researchers have indicated the importance of loyalty to business’ success. Oliver (1997) defined customer loyalty as “a deeply commitment to repurchase or re-patronize a preferred products or services in the future which cause repetitive same-brand or same-brand set purchasing”. Loyalty has two main criteria: behavior and attitude (Ranaweera et al, 2003). Customer commitment means a strength of good relationship among customer and the entity and a desire to keep using its products and services. When customers are satisfied, they come to repurchase products more frequently; tend to be willing to try new products and services; buy only from you and also suggest recommendations and give feedback to improve.
with both existing and potential customers. This is called the transformation process which describes how a business makes customers be loyal. It is critical to note that a satisfied customer does not necessarily mean a loyal customer. Any breach of trust from previous transactions can seriously result a negative relationship with customers. It is quite difficult and challenging to make a customer from satisfied to loyal. This is why it is so essential to keep an eye on customer satisfaction, and correct any possibly bad situations. Delivering outstanding service to customer and always paying close attention to customers’ needs and are a must. Therefore, it is essential and necessary to keep in mind that customer satisfaction is an important element to create customer loyalty.
H4: There is a positive relationship between customer loyalty and customer satisfaction.
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY
In term of aim and nature of studied problem, this chapter mainly describes main steps of methodology process. Firstly, the study starts with conceptual framework. Next is research design. Sampling design and data collection is the next step to collect information from respondents. And then the study explains operational definitions of variables discussed on this thesis. Finally, data are sorted and inserted in SPSS software to get statistic outputs.
3.1. Conceptual Framework
Based on chapter 2 “literature review”, Figure 3.1 demonstrates the research conceptual framework which gives explanation about the relationship among customer satisfaction and the determinants including perceived value, service quality, customer loyalty and brand reputation in Vietnam Internet Banking Sector.
3.2. Research Design
The methodology has two main categories: quantitative method and qualitative method. Quantitative method is “to generate statistics through the use of large-scale survey research, using methods such as questionnaires or structured interviews” whilst qualitative method is “to explore attitudes, behavior and experiences through such methods as interviews or focus groups” (Saunders et al. 2009). In the study, quantitative approach is chosen to explore customer satisfaction in Internet banking sector, using survey as method of investigation.
The variables of our research are service quality, perceived value, brand reputation, customer loyalty and customer satisfaction. The hypotheses will be established basing on the framework. Questionnaire will be made and delivered to the respondent in order to collect data. The respondent is customers using Internet Banking in Vietnam. The following steps illustrate the process of preparing questionnaire and collecting the data for the research:
(1) Questionnaire Back - Translation
Questionnaires were translated into Vietnamese because they will be delivered to Vietnamese people using Internet banking. This is necessary to make clear and avoid misunderstanding, and it needs to make sure that the questionnaire is designed carefully based on research objectives. Originally, the questionnaire is designed in English version since the thesis is processed in English. Thus, it is necessarily translated into Vietnamese version in order to receive accurate information and assessment from respondents.
(2) Pre-test
Before spreading the questionnaire, it must be rechecked carefully to avoid any misunderstanding or unclear meaning
(3) Pilot Study
A pilot study is to verify the reliability of the scale items: I give my questionnaire for 3 professors, 3 bankers, 4 customers, 3 classmates who can help me for pre-check my questionnaire before I spread it to customers.
(4) Questionnaire survey
The questionnaire will be sent to respondents in three big cities. There are two main methods of data collection, i.e. by emails through Internet: Google email, Skype, Facebook, Yahoo and by hard copies directly from customers who uses banks’ services over the counter. Questionnaires were translated into Vietnamese to get easily understanding and accurate information from respondents. The main collection data method is depended on the questionnaires from customers through internet Google doc via email, Skype, Facebook, Yahoo. It finds very useful in limited time and receives a large number of reply.
3.3. Sampling
Population is defined as “the complete set of units of analysis that are under investigation, while element is the unit from which the necessary data is collected” (Stapleton, 2006). The core function of this study is to investigate determinant factors and consequences of customer satisfaction using Internet banking in Vietnam. Therefore, the target population is residents in Vietnam. However the research can only carried out in Ha Noi Capital, Ho Chi Minh City and Da Nang city because of limitation of time. In this paper, a convenience sampling method is employed because of the ease to access. According to Saunders et al. (2009), a larger sample size will be more representative for the population rather than the smaller one. Thus, the mean of the sample is more representative to population mean which is explained as the law of large numbers. Hence, 250 surveys are delivered to respondents from different ages, gender, jobs and
education background. Respondents are chosen from customer lists with odd listing numbers up to collect enough 250 surveys during a week in three cities. Surveys are uploaded to “Google” website and then the link is going to be sent to respondent’s email. The research surveys are under questionnaire type.
3.4. Measures
3.4.1 Measures
In the thesis, several rating scales will be used due to different functions and characteristics. Firstly, dichotomous scale is a measurement to answer questions under “yes” or “no” choice. It deals with respondents’ demographic characteristics in the first part of the survey. Secondly, ranking scale is mainly employed to rank variables. The questionnaire is divided into two main sections: demographic and determinant factors and consequences of customer satisfaction. The demographic section is general information about a respondent such as age, gender, income level, marital status, and education level. The second section consists of five subsections: quality, perceived value, customer loyalty and brand reputation. These subsections used a five point Likert Scale with ratings from “strongly disagree” (1) to “strongly agree” (5). Likert scale is the most popular instrument to measure factors affecting customer satisfaction and their possible consequences using Internet banking services. Five-point Likert scale with ratings from “strongly disagree” (1) to “strongly agree” (5) is chosen.
3.4.2 Key Variables
Customer satisfaction is an experiencing process of purchasing and using products and services. Customers set their own of expectations and if the products and services met the requirements, customers are satisfied. But how does it measure? Customer satisfaction is assessed by service quality and perceived value. Therefore, it is
a dependent variable. Plus, customer loyalty and brand reputation is an achievement of customer satisfaction; hence they are dependent variables as well. Service quality and perceived value are independent variables since they are essential elements affecting customer satisfaction using Internet Banking.
The variable Service Quality was measured by Maroofi (2013) & Mojares (2014); they are 6 items in the scale. The variable Perceived Value was measured for Moore and Benbasat (1991); they are 9 items in the scale. The variable Brand Reputation was measured for Homburg and Giering (2001); they are 9 items in the scale. The variable Customer Loyalty were measured for Maroofi (2013)/ Homburg and Giering (2001); they are 6 items in the scale. And the variable Customer Satisfaction was measured for Homburg and Giering (2001); they are 9 items in the scale. The items of each scale perform clearly through this figure.
Table 3.1: The sources of measurement scale
Constructs Items Adapted from
Service Quality
1. Full information on product features and services offered 2. Internet banking is clear and easy to use
3. Website information is regularly updated 4. Internet banking is convenience and saves time 5. The confidentiality of customer’s data is ensured 6. Internet banking transactions are satisfactory worked
in term of security and privacy protection
Maroofi (2013)/ Mojares (2014)
Perceived Value
1. Internet banking gives me greater control over my finances
2. Transaction fees are reasonable
3. Internet banking service is good value of money 4. The use of Internet banking is relaxed
5. Internet banking is interesting to use
6. Using Internet banking for my banking services increase my productivity
7. Using Internet banking improves my performance of utilize banking service
8. Internet banking is compatible with my life and working style
9. Internet banking offers a convienient cross-linked transactions among banks
Moore and Benbasat (1991)
Customer Satisfaction
1. Internet banking makes it easy to find what I need
2. My expectation before using Internet banking is met with my experience
3. Basing on my experience, Internet banking application is quite pleasant
4. I am satisfied with Internet banking application
5. I am satisfied with the delivery of the overall service of Internet banking
6. I am satisfied with quality and fee of Internet banking service
7. I am satisfied with the first time installing and using Internet banking
8. I am able to make transactions anywhere at any time I want 9. Customer service of Internet banking system is quick and
highly satisfied
Homburg and Giering (2001)
Brand
Reputation
1. Internet banking has a good image in customer’s mind 2. Internet banking has a good reputation compared to
traditional banking services
3. Banking websites has a good reputation for offering wide range and high quality of banking services
4. Banking websites have a good reputation on secure customer’s confidential information
5. Internet banking has a good reputation on specialists’ ability to detect fraud and information theft
Mojares (2014)
Customer Loyalty
1. I commit in frequent use of Internet banking service 2. I will use Internet banking service in the future
3. I will recommend friends and relatives using Internet banking service
4. I will recommend Internet banking services to someone who seeks my advice
5. I am eager to send feedback to improve futurely supplied services
6. It is difficult to change my beliefs about Internet banking
Maroofi (2013)/ Homburg and Giering (2001)
3.5. Data Analysis
After gathering the questionnaires, raw data was sorted, checked for usability, and inputted into an Excel file. In order to avoid duplicated or inaccurate data, it is essential to apply a data treatment procedure. These include of checking errors due to wrong typing or invalid questionnaires and then correct any wrong records. After that, the data analysis will use SPSS version 20 software as a major tool to analysis the collected data. The statistical procedures for quantitative research include Descriptive Statistic, Reliability, Linear Regression Analysis and ANOVA Analysis. Descriptive statistics is selected in order to understand the characteristics of the sample and included measures
of central tendency and variability (frequency, distribution, range and standard deviation) for selected variables. Descriptive statistics is selected in order to measure selected variables’ central tendency and variability (frequency, distribution, range and standard deviation). ANOVA is performed to consider the difference in the assessment of factors of each different customer’s perception on perceived value, service quality, and company brand image, and customer satisfaction with customer satisfaction. Linear Regressions would explain the interrelated relationship among testes variables with customer satisfaction factor.
CHAPTER 4: RESULT AND DISCUSSION
This chapter is the analysis of collected data gathered from 205 respondent (return rate is 82% out of 250 respondents) about Determinant Factors and Consequences of Customer Satisfaction in Vietnamese Internet Banking Sector. The statistical analysis includes:
- Description of respondents: Demographic analysis - Compare mean and standard deviation
- Cronbach’s Alpha test - Testing of hypotheses - ANOVA analysis
To help clarify analysis, bar charts, tables, graphs showing percentages and trends are employed to present collected data.
4.1 Descriptive Analysis
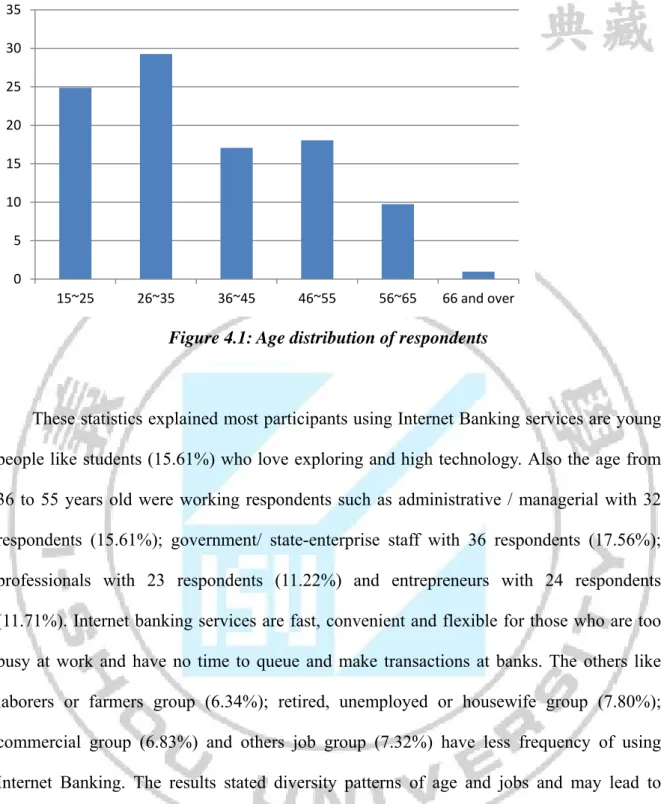
Data is collected and analyzed by SPSS version 20. Total participated respondents are 250, and 205 questionnaires were pretreated and yielding an 82% respondents. After categorizing data, 48.29 % of respondents were male and 51.71 % of respondents were female. The age statistics clearly stated that the largest group of interviewees was those from 26 to 35 years old accounted for 29.27% of 205 respondents. The age from 15 to 25 years old was the second rank with 24.88% (51 out of 205 respondents). The age group from 46 to 55 has 18.05% while the group of 36 to 45 has 17.07%. The least age group was those above 66 years old with only 0.98% of total participants. The below graph showed frequency of age group (see Figure 4.1).
Figure 4.1: Age distribution of respondents
These statistics explained most participants using Internet Banking services are young people like students (15.61%) who love exploring and high technology. Also the age from 36 to 55 years old were working respondents such as administrative / managerial with 32 respondents (15.61%); government/ state-enterprise staff with 36 respondents (17.56%); professionals with 23 respondents (11.22%) and entrepreneurs with 24 respondents (11.71%). Internet banking services are fast, convenient and flexible for those who are too busy at work and have no time to queue and make transactions at banks. The others like laborers or farmers group (6.34%); retired, unemployed or housewife group (7.80%); commercial group (6.83%) and others job group (7.32%) have less frequency of using Internet Banking. The results stated diversity patterns of age and jobs and may lead to different levels of satisfaction of using Internet Banking services (see Table 4.1).
Table 4.1 Demographic characteristics for overall respondents
Variable Frequency (N) Percentage (%)
Total participants 205 100 Gender 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 15~25 26~35 36~45 46~55 56~65 66 and over
Male 99 48.29 Female 106 51.71 Age 15~25 51 24.88 26~35 60 29.27 36~45 35 17.07 46~55 37 18.05 56~65 20 9.76 66 and over 2 0.98 Monthly Income Under3 million VND 29 14.15 3~7 million VND 62 30.24 7~ 15 million VND 75 36.59 Over 15 million VND 39 19.02 Level of education
Less than High School 10 4.88
High School 28 13.66 College 117 57.07 Graduate 50 24.39 Job Professionals 23 11.22 Laborers/Farmers 13 6.34
Variable Frequency (N) Percentage (%)
Total participants 205 100 Students 32 15.61 Entrepreneurs 24 11.71 Administrative/Managerial 32 15.61 Government/State Enterprise 36 17.56 Retired/ Unemployed/Housewife 16 7.80 Commercial 14 6.83 Others 15 7.32
In term of education, most of participants were college graduated (117 out of 205 participants – 57.07%) and postgraduate (50 participants with 24.39%). Lower level was high school graduated with 13.66% and the least were less than high school graduated with 4.88%. The majority of respondents (36.59 % and 30.24%) were those who had average monthly income at VND 7 million to 15 million and VND 3 million to 7 million. 19.02% had monthly income over VND 15 million. Monthly income under VND 3 million had 14.15% of respondents. These revealed that diversity of level of education and income level would differently affect satisfaction levels of using IB services. The following chart
represented frequencies of respondents’ level of income:
Figure 4.3: Monthly income distribution
4. 2 Mean and Standard Deviation
Mean value is an important measure of respondent’s response in quantitative research. Mean using in Likert 5 points indicates the level of agreement. In the study, four elements of customers satisfaction model are (1) Perceived value, (2 ) Service quality, (3) Brand reputation and (4) Customer loyalty.
14.15%, 30.24% 36.59% 19.02% Under3 million VND 3~7 million VND 7~ 15 million VND Over 15 million VND
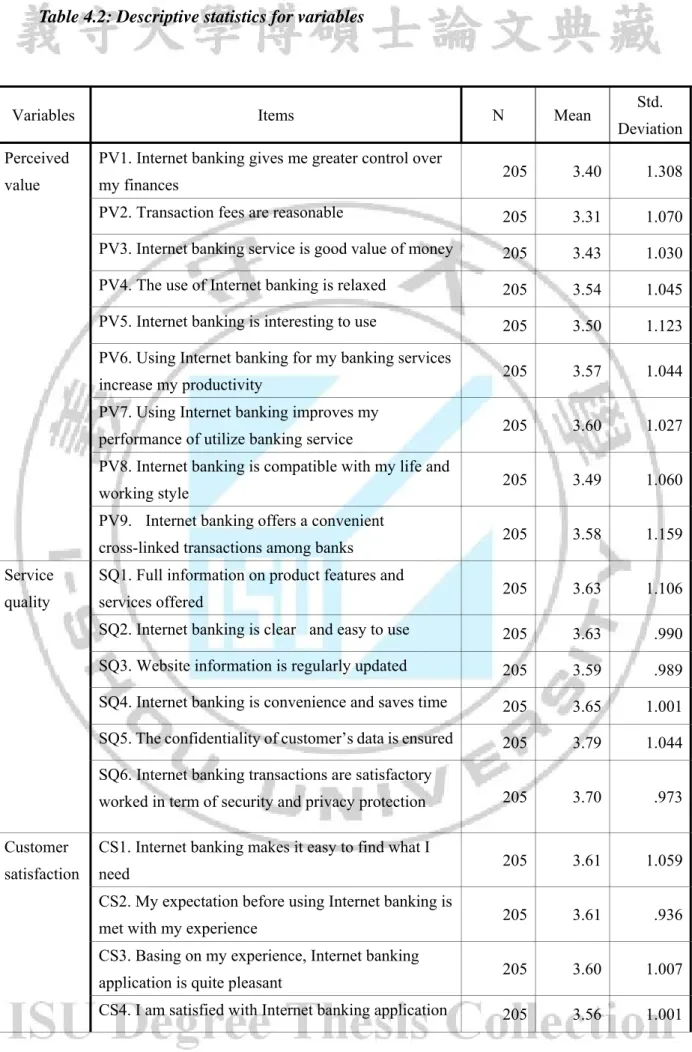
Table 4.2: Descriptive statistics for variables
Variables Items N Mean Std.
Deviation Perceived
value
PV1. Internet banking gives me greater control over
my finances 205 3.40 1.308
PV2. Transaction fees are reasonable 205 3.31 1.070 PV3. Internet banking service is good value of money 205 3.43 1.030 PV4. The use of Internet banking is relaxed 205 3.54 1.045 PV5. Internet banking is interesting to use 205 3.50 1.123 PV6. Using Internet banking for my banking services
increase my productivity 205 3.57 1.044 PV7. Using Internet banking improves my
performance of utilize banking service 205 3.60 1.027 PV8. Internet banking is compatible with my life and
working style 205 3.49 1.060
PV9. Internet banking offers a convenient
cross-linked transactions among banks 205 3.58 1.159 Service
quality
SQ1. Full information on product features and
services offered 205 3.63 1.106
SQ2. Internet banking is clear and easy to use 205 3.63 .990 SQ3. Website information is regularly updated 205 3.59 .989 SQ4. Internet banking is convenience and saves time 205 3.65 1.001 SQ5. The confidentiality of customer’s data is ensured 205 3.79 1.044 SQ6. Internet banking transactions are satisfactory
worked in term of security and privacy protection 205 3.70 .973 Customer
satisfaction
CS1. Internet banking makes it easy to find what I
need 205 3.61 1.059
CS2. My expectation before using Internet banking is
met with my experience 205 3.61 .936
CS3. Basing on my experience, Internet banking
application is quite pleasant 205 3.60 1.007 CS4. I am satisfied with Internet banking application 205 3.56 1.001
Customer satisfaction
CS5. I am satisfied with the delivery of the overall
service of Internet banking 205 3.60 1.007 CS6. I am satisfied with quality and fee of Internet
banking service 205 3.56 .893
CS7. I am satisfied with the first time installing and
using Internet banking 205 3.61 1.006
CS8. I am able to make transactions anywhere at any
time I want 205 3.59 1.014
CS9. Customer service of Internet banking system is
quick and highly satisfied 205 3.75 2.295 Brand
reputation
BR1. Internet banking has a good image in customer’s
mind 205 3.60 1.003
BR2. Internet banking has a good reputation
compared to traditional banking services 205 3.50 .953 BR3. Banking websites has a good reputation for
offering wide range and high quality of banking services
205 3.40 1.088 BR4. Banking websites have a good reputation on
secure customer’s confidential information 205 3.45 .941 BR5. Internet banking has a good reputation on
specialists’ ability to detect fraud and information theft
205 3.51 1.055 Customer
loyalty
CL1. I commit in frequent use of Internet banking
service 205 3.48 1.083
CL2. I will use Internet banking service in the future 205 3.59 .989 CL3. I will recommend friends and relatives using
Internet banking service 205 3.56 .946 CL4. I will recommend Internet banking services to
someone who seeks my advice 205 3.51 1.065 CL5. I am eager to send feedback to improve future
supplied services 205 3.68 1.053
CL6. It is difficult to change my beliefs about Internet
The mean values were greater than 3 for all four variables. These results mean a positive evaluation of Internet banking services. Customers had a quite high and satisfied perception of Internet banking and its services. The average mean of variables equaled 3.49 for perceived value, 3.67 for service quality, 3.61 for customer satisfaction, 3.49 for brand reputation, and 3.57 for customer loyalty.
Besides, standard deviation was also critical measurement to assess the level of agreement. It showed a deviation of responses from the mean value. According to table 4.2, standard deviation fluctuated from 0.893 to 2.295 which explained that observations were around mean value of above variables. Therefore, respondents were slightly satisfied with Internet banking services.
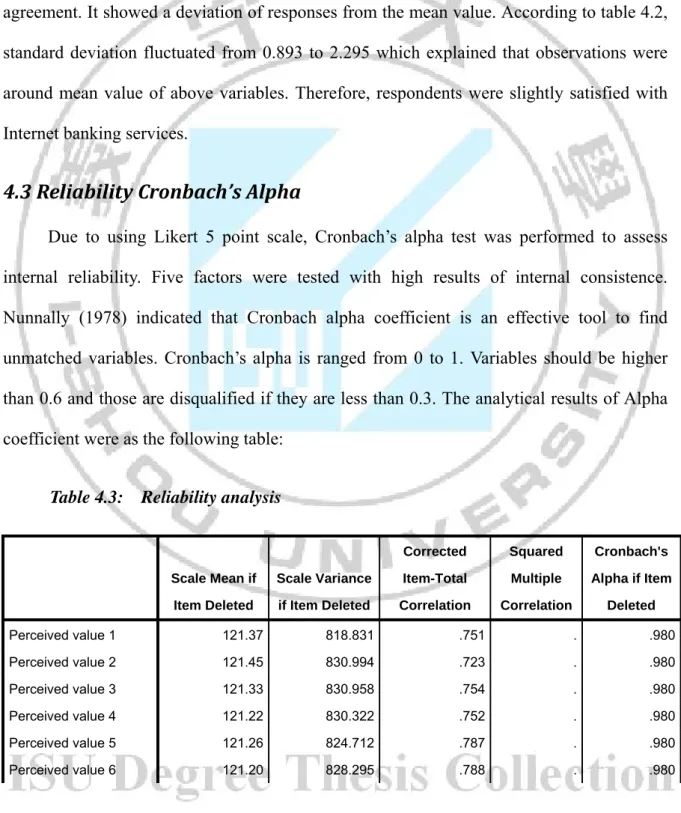
4.3 Reliability Cronbach’s Alpha
Due to using Likert 5 point scale, Cronbach’s alpha test was performed to assess internal reliability. Five factors were tested with high results of internal consistence. Nunnally (1978) indicated that Cronbach alpha coefficient is an effective tool to find unmatched variables. Cronbach’s alpha is ranged from 0 to 1. Variables should be higher than 0.6 and those are disqualified if they are less than 0.3. The analytical results of Alpha coefficient were as the following table:
Table 4.3: Reliability analysis
Scale Mean if Item Deleted Scale Variance if Item Deleted Corrected Item-Total Correlation Squared Multiple Correlation Cronbach's Alpha if Item Deleted Perceived value 1 121.37 818.831 .751 . .980 Perceived value 2 121.45 830.994 .723 . .980 Perceived value 3 121.33 830.958 .754 . .980 Perceived value 4 121.22 830.322 .752 . .980 Perceived value 5 121.26 824.712 .787 . .980 Perceived value 6 121.20 828.295 .788 . .980
Scale Mean if Item Deleted Scale Variance if Item Deleted Corrected Item-Total Correlation Squared Multiple Correlation Cronbach's Alpha if Item Deleted Perceived value 8 121.27 826.484 .806 . .980 Perceived value 9 121.19 821.956 .804 . .980 Service quality 1 121.13 823.778 .815 . .980 Service quality 2 121.13 830.399 .795 . .980 Service quality 3 121.17 831.574 .775 . .980 Service quality 4 121.11 827.773 .833 . .980 Service quality 5 120.98 829.730 .763 . .980 Service quality 6 121.06 830.236 .812 . .980 Customer satisfaction 1 121.15 826.198 .812 . .980 Customer satisfaction 2 121.15 831.276 .826 . .980 Customer satisfaction 3 121.16 828.456 .815 . .980 Customer satisfaction 4 121.20 827.347 .840 . .980 Customer satisfaction 5 121.16 829.025 .805 . .980 Customer satisfaction 6 121.20 835.517 .783 . .980 Customer satisfaction 7 121.15 828.988 .807 . .980 Customer satisfaction 8 121.18 827.802 .821 . .980 Customer satisfaction 9 121.01 823.451 .365 . .985 Brand reputation 1 121.16 825.724 .868 . .980 Brand reputation 2 121.26 831.136 .814 . .980 Brand reputation 3 121.36 824.054 .825 . .980 Brand reputation 4 121.31 833.059 .788 . .980 Brand reputation 5 121.25 825.707 .823 . .980 Customer loyalty 1 121.28 822.929 .848 . .980 Customer loyalty 2 121.17 825.848 .878 . .980 Customer loyalty 3 121.20 830.321 .835 . .980 Customer loyalty 4 121.25 824.541 .835 . .980 Customer loyalty 5 121.08 827.043 .802 . .980 Customer loyalty 6 121.18 829.744 .768 . .980
Table 4.4: Reliability Cronbach’s alpha of respective factors
Factor Items Items deleted Cronbach’s Alpha
Perceived Value 9 No 0.951
Service Quality 6 No 0.942
Customer Satisfaction 9 No 0.898
Brand Reputation 5 No 0.933
Customer Loyalty 6 No 0.953
Nunnally and Bernstein (1994) stated that Cronbach’ alpha scores greater than 0.7 are highly internal reliability. From table 4.2, in this research, the results show the Cronbach’s alpha of respective factors in Perceived Value is 0.951; in Service Quality is 0.942; in Brand Reputation is 0.933; in Customer Loyalty is 0.953 and in Customer Satisfaction is 0.898 so all factors were above 0.7 meaning that they were highly reliable.
4.3.1 Perceived value
Perceived value is one independent variable of Customer satisfaction model using Internet banking services in Vietnam. Item-to-total correlation of 9 items indicated that all are satisfied and the cronbach’s alpha is higher than 0.6 (the standard measure). There were no deleted items.
4.3.2 Service quality
As indicating in table 4.3 and 4.4 service quality has high degree of internal consistency. There are no deleted items out of total of 6 items. The Cronbach alpha equals 0.942 which mean a high reliability of questionnaires. The total variance is also high with strong loadings.
4.3.3 Customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction had a total of nine items. They all have a high cronbach’s alpha, all are greater than 8 while the accepted level is from 6. It proved that the questionnaire items are highly reliable.
4.3.4 Brand reputation
Average Cronbach’s alpha of this 5 items were 0.933 which has a highly reliability. There is no items are deleted. Brand reputation is considered as a strong loading variance.
4.3.5 Customer loyalty
Customer loyalty had a Cronbach’s alpha greater than 7 and there were no deleted items. This means customer loyalty is one strongly reliable element of these below tests.
4.3 Hypothesis testing
After implementing Cronbach’s alpha test, this part of chapter tested four hypotheses of this study:
H1: There is a positive relationship between perceived value and customer satisfaction H2: There is a positive relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction H3: There is a positive relationship between brand reputation and customer satisfaction
H4: There is a positive relationship between customer loyalty and customer satisfaction
For the core purpose of the study was investigating four independent variables: perceived value (PV), service quality (SQ), brand reputation (BR) and customer loyalty (CL) toward the dependent variable: customer satisfaction (CS).the correlation test and simple linear regression were conducted.
4.3.1 Correlation test
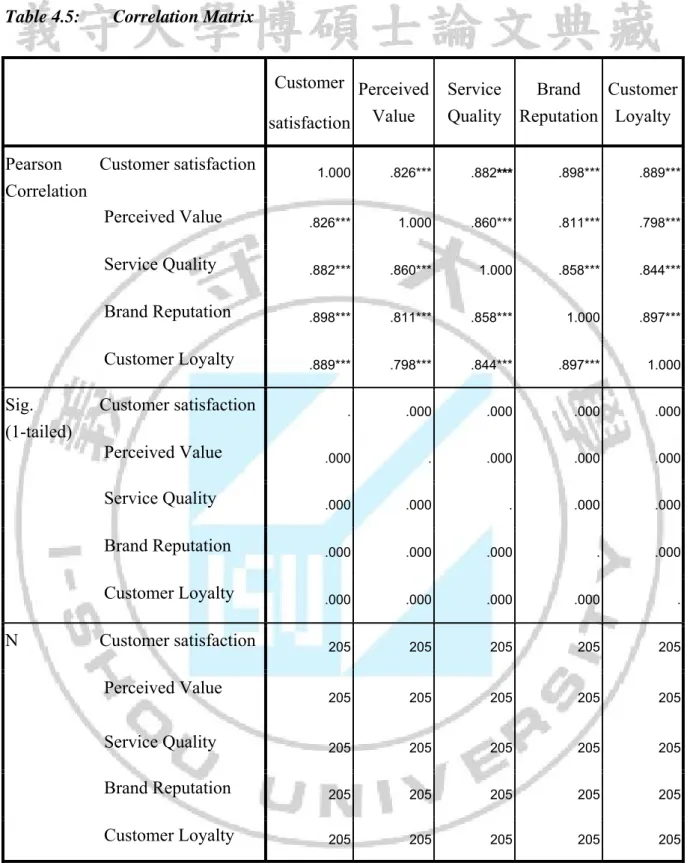
Correlation is a critical measure to describe the relationship between two variables. Pearson correlation coefficient, the most common measure, were used to test correlation among variables perceived value, service quality, customer satisfaction, brand reputation and customer loyalty. The measuring interval scale is between -1 and +1 showing fluctuations of variables together. Value -1 means that variables have perfect direct linear relation while value +1 means a perfect inverse linear relation between variables. Value 0 represents no linear relation. As proving, the closer is to value -1 or +1, the stronger relations variables have (Evan, 1996).
The Table 4.5 showed positive relations among tested variables. Therefore, the correlation between customer satisfaction and brand reputation were the strongest relationship with r =.898 and Sig. (1-tailed) = .000< .05. Others variables (ie. customer loyalty with r =.889, service quality with r =.882, perceived value with r =.826) had a decreasing strength with the dependent element customers satisfaction. Customer satisfaction is significantly correlated to perceived value (r=.826), service quality (r=.882), customer loyalty (r=.889) and brand reputation (r=.898). Perceived value is significantly correlated to customer satisfaction (r=.826), service quality (r=.860), customer loyalty (r=.798) and brand reputation (r=.811). Service quality is significantly correlated to customer satisfaction (r=.882), perceived value (r=.860), customer loyalty (r=.844) and brand reputation (r=.858). Brand reputation is significantly correlated to customer satisfaction (r=.898), perceived value (r=.811), service quality (r=.858) and customer loyalty (r=.897). Customer Loyalty is significantly correlated to customer satisfaction (r=.889), perceived value (r=.798), service quality (r=.844) and brand reputation (r=.897). The result of Pearson ranked hypotheses indicated that all variables used in this study was positive significance to customer satisfaction.
Table 4.5: Correlation Matrix Customer satisfaction Perceived Value Service Quality Brand Reputation Customer Loyalty Pearson Correlation Customer satisfaction 1.000 .826*** .882*** .898*** .889*** Perceived Value .826*** 1.000 .860*** .811*** .798*** Service Quality .882*** .860*** 1.000 .858*** .844*** Brand Reputation .898*** .811*** .858*** 1.000 .897*** Customer Loyalty .889*** .798*** .844*** .897*** 1.000 Sig. (1-tailed) Customer satisfaction . .000 .000 .000 .000 Perceived Value .000 . .000 .000 .000 Service Quality .000 .000 . .000 .000 Brand Reputation .000 .000 .000 . .000 Customer Loyalty .000 .000 .000 .000 . N Customer satisfaction 205 205 205 205 205 Perceived Value 205 205 205 205 205 Service Quality 205 205 205 205 205 Brand Reputation 205 205 205 205 205 Customer Loyalty 205 205 205 205 205
4.3.2 Linear regression analysis
Table 4.6: ANOVA summary
Model Sum of Squares Df. Mean
Square F Sig.
1 Regression 125.454 4 31.364 379.401 .000
Residual 16.533 200 .083
Total 141.988 204
R Square= .884 (Adjusted R Square=.881)
Linear Regression model was used to measure how close the relationship of dependent variable (CS) and others independent variables (PV, SQ, BR, CL) is. The equation of this customer satisfaction is as the following:
Y (CS) = β0 + β1PV + β2SQ + β3BR + β4CL
According to table 4.6, where β0 = 0.245, β1 = 0.79, β2 = 0.258, β3 = 0.436 and β4 = 0.215;
and R square is 0.884, it means that the four variables explained 88.40% of customer satisfaction variance in the attitude towards Internet banking services. It shows a high level of variability of response data around its mean. Therefore, we have got regression model as below:
Table 4.7: Coefficient summary Model Unstandardized Coefficients Standardized Coefficients t Sig. B Std. Error Beta (Constant) .245 .097 2.516 .013 Perceived Value .070 .044 .079 1.602 .111 Service Quality .253 .056 .258 4.507 .000 Brand Reputation .410 .058 .436 7.013 .000 Customer Loyalty .209 .058 .215 3.622 .000
a. Dependent Variable: Customer satisfaction
b. Indepent Variable: Perceived Value, Service Quality, Brand Reputation, Customer Loyalty
Among independent variables, brand reputation got the highest positive relation with B=.436. The second rank was service quality with B=.258, the third was customer loyalty with B=.215 and the least was perceived value with B=.079. Therefore, 88.40% of customer satisfaction depended on PV, SQ, BR and CL, while the remaining of 11.60% was based on other unstated variables in this study.
In short, all above results stated that the four null hypotheses are accepted. The four variables (PV, SQ, BR and CL) had a positive relationship with variable customer satisfaction.
4.4 One way ANOVA analysis
In this part, ANOVA (Analysis of Variation) is used to investigate the differences of perceived value, service quality, brand reputation, customer loyalty and customer satisfaction among demographic factors such as job, monthly income and age.
4.4.1 The differences of perceived value, service quality, brand reputation, customer loyalty and customer satisfaction among respondents’ age
According to table 4.8 and an assumption of equal attitudes towards age groups, there is no difference in respondents’ evaluation of perceived value among six groups of age with F<3 and Sig>0.05. This means that all groups of age are offered the same value of Internet banking services. Also other variables like service quality, brand reputation, customer satisfaction and customer satisfaction offered homogeneous quality.
Table 4.8: One way ANOVA tests of variables among respondent’s age
Variables Age Mean
Standard deviation F Sig. Accept Perceived value 15-25 3.9020 1.04837 0.927 0.465 No 26-35 3.8830 0.86944 36-45 4.0300 0.90973 46-55 3.6550 0.90775 55-65 3.6722 0.99019 Over 66 3.2778 1.02138 Service quality 15-25 4.0294 0.97280 1.156 0.332 No 26-35 3.8918 0.81679 36-45 4.0811 0.69235 46-55 3.7149 0.80809 55-65 3.7667 0.94188 Over 66 3.4167 0.82496
Customer satisfaction 15-25 3.9586 1.00122 0.912 .474 No 26-35 3.8441 0.81213 36-45 3.9970 0.75925 46-55 3.7982 0.69550 55-65 3.7222 0.76429 Over 66 3.0000 1.41421 Brand reputation 15-25 3.9412 1.04234 1.157 0.332 No 26-35 3.7690 .88850 36-45 4.0676 .66488 46-55 3.7675 .76674 55-65 3.8083 .66066 Over 66 3.0000 1.41421 Customer loyalty 15-25 3.9412 1.04234 1.486 0.165 No 26-35 3.7690 .88850 36-45 4.0676 .66488 46-55 3.7675 .76674 55-65 3.8083 .66066 Over 66 3.0000 1.41421 *F<3; Sig >0.05
4.4.2 The differences of perceived value, service quality, brand reputation, customer loyalty and customer satisfaction among respondents’ job
Table 4.9: One way ANOVA tests of variables among respondent’s job
Variables Job Mean
Standard
deviation F Sig. Accept
Perceived value 1.Professionals 3.9275 .93900
1.486 0.165 No 2.Laborers/Farmers 3.7778 .93073 3.Students 3.4028 1.08012 4.Entrepreneurs 3.8889 .89427 5.Administrative/ 6.Managerial 3.9132 .91002
7.Government/State Enterprises 3.9691 .94229 8.Retired/Unemploy ed/Housewife 4.1528 .66775 9.Commercial 4.1481 .75554 10.Others 3.8741 .85539
Service quality 1.Professionals 4.0145 .81945
0.862 0.549 No 3.Students 3.5885 1.02826 4.Entrepreneurs 3.8860 .76991 5.Administrative/ .M anagerial 3.9635 .86004 7.Government/State Enterprises 4.0139 .77087 8.Retired/Unemploy ed/Housewife 4.0938 .65819 9.Commercial 3.9778 .87484 10.Others 4.0333 .85030 Customer satisfaction 1.Professionals 3.9275 .84527 1.211 0.294 No 2.Laborers/Farmers 4.0171 .92613 3.Students 3.5313 .97632 4.Entrepreneurs 3.7661 .69477 5.Administrative/ 6.Managerial 3.9514 .89822 7.Government/State Enterprises 3.9722 .57605 8.Retired/Unemploy ed/Housewife 4.2083 .63619 9.Commercial 3.9185 .90897 10.Others 3.8000 1.04079 Brand reputation 1.Professionals 3.7652 .97169 0.850 0.560 2.Laborers/Farmers 3.8615 .86172 3.Students 3.4938 1.06799 4.Entrepreneurs 3.7895 .63060 5.Administrative/ 6.Managerial 3.8563 .93841
7.Government/State Enterprises 3.9556 .77991 8.Retired/Unemploy ed/Housewife 4.1000 .68896 9.Commercial 3.8267 .93462 10.Others 3.8400 1.02036 Customer loyalty 1.Professionals 3.8478 .99483 1.286 0.253 No 2.Laborers/Farmers 3.9744 .76934 3.Students 3.4688 1.07133 4.Entrepreneurs 3.7544 .58628 5.Administrative/ 6.Managerial 3.9010 .92444 7.Government/State Enterprises 3.9861 .62154 8.Retired/Unemploy ed/Housewife 4.1562 .66797 9.Commercial 3.9667 .85263 10.Others 3.9444 1.00725 *F<3; Sig >0.05
Table 4.9 indicated that there is no significant difference in respondents’ perceived value, service quality, brand reputation, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty. All F value is lower than 3 and sig. > 0.05. this explained that Anova succeed in showing exact results.
4.4.3 The differences of perceived value, service quality, brand reputation, customer loyalty and customer satisfaction among respondents’ monthly income Table 4.10: One way ANOVA of monthly income
Variables Monthly income Mean
Standard deviation F Sig. Accept Perceived value Under VND 3 million 3.8889 .94426 0.442 0.723 No VND 3~7 million 3.9462 .94404 VND 7~15 million 3.7911 .87374 Over VND 15 million 3.7611 1.07713
Service quality Under VND 3 million 3.9524 .99882 0.769 0.513 No VND 3~7 million 4.0269 .84187 VND 7~15 million 3.8089 .79114 Over VND 15 million 3.8917 .87180 Customer satisfaction Under VND 3 million 3.8730 .97181 0.266 0.850 No VND 3~7 million 3.9480 .86902 VND 7~15 million 3.8281 .78191 Over VND 15 million 3.8333 .79449 Brand reputation Under VND 3 million 3.9000 1.05057 0.334 0.801 No VND 3~7 million 3.8710 .89596 VND 7~15 million 3.7440 .82760 Over VND 15 million 3.7900 .88746 Customer loyalty Under VND 3 million 3.9107 .99224 1.252 0.292 No VND 3~7 million 4.0161 .81967 VND 7~15 million 3.7378 .79845 Over VND 15 million 3.8208 .92326 *F<3; Sig >0.05
As we can see the data from table 4.10, there was no significant difference in respondent’s perceived value, service quality, brand reputation, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty. F-value is smaller than 3 and Sig > 0.05, it mean that no variable is different from others.
CHAPTER 5: CONCLUSION AND
RECOMMENDATIONS
In this chapter, a summary and implication of findings are presented. Also some limitations are also listed. After all, the chapter ends with recommendations for further research and concluding statement.
5.1 Research summary
Internet banking services in Vietnam is more and more common even most Vietnamese people prefer to use cash. The tendency of using Internet banking is among young people who love convenient, flexible and time saving characteristics provided. Thus, this study had contributed to exploring determinant factors and consequences of customer satisfaction element in Vietnamese Internet banking sector.
Firstly, the findings of this study are sorted into three main parts which are the analysis of demographic data, reliability test and hypotheses testing. It reveals the fact that more slightly females using Internet banking than the males. In respect of age, most of Internet banking users is young people from 15 to 35 years old. The mode monthly income is from VND 3 million to 15 million. The highest participants of the survey has educated at college level. Furthermore, major jobs of respondents are students, administrators or managerial and stated-owned enterprises’ staff. Secondly, the Cronbach alpha test for reliability stated that all variables exceeded Nunnally and Bernstein’s criteria of 0.7. These analytics indicated that variable cases are highly reliable.
Secondly, hypothesis testing includes a test of four hypotheses using Regression analysis. The four independent variables have a highly positive relationship with the dependent one. Research findings showed that there is positive relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction, perceived value and customer satisfaction, brand reputation and customer satisfaction, as well as customer loyalty and customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, perceived value and service quality are elements which determining how satisfied customers are. Internet banking services provides a number of advantageous characteristics like convenience and flexibility, easy to use, and time saving. Customers can log into Internet and use baking services as normal. They can immediately check account balance; making transactions anywhere and anytime even at weekend. Customers do not need to directly go banks. Also it is so easy to use with a laptop connected to Internet or a digital device like smart phone, PDA and so on. Most of participants were educated at college level, thus they can quickly adapt to high technology. Both service quality and perceived value determines the level of customer satisfaction. Higher service quality provided that met or exceed customer expectations would lead to a relatively high satisfaction.
According to Pearson test, the brand reputation is the most important variable of customer satisfaction. The more customers are satisfied or Internet banking services meet or exceed the customers’ expectation, the more brand reputation is well known. Word of mouth experiences are the fastest and the most effective way to advertise about a product’s or service’s brand. People tend to believe one’s experience rather than an advertisement. Therefore, customer satisfaction is critically affecting a brand’ awareness. The second rank related to customer satisfaction is customer loyalty. As stated, the more customers are satisfied, the more customers are loyal to banking services. It was a positively linear relation.
5.2 Theoretical and Practical implication
This study has critical implication for managers of various banks participated in the survey; especially in Internet Banking service areas. Firstly, service quality and perceived value is a predictor of customer satisfaction using Internet banking in Viet Nam. Under customer’s perspective, they want services provided with outstanding quality and the