Department of Business Administration
I-Shou University
Master Thesis
A Study on Satisfaction of Corporate Customers with
Products and Services of Banks
Advisor: Dr.Liou Jin Pin
Co-advisor: Dr.Ho Sy Tan
Graduate Student: Tran Dinh Nam
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
First of all, I would like to thank all the professors of I-Shou University, Hong Bang University and University of Electricity for their teaching and support for the last two years of my MBA course. In particular, I would like to thank Dr. Liu Jin Pin and Dr.Ho Sy Tan for being my thesis advisors. Their knowledge and advices are essential for me to finish my thesis. I also want to thank my classmates for the wonderful experience in class and in life they have shared with me. I believe that the time with them in this master class is just a beginning of a sustaining relationship in the future.
Last but not least, I would like to thank my family members who have supported and motivated me to pursuit and finish this course. Thank you very much!
ABSTRACT
In this fierce competitive environment, customer is the core factor deciding the existence of banks. Banks which have ability to get attention and build loyalty of customers will win the battle and continue to develop. Business strategies towards customers are becoming the main strategy with a high importance. Cooperating with customers in business, attracting new customers and maintaining current customers become the useful business tools with low fees but they cancreate high business efficiency. Making customers feel very satisfied is always the matter that all banks try to handle with all their capacities. . Result show that what customers want most is that the Bank performs services accurately, quickly with competitive prices. Besides, factors affecting customer satisfaction include service style, convenience, credibility, tangibles, prices and corporate image.
Keywords: bank, customer satisfaction, service quality, image, price
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... i
ABSTRACT ... ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... iii
LIST OF FIGURES ... vi
LIST OF TABLES ... vii
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ... 1
1.1 REASONS TO CHOOSE THIS RESEARCH TOPIC ... 1
1.2 RESEARCH OBJECTIVES ... 2
1.3 SUBJECT AND SCOPE OF RESEARCH ... 2
1.4 PRACTICAL MEANING OF THE RESEARCH TOPIC ... 2
1.5 CONTENTS OF THE RESEARCH TOPIC ... 3
CHAPTER 2 THEORETICAL FOUNDATION AND RESEARCH MODEL ... 4
2.1 SERVICE ... 4
2.1.1 Concept of service ... 4
2.1.2 Characteristics of service ... 4
2.2 SERVICE QUALITY ... 5
2.2.1 Concept of service quality ... 5
2.2.2 The relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction ... 5
2.2.3 Service quality models in retail banking ... 6
Measurement scales of functional service quality ... 9
2.3 THE UNDERSTANDING OF PRICE ... 10
2.3.1 Effects of price on customer satisfaction ... 10
2.3.2 The relationship between price, value and perceived price ... 11
2.4 UNDERSTANDING CUSTOMER SATISFACTION ... 12
2.4.1 Concept ... 12
2.4.2 Decisive factors of customer satisfaction ... 12
2.5 RESEARCH MODEL OF DECISIVE FACTORS TOWARDS CUSTOMER SATISFACTION ... 14
2.5.1 Research model ... 14
2.5.2 Hypotheses ... 16 iii
2.5.3 Research models of customer satisfaction ... 16
2.6 INTRODUCTION OF HSBC BANK ... 18
2.6.1 Operation of HSBC Bank ... 18
2.6.2 The development strategy “All for customer satisfaction” of HSBC Bank ... 20
CHAPTER 3: RESEARCH METHODS ... 21
3.1 RESEARCH PROCESS ... 21 3.2 DATA COLLECTION ... 22 3.2.1 Primary data ... 22 3.2.2 Secondary data ... 22 3.3 RESEARCH DESIGN ... 22 3.3.1 Qualitative research ... 22 3.3.2 Quantitative research ... 23 3.3.3 Design of questionnaire ... 25
CHAPTER 4: RESEARCH RESULTS ... 27
4.1 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTIC ANALYSIS ... 27
4.1.1 Identifying customer’s needs ... 27
4.1.2 Factors affecting customer satisfaction... 27
4.1.3 Customer satisfaction measurement ... 29
4.2 SCALE ANALYSIS ... 29
4.2.1 Cronbach’s alpha ... 30
4.2.2 Exploratory factor analysis ... 32
4.3 GENERAL RESEARCH MODEL ... 34
4.3.1 Research model ... 34
4.3.2 Hypotheses: ... 35
4.4 TESTING RESEARCH MODEL ... 35
4.4.1 Analyzing the Pearson correlation coefficient ... 35
4.4.2 Regression analysis ... 38
4.4.3 ANOVA analysis ... 42
4.5 RESEARCH RESULTS ... 43
4.5.1 Identifying customer needs ... 43
4.5.2 Factors affecting satisfaction of customers ... 43
4.5.3 Customer satisfaction measurement ... 48 iv
4.5.4 Relationship between length of use as well as number of banks for transactions
and customer satisfaction ... 48
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS ... 49
5.1 CONCLUSION ... 49
5.2 SOME RECOMMENDATIONS FOR IMPROVING CUSTOMER SATISFACTION ... 50
5.2.1 Oriented development strategy ... 50
5.2.2 Improving the service quality ... 50
5.2.3 Completing the professional service style of staffs ... 51
5.2.4 Ensuring competitive pricing ... 51
5.2.5 Creating professional working environment ... 51
5.2.6 Developing and cooperating with other financial institutions ... 52
5.2.7 Reinforcing good image of the Bank ... 52
5.3 LIMITATIONS AND FURTHER RESEARCHES ... 52
REFERENCES ... 53
APPENDIX ... 55
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1: The relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction(Spreng and
Mackoy, 1996) ... 5
Figure 2.2: Service quality model of Gronroos ... 8
Figure 2.3: Research model of factors affecting customer satisfaction ... 16
Figure 3.1 Research process ... 21
Figure 4.1 The general research model ... 35
Figure 4.4: Model of factors affecting customer satisfaction ... 44
LIST OF TABLES
Table 3.1: Summary of encoding scales ... 25
Table 4.1 Descriptive statistics on customer’s expectation ... 27
Table 4.2: Descriptive statistics on service quality scales ... 28
Table 4.3: Descriptive statistics on price scale ... 28
Table 4.4: Descriptive Statistics on corporate image scales ... 29
Table 4.5 Descriptive statistics on customer satisfaction ... 29
Table 4.6: Result of analyzingCronbach’s Alpha ... 32
Table 4.7 The result of explanatory factor analysis ... 34
Table 4.8 Results of Pearson correlation coefficient analysis of factors affecting customer satisfaction ... 37
Table 4.9 Result of Pearson correlation coefficient analysis of customer satisfaction level . 38 Table 4.10: Regression analysis result ... 42
Table 4.11: Synthesis of scales of customer satisfaction ... 47
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 REASONS TO CHOOSE THIS RESEARCH TOPICAt present, trend of globalization, international and regional economic integrations are happening strongly. Together with technology development and open market, in banking sector, there are fierce competitions between state banks, joint-stock commercial banks and foreign banks which provide services in the Vietnamese financial and banking market.
In this fierce competitive environment, customer is the core factor deciding the existence of banks. Banks which have ability to get attention and build loyalty of customers will win the battle and continue to develop. Business strategies towards customers are becoming the main strategy with a high importance. Cooperating with customers in business, attracting new customers and maintaining current customers become the useful business tools with low fees but they cancreate high business efficiency. Making customers feel very satisfied is always the matter that all banks try to handle with all their capacities.
Moreover, customer satisfaction will help to build customer loyalty which is necessary to ensure the regular operations of banks. However, in the competition, building customer loyalty does not assure that customers will go with banks in the long time. Customer relations are like “a live creature”, thus,banks need to take care of “this live
creature” regularly. It means that bankshave the responsibilities to develop and maintain
customer relations and make them feel pleased. Banks should be active in maintaining and developing this relationship.
Therefore, the research of customer satisfaction towards banks is an important work which needs to be conducted regularly and continuously to meet demands of changes in customer needs timely, thereby, serving customers in a better way and making them always feel satisfied when using products and services of banks. The research topic“Research on satisfaction of corporate customerswith products and services of Banks”is carried out at HSBC Bank. For this purpose, I do hope to receive contributions to make this research matter become more completely.
1.2 RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
Based on business situation and development strategy of HSBC Bank, the research topic is carried out with below objectives:
To identify customer needstowards the bank
To build research model to measure customer satisfaction on the ground of discovery of factors affecting customer satisfaction
To evaluate customer satisfaction with products, services of the bank.
To recommend some measures to increase the level of customer satisfaction with products, services of the bank
1.3 SUBJECT AND SCOPE OF RESEARCH
Subject of the research is corporate customers. Therefore, individual customers and financial organizations are not the subjects of this research.
Scope of researchis enterprises which use products and services of HSBC Bank, Ho Chi Minh City Branch.
1.4 PRACTICAL MEANING OF THE RESEARCH TOPIC
The research topic identifies factors affecting the level of customer satisfaction in a more complete and accurate way. From there, the Bank will have appropriate improvements to enhance performance of the bank and help customers feel pleased when they come to the bank.
Research results are the foundation for implementing new products and services to meet demands of customers.
With the analysis of related factors of the level of customer satisfaction, the Bank will understand more clearly about customer needs as well as service quality which the bank are offering. This is the objective evaluation with high generality to measure the performance of the bank through the eyes of customers.
Based on the research related to customer satisfaction with services of HSBC Bank, Ho Chi Minh City Branch in last time, the author will recommend some measures to improve the customer satisfaction.
The research also contributes to serving the development strategy “All for customer
satisfaction” proposed by Board Directors of HSBC Bank.
1.5 CONTENTS OF THE RESEARCH TOPIC
The research topic is divided into four chapters with specificcontents as follows: Chapter 1 – Introduction
Chapter 2 – Theoretical foundation and research model Chapter 3 – Research model and Research methods Chapter 4 – Research results
Chapter 5 – Conclusion & Recommendations
CHAPTER 2 THEORETICAL FOUNDATION AND RESEARCH
MODEL
2.1 SERVICE
2.1.1 Concept of service
Service is a common conceptin marketing and business. There are several concepts of service; however,according to Valarie A Zeithaml and Mary J Bitner (2000), “services are
behaviors, processes and ways to implement one work with the aims to create use value for customers that satisfy their needs and expectations”.
2.1.2 Characteristics of service
Service is a “special product” which has many characteristics compared to other products such as intangibility, heterogeneity, inseparability and perishability. These factors make service become difficult to quantify and it cannot be identified with the naked eye.
2.1.2.1 Intangibility
Service does not have detailed shapes; they cannot be touched, measured in the specific way like visible material products. When buying material products, customers can ask for inspection and check quality before deciding to buy them but service products cannot be evaluated that way. Due to its intangibility, service does not have “sample” or “trial” like material products. Only through the use of services, customers can feel and evaluate the quality in the most properly way.
2.1.2.2 Heterogeneity
It is also called the distinctness of service. Based on that, service implementation is normally different depending on ways of serving, suppliers, service persons, implementation duration, service fields, targets and service locations. Moreover, for the same kind of service, there are several implementation levels from “luxury”, “universal” to “secondary”. Therefore, evaluating whether service quality is perfect or bad is hard to define if we only reply on a standard measurement scale. It is required to examine related factors in a certain situation.
2.1.2.3 Inseparability
Inseparability of service is presented by the difficulty to divide service into two clear periods as production and consumption. The creation and use of services normally happen at the same time. If goods are regularly produced, stored, distributed and then brought to customers then servicesare also created and used during the process of creation. For commodity product, customers only use them at the last period (end-users), but for service, customers will go through all the process or part of the service creation. In other words, the
bond between these two processes makes servicesbecomes complete.
2.1.2.4 Perishability
Service cannot be saved, stored and sold like other products. We can give priority to service implementation but cannot store them and use later because services done are also the end, we cannot store them for “reuse” or “recovery”. Thus, services are products which are used when being created and then are ended right after that.
2.2 SERVICE QUALITY
2.2.1 Concept of service quality
Service quality has several different definitions depending on research subject and environment of research. Understanding service quality is the foundation to deploy measures with the aims to enhance service quality of enterprises. Therefore, defining service quality not only plays an important role in building development targets but also gives enterprises ways to exploit their strengths fully.
2.2.2 The relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction
Service quality is the factor that has the most influence on customer satisfaction (Cronin and Taylor, 1992; Yavas et al, 1997; Ahmad and Kamal, 2002). If a supplier brings customers the best products which satisfy their demands, then that enterprise firstly makes customers satisfied.
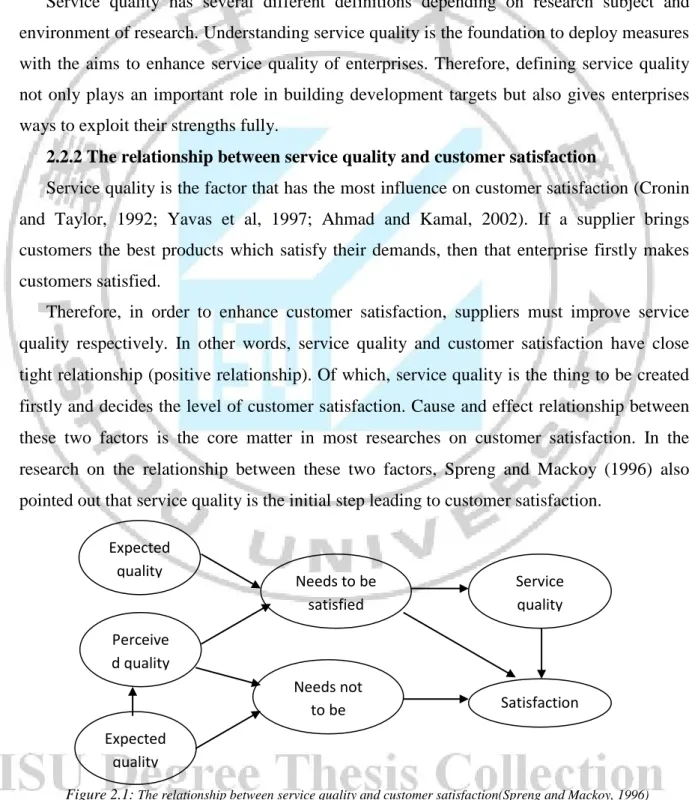
Therefore, in order to enhance customer satisfaction, suppliers must improve service quality respectively. In other words, service quality and customer satisfaction have close tight relationship (positive relationship). Of which, service quality is the thing to be created firstly and decides the level of customer satisfaction. Cause and effect relationship between these two factors is the core matter in most researches on customer satisfaction. In the research on the relationship between these two factors, Spreng and Mackoy (1996) also pointed out that service quality is the initial step leading to customer satisfaction.
Figure 2.1: The relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction(Spreng and Mackoy, 1996) Needs to be satisfied Needs not to be Service quality Satisfaction Expected quality Perceive d quality Expected quality 5
2.2.3 Service quality models in retail banking 2.2.3.1 SERVQUAL model (Parasuraman, 1988)
This is the most common and most applied research model in marketing research. By Parasuraman, service quality cannot be identified generally but it must depend on customer feelings towards this service. This feeling is considered on the ground of several factors. SERVQUAL model is built based on the conception that the feeling of service quality is the comparison between expectationsand perception.
SERVQUAL examines two main aspects of service quality including service outcome and service process which are researched through 22 scales of five following criteria:reliability, responsiveness, tangibles, assurance and empathy.
Reliability
Reliability reflects the ability to provide service exactly, timely and prestigiously. It requires the consistency when providing services, respecting commitments as well as keeping promises with customers. In banking sector, this criterion is measured by the following scales:
The Bank conducts right service at the first time.
The Bank provides servicesat the time that they made promise. The Bankconducts services exactly without mistakes.
Employees of the Bank are willing to serve customers.
The Bank always has consultant staffs at the front desk to help customers. The Bank sendsbank statements regularly and promptly.
Responsiveness
This is the criterion to measure the ability to solve problemquickly, handle complaints effectively, help customers and meet their demands willingly. In other words, service efficiency is the responses from suppliers towards what customers want, namely:
Employees of the Bank are eager to help customers. The Bank provides services quickly and timely.
The Bank positively responds to the requirements of customers. The Bank has hotline to serve customers 24/24.
The Bank always makes efforts to solve customers’ difficulties.
Tangibility
Tangibility is the outward appearanceof facilities, devices, machines, attitude of employees, materials, manuals and communication system of the Bank. Generally, all that customers can see and feel directly by their naked eyes can influence this factor:
The Bankhas adequate facilities.
The Bank has modern equipment and machines.
Employees of the Bank look professional and well-dressed.
The Bank arranges transaction counters, timetables and material shelves in the scientific and convenient way.
Assurance
This is the factor formulating customer belief which is felt through professional service manner, advanced qualifications, courteous attitude and good communicating skills; thanks to them, customers feel secured when using bank services.
Employees of the Bank serve customers courteously. Transaction documents are clear and easy to understand.
Employees of the Bank always provide necessary information to customers. Employees of the Bank exactly and clearlyrespond to customer questions.
Empathy
Empathy is the thoughtful attention and care given to customers, which give them best attention, helpingthem feel as “esteemed customers” of the Bankand be treated well everytime and everywhere. Human factor is the core part which creates this success.The more the Bankcare about its customers, the more the sympathy increases:
Employees of the Bank pay attention to needs of each customer. Customers do not need to wait in line to be served.
The Bank Banks has convenient transaction locations for customers. The Bank has modern ATM system which is easy to use.
Employees of the Bank always treat customers courteously. 2.2.3.2 SERVPERF model (Cronin and Taylor, 1992)
SERVPERF model is developed on the ground of SERVQUAL model but it measures service quality upon the evaluation of performance-based service quality, not the gap between expected quality (expectation) and perceived quality (perception).
2.2.3.3 FSQ model and TSQ model(GrÖnroos,1984)
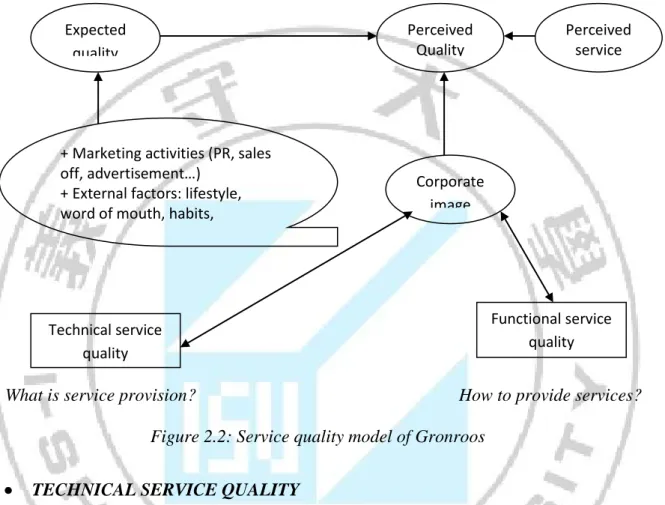
According to GrÖnroos, service quality is considered on the ground of two criteria
including functional service quality (FSQ) and technical service quality (TSQ). In addition, service quality is greatly affected by corporate image. Therefore, GrÖnroos proposed three
factors affecting service quality: functional service quality, technical service quality and corporate image (called as FTSQ sample in abbreviation)
What is service provision? How to provide services? Figure 2.2: Service quality model of Gronroos
• TECHNICAL SERVICE QUALITY
This is the quality that customers received through the interaction with enterprises and it is felt important towards customers. In other words, technical service quality is the results of interaction process between enterprises and customers; of which, enterprises provide service (What?) and customers receive such service. There are five criteria to evaluate this factor:
Problem solving skills Qualifications skills Operational level Modern equipment
Information storage system
Measurement scales of technical service quality
Employees of the Bank have ability to make decisions promptly.
Employees of the Bank have ability to handle customer complaints reasonably. Expected
quality
+ Marketing activities (PR, sales off, advertisement…)
+ External factors: lifestyle, word of mouth, habits,
Technical service quality Perceived Quality Corporate image Perceived service Functional service quality 8
Employees of the Bank have good qualifications.
Employees of the Bank conduct services exactly and promptly. Employees of the Bank have full-time training regularly.
Employees of the Bank respond to customer questions effectively.
The Bankprotects confidential information about customers and transactions.
The Bank always informs to customers about the process as well as transaction results. The Bank gives full attention to customer needs.
The Bankhas modern equipment such as backup system to make sure the quick and accurate bank operations.
The Bankhas modern ATM system which is convenient for customers.
The Bank hasclear transaction documents and related documents without mistakes. The Bank hasbroad and easy-to-use communication system.
The Bank provides information about account balance and transaction account promptly. • FUNCTIONAL SERVICE QUALITY
Functional service quality depictsthe process to conduct service of enterprises, reflecting the way service is provided (How?). In the correlation between two above aspects of quality, functional quality plays more important role that is represented through the following seven criteria:
The convenience in transaction Behaviors
Service attitude Corporate organization Customer interaction Service manner
The spirit of all-for-customers
Measurement scales of functional service quality
The Bank has convenient transaction locations for customers. The Bank has broad dealer network.
The Bank hasreasonable and convenient operating time. Information access system is easy to use.
Employees of the Bank win the credibility and trust of customers. Employees of the Bank are willing to serve customers.
Employees of the Bank courteouslyhelp customers.
Employees of the Bank are tactful and consideratetowards customers. Employees of the Bank are willing to listen tocomments of customers.
Leaders have a strong attachment to employees of the Bank.
The Bank always cares about employee benefits and has reasonable compensations. Employees of the Bank always contact customers regularly.
The Bank always organizes thank-you party to customers at the end of each year to recognize their contributions.
Employees of the Bank answer telephone promptly. The Bank has nice interior design.
The Bank hasfascinating documents, books and images of services.
Transaction documents are designed scientifically and they are easy to understand. Employees of the Bank dress politely and impressively.
The Bank placescustomers’ benefits at the top.
The Bank has flexible policies because of customer requirements. The Bank always correctly performs its commitments to customers. • CORPORATE IMAGE
Corporate image is seen as feeling/general impression of customers towards enterprises; by this way, if they create good image for their enterprisesthen it is easy for customer to skip mistakes happened when using services. GrÖnroos stated that corporate image is the
invaluable property of enterprisesthat has positive effect on customerevaluation of service quality, value of product and their satisfaction.
Moreover, corporate image will also help customers trust more in enterprises and become loyal customers (Andreassen & Lindestand, 1998). Therefore, corporate image influences and is influenced by service quality and customer satisfaction as well. It is also noted that customers who use services frequently will have more accurate feeling about corporate image compared to other customers (Johnson, Fornell, Andreassen, Lervik, and Cha, 2001).
Corporate image is also seen as a “filter” which helps the relationship between customers and enterprises become better and more stable. Besides, customers evaluate whether corporate image is good or not through their feelings towardsenterprises and compare this corporate image with that of other competitors. However, level of influence is subject to each specific enterprise.
2.3 THE UNDERSTANDING OF PRICE 2.3.1 Effects of price on customer satisfaction
Price is the expression in the form of money currency of goods and services values which are defined on the ground of use valueand feelings of customers about products and services they are using. Customers are not required to buy products and services which have
highest quality; on the other hand, they will buy products and services which bring them the highest satisfaction. Therefore, factors such as customer feelings about price and fees (usage cost) will not affect service quality but customer satisfaction(Cronin andTaylor, 1992).
In the previous researches on customer satisfaction, the effects of price factor received little attention compared to other criteria (Voss et at., 1998). Nevertheless, together with stronger competitions in the market and changes of customer conceptions about products and services, researches have determined that price and customer satisfaction have tight relationship (Patterson et al., 1997). As a result, if ignoring this factor, the researches on customer satisfaction will lack of accuracy.
2.3.2 The relationship between price, value and perceived price
When buying products and services, customers must pay an amount of fees to have usagevaluethey need. Therefore, it is called fee of exchangewhich aim at receiving desirable value from products and services. If we put quantification of price into the correlation values obtained, customers will have feelings about price competition to see whether it is worthy or not. Only when customers feel that perceived service quality is much more than perceived price, price is competitive and customers will be satisfied. On the other hand, customers are not satisfied because they feel that they have to pay more than what they receive. Price factor in this situation will negatively affectcustomer satisfaction.
This is the relationship between price, value and perceived price. However, perceived price is the decisive factor towards customer satisfaction. In case the price they have to pay is higher than perceived value, customers still feel that it is reasonable, so they are satisfied and vice versa. In the research on the relationship between perceived value and customer satisfaction, Varki and Colgate (2001) proved that these two factors affect each other, depending on the sensitivity of customers towards price as well as the relationship between service users and suppliers. Besides, in order to evaluate the influence of price factor on customer satisfaction, we have to consider three following aspects fully: (Maythew and Winer, 1982).
Price compared to quality Price compared to competitors
Price compared to customer expectation
Therefore, when considering influence of price on customer satisfaction, we should have full awareness. Price here includes production cost and opportunity cost to get products and services as well as the correlation of price towardsmentioned above aspects. In the scope of this thesis, price factor we look for is the competitivenessof perceived value. The higher perceived value customers feel, the more they will be satisfied and vice versa.
2.4 UNDERSTANDING CUSTOMER SATISFACTION 2.4.1 Concept
There are several researches related to customer satisfaction with more than 15,000 essays and projects of many authors (Peterson and Wilson, 1992).In reality, there are many understandings of this concept.
In the simple way, customer satisfaction is the feelings/emotion of customers towards service suppliers after experiencing it (Terrence Levesque and Gordon H.G McDougall, 1996).
More particularly, customer satisfaction is the response of emotion/all feelings of customer towards service suppliers on the ground of comparisonbetween what they receive and what they expect before (Oliver, 1999 and Zineldin, 2000). Moreover, Kotler (2000) assumed that customer satisfaction is defined on the ground of comparison between perceived value from service and customer expectation which are considered as three following levels:
If perceived value is less than expectation, customers will not feel satisfied. If perceived value and expectation are the same, customers will feel satisfied.
If perceived value is more than expectation, customers will be very satisfied and interested in this service.
During that time, Oliva, Oliver, and Bearden (1995) stated that customer satisfaction is a mission of enterprises which is expressed through the relationship between services and values of products compared to previous expectations of customers. Clearly, even there are many different concepts, the common thing about customer satisfaction is always attached to the below factors:
Emotions/attitudes of customerstowards service suppliers
Customer expectations about the ability to meet demands of service suppliers Results came from service implementation/Values come with services
The intention to continue using services
2.4.2 Decisive factors of customer satisfaction
In the principle of finding out service characteristics and surveys about service quality modelas well as measurement scales of service quality in banking sector (see section 1.2, 1.3, 1.4); the author brings out decisive factors towards customer satisfaction including service quality, price competition and corporate image with detailed scales as follows:
2.4.2.1 Convenience
The Bank has convenient transaction locations for customers. The Bank has broad dealer network.
The Bank has reasonable and convenient operating time. Information access system is easy to use.
Transaction procedures are easy and quick.
The Bank has modern ATM system which is convenient for customers.
The Bank provides information about account balance and transaction account promptly.
2.4.2.2Tangibles
The Bank has modern equipment and machines. The Bank has nice interior design.
The Bank has fascinating documents, books and images of services.
The Bank has clear transaction documents and related documents without mistakes. Employees of the Bank dress politely and impressively.
The Bank has adequate facilities.
2.4.2.3 Staff conduct
Employees of the Bank have ability to handle customer complaints reasonably. Employees of the Bank have good qualifications.
Employees of the Bank conduct services exactly and promptly. Employees of the Bank respond to customer questions effectively. Employees of the Bank are willing to serve customers.
Employees of the Bank courteously help customers.
Employees of the Bank are tactful and considerate towards customers.
2.4.2.4 Service portfolios
The Bank has diversified service portfolios.
The Bank is the pioneer in providing new services to meet higher customer demands. The Bank has activities to introduce services effectively.
The Bank always has good preparation before service deployment.
2.4.2.5 Customer interaction
Employees of the Bank contact customers regularly.
The Bank always organizes thank-you party to customers at the end of each year to recognize their contributions.
Employees of the Bank answer telephone promptly. The Bank has hotline to serve customers 24/24.
Employees of the Bank are willing to listen to comments of customers.
2.4.2.6 Price competitiveness
The Bank has flexible price policy.
The Bank applies competitive interest rate.
The Bank has reasonable transaction fees.
The Bank has consulting/updated programs about market information.
2.4.2.7 Credibility
The Bank conducts right service at the first time.
The Bank provides services at the time that they made promise. The Bank conducts services exactly without mistakes.
The Bank always correctly performs its commitments to customers.
The Bank protects confidential information about customers and transactions. The Bank sends bank statements regularly and promptly.
2.4.2.8 Corporate image
The Bank places customers’ benefits at the top. The Bank always keeps promises to customers.
The Bank is always the pioneers in renovation and social activities.
The Bank has effective and impressive marketing activities.
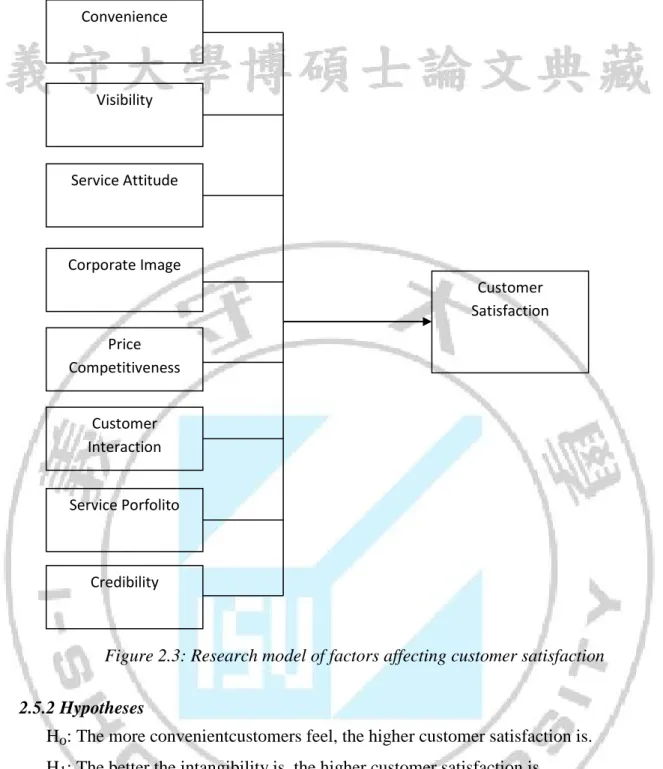
2.5 RESEARCH MODEL OF DECISIVE FACTORS TOWARDS CUSTOMER SATISFACTION
2.5.1 Research model
Although SERVQUAL model is the common and widely used in research marketing which is helpful to generalize criteria for measuring service quality, it still has had many weaknesses (Babakus & Boller, 1992; Brown et al, 1993; Buttle, 1996; Genestre & Herbig, 1996; Gilmore & Carson, 1992; Robinson, 1999; Hemmasi et al, 1994).If we entirely apply the measurement ofbanking service quality, then it is not appropriate by the following aspects:
- It is hard to implement in reality due to the generality of criteria for measurement. - Measurement process provides more things than results of service implementation. - It does not examine external factors as well as marketing activities but only focuses on “internal” factors.
- The comparison of gap between expected quality and perceived quality is hard to define because we have to judge several different scales and cannot define them directly on the ground of reality of service implementation.
Therefore, SERVQUAL criteria for measuring quality cannot be applied in the series of all fields. It needs to be adjusted properly to each research situation to assure high accuracy. SERVPERF model has inheritance feature and focuses on implemented service quality and also includes five criteria as mentioned above (reliability, service efficiency, tangibles, assurance and empathy). Thus, it is not selected as research model.
For researches on customer satisfaction in banking section, the models of technical service quality and functional service quality of GrÖnroos become more suitable (Lassar et al, 1998) because of the following reasons:
Firstly, FTSQ model concentrates on two main aspects of service quality including functional quality (how enterprises conduct services) and technical quality (what services enterprises provide). Banking is the sector which requires regular communications and contacts between customers and employees of the bank (high-contact service). Thus,the process in which services are implemented is very important towards customers in their evaluations of service quality. Whereas, SERVQUAL model does not analyze what services provided by banks and the way they provide them.
Secondly, when banks provide the same services without mistakes then customers pay more attention to the process of services implementation and from there, they will evaluate service quality of banks. For deployment of high-end services for customers, functional quality becomes more important because it proves the level of service providers and marks the difference between the enterprise and other competitors.
Thirdly, some criteria of SERQUAL model are considered in FTSQ model through research scales, helping to analyze service quality more feasibly and reasonably.
Starting from above strengths and weaknesses, SERVQUAL and FTSQ models are the reference foundation for the author to bring out research modelof this thesis. At first, when creating a model, the author still focuses on decisive factors affecting customer satisfaction such as service quality (6 factors: Intangibility, Style of service, Corporate image, Reliability, Service portfolio, Customer interaction), then Price factor, and at last Corporate image with criteria and scales which are general and are adjusted in a detailed way. Research model is built as follows:
Figure 2.3: Research model of factors affecting customer satisfaction
2.5.2 Hypotheses
Ho: The more convenientcustomers feel, the higher customer satisfaction is.
H1: The better the intangibility is, the higher customer satisfaction is.
H2: The better the service attitude is, the more satisfied customers are.
H3: The more service portfolio offered for customers, the more satisfied customers are.
H4: The more interaction to customers, the more satisfied customers are.
H5: The higher price competitiveness is, the more satisfied customers are. H6: The higher reliability is, the more satisfied customers are.
H7: The better corporate image is, the more satisfied customers are.
2.5.3 Research models of customer satisfaction 2.5.3.1 Qualitative model
According to Bernd Stauss and Patricia Neuhaus (1997), we can divide levels of customer Convenience Visibility Service Attitude Corporate Image Price Competitiveness Customer Interaction Customer Satisfaction Service Porfolito Credibility 16
satisfaction into three categories and they have different effects on service providers:
Demanding customer satisfaction: is the active satisfaction with responses through
higher needs towards service providers. For customers who have positive satisfaction, they and service providers will have good relationship, trust each other and feel satisfied when making transactions. Moreover, they do hope that providers will have ability to meet their higher demands. Therefore, this is the customer group which is easy to become loyalty customer of enterprises only when they realize that enterprises have more improvements in providing them with services. The satisfaction factor is also expressed when customer demands are getting higher and service providers make efforts in enhancing service quality to be more completely.
Stable customer satisfaction: For customers who have stable satisfaction, they will feel
comfortable and satisfied with what are happening and do not want the changes in the way of providing services of enterprises. Therefore, these customers becomecomfortable and have high reliability towardsenterprises and they are willing to continue using enterprises’ services.
Resigned customer satisfaction: Customers who have resigned customer satisfaction are
less trusted in enterprises and they assume that enterprises hardly improve service quality and changes as their desires. They are satisfied not because enterprises meet their demands completely. However, they consider that they cannot require enterprises to improve better. Therefore, they will not contribute their ideas positively or they become nonchalant with improvement efforts of enterprises.
It is noted that aside from classifying customer satisfaction, Bernd and Patricia Neuhaus affirmed that satisfaction level will greatly affect customer behaviors. Even when customers have positive satisfaction towardsenterprises, the satisfaction level is just as “satisfied”.They can come to the others and do not continue to use services of the enterprises. Only customers who have highest satisfaction level as “very satisfied”, certainly they are loyal customers and always support the enterprises.
Therefore, when we do researches on satisfaction of corporate customers, it is needful to pay attention to the thing that makes customers satisfied. In addition, making them very satisfied is much more important. For customers who have general satisfaction, they can leave enterprises anytime whereas customers who are very satisfied become loyal customers of enterprises. This understanding will help enterprises have flexible methods of service quality improvement for each different customer group.
2.5.3.2 Model to measure customer satisfaction
To measure customer satisfaction, several authors such as Hausknecht, 1990; Heskett et al,
1994; Jones and Sasser, 1995; Terrence Levesque and Gordon H.G McDougall, 1996 presented many different criteria. However, in order to arrive at correct conclusion about customer satisfaction towards HSBC Bank, the author used five criteria (summarized from researches of the above authors) as follows:
General service quality
Ability to meet customer demands
The level of customer satisfaction
Introduction of the Bank to the third party
Continuationto use bank services
2.6 INTRODUCTION OF HSBC BANK
The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC) is the founder of HSBC Group in 1959. HSBC Group is one of the largest banking and financial service institutions all over the world. The symbol of HSBC is “Honesty, Reliability and Perfect Services”.
HSBC opened its representative office in Saigon in 1870 and had operated over 100 years in Vietnam until 1975. HSBC opened an agency of the bank in Hai Phong in 1884. This agency was upgraded to a sub-office at the beginning of the 1920s and had continued to operate until 1954. HSBC Bank also opened an additional agency in Hanoi in 1907.
HSBC Bank consolidated and strengthened the relationship with Vietnam through the opening of representative offices in Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi in 1992. The Ho Chi Minh City representative office became a full service branch in 1995. On February 28, 2005, HSBC opened its second branch in Hanoi. The bank also established the Can Tho representative office in May of 2005.
HSBC Vietnam is always a pioneer of providing unique, diversified and creative products for customers who use personal financial services. Especially, HSBC Vietnam was the first bank and the first foreign bank in Vietnam to offer unsecured loan. In addition, it is also the first one to introduce ATM service, to open personal account and to invest in foreign countries. Moreover, it is the first bank and the first foreign bank which sells life insurance through the system of branch offices (AIA – 2001)
With considerable achievements and activities in recent years, HSBC is the largest foreign bank in Vietnam in terms of capital, transaction network, kinds of products, number of employees and customers, stable development rate, business capacity, risk management, application of modern technology, efficiency of distribution system, market penetration ability and specialized qualifications…
2.6.1 Operation of HSBC Bank
The operations of HSBC Bank in Vietnam are very abundant and diversified including main sectors as follows:
1. Financial services for personal customers, corporations, financial institutions. 2. Commercial and consumer sponsorship, securities services and deposits.
3. Foreign exchange and capital market services, currency management, international
payment.
Personal banking services
Vietnamese and foreign accounts (current and savings account) Overdraft, consumer loan, personal loan, car loan, house loan International ATM cards, credit cards (visa and master)
Withdrawal of cash from credit card, travel check, transfer foreign exchanges… Corporate banking services include domestic and international customers
• Scope of supply: supply all services • Quality of supply: top quality in Vietnam
Commercial sponsorship and working capital: guarantees (bid security, contract implementation, prepayment, factoring service, overdraft, inventory sponsorship…) International payment: open a letter of credit, notification and confirmation, discount export documents, import and export documents collection, shipping guarantee and open backup letter of credit…
Credit activities: short-term, middle-term and long-term loans (secured and unsecured loans), syndication loan.
Currency and payment management. In the context of lacking a complete automatic interbank payment system, HSBC set up internet connection network and signed cooperation agreements with major banks in the country to meet demands of using money of customers. Besides, internet banking system of HSBC (HSBCnet) is the global system based on internet of HSBC Group that helps customers to view online account information opened at HSBC, to process internet payment, to update new information about financial market and to integrate with account system of the corporation.
Securities custody and clearing payment
HSBC is the first international bank to be offered licenses of securities custody issued by State Securities Commission of Vietnam in July of 2000 with services including custody, receipt and transfer, handling upon requests/commands of corporations, receipt of income, report on fund and investment, authorized services…
Foreign exchange service and capital market 19
Forex Spot Transactions (SPOT) Forward Transactions (FORWARD) Swap (SWAP)
Currency Derivatives (DERIVATIVE): options transaction, interest rate swaps, currency swaps
Risk management consulting, investment tools on capital market Forex trading
2.6.2 The development strategy “All for customer satisfaction” of HSBC Bank
During the recent years, HSBC is the bank which has impressive achievements and activities in finance sector with series of prestigious awards and more importantly, it has built the loyalty of customers towards the bank. With the principle to meet all demands of customers, Board of Directors of HSBC do believe customer satisfaction is the measurement of success and the most important target in development strategy of the bank.
Standing before the strong increase of banking operations, customer needs are getting more diversified and abundant.Thus, certainly, they will come to banks which satisfy their needs in the best way. Moreover, banks also make efforts to find their own customers and increase business efficiency. Therefore, discovering and enhancing customer satisfaction is necessary and useful for long-term development strategy, thereby proving the top position of
“Best Foreign Bank in Vietnam” that HSBC Bank has created during the recent time.
CHAPTER 3: RESEARCH METHODS
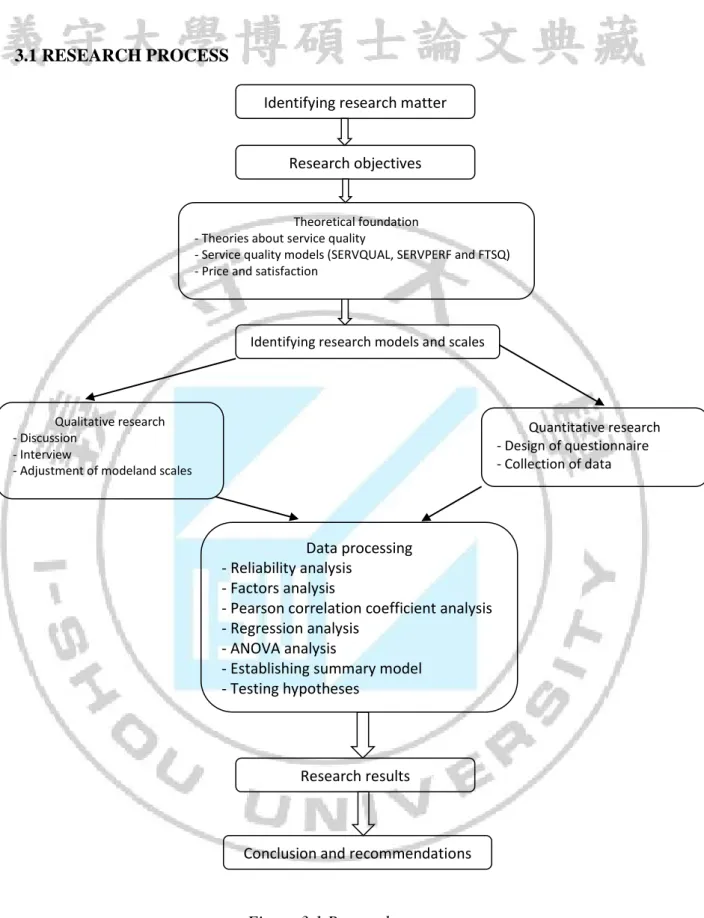
3.1 RESEARCH PROCESS
Figure 3.1 Research process
Identifying research matter Research objectives
Theoretical foundation - Theories about service quality
- Service quality models (SERVQUAL, SERVPERF and FTSQ) - Price and satisfaction
Identifying research models and scales
Qualitative research - Discussion
- Interview
- Adjustment of modeland scales
Quantitative research - Design of questionnaire - Collection of data Data processing - Reliability analysis - Factors analysis
- Pearson correlation coefficient analysis - Regression analysis
- ANOVA analysis
- Establishing summary model - Testing hypotheses
Research results
Conclusion and recommendations
3.2 DATA COLLECTION
During the research, the author used two following data sources: 3.2.1 Primary data
- Survey forms received from customers.
- The results of interviews, discussions with employees/bank managers to acquire their opinions, plans as well as their evaluations of the research matter.
3.2.2 Secondary data
Theoretical foundation and articles chosen on marketing and banking magazines are the important secondary data serving the research. The sources of secondary data collection are:
Library at University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City
Banking magazine
Marketing magazine
Reports on services and service quality
Lectures about research method and data analysis SPSS
Performance reportof HSBC Bank
Internet
3.3 RESEARCH DESIGN 3.3.1 Qualitative research 3.3.1.1 Objectives
This is the preliminary research step to select variables carefully then the author bringsthem into research model, checks used scales, consults ideas from the bank side and customers about the research matters. By that means, we will build scales to apply in research model and establish questionnaire.
3.3.1.2 Process
At first, the author will prepare some questions to discuss and communicate with employees/bank managers about contents focusing on researches on customer satisfaction such as:
How does the Bank evaluatecustomersatisfaction with bank services?
What does the bank consider about the model of service quality in banking sector?
What comments does the bank give about criteria for service quality measurement?
What does the Bank think about customer expectations in the future?
Are measurement scales of customer satisfaction reasonable or not?
Which scales does the Bank uses to measure the level of customer satisfaction?
How does the Bank bringsatisfaction to customers?
Then,the author will conduct discussions with participants including Executive Directors, Leaders of Planning Department, Marketing, Currency Business Department, International Payment and Customer Service Department, employees of Payment Department, employees at counters, employees of Marketing Department and employees of Product Development Department.
Regarding to customers, the author randomly selected 10 customers to attend dual interviews and then record their opinions about banking services and their expectations towards the Bank.
3.3.1.3 Results
After the deployment of qualitative research, eight factors of research model about customer satisfaction are agreed and can be used for further quantitative research; five criteria to measure customer satisfaction decreased to three (removing two criteria of “Introducing the bank to third party” and “The level of customer satisfaction”):
The general service quality
The ability to meet customer demands
Continuationto use bank services
However, scales mentioned in the research model are needed to be adjusted more properly. Therefore, through the step of qualitative research, scales which are used to measure affecting factors towards customers are identified as Table 3.1.
Through the step of qualitative research, scales are identified fully (including 28 scales of 8 affecting factors towards customer satisfaction and 3 scales used to measure the level of customer satisfaction), serving the establishment of questionnaires and further quantitative research.
3.3.2 Quantitative research 3.3.2.1 Objectives
Quantitative research is performed to recheck scales in the research model. This is the detailed analysis step of collected data through survey forms sent to customers with the purpose to identify logicality, correlations between factors, thereby coming to specific conclusion about research topic.
3.3.2.2 Process
a. Building questionnaires
b. Identifying required number of samples for the research c. Sending survey forms to customers
d. Contacting customers to follow responses e. Collecting feedbacks from customers
f. Analyzing data through the use of analysis tool SPSS in the below order: ♦Descriptive analysis
♦ Credibility analysis of measurement scales ♦ Factors analysis
♦ Building general research model
♦Testing model through Pearson analysis, recurrent analysis and ANOVA analysis
3.3.2.3 Results
There are total 550 questionnaires sent to customers through post office (250), e-mail (200), and at counters (100) with the supports of Customer Service Department. Lists of customers received survey form through post office and e-mail are randomly selected on the ground of data system of the Bank.
After two weeks without receiving feedbacks, senders will call and ask customers directly. For survey forms at counters, customers who come to make transaction at the Bank can answer and send back to employees immediately. There are 167 survey forms received (77 forms by post office, 49 forms by e-mail and 41 forms at counters) with response ratio as 30.36%, including 25 forms eliminated due to invalidity. Therefore, the remained number of forms to analyze is 142 forms.
As a result, after collecting the appropriate number of forms, the author will use SPSS tool to analyze data with encoding measurement scales as the following table and detailed results will be represented as below:
No. Encoding Description
1 STT01 The Bank has broad dealer network. 2 STT02 Transaction procedures are easy and quick.
3 STT03 The Bank has convenient transaction locations for customers. 4 SHH01 The Bank has modern equipment and machines.
5 SHH02 The Bank has fascinating documents, books and images of services.
6 SHH03
The Bank has clear transaction documents and related documents without mistakes.
7 SHH04 Employees of the Bank dress politely and impressively. 8 PCPV01 Employees of the Bank have good qualifications.
9 PCPV02 Employees of the Bank conduct services exactly and promptly. 10 PCPV03 Employees of the Bank respond to customer questions effectively. 11 PCPV04 Employees of the Bank are willing to serve customers.
No. Encoding Description
12 PCPV05 Employees of the Bank are tactful and considerate towards customers. 13 DMDV01 The Bank has diversified service portfolios.
14 DMDV02
The Bank is always the pioneers in providing new services to meet higher demands of customers.
15 TXKH01 The Bank has hotline to serve customers 24/24.
16 TXKH02 Employees of the Bank always contact customers regularly.
17 TXKH03
The Bank always organizes thank-you party to customers at the end of each year to recognize their contributions.
18 TXKH04 The Bank always pays attention to customer contributions. 19 STN01 The Bank conducts right service at the first time.
20 STN02
The Bank protects confidential information about customers and transactions.
21 STN03 The Bank sends bank statements regularly and promptly. 22 TCTG01 The Bank applies competitive interest rate.
23 TCTG02 Reasonable transaction fees
24 TCTG03 The Bank has flexible price policy.
25 HADN01 The Bank is always the pioneers in renovation and social activities. 26 HADN02 The Bank always keeps promises to customers.
27 HADN03 The Bank has stable development strategy.
28 HADN04 The Bankhas effective and impressive marketing activities. 29 SHL01 The general service quality
30 SHL02 The ability to meet customer demands 31 SHL03 Continuation to use bank services
Table 3.1: Summary of encoding scales
3.3.3 Design of questionnaire 3.3.3.1 Objectives
To find out customer expectations towards theBank
To measure customer satisfaction
To inspect factors affecting customer satisfaction
To identify correlations between usage time, number of transaction with customer satisfaction of the Bank
3.3.3.2 Contents
After qualitative research, questionnaires are established with 28 measurement scales to identify factors which bring pleasure to customers and 3 scales to identify the level of customer satisfaction towardsthe Bank including 5 main parts with 8 questions.
CHAPTER 4: RESEARCH RESULTS
4.1 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTIC ANALYSIS4.1.1 Identifying customer’s needs
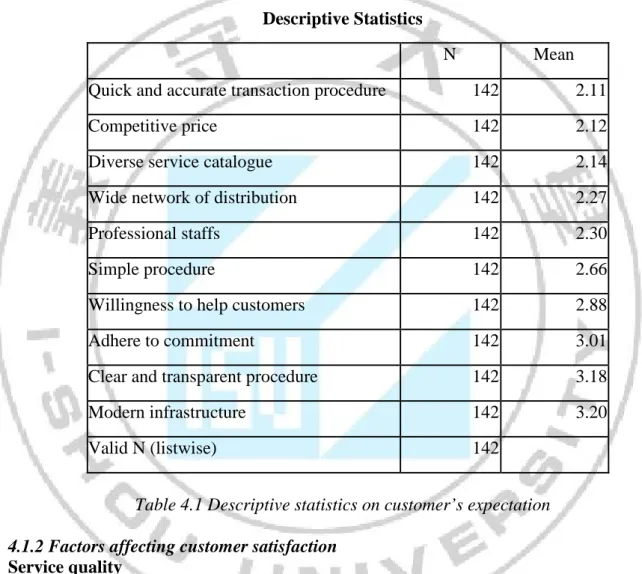
For customers, the customer’s expectations about bank are ranked as follows: (1): Quick and accurate transaction procedure; (2): Competitive price; (3): Diverse service catalogue. After processing data, the most expected factors were given scores according to the order of priorities by the scale from 1 to 3 and other factors were given the score of 4 to make calculation.
Descriptive Statistics
N Mean
Quick and accurate transaction procedure 142 2.11
Competitive price 142 2.12
Diverse service catalogue 142 2.14
Wide network of distribution 142 2.27
Professional staffs 142 2.30
Simple procedure 142 2.66
Willingness to help customers 142 2.88
Adhere to commitment 142 3.01
Clear and transparent procedure 142 3.18
Modern infrastructure 142 3.20
Valid N (listwise) 142
Table 4.1 Descriptive statistics on customer’s expectation
4.1.2 Factors affecting customer satisfaction Service quality
In 21 scales of service quality of the Bank (Table 4.2), customers most agree with the factor TXKH04_The Bank always listens to comments (Mean: 4.60); TXKH03_the Bank annually organizes customer appreciation party (Mean: 4.24), SHH01_the Bank has modern equipment (Mean: 4.15); PCPV05_Friendly and helpful staffs (Mean : 4.08); and TXKH01_ 24 hour customer service line (Mean: 4.06). However, Table 3.4 also shows that there are 05 scales which have the lowest mean, indicating various degree of customer’s agreement with the variables. These are the variables DMDV01_Diverse service catalogue (Mean : 3.42); STT03_ the Bank has convenient location (Mean: 3.43); Simple procedure (Mean: 3.49);
DMDV02_ New available service (Mean: 3.54); and SHH02_Appealing bank introduction documents (Mean: 3.56)
Descriptive Statistics
Std. N Minimum Maximum Mean Deviation
STT01 142 2 5 3,59 .939 STT02 142 1 5 3.49 .973 STT03 142 1 5 3.43 1.034 SHH01 142 3 5 4.15 .743 SHH02 142 1 5 3.56 1.082 SHH03 142 1 5 3.87 .959 SHH04 142 2 5 3.99 .911 PCPV01 142 2 5 3.79 .937 PCPV02 142 1 5 3.63 .971 PCPV03 142 2 5 3.80 .869 PCPV04 142 2 5 3.81 .816 PCPV05 142 3 5 4.08 .744 DMDV01 142 1 5 3.42 .999 DMDV02 142 1 5 3.54 1.165 TXKH01 142 2 5 4.06 .815 TXKH02 142 2 5 3.87 .909 TXKH03 142 1 5 4.24 .891 TXKH04 142 2 5 4.60 .584 STN01 142 1 5 3.71 1.001 STN02 142 1 5 3.59 .924 STN03 142 1 5 3.61 1.103 Valid N (listwise) 142
Table 4.2: Descriptive statistics on service quality scales
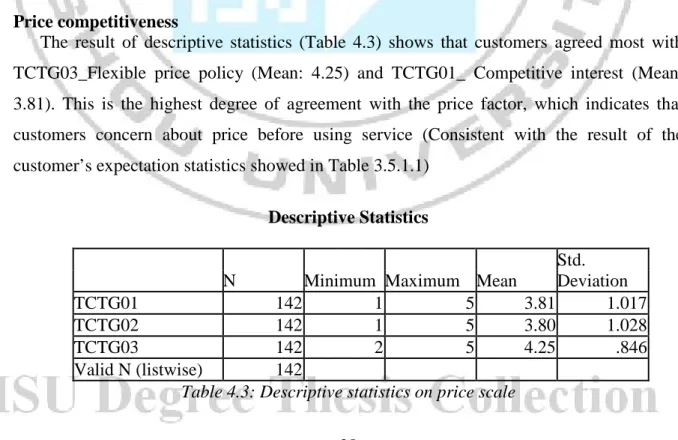
Price competitiveness
The result of descriptive statistics (Table 4.3) shows that customers agreed most with TCTG03_Flexible price policy (Mean: 4.25) and TCTG01_ Competitive interest (Mean: 3.81). This is the highest degree of agreement with the price factor, which indicates that customers concern about price before using service (Consistent with the result of the customer’s expectation statistics showed in Table 3.5.1.1)
Descriptive Statistics
Std.
N Minimum Maximum Mean Deviation
TCTG01 142 1 5 3.81 1.017
TCTG02 142 1 5 3.80 1.028
TCTG03 142 2 5 4.25 .846
Valid N (listwise) 142
Table 4.3: Descriptive statistics on price scale
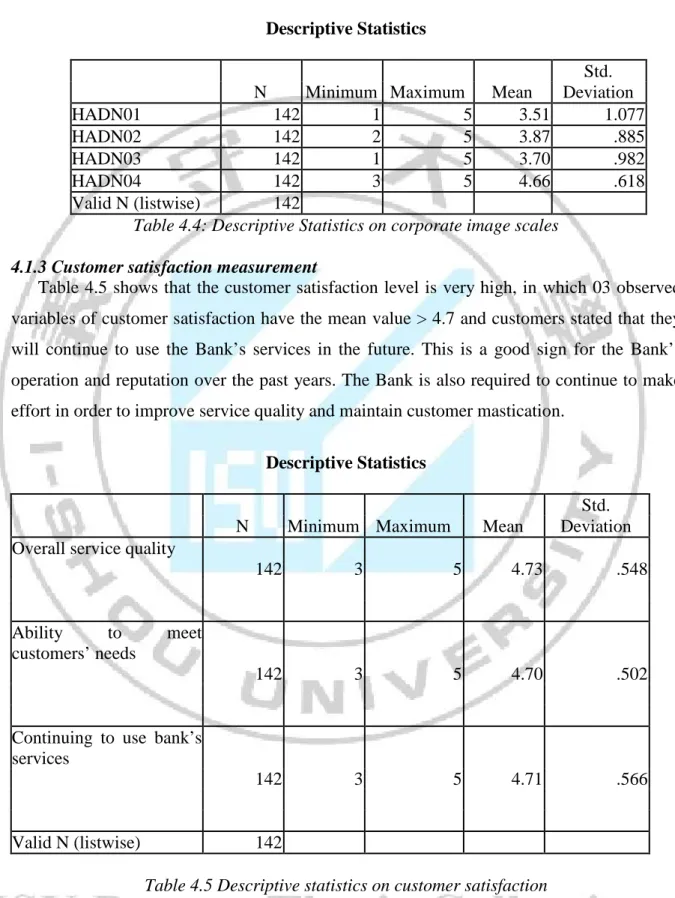
Corporate image
According to Table 4.4, when assessing criteria for measuring corporate image, customers agree most with two scales HADN04_The Bank has impressive and effective marketing activities (Mean: 4.66), and HADN02_The bank always adheres to commitment (Mean: 3.87)
Descriptive Statistics
Std. N Minimum Maximum Mean Deviation
HADN01 142 1 5 3.51 1.077
HADN02 142 2 5 3.87 .885
HADN03 142 1 5 3.70 .982
HADN04 142 3 5 4.66 .618
Valid N (listwise) 142
Table 4.4: Descriptive Statistics on corporate image scales
4.1.3 Customer satisfaction measurement
Table 4.5 shows that the customer satisfaction level is very high, in which 03 observed variables of customer satisfaction have the mean value > 4.7 and customers stated that they will continue to use the Bank’s services in the future. This is a good sign for the Bank’s operation and reputation over the past years. The Bank is also required to continue to make effort in order to improve service quality and maintain customer mastication.
Descriptive Statistics
Std. N Minimum Maximum Mean Deviation Overall service quality
142 3 5 4.73 .548 Ability to meet customers’ needs 142 3 5 4.70 .502 Continuing to use bank’s
services
142 3 5 4.71 .566
Valid N (listwise) 142
Table 4.5 Descriptive statistics on customer satisfaction
4.2 SCALE ANALYSIS
4.2.1 Cronbach’s alpha
Cronbach’s alpha is a statistical test to check the closeness and the correlation between observed variables. It is involved in the two aspects including the correlation of variables themselves and the correlation of the score of every single observed variable with the total score of variables of each respondent.
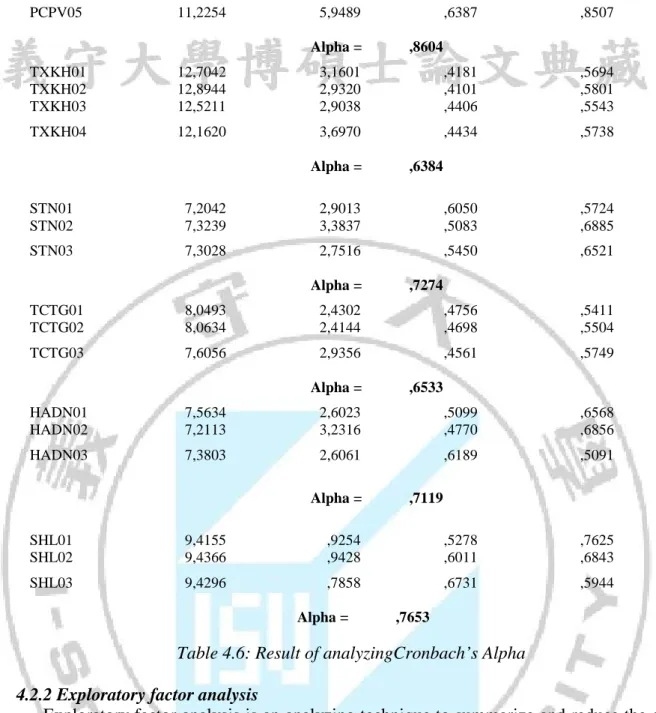
This method allows analyst to eliminate the inappropriate variables and minimize the amount of unwanted variables in the model. The reason is that, if not doing that, we cannot know variability and deviation of variables. According to the method, only variables with Corrected Item-Total Correction > 0.3 and the Alpha coefficient > 0.6 are acceptable and suitable to be analyzed in the next step (Nunnally and BernStein, 1994). According to many researchers, if a scale has Cronbach’s alpha >= 0.8, it is a good scale and its level of correlation will be higher. Looking at the Table 4.6, we can know the result of reliability analysis as follows:
As for the factor of CONVENIENCE, all 3 observed variables have the Corrected Item- Total Correction > 0.3 so they are chosen. Meanwhile the factor SERVICE CATALOGUE does not satisfy the condition, so it is eliminated. However, when combining two factors CONVENIENCEand SERVICE CATALOGUE, the 5 observed variables STT01, STT02, DMDV01, DMDV02 have the suitable corrected item-total correction > 0.3 and their Alpha coefficient = 0.7611, which is high (while Alpha coefficient of every single variables STT01, STT02, STT03 is only 0.6779). Thus, they are eligible to be included in factor analysis. In conclusion, the factor of CONVENIENCE is the combination of measured variables of two smaller factors that are CONVENIENCEand SERVICE CATALOGUE. The reason is that SERVICE CATALOGUE is a component of CONVENIENCE.
As for the factor of TANGIBLES, all the observed variables have the Corrected Item- Total Correction > 0.3 and Alpha coefficient > 0.6 (0.7121),so they meet the requirement of reliability to be analyzed in factor analysis.
About the factor of SERVICE STYLE, the variable PCPV04 is not eligible because Corrected Item-Total Correction of 0.1410 < 0.3, so it is eliminated. Other variables have corrected item-total correction > 0.3 and Alpha coefficient = 0.8604, which is qualified to be included in factor analysis.
As for the factor of APPROACHING THE CUSTOMERS, 4 variables are qualified to be analyzed in exploratory factor analysis because they have Corrected Item-Total Correction > 0.3 and Alpha coefficient = 0.6384.
About the factor of CREDIBIITY, 3 observed variables have Corrected Item-Total Correction > 0.3 and Alpha coefficient = 0.7274 so they are qualified to be included in
exploratory factor analysis.
As for the factor of PRICE COMPETITIVENESS, all the variables qualify the condition of reliability testing (Corrected Item-Total Correction > 0.3 and Alpha coefficient = 0.6533) so they can be included in exploratory factor analysis.
As for the factor of CORPORATE IMAGE, the observed variable of HADN04 has unsuitable corrected item-total correction 0.0551<0.3, so it is eliminated. The other 3 variables including HADN01, HADN02, HADN03 have corrected item-total correction > 0.3 and Alpha coefficient = 0.7119, so they are qualified to be included in exploratory factor analysis.
About the factor of CUSTOMER SACTISFACTION, 03 observed variables have corrected item-total correction > 0.3 and Alpha coefficient= 0.7653 so they are included in exploratory factor analysis.
In conclusion, in total, there are 26 variables (Table 4.6) of 7 scales compared with 28 observed variables of 8 initial scales (PCPV04, HADN04 are eliminated). In addition, the three variables measuring the customer satisfactionis also included in exploratory factor analysis
RELIABILITY ANALYSIS
Item-total Statistics
Scale Scale Corrected
Alpha
Mean Variance Item-
if Item if Item Total if Item
Deleted Deleted Correlation Deleted
STT01 13,5745 9,4319 ,5696 ,7349 STT02 13,6667 8,9524 ,6289 ,7145 STT03 13,7163 9,4618 ,4812 ,7634 DMDV01 13,7305 9,1268 ,5693 ,7339 DMDV02 13,9362 8,8602 ,5332 ,7478 Alpha = ,7798 SHH01 11,4296 5,6936 ,3398 ,7309 SHH02 12,0141 4,2126 ,4661 ,6802 SHH03 11,7042 4,1956 ,5945 ,5877 SHH04 11,5845 4,2729 ,6237 ,5725 Alpha = ,7121 PCPV01 11,5141 4,7197 ,7928 ,7842 PCPV02 11,6690 4,8187 ,7180 ,8194 PCPV03 11,5000 5,2872 ,6957 ,8264 31
PCPV05 11,2254 5,9489 ,6387 ,8507 Alpha = ,8604 TXKH01 12,7042 3,1601 ,4181 ,5694 TXKH02 12,8944 2,9320 ,4101 ,5801 TXKH03 12,5211 2,9038 ,4406 ,5543 TXKH04 12,1620 3,6970 ,4434 ,5738 Alpha = ,6384 STN01 7,2042 2,9013 ,6050 ,5724 STN02 7,3239 3,3837 ,5083 ,6885 STN03 7,3028 2,7516 ,5450 ,6521 Alpha = ,7274 TCTG01 8,0493 2,4302 ,4756 ,5411 TCTG02 8,0634 2,4144 ,4698 ,5504 TCTG03 7,6056 2,9356 ,4561 ,5749 Alpha = ,6533 HADN01 7,5634 2,6023 ,5099 ,6568 HADN02 7,2113 3,2316 ,4770 ,6856 HADN03 7,3803 2,6061 ,6189 ,5091 Alpha = ,7119 SHL01 9,4155 ,9254 ,5278 ,7625 SHL02 9,4366 ,9428 ,6011 ,6843 SHL03 9,4296 ,7858 ,6731 ,5944 Alpha = ,7653
Table 4.6: Result of analyzingCronbach’s Alpha
4.2.2 Exploratory factor analysis
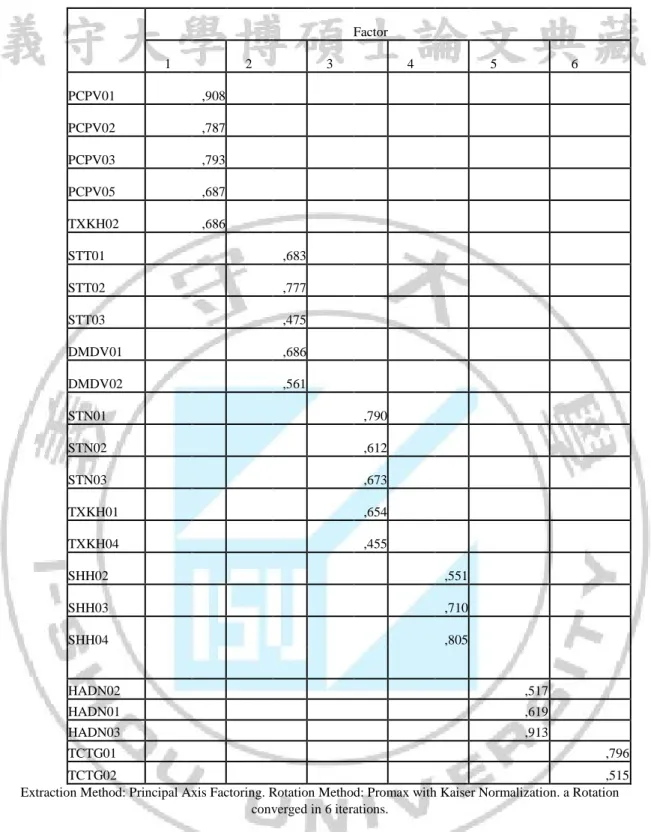
Exploratory factor analysis is an analyzing technique to summarize and reduce the data, which is necessary to identify the set of variables for the research. The correlation between groups of variables is considered as the number of basic factors. Each observed variable will be calculated a ratio called factor loading. Each factor loading will tell the researcher each measured variable belongs to which factors.
In exploratory factor analysis, a necessary condition is the indicator KMO (Kaiser-Meyer –Olkin (KMO) must has big value (0.5<KMO<1), which shows that the exploratory factor analysis is suitable. If the KMO < 0.5, the exploratory factor analysis can be unsuitable for data. According to Gerbing & Anderson, 1988, additionally, for satisfying the condition of exploratory factor analysis, factor loading of each variable must be greater than 0.45, the stop point at Eigenvalue (representing the variation explained by each factor) > 1 (default in the SPSS program) and the total variance must be > 50%. When conducting exploratory
factor analysis, the author uses extraction method, which includes Principal Axis factoring and Promax rotation and the Regression.
The process of exploratory factor analysis is presented as follows: Step 1:
The collection of observed variables satisfies the condition of reliabilityand included in the exploratory factor analysis (26 measured variables of factors affecting customer satisfaction and 03 observed variables measuring the level of customer satisfaction). This process is called the first exploratory factor analysis (APPENDIX 2) with the following results:
About the factors affecting customer satisfaction: KMO = 0.776 and there are two variables are eliminated that are TXKH03 and TCTG03 (factor loading < 0.45). The rest of other variables will be analyzed in the second exploratory factor analysis.
About the level of customer satisfaction: KMO = 0.665, Eigenvalue > 1, total variance > 50% (54.058%), which is eligible to conduct exploratory factor analysis. In conclusion, the result of exploratory factor analysis of the level of customer satisfaction (APPENDIX 5) shows that 3 observed variables SHL01, SHL02, and SHL03 all have factor loading > 0.45 and it is appropriate to use to explained the scale of the level of customer satisfaction.
Step 2:
Qualified observed variables in the first exploratory factor analysis (24 variables) included in the second exploratory factor analysis (APPENDIX 3) show that the KMO is slightly reduced to 0.765 and another observed variable is eliminated (SHH01).
Step 3:
The third exploratory factor analysis (APPENDIX 4) includes the rest of 23 observed variables and has the following results:
KMO: 0.765
EIGENVALUE: 1.221 Total variance: 51.49% The number of factors: 6
PCPV: including 4 variables of PCPV and 1 variable of TXKH STT: including 3 variables of PCPV and 2 variables of DMDV STN : including 3 variables of STN and 2 variables of TXKH SHH: including 3 variables of SHH
HADN: including 3 variables of HADN TCTG : including 2 variables of TCTG